Spring Type Conversion(Spring类型转换源码探究)
1:概述
类型转换系统负责Spring框架中对象类型转换和格式化工作。
ConversionService默认实现UML图如下所示:

GenericConversionService(通用类型转换服务),是整个类型转换系统的完整实现。作为容器,
管理转换器,同时调用这些转换器进行类型转换,是一个空的容器,内部没有任何转换器。是线程安全。
2:GenericConversionService(通用类型转换服务)学习
(1):转换器缓存设计
//自定义Map Key实现
private final Map<ConverterCacheKey, GenericConverter> converterCache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(64);
/**
* Key for use with the converter cache.
*/
private static final class ConverterCacheKey implements Comparable<ConverterCacheKey> {
private final TypeDescriptor sourceType;
private final TypeDescriptor targetType;
public ConverterCacheKey(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
this.sourceType = sourceType;
this.targetType = targetType;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
if (!(other instanceof ConverterCacheKey)) {
return false;
}
ConverterCacheKey otherKey = (ConverterCacheKey) other;
return (this.sourceType.equals(otherKey.sourceType)) &&
this.targetType.equals(otherKey.targetType);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (this.sourceType.hashCode() * 29 + this.targetType.hashCode());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return ("ConverterCacheKey [sourceType = " + this.sourceType +
", targetType = " + this.targetType + "]");
}
@Override
public int compareTo(ConverterCacheKey other) {
int result = this.sourceType.getResolvableType().toString().compareTo(
other.sourceType.getResolvableType().toString());
if (result == 0) {
result = this.targetType.getResolvableType().toString().compareTo(
other.targetType.getResolvableType().toString());
}
return result;
}
}
(2):转换器类型适配器设计(适配器模式)
/**
* Adapts a {@link Converter} to a {@link GenericConverter}.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private final class ConverterAdapter implements ConditionalGenericConverter { private final Converter<Object, Object> converter; private final ConvertiblePair typeInfo; private final ResolvableType targetType; public ConverterAdapter(Converter<?, ?> converter, ResolvableType sourceType, ResolvableType targetType) {
this.converter = (Converter<Object, Object>) converter;
this.typeInfo = new ConvertiblePair(sourceType.resolve(Object.class), targetType.resolve(Object.class));
this.targetType = targetType;
} @Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(this.typeInfo);
} @Override
public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
// Check raw type first...
if (this.typeInfo.getTargetType() != targetType.getObjectType()) {
return false;
}
// Full check for complex generic type match required?
ResolvableType rt = targetType.getResolvableType();
if (!(rt.getType() instanceof Class) && !rt.isAssignableFrom(this.targetType) &&
!this.targetType.hasUnresolvableGenerics()) {
return false;
}
return !(this.converter instanceof ConditionalConverter) ||
((ConditionalConverter) this.converter).matches(sourceType, targetType);
} @Override
@Nullable
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
if (source == null) {
return convertNullSource(sourceType, targetType);
}
return this.converter.convert(source);
} @Override
public String toString() {
return (this.typeInfo + " : " + this.converter);
}
} private final class ConverterFactoryAdapter implements ConditionalGenericConverter { private final ConverterFactory<Object, Object> converterFactory; private final ConvertiblePair typeInfo; public ConverterFactoryAdapter(ConverterFactory<?, ?> converterFactory, ConvertiblePair typeInfo) {
this.converterFactory = (ConverterFactory<Object, Object>) converterFactory;
this.typeInfo = typeInfo;
} @Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(this.typeInfo);
} @Override
public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
boolean matches = true;
if (this.converterFactory instanceof ConditionalConverter) {
matches = ((ConditionalConverter) this.converterFactory).matches(sourceType, targetType);
}
if (matches) {
Converter<?, ?> converter = this.converterFactory.getConverter(targetType.getType());
if (converter instanceof ConditionalConverter) {
matches = ((ConditionalConverter) converter).matches(sourceType, targetType);
}
}
return matches;
} @Override
@Nullable
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
if (source == null) {
return convertNullSource(sourceType, targetType);
}
return this.converterFactory.getConverter(targetType.getObjectType()).convert(source);
} @Override
public String toString() {
return (this.typeInfo + " : " + this.converterFactory);
}
}
(3):转换器存储设计
private final Converters converters = new Converters();
/**
* Manages all converters registered with the service.
*/
private static class Converters {
private final Set<GenericConverter> globalConverters = new LinkedHashSet<>();
private final Map<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair> converters = new LinkedHashMap<>(36);
}
(4):没有操作和没有匹配类型设计
/**
* General NO-OP converter used when conversion is not required.
*/
private static final GenericConverter NO_OP_CONVERTER = new NoOpConverter("NO_OP");
/**
* Used as a cache entry when no converter is available.
* This converter is never returned.
*/
private static final GenericConverter NO_MATCH = new NoOpConverter("NO_MATCH");
/**
* Internal converter that performs no operation.
*/
private static class NoOpConverter implements GenericConverter {
private final String name;
public NoOpConverter(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return null;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
return source;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.name;
}
}
总结
适配器合理设计
缓存合理设计
存储合理设计
不匹配和不操作合理设计
读操作设计成一个接口(参照
ConversionService)注册操作设计成一个接口(参照
ConverterRegistry)写操作设计成一个接口(参照
ConfigurableConversionService)
(3):DefaultConversionService源码学习
默认的类型转换系统,继承了GenericConversionService类。在构造方法调用添加默认的转换器。
public class DefaultConversionService extends GenericConversionService {
@Nullable
private static volatile DefaultConversionService sharedInstance;
/**
* Create a new {@code DefaultConversionService} with the set of
* {@linkplain DefaultConversionService#addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry) default converters}.
*/
public DefaultConversionService() {
addDefaultConverters(this);
}
/**
* Return a shared default {@code ConversionService} instance,
* lazily building it once needed.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> We highly recommend constructing individual
* {@code ConversionService} instances for customization purposes.
* This accessor is only meant as a fallback for code paths which
* need simple type coercion but cannot access a longer-lived
* {@code ConversionService} instance any other way.
* @return the shared {@code ConversionService} instance (never {@code null})
* @since 4.3.5
*/
public static ConversionService getSharedInstance() {
DefaultConversionService cs = sharedInstance;
if (cs == null) {
synchronized (DefaultConversionService.class) {
cs = sharedInstance;
if (cs == null) {
cs = new DefaultConversionService();
sharedInstance = cs;
}
}
}
return cs;
}
}
总结
单例模式之双重检锁模式正确运用
(4):ConversionServiceFactoryBean(类型转换器注册工厂Bean)
/**
* A factory providing convenient access to a ConversionService configured with
* converters appropriate for most environments. Set the
* {@link #setConverters "converters"} property to supplement the default converters.
*
* <p>This implementation creates a {@link DefaultConversionService}.
* Subclasses may override {@link #createConversionService()} in order to return
* a {@link GenericConversionService} instance of their choosing.
*
* <p>Like all {@code FactoryBean} implementations, this class is suitable for
* use when configuring a Spring application context using Spring {@code <beans>}
* XML. When configuring the container with
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration @Configuration}
* classes, simply instantiate, configure and return the appropriate
* {@code ConversionService} object from a {@link
* org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean @Bean} method.
* @since 3.0
*/
public class ConversionServiceFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<ConversionService>, InitializingBean {
@Nullable
private Set<?> converters;
@Nullable
private GenericConversionService conversionService;
/**
* Configure the set of custom converter objects that should be added:
* implementing {@link org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter},
* {@link org.springframework.core.convert.converter.ConverterFactory},
* or {@link org.springframework.core.convert.converter.GenericConverter}.
*/
public void setConverters(Set<?> converters) {
this.converters = converters;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.conversionService = createConversionService();
ConversionServiceFactory.registerConverters(this.converters, this.conversionService);
}
/**
* Create the ConversionService instance returned by this factory bean.
* <p>Creates a simple {@link GenericConversionService} instance by default.
* Subclasses may override to customize the ConversionService instance that
* gets created.
*/
protected GenericConversionService createConversionService() {
return new DefaultConversionService();
}
// implementing FactoryBean
@Override
@Nullable
public ConversionService getObject() {
return this.conversionService;
}
@Override
public Class<? extends ConversionService> getObjectType() {
return GenericConversionService.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
/**
* A factory for common {@link org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService}
* configurations.
* @since 3.0
*/
public abstract class ConversionServiceFactory {
/**
* Register the given Converter objects with the given target ConverterRegistry.
* @param converters the converter objects: implementing {@link Converter},
* {@link ConverterFactory}, or {@link GenericConverter}
* @param registry the target registry
*/
public static void registerConverters(@Nullable Set<?> converters, ConverterRegistry registry) {
if (converters != null) {
for (Object converter : converters) {
if (converter instanceof GenericConverter) {
registry.addConverter((GenericConverter) converter);
}
else if (converter instanceof Converter<?, ?>) {
registry.addConverter((Converter<?, ?>) converter);
}
else if (converter instanceof ConverterFactory<?, ?>) {
registry.addConverterFactory((ConverterFactory<?, ?>) converter);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Each converter object must implement one of the " +
"Converter, ConverterFactory, or GenericConverter interfaces");
}
}
}
}
}
总结
简单工厂模式运用
FactoryBean使用
(5):格式化Formatter体系
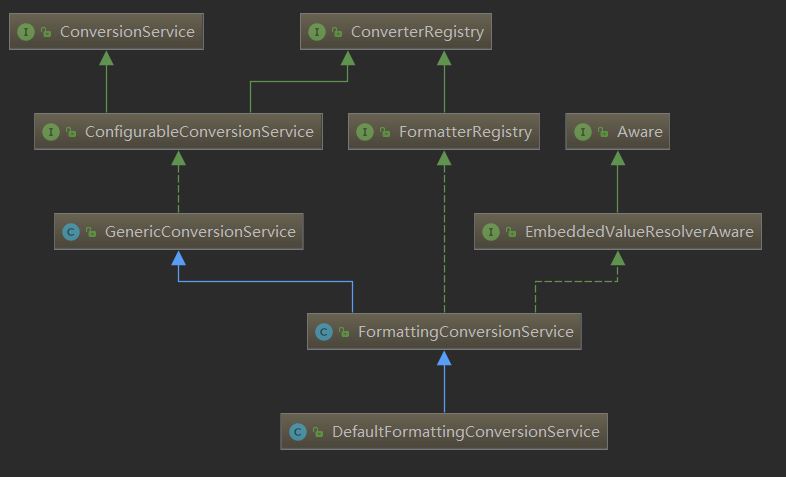
总结
往Spring类型转换系统靠.
(6):DefaultConversionService可支持转换的列表
格式:sourceType-targetType
//
简单类型Number-->Number
String-->Number Number-->String
String-->Character Character-->String
Number-->Character Character-->Number
String-->Boolean Boolean-->String
String-->Enum Enum-->String
Integer-->Enum Enum-->Integer
String-->Locale Locale-->String
String-->Charset Charset->String
String-->Currency(货币) Currency-->String
String-->Properties Properties-->String
String-->UUID UUID-->String
//
集合类型和数组类型Object[]-->Collection Collection-->Object[]
Object[]-->Object[]
Collection-->Collection
Map-->Map
Object[]-->String String-->Object[]
Object[]-->Object Object-->Object[]
Collection-->String String-->Collection
Collection-->Object Object-->Collection
Stream-->Collection Collection-->Stream
Stream-->Object[] Object[]-->Stream
//
其他类型ByteBuffer-->Object Object-->ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer-->byte[] byte[]-->ByteBuffer
String-->TimeZone
ZoneId-->TimeZone
ZonedDateTime-->Calendar
Object-->Object
Object-->String
Object-->Optional
Collection-->Optional
Object[]-->Optional
Spring Type Conversion(Spring类型转换源码探究)的更多相关文章
- Spring Type Conversion(Spring类型转换)
Spring Type Conversion(Spring类型转换) 1:概述: Spring3引入了core.convert包,提供了通用类型转换系统,定义了实现类型转换和运行时执行类型的SPI. ...
- Mybatis的初始化和结合Spring Framework后初始化的源码探究
带着下面的问题进行学习: (1)Mybatis 框架或 Spring Framework 框架对数据层 Mapper 接口做了代理,那是做了 JDK 动态代理还是 CGLIB 代理? (2)Mappe ...
- Mybatis一级缓存和结合Spring Framework后失效的源码探究
1.在下面的案例中,执行两次查询控制台只会输出一次 SQL 查询: mybatis-config.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding=" ...
- Spring Framework自动装配setAutowireMode和Mybatis案例的源码探究
由前文可得知, Spring Framework的自动装配有两种方式:xml配置和注解配置: 自动装配的类型有: (1)xml配置中的byType根据类型查找(@Autowired注解是默认根据类型查 ...
- Spring Environment(二)源码分析
Spring Environment(二)源码分析 Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10198698.html) Spring Envi ...
- 七、Spring之深入理解AOP源码
Spring之深入理解AOP源码 在上一篇博文中,我们对AOP有了初步的了解,那么接下来我们就对AOP的实现原理进行深入的分析. 在之前写的那个AOP示例代码当中有这样一个注解:@Enable ...
- Spring框架之spring-web http源码完全解析
Spring框架之spring-web http源码完全解析 Spring-web是Spring webMVC的基础,由http.remoting.web三部分组成. http:封装了http协议中的 ...
- Spring框架之spring-web web源码完全解析
Spring框架之spring-web web源码完全解析 spring-web是Spring webMVC的基础,由http.remoting.web三部分组成,核心为web模块.http模块封装了 ...
- 一文读懂Spring动态配置多数据源---源码详细分析
Spring动态多数据源源码分析及解读 一.为什么要研究Spring动态多数据源 期初,最开始的原因是:想将答题服务中发送主观题答题数据给批改中间件这块抽象出来, 但这块主要使用的是mq消息的方式 ...
随机推荐
- android 流量统计
1 android通过架构流量统计TrafficStats类可以直接获得 获得总流量受理TrafficStats.getTotalRxBytes(), 获得总传出流量TrafficSt ...
- Android ActionBar相关
1.Android 5.0 删除ActionBar下面的阴影 于Android 5.0假设你发现的ActionBar下面出现了阴影,例如,下面的设置,以消除阴影: getActionBar().set ...
- 1.通过模板创建MAP版本项目
1.选择mpa+ef+module-zero 取名字 2.用vs打开项目后,在解决方案上右键 还原nuget包 3.打开程序包管理器控制台,选择以EntityFramework结尾的项目,并执行upd ...
- 《得知opencv》注意事项——矩阵和图像处理——cvAdd、cvAddS and cvAddWeighted
矩阵和图像操作 (1)cvAdd函数 其结构 void cvAdd(//图像加和 const CvArr* src1,//第一个原矩阵 const CvArr* src2,//第二个原矩阵 CvArr ...
- blockchain_eth客户端安装 & geth使用 &批量转账(一)
这里是第一篇,主要讲eth客户端安装 eth官网 https://ethereum.org/ 国内有一个论坛内容挺多的,可以参考 http://ethfans.org/ eth客户端: eth客户端 ...
- RGB565与RGB555标志识别位图文件格式
近日从本地16比特位图读出象素彩色数据,并填充ANDROID的BITMAP数据.发现,使用CAVAS当屏幕显示,照片显示的颜色不正确,找了很多资料,原来发现两个原因: 1.将位图的颜色分量掩码弄错了, ...
- WPF中画虚线
原文:WPF中画虚线 在WPF中,画线的方法十分简单,只要声明一个Line然后添加到指定的位置就可以了,但Line并不仅仅只能画一条直线,还可以对直线进行修饰. 1.Line.StrokeDashAr ...
- SSM导出报表为csv文件
报表导出思路为,在后台用iDataReader将查询得到的数据写进文件并压缩,向前端返回文件位置的链接,在前端执行下载操作. web端: 1. ajax请求url,将返回的路径json字符串解析并执行 ...
- Java数据存储机制的实现
原文地址:http://yanwushu.sinaapp.com/java_data_storage/ Java程序在执行时须要为一系列的值或者对象分配内存,这些值都存在什么地方?用什么样的数据结构存 ...
- 持续集成及部署利器:Go(不要和Google的编程语言Go混淆了!)
Go是一款先进的持续集成和发布管理系统,由ThoughtWorks开发.(不要和Google的编程语言Go混淆了!)其前身为CruiseControl,是ThoughtWorks在做咨询和交付交付项目 ...
