HOWTO: Use STM32 SPI half duplex mode
HOWTO: Use STM32 SPI half duplex mode
I’ve got my hands onto some STM32F030F4P6 ARM-Cortex M0 processors.
Though touted as “32 cents 32-bit micro”, it is not that inexpensive from DigiKey in one-off quantity ($1.45).
However it is still cheaper than ATmegas and offers 3 times the performance.
The chip comes in 20-pin TSSOP package.
Limited pins require much more thoughts when assigning pin function.
For example, using 3-pin half-duplex SPI instead of 4-pin full-duplex SPI saves me 1 very precious GPIO pin.
It should be noted that not all SPI slave devices support half duplex mode,
and most devices will not mention half-duplex mode in the datasheets.
Generally, a SPI slave device supports half duplex SPI mode if:
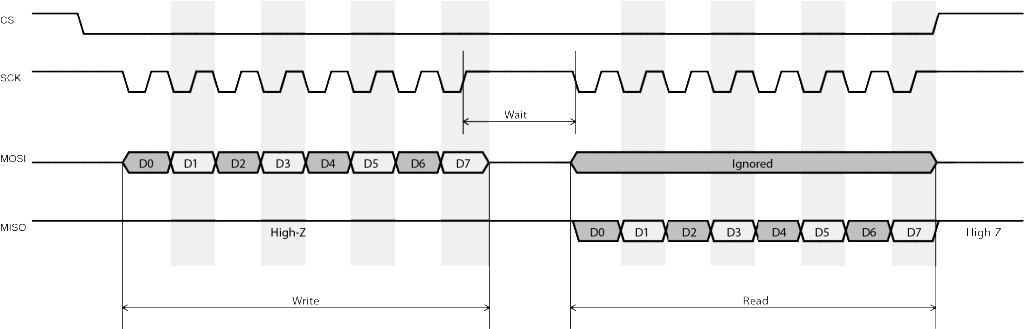
- The device’s MISO (or DOUT) pin uses open-drain output.
- This is usually true because open-drain allows multiple SPI slaves to share the same MISO line.
- In the communication protocol, the slave device always waits for the master to send fixed number of bytes (commands) from MOSI,
- then returns a fixed number of bytes to MISO.
- Some devices which transmit and receive data simultaneously cannot be used in half-duplex mode.
- The slave ignores whatever appears on the MOSI pin when transmitting data to the master.
- This is usually not mentioned in the datasheet.
- However, if the slave device mandates a CS or STROBE signal to be asserted at the beginning of each data exchange,
- we can usually assume this is true.
- Reason being that the slave device is using CS to reset its internal state
- rather than always listening and parsing command byte(s) from the master.
Half-duplex wiring of STM32 SPI is as follows:
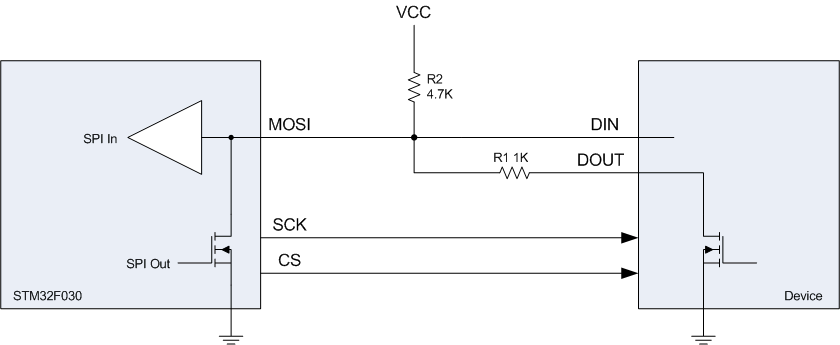
In particular, MOSI and SCK are configured as “Alternate Function” mode.
Hardware CS (NSS) management must be disabled and user shall manually control CS using GPIO output.
R2 is pull-up resistor as required by SPI.
R1 works as protection resistor in case STM32 MOSI pin somehow enters into push-pull output mode.
The SPI setup code is as follows:
void SPI_Configure()
{
SPI_InitTypeDef SPI_InitStructure;
// Enable SPI1 clock
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_SPI1, ENABLE);
// SPI1 configuration
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Direction = SPI_Direction_1Line_Tx; // Initially Tx
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Mode = SPI_Mode_Master;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_DataSize = SPI_DataSize_8b;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPOL = SPI_CPOL_High; // Clock steady high
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPHA = SPI_CPHA_2Edge; // Data write on rising (second) edge
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_NSS = SPI_NSS_Soft;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_64;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_FirstBit = SPI_FirstBit_LSB;
SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CRCPolynomial = ;
SPI_Init(SPI1, &SPI_InitStructure);
SPI_RxFIFOThresholdConfig(SPI1, SPI_RxFIFOThreshold_QF);
SPI_Cmd(SPI1, ENABLE);
}
Line 7 sets the SPI peripheral to half-dulex transmission mode.
Line 17 sets the SPI FIFO buffer threshold to quarter full.
This is new in STM32F0 with 4-byte SPI FIFO buffer.
SPI_RxFIFOThreshold_QF meaning that the SPI_I2S_FLAG_RXNE flag will be set as soon as 1 byte
(quarter buffer) is shifted into receiving FIFO.
SPI master sending data to slave is as simple as:
void send_byte(uint8_t val)
{
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOA, GPIO_Pin_4); // CS low
while (SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI1, SPI_I2S_FLAG_TXE) == RESET); //wait buffer empty
SPI_SendData8(SPI1, val);
while (SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI1, SPI_I2S_FLAG_BSY) == SET); //wait finish sending
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOA, GPIO_Pin_4); // CS high
}
The following code demonstrates master sends 1 byte command to slave and reads 1 byte back.
uint8_t send_and_read_byte(uint8_t cmd)
{
uint8_t result;
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOA, GPIO_Pin_4); // CS low
while (SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI1, SPI_I2S_FLAG_TXE) == RESET); //wait buffer empty
SPI_SendData8(SPI1, cmd);
while (SPI_I2S_GetFlagStatus(SPI1, SPI_I2S_FLAG_BSY) == SET); //wait finish sending
// Read receiving FIFO until it is empty
while (SPI_GetReceptionFIFOStatus(SPI1) != SPI_ReceptionFIFOStatus_Empty)
SPI_ReceiveData8(SPI1);
SPI_BiDirectionalLineConfig(SPI1, SPI_Direction_Rx);
while (!(SPI1->SR & SPI_I2S_FLAG_RXNE)) ; // wait data received
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOA, GPIO_Pin_4); // CS high
SPI1->CR1 |= SPI_Direction_Tx; // Set Tx mode to stop Rx clock
result = SPI_ReceiveData8(SPI1);
return result;
}
Immediately after one byte is sent, the program empties all stale data in the FIFO (line 9, 10),
then sets SPI direction to receiving mode (line 11).
As soon as SPI enters into receiving mode, STM32 will continuously generate clock on SCK pin until receiving mode is disabled.
Along with the clock toggling, data are shifted from MOSI pin into receiving FIFO,
and SPI_I2S_FLAG_RXNE flag is set once 1 byte of data is received (line 12).
The program then disables CS (line 13, to disable slave output)
and switches SPI back to transmitting mode (line 14, to stop the clock).
These two steps must be executed fast enough before the next clock is sent out to prevent the slave device enter into any undefined state.
Timing is very critical here especially when SPI clock is high.
To receive multiple bytes from the slave, put line 9-15 into a loop but disable CS only after all data are read.
Important thing is to always disable receiving mode immediately after FIFO is quarter full,
and verify using a scope or logic analyser to ensure exact 8 clocks are send in-between each reading.
HOWTO: Use STM32 SPI half duplex mode的更多相关文章
- The STM32 SPI and FPGA communication
The STM32 SPI and FPGA communication STM32 spi bus communication SPI bus in the study, the protocol ...
- 关于STM32 SPI NSS的讨论
NSS分为内部引脚和外部引脚. NSS外部引脚可以作为输入信号或者输出信号, 输入信号一般用作硬件方式从机的片选, 而输出信号一般用于主SPI去片选与之相连的从SPI. NSS从设备选择有两种模式: ...
- stm32 SPI介绍和配置
SPI是一种高速的,全双工同步的通信总线,在芯片管脚上占用了四根线,节约了芯片的管脚,同时为PCB的布局节省了空间,提供了方便,因此越来越多的芯片集成了这种通信协议,STM32也就有了SPI接口. 有 ...
- STM32 SPI 发送第一个数据不成功问题
STM32的标准库,跟HAL库都是很实用的, 在使用SPI库的过程中一定要注意时序的问题. 我在调试SPI过程中,调试了两个IC,都是用HAL库, 第一个IC没出问题,第二个IC出现了第一次发送数据不 ...
- STM32—SPI读写FLASH
目录 FLASH简介 W25Q64 W25Q64简介 FLASH控制指令 FLASH内部存储结构 代码讲解 读取芯片ID 发送写使能信号 等待FLASH不忙 擦除扇区 写入数据 读取数据 注 FLAS ...
- STM32—SPI详解
目录 一.什么是SPI 二.SPI协议 物理层 协议层 1.通讯时序图 2.起始和停止信号 3.数据有效性 4.通讯模式 三.STM32中的SPI 简介 功能框图 1.通讯引脚 2.时钟控制逻辑 3. ...
- STM32 SPI DMA 的使用
一是想总结一下SPI总线的特点与注意点,二是总结一下SPI DMA的使用 一.SPI信号线说明 通常SPI通过4个引脚与外部器件相连: MISO:主设备输入/从设备输出引脚.该引脚在从模式下发送数据, ...
- STM32.SPI(25Q16)
1.首先认识下W25Q16DVSIG, SOP8 SPI FLASH 16MBIT 2MB(4096个字节) (里面可以放字库,图片,也可以程序掉电不丢失数据放里面) 例程讲解: ① 1.用到SPI ...
- 2.2寸(14PIN)TFT液晶屏STM32 SPI 控制
屏幕如图所示,共14个IO口(也可能只有13个),控制屏幕的有9个IO口 详细版介绍见:http://www.ciast.net/post/20151112.html 反面IO口图: 连接通过SPI方 ...
随机推荐
- bash脚本:集群资源争夺战crazy-killer
背景 公司的集群很多人一起用,有时候就难免资源紧张,某次需要用的时候没资源等了半天还是没资源,再等半天还是没资源,于是就写了个脚本泄愤,建议看到的人拷走放在自己公司集群上长期运行 :) 实现 此脚本运 ...
- 数链剖分(Tree)
题目链接:https://cn.vjudge.net/contest/279350#problem/D 题目大意:操作,单点查询,区间取反,询问区间最大值. AC代码: #include<ios ...
- Maven私服安装及配置——(十二)
0.私服实际是B/S架构的,需要通过浏览器访问.访问地址在 nexus-2.12.0-01\conf\nexus.properties中查看.
- 【API】网络编程模型、多线程
1.网络通信编程 1)网络通信模型基础知识 TCP Server: WSAStartup() socket() bind() linsten() accept() send/recv() closes ...
- phantomjs 长图截屏
var page = require('webpage').create(); var url = 'http://cardloan9.hateblo.jp/'; page.settings = { ...
- MVC Autofac依赖注入
通过Dll实现全部类的属性注入,该演示实例主要通过多层架构中单一的对象方式来演示,没有采取接口的方式, 新建AutoFacHelper类,如下代码: public class AutoFacHelpe ...
- 利用CSS改变输入框的光标颜色
转:http://www.cnblogs.com/gymmer/p/6810367.html 代码: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" ...
- 前后端分离之mockjs基本介绍
安装与使用 # 安装 npm install mockjs #使用 Mock var Mock = require('mockjs') var data = Mock.mock({ // 属性 lis ...
- python实战之原生爬虫(爬取熊猫主播排行榜)
""" this is a module,多行注释 """ import re from urllib import request # B ...
- 洛谷P3375KMP字符串匹配
传送门 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorith ...
