Persistent Bookcase CodeForces - 707D (dfs 离线处理有根树模型的问题&&Bitset)
Persistent Bookcase
time limit per test 2 seconds
memory limit per test 512 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are data structures that always preserves the previous version of itself and access to it when it is modified.
After reaching home Alina decided to invent her own persistent data structure. Inventing didn't take long: there is a bookcase right behind her bed. Alina thinks that the bookcase is a good choice for a persistent data structure. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf.
The bookcase consists of n shelves, and each shelf has exactly m positions for books at it. Alina enumerates shelves by integers from 1 to n and positions at shelves — from 1 to m. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf in it.
Alina wrote down q operations, which will be consecutively applied to the bookcase. Each of the operations has one of four types:
- 1 i j — Place a book at position j at shelf i if there is no book at it.
- 2 i j — Remove the book from position j at shelf i if there is a book at it.
- 3 i — Invert book placing at shelf i. This means that from every position at shelf i which has a book at it, the book should be removed, and at every position at shelf i which has not book at it, a book should be placed.
- 4 k — Return the books in the bookcase in a state they were after applying k-th operation. In particular, k = 0 means that the bookcase should be in initial state, thus every book in the bookcase should be removed from its position.
After applying each of operation Alina is interested in the number of books in the bookcase. Alina got 'A' in the school and had no problem finding this values. Will you do so?
Input
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 103, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the bookcase dimensions and the number of operations respectively.
The next q lines describes operations in chronological order — i-th of them describes i-th operation in one of the four formats described in the statement.
It is guaranteed that shelf indices and position indices are correct, and in each of fourth-type operation the number k corresponds to some operation before it or equals to 0.
Output
For each operation, print the number of books in the bookcase after applying it in a separate line. The answers should be printed in chronological order.
Examples
input
Copy
2 3 31 1 13 24 0
output
Copy
140
input
Copy
4 2 63 22 2 23 33 22 2 23 2
output
Copy
213324
input
Copy
2 2 23 22 2 1
output
Copy
21
Note
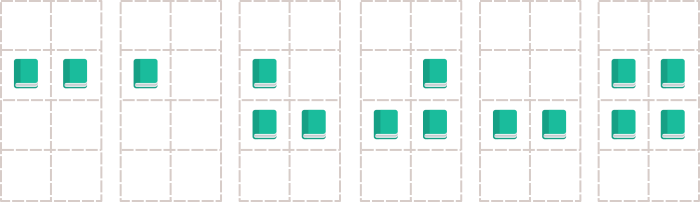
This image illustrates the second sample case.
题意:
现在有一个N*M的书架,有Q个操作,对于每个操作,输入opt:
如果opt==1,那么输入x,y,如果第x行第y列无书,则放一本书。
如果opt==2,那么输入x,y,如果第x行第y列有书,则取走那本书。
如果opt==3,那么输入x,将第x行有书的取走,无书的位置放一本。
如果opt==4,那么输入k,表示把书架的情况恢复为第k次操作后的样貌,k在当前操作之前。
思路:
注意到整体操作顺序为有根树,可以DFS回溯处理,对于书架上的书个数情况,可以直接用bitset。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <iomanip>
#define ALL(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define sz(a) int(a.size())
#define rep(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<n;i++)
#define repd(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define pll pair<long long ,long long>
#define gbtb ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define MS0(X) memset((X), 0, sizeof((X)))
#define MSC0(X) memset((X), '\0', sizeof((X)))
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define eps 1e-6
#define gg(x) getInt(&x)
#define chu(x) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]"<<endl
#define du3(a,b,c) scanf("%d %d %d",&(a),&(b),&(c))
#define du2(a,b) scanf("%d %d",&(a),&(b))
#define du1(a) scanf("%d",&(a));
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;}
ll lcm(ll a, ll b) {return a / gcd(a, b) * b;}
ll powmod(ll a, ll b, ll MOD) {a %= MOD; if (a == 0ll) {return 0ll;} ll ans = 1; while (b) {if (b & 1) {ans = ans * a % MOD;} a = a * a % MOD; b >>= 1;} return ans;}
void Pv(const vector<int> &V) {int Len = sz(V); for (int i = 0; i < Len; ++i) {printf("%d", V[i] ); if (i != Len - 1) {printf(" ");} else {printf("\n");}}}
void Pvl(const vector<ll> &V) {int Len = sz(V); for (int i = 0; i < Len; ++i) {printf("%lld", V[i] ); if (i != Len - 1) {printf(" ");} else {printf("\n");}}}
inline void getInt(int *p);
const int maxn = 1010;
const int manq = 1e5 + 10;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*** TEMPLATE CODE * * STARTS HERE ***/
bitset<maxn> a[maxn], p;
int n, m;
int q;
int op[manq];
int x[manq];
int y[manq];
std::vector<int> son[manq];
int ans[manq];
void dfs(int u, int now)
{
for (auto v : son[u]) {
if (op[v] == 1) {
if (a[x[v]][y[v]] == 0) {
a[x[v]][y[v]] = 1;
ans[v] = now + 1;
dfs(v, now + 1);
a[x[v]][y[v]] = 0;
} else {
ans[v] = now ;
dfs(v, now );
}
} else if (op[v] == 2) {
if (a[x[v]][y[v]] == 1) {
a[x[v]][y[v]] = 0;
ans[v] = now - 1;
dfs(v, now - 1);
a[x[v]][y[v]] = 1;
} else {
ans[v] = now ;
dfs(v, now );
}
} else if (op[v] == 3) {
ans[v] = now - a[x[v]].count();
a[x[v]] ^= p;
ans[v] += a[x[v]].count();
dfs(v, ans[v]);
a[x[v]] ^= p;
} else if (op[v] == 4) {
ans[v] = ans[x[v]];
dfs(v, ans[v]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen("D:\\code\\text\\input.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("D:\\code\\text\\output.txt","w",stdout);
du3(n, m, q);
repd(i, 1, m) {
p.set(i);
}
repd(i, 1, q) {
du1(op[i]);
if (op[i] <= 2) {
du2(x[i], y[i]);
} else {
du1(x[i]);
}
if (op[i] <= 3) {
son[i - 1].push_back(i);
} else {
son[x[i]].push_back(i);
}
}
dfs(0, 0);
repd(i, 1, q) {
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}
inline void getInt(int *p)
{
char ch;
do {
ch = getchar();
} while (ch == ' ' || ch == '\n');
if (ch == '-') {
*p = -(getchar() - '0');
while ((ch = getchar()) >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
*p = *p * 10 - ch + '0';
}
} else {
*p = ch - '0';
while ((ch = getchar()) >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
*p = *p * 10 + ch - '0';
}
}
}
Persistent Bookcase CodeForces - 707D (dfs 离线处理有根树模型的问题&&Bitset)的更多相关文章
- D. Persistent Bookcase(Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2))
D. Persistent Bookcase time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input stand ...
- codeforces 707D D. Persistent Bookcase(dfs)
题目链接: D. Persistent Bookcase time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input ...
- CodeForces #368 div2 D Persistent Bookcase DFS
题目链接:D Persistent Bookcase 题意:有一个n*m的书架,开始是空的,现在有k种操作: 1 x y 这个位置如果没书,放书. 2 x y 这个位置如果有书,拿走. 3 x 反转这 ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) D. Persistent Bookcase 离线 暴力
D. Persistent Bookcase 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/D Description Recently in ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) D. Persistent Bookcase
Persistent Bookcase Problem Description: Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persisten ...
- 【Codeforces-707D】Persistent Bookcase DFS + 线段树
D. Persistent Bookcase Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: ...
- CF707D Persistent Bookcase
CF707D Persistent Bookcase 洛谷评测传送门 题目描述 Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent ...
- Persistent Bookcase
Persistent Bookcase time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input standard ...
- CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树
CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树 题意 就是树上有n个点,然后每个点都有一盏灯,给出初始的状态,1表示亮,0表示不亮,然后有两种操作,第一种是get x,表示你需要输出x的子树和x本身 ...
随机推荐
- utgard OPC 主要功能简介
度娘还行,尽管不好用,但所有的开发人员不懈努力地写博客,能得到很多东西! 这里向所有未谋面的博主们致敬! 搜了一堆OPC资料,在这里整理一下,用一个封装类来说明utgard的主要接口.使用了java自 ...
- 在vue项目中获取当前城市
在vue项目中使用百度地图获取当前城市:https://www.jianshu.com/p/0819cfd46712 Vue2 :百度地图bmap:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ ...
- 前端JS之HTML利用XMLHttpRequest()和FormData()进行大文件分段上传
用于网页向后端上传大文件 ### 前端代码<body> <input type="file" name="video" id="fi ...
- nginx 配置用户认证
nginx 配置用户认证有两种方式: 1.auth_basic 本机认证,由ngx_http_auth_basic_module模块实现.配置段: http, server, location, li ...
- POJ2406 kmp算法next数组-串的最小循环节/循环周期
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2406 题目大意:问给出的字符串最多由多少个子串相乘得来的. 思路:利用next数组的含义来解. 1.一个串的最小循环节长度:len - ...
- [Agc030B]Tree Burning_贪心
Tree Burning 题目链接:https://atcoder.jp/contests/agc030/tasks/agc030_b 数据范围:略. 题解: 开始以为是左右左右这样,发现过不去样例. ...
- 怎样理解JS的预解析机制
JS的预解析包括两部分: 1. 变量提升 2. 函数声明 对于变量提升, 可以看下下面这块代码 console.log(name); // undefined var name = "Lil ...
- 第一讲,DOS头文件格式
今天讲解PE文件格式的DOS头文件格式 首先我们要理解,什么是文件格式,我们常说的EXE可执行程序,就是一个文件格式,那么我们要了解它里面到底存了什么内容 简短的说明. 我们要知道,PE文件格式,是微 ...
- BFS以及hash表判重的应用~
主要还是讲下hash判重的问题吧 这道题目用的是除法求余散列方式 前几天看了下算法导论 由于我们用的是线性再寻址的方式来解决冲突问题 所以hash表的大小(余数的范围)要包含我们要求的范围 对mod的 ...
- 计算两个坐标点的距离(高德or百度)
/// <summary> /// 获取两个坐标之间的距离 /// </summary> /// <param name="lat1">第一个坐 ...
