[ML] Load and preview large scale data
Ref: [Feature] Preprocessing tutorial
主要是 “无量纲化” 之前的部分。
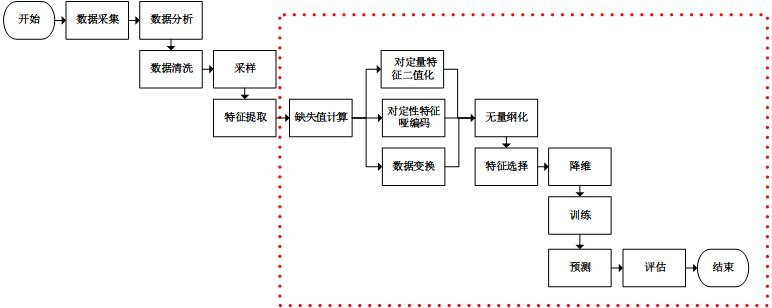
加载数据
一、大数据源
http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/
http://aws.amazon.com/publicdatasets/
http://www.kaggle.com/
http://www.kdnuggets.com/datasets/index.html
二、初步查看
了解需求
Swipejobs is all about matching Jobs to Workers. Your challenge is to analyse the data provided and answer the questions below. You can access the data by opening the following S3 bucket: /* somewhere */ Please note that Worker (worker parquet files) has one or more job tickets (jobticket parquet files) associated with it. Using these parquet files: 求相关性
1. Is there a co-relation between jobticket.jobTicketState, jobticket.clickedCalloff and jobticket.assignedBySwipeJobs values across workers. 预测
2. Looking at Worker.profileLastUpdatedDate values, calculate an estimation for workers who will update their profile in the next two weeks. requirement
Requirement
粗看数据
head -5 <file>
less <file>
三、数据读取
python读取txt文件
没有格式,就要split出格式,还是建议之后转到df格式,操作方便些。
PATH = "/home/ubuntu/work/rajdeepd-spark-ml/spark-ml/data"
user_data = sc.textFile("%s/ml-100k/u.user" % PATH) user_fields = user_data.map(lambda line: line.split("|"))
print(user_fields)
user_fields.take(5)
PythonRDD[29] at RDD at PythonRDD.scala:53
Out[19]:
[['', '', 'M', 'technician', ''],
['', '', 'F', 'other', ''],
['', '', 'M', 'writer', ''],
['', '', 'M', 'technician', ''],
['', '', 'F', 'other', '']]
python读取parquet文件
Spark SQL还是作为首选工具,参见:[Spark] 03 - Spark SQL
Ref: 读写parquet格式文件的几种方式
本文将介绍常用parquet文件读写的几种方式
2. 用 sparkSql 读写hive中的parquet。
3. 用新旧MapReduce读写parquet格式文件。
Ref: How to read parquet data from S3 to spark dataframe Python?
spark = SparkSession.builder
.master("local")
.appName("app name")
.config("spark.some.config.option", true).getOrCreate() df = spark.read.parquet("s3://path/to/parquet/file.parquet")
python读取csv文件
# define the schema, corresponding to a line in the csv data file.
schema = StructType([
StructField("long", FloatType(), nullable=True),
StructField("lat", FloatType(), nullable=True),
StructField("medage", FloatType(), nullable=True),
StructField("totrooms", FloatType(), nullable=True),
StructField("totbdrms", FloatType(), nullable=True),
StructField("pop", FloatType(), nullable=True),
StructField("houshlds", FloatType(), nullable=True),
StructField("medinc", FloatType(), nullable=True),
StructField("medhv", FloatType(), nullable=True)]
)
schema
# 参数中包含了column的定义
housing_df = spark.read.csv(path=HOUSING_DATA, schema=schema).cache()
# User-friendly的表格显示
housing_df.show(5)
# 包括了列的性质
housing_df.printSchema()
四、数据库到HBase
MySQL (binlog) --> Maxwell --> Kafka --> HBase --> Parquet.
抛出问题
对应方案
(1) MySQL到HBase
(2) HBase到Parquet
Ref: How to move HBase tables to HDFS in Parquet format?
Ref: spark 读 hbase parquet 哪个快
Spark读hbase,生成task受所查询table的region个数限制,任务数有限,例如查询的40G数据,10G一个region,很可能就4~6个region,初始的task数就只有4~6个左右,RDD后续可以partition设置task数;spark读parquet按默认的bolck个数生成task个数,例如128M一个bolck,差不多就是300多个task,初始载入情况就比hbase快,而且直接载入parquet文件到spark的内存,而hbase还需要同regionserver交互把数据传到spark的内存也是需要消耗时间的。
总体来说,读parquet更快。
了解数据
—— RDD方式,以及正统的高阶方法:[Spark] 03 - Spark SQL
一、初步清理数据
前期发现缺失数据、不合格的数据。
# 可用于检查“空数据”、“不合格的数据”
def convert_year(x):
try:
return int(x[-4:])
except:
return 1900 # there is a 'bad' data point with a blank year, which we set to 1900 and will filter out later movie_fields = movie_data.map(lambda lines: lines.split("|"))
years = movie_fields.map(lambda fields: fields[2]).map(lambda x: convert_year(x))
二、特征内部类别数
num_genders = user_fields.map(lambda fields: fields[2]).distinct().count()
num_occupations = user_fields.map(lambda fields: fields[3]).distinct().count()
num_zipcodes = user_fields.map(lambda fields: fields[4]).distinct().count()
也就是下图中惨素hist中的bins的原始值。
三、某个特征可视化
是否符合正态分布,可视化后甄别“异常值”。
数据如果有偏,可以通过log转换。
plt.hist 方法
简单地,使用hist直接得到柱状图;如果数据量太大,可以先抽样,再显示。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ages = user_fields.map(lambda x: int(x[1])).collect()
plt.hist(ages, bins=30, color='gray', normed=True)
fig = matplotlib.pyplot.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(8, 5)
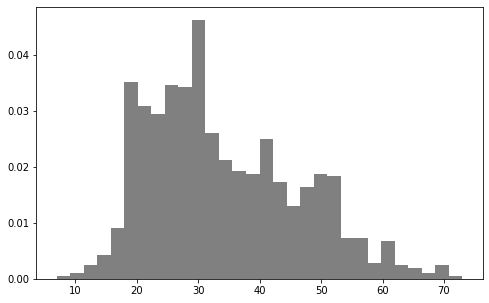
* Pandas.plot 方法
显示特征列 “medage" 的直方图。
result_df.toPandas().plot.bar(x='medage',figsize=(14, 6))
reduceByKey 方法
import numpy as np count_by_occupation = user_fields.map(lambda fields: (fields[3], 1)).reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y).collect()
# count_by_occupation2 = user_fields.map(lambda fields: fields[3]).countByValue() #######################################################
# 以下怎么用了 np 这个处理小数据的东东。
#######################################################
x_axis1 = np.array([c[0] for c in count_by_occupation])
y_axis1 = np.array([c[1] for c in count_by_occupation]) # sort by y_axis1
x_axis = x_axis1[np.argsort(y_axis1)]
y_axis = y_axis1[np.argsort(y_axis1)] pos = np.arange(len(x_axis))
width = 1.0 ax = plt.axes()
ax.set_xticks(pos + (width / 2))
ax.set_xticklabels(x_axis) plt.bar(pos, y_axis, width, color='lightblue')
plt.xticks(rotation=30)
fig = matplotlib.pyplot.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(16, 5)
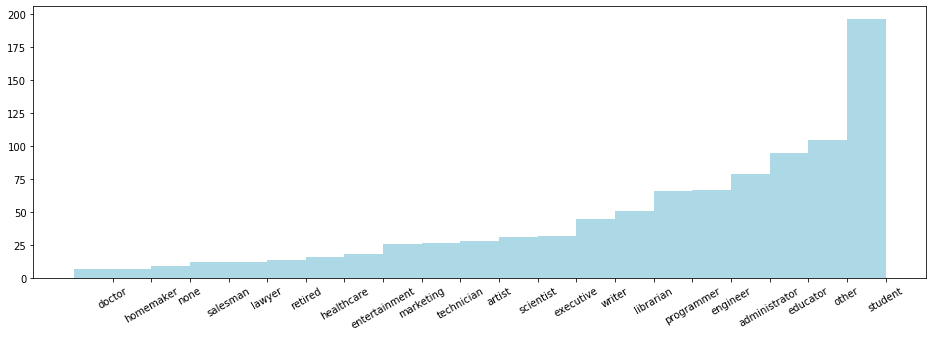
四、特征统计量
RDD 获取一列
rating_data = rating_data_raw.map(lambda line: line.split("\t"))
ratings = rating_data.map(lambda fields: int(fields[2]))
max_rating = ratings.reduce(lambda x, y: max(x, y))
min_rating = ratings.reduce(lambda x, y: min(x, y))
mean_rating = ratings.reduce(lambda x, y: x + y) / float(num_ratings)
median_rating = np.median(ratings.collect())
We can also use the stats function to get some similar information to the above.
ratings.stats() Out[11]:
(count: 100000, mean: 3.52986, stdev: 1.12566797076, max: 5.0, min: 1.0)
* Summary Statistics
(housing_df.describe().select(
"summary",
F.round("medage", 4).alias("medage"),
F.round("totrooms", 4).alias("totrooms"),
F.round("totbdrms", 4).alias("totbdrms"),
F.round("pop", 4).alias("pop"),
F.round("houshlds", 4).alias("houshlds"),
F.round("medinc", 4).alias("medinc"),
F.round("medhv", 4).alias("medhv"))
.show())
+-------+-------+---------+--------+---------+--------+-------+-----------+
|summary| medage| totrooms|totbdrms| pop|houshlds| medinc| medhv|
+-------+-------+---------+--------+---------+--------+-------+-----------+
| count|20640.0| 20640.0| 20640.0| 20640.0| 20640.0|20640.0| 20640.0|
| mean|28.6395|2635.7631| 537.898|1425.4767|499.5397| 3.8707|206855.8169|
| stddev|12.5856|2181.6153|421.2479|1132.4621|382.3298| 1.8998|115395.6159|
| min| 1.0| 2.0| 1.0| 3.0| 1.0| 0.4999| 14999.0|
| max| 52.0| 39320.0| 6445.0| 35682.0| 6082.0|15.0001| 500001.0|
+-------+-------+---------+--------+---------+--------+-------+-----------+
清洗数据
—— Spark SQL's DataFrame为主力工具,参考: [Spark] 03 - Spark SQL
一、重复数据
Ref: https://github.com/drabastomek/learningPySpark/blob/master/Chapter04/LearningPySpark_Chapter04.ipynb
df可以通过rdd转变而来。
1. 找重复的行
print('Count of rows: {0}'.format(df.count()))
print('Count of distinct rows: {0}'.format(df.distinct().count())) # 所有列的集合
print('Count of distinct ids: {0}'.format(df.select([c for c in df.columns if c != 'id']).distinct().count())) # 自定义某些列的集合
2. 去除 "完全相同的 row",包括 index
df = df.dropDuplicates()
df.show()
3. 去除 "相同的 row",不包括 index
df = df.dropDuplicates(subset=[c for c in df.columns if c != 'id'])
df.show()
二、缺失值
构造一个典型的 “问题数据表”。
df_miss = spark.createDataFrame([
(1, 143.5, 5.6, 28, 'M', 100000),
(2, 167.2, 5.4, 45, 'M', None),
(3, None , 5.2, None, None, None),
(4, 144.5, 5.9, 33, 'M', None),
(5, 133.2, 5.7, 54, 'F', None),
(6, 124.1, 5.2, None, 'F', None),
(7, 129.2, 5.3, 42, 'M', 76000),
], ['id', 'weight', 'height', 'age', 'gender', 'income'])
(1) 哪些行有缺失值?
df_miss.rdd.map(
lambda row: (row['id'], sum([c == None for c in row]))
).collect()
[(1, 0), (2, 1), (3, 4), (4, 1), (5, 1), (6, 2), (7, 0)]
(2) 瞧瞧细节
df_miss.where('id == 3').show()
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
| id|weight|height| age|gender|income|
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
| 3| null| 5.2|null| null| null|
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
(3) 每列的缺失率如何?
df_miss.agg(*[
(1 - (fn.count(c) / fn.count('*'))).alias(c + '_missing')
for c in df_miss.columns
]).show()
+----------+------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+
|id_missing| weight_missing|height_missing| age_missing| gender_missing| income_missing|
+----------+------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+
| 0.0|0.1428571428571429| 0.0|0.2857142857142857|0.1428571428571429|0.7142857142857143|
+----------+------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+
(4) 缺失太多的特征,则“废”
df_miss_no_income = df_miss.select([c for c in df_miss.columns if c != 'income'])
df_miss_no_income.show()
+---+------+------+----+------+
| id|weight|height| age|gender|
+---+------+------+----+------+
| 1| 143.5| 5.6| 28| M|
| 2| 167.2| 5.4| 45| M|
| 3| null| 5.2|null| null|
| 4| 144.5| 5.9| 33| M|
| 5| 133.2| 5.7| 54| F|
| 6| 124.1| 5.2|null| F|
| 7| 129.2| 5.3| 42| M|
+---+------+------+----+------+
(5) 缺失太多的行,则“废”
df_miss_no_income.dropna(thresh=3).show()
+---+------+------+----+------+
| id|weight|height| age|gender|
+---+------+------+----+------+
| 1| 143.5| 5.6| 28| M|
| 2| 167.2| 5.4| 45| M|
| 4| 144.5| 5.9| 33| M|
| 5| 133.2| 5.7| 54| F|
| 6| 124.1| 5.2|null| F|
| 7| 129.2| 5.3| 42| M|
+---+------+------+----+------+
(6) 填补缺失值
means = df_miss_no_income.agg(
*[fn.mean(c).alias(c) for c in df_miss_no_income.columns if c != 'gender']
).toPandas().to_dict('records')[0] means['gender'] = 'missing' df_miss_no_income.fillna(means).show()
+---+------------------+------+---+-------+
| id| weight|height|age| gender|
+---+------------------+------+---+-------+
| 1| 143.5| 5.6| 28| M|
| 2| 167.2| 5.4| 45| M|
| 3|140.28333333333333| 5.2| 40|missing|
| 4| 144.5| 5.9| 33| M|
| 5| 133.2| 5.7| 54| F|
| 6| 124.1| 5.2| 40| F|
| 7| 129.2| 5.3| 42| M|
+---+------------------+------+---+-------+
或者,通过 Imputer 填补缺失值,如下。
from pyspark.ml.feature import Imputer df = spark.createDataFrame([
(1.0, float("nan")),
(2.0, float("nan")),
(float("nan"), 3.0),
(4.0, 4.0),
(5.0, 5.0)
], ["a", "b"]) imputer = Imputer(inputCols=["a", "b"], outputCols=["out_a", "out_b"])
model = imputer.fit(df) model.transform(df).show()
三、异常值
1. 基本策略
- 判定为“outlier”,首先要通过统计描述可视化数据。
- 常识以外的数据点也可以直接祛除,比如:age = 300
df_outliers = spark.createDataFrame([
(1, 143.5, 5.3, 28),
(2, 154.2, 5.5, 45),
(3, 342.3, 5.1, 99),
(4, 144.5, 5.5, 33),
(5, 133.2, 5.4, 54),
(6, 124.1, 5.1, 21),
(7, 129.2, 5.3, 42),
], ['id', 'weight', 'height', 'age'])
2. 定义有效区间
cols = ['weight', 'height', 'age']
bounds = {} for col in cols:
quantiles = df_outliers.approxQuantile(col, [0.25, 0.75], 0.05)
IQR = quantiles[1] - quantiles[0]
bounds[col] = [quantiles[0] - 1.5 * IQR, quantiles[1] + 1.5 * IQR] bounds
{'age': [-11.0, 93.0],
'height': [4.499999999999999, 6.1000000000000005],
'weight': [91.69999999999999, 191.7]}
3. filter有效区间
outliers = df_outliers.select(*['id'] + [
(
(df_outliers[c] < bounds[c][0]) |
(df_outliers[c] > bounds[c][1])
).alias(c + '_o') for c in cols
])
outliers.show()
+---+--------+--------+-----+
| id|weight_o|height_o|age_o|
+---+--------+--------+-----+
| 1| false| false|false|
| 2| false| false|false|
| 3| true| false| true|
| 4| false| false|false|
| 5| false| false|false|
| 6| false| false|false|
| 7| false| false|false|
+---+--------+--------+-----+
并查看细节,如下。
df_outliers = df_outliers.join(outliers, on='id')
df_outliers.filter('weight_o').select('id', 'weight').show()
df_outliers.filter('age_o').select('id', 'age').show()
+---+------+
| id|weight|
+---+------+
| 3| 342.3|
+---+------+ +---+---+
| id|age|
+---+---+
| 3| 99|
+---+---+
[ML] Load and preview large scale data的更多相关文章
- Introducing DataFrames in Apache Spark for Large Scale Data Science(中英双语)
文章标题 Introducing DataFrames in Apache Spark for Large Scale Data Science 一个用于大规模数据科学的API——DataFrame ...
- 论文笔记之:Large Scale Distributed Semi-Supervised Learning Using Streaming Approximation
Large Scale Distributed Semi-Supervised Learning Using Streaming Approximation Google 2016.10.06 官方 ...
- 大规模视觉识别挑战赛ILSVRC2015各团队结果和方法 Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2015
Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2015 (ILSVRC2015) Legend: Yellow background = winner in thi ...
- Lessons learned developing a practical large scale machine learning system
原文:http://googleresearch.blogspot.jp/2010/04/lessons-learned-developing-practical.html Lessons learn ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 17—Large Scale Machine Learning 大规模机器学习
Lecture17 Large Scale Machine Learning大规模机器学习 17.1 大型数据集的学习 Learning With Large Datasets 如果有一个低方差的模型 ...
- [C12] 大规模机器学习(Large Scale Machine Learning)
大规模机器学习(Large Scale Machine Learning) 大型数据集的学习(Learning With Large Datasets) 如果你回顾一下最近5年或10年的机器学习历史. ...
- Could not load file or assembly 'MySql.Data.CF,
Could not load file or assembly 'MySql.Data.CF, Version=6.4.4.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=c56 ...
- Could not load file or assembly 'System.Data.SQLite' or one of its dependencies
试图加载格式不正确的程 异常类型 异常消息Could not load file or assembly 'System.Data.SQLite' or one of its dependencies ...
- SQLite 解决:Could not load file or assembly 'System.Data.SQLite ... 试图加载格式不正确的程序/or one of its dependencies. 找不到指定的模块。
Could not load file or assembly 'System.Data.SQLite.dll' or one of its dependencies. 找不到指定的模块. 错误提示 ...
随机推荐
- vim文本编辑及文件查找应用3
文件查找 locate,find两个命令 在文件系统上查找符合条件的文件: 实现工具:locate,find locate命令: 依赖于事先构建好的索引库,索引库可以由下边两种方式构建 系统自动实现( ...
- anaconda环境---ubuntu下重装
anaconda环境---ubuntu下重装 @wp20190312 为何重装? 配置一个环境,意外发现conda命令不好用了,提示“找不到conda模块”,整个conda虚拟环境中的工程项目无法使用 ...
- jenkins"控制台输出"乱码问题解决
今天在搭建Jenkins环境时,安装完Tomcat.Jenkins.创建项目进行构建后,在查看控制台输出时,结果中文全部显示乱码.然后呢,就是漫长的解决历程,最终呢,解决乱码问题的时间终于超过了环境搭 ...
- shell字符串处理
一.字符串切片: ${#var}:返回字符串变量var的长度${var:offset}:返回字符串变量var中从第offset个字符后(不包括第offset个字符)的字符开始,到最后的部分,offse ...
- Excel 中大量图片如何快速导出? 转载自:http://www.zhihu.com/question/20800948
我的办法如下,应该也不慢. 如果是针对以.xlsx为后缀的表格(Excel2007以上的版本),这样做:显示后缀的情况下,直接重命名,把后缀.xlsx改成.rar或者.zip,然后解压出里面的图片文件 ...
- mysql查询疯狂41例
援引自 http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5748496.html 一.表关系请创建如下表,并创建相关约束 二.操作表 1.自行创建测试数据 2.查询“生 ...
- qt 启动参数 -qws
运行嵌入式程序 在嵌入式QT版本中,程序需要服务器或自己作为服务器程序. 服务器程序构造的方法是构造一个QApplication::GuiServe类型的QApplication对象.或者使用-qws ...
- Vue公共结果页面实现
需求 我希望写一个公共结果页面,满足所有模块的结果展示,页面设计要素如下: 结果图标type(成功图标,失败图标) 标题title(如:提交成功) 描述descripton(如:您的工单已提交,请等待 ...
- React组件间通信-sub/pub机制
React生命周期第二个demo演示了兄弟组件的通信,需要通过父组件,比较麻烦:下面介绍sub/pub机制来事项组件间通信. 1.导包 npm i pubsub-js 2.UserSearch.jsx ...
- Monkey实战测试步骤
1,adb devices 确保设备在线 2,adb shell pm list packages 查看包名 3,adb shell monkey -p com.xzck.wangcai --ig ...
