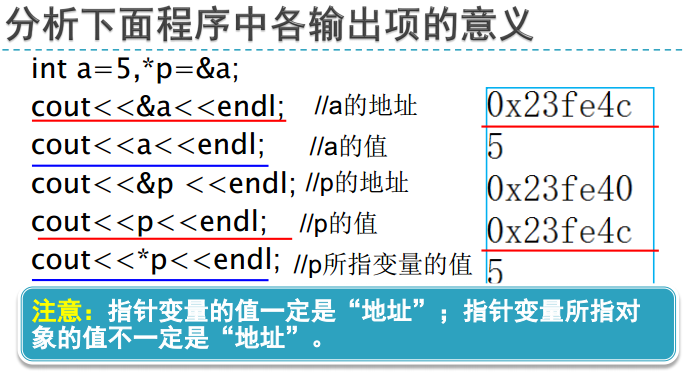
C++ 按址操作
一、指针
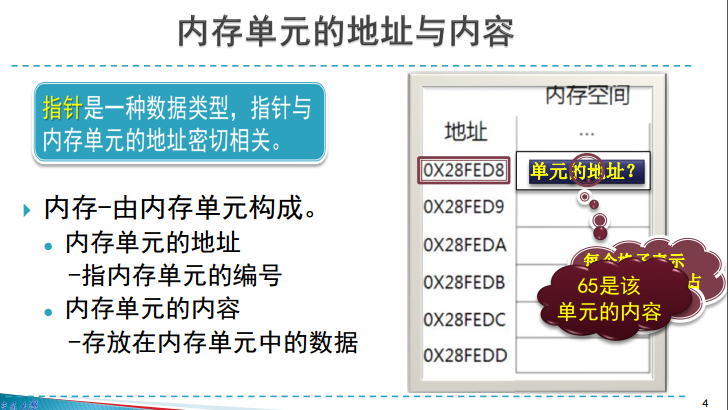

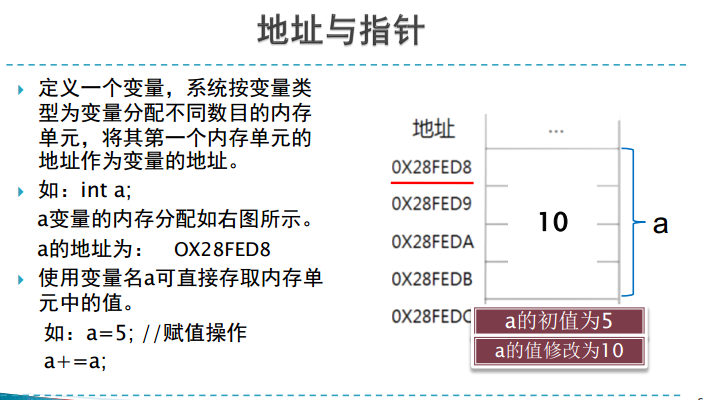
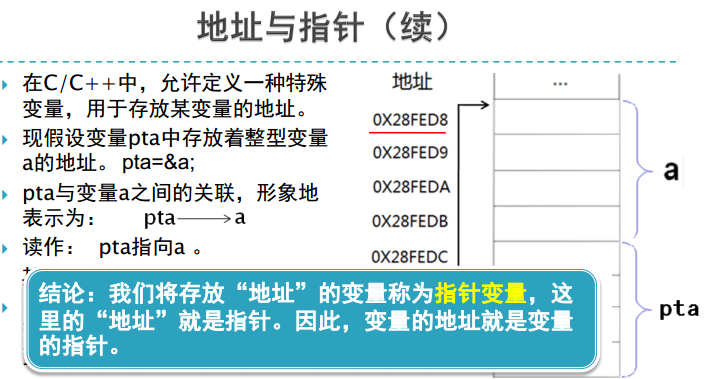
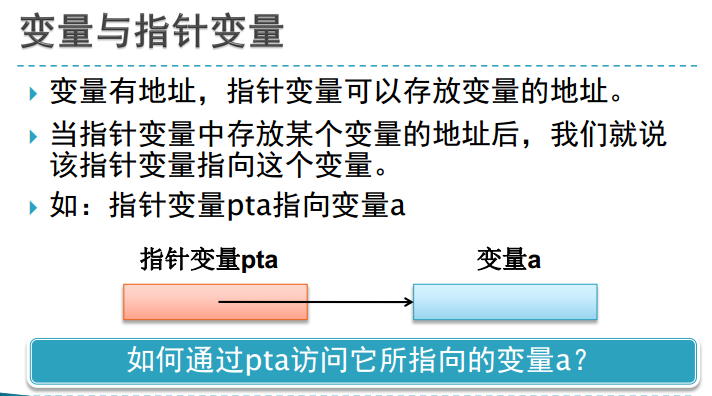
二、变量与指针


 注意区别char 和char *。
注意区别char 和char *。

 !!!!!!!
!!!!!!!




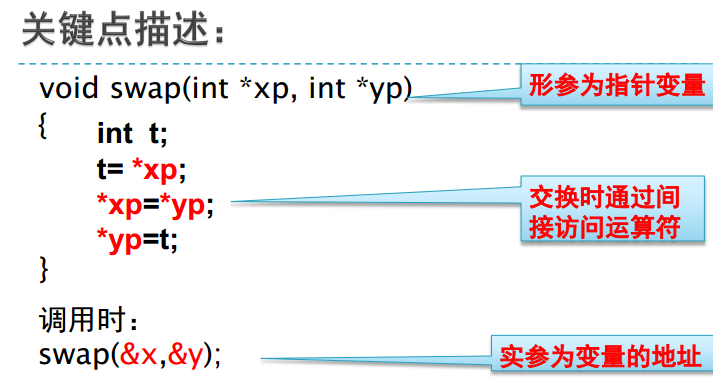
二、函数与指针


#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *px,int *py)
{
int t;
t=*px;
*px=*py;
*py=t;
};
int main()
{
int x=2,y=3;
cout<<"调用前:x="<<x<<",y="<<y<<endl;
swap(&x,&y);
cout<<"调用后:x="<<x<<",y="<<y<<endl;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std;
double faver(int a[],int n,int *max,int *min)
{
double aver=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
aver+=a[i];
*max=*min=a[0];
if(*max<a[i])
*max=a[i];
if(*min>a[i])
*min=a[i];
}
return aver/n;
}; int main()
{
int s[]={1,3,5,6,7,8},min,max,n=6;
double aver;
aver=faver(s,n,&max,&min);
cout<<"average="<<aver<<endl;
cout<<"max="<<max<<" min="<<min<<endl; }
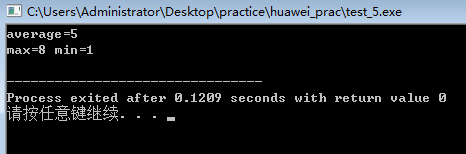
注意1、通过指针这种形式,可以将最大和最小值,平均值带回主函数,通过return的话只能带回一个数。2、调用就用&,定义就用*。


#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std; char *noblank(char *str)
{
while(*str=='')
str++;
return str;
}
int main()
{
char *s1=" using namespace std;";
char *s2;
s2=noblank(s1);
cout<<s2<<endl;
return 0; }
觉得这个例子有点扯

三、数组与指针

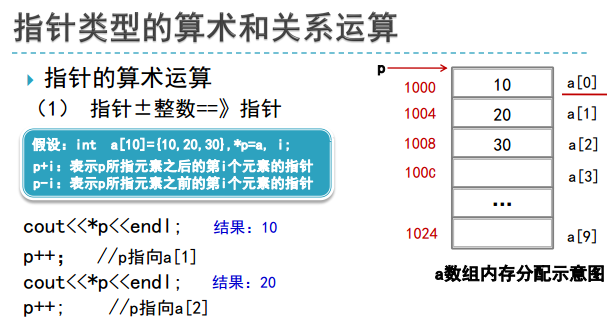
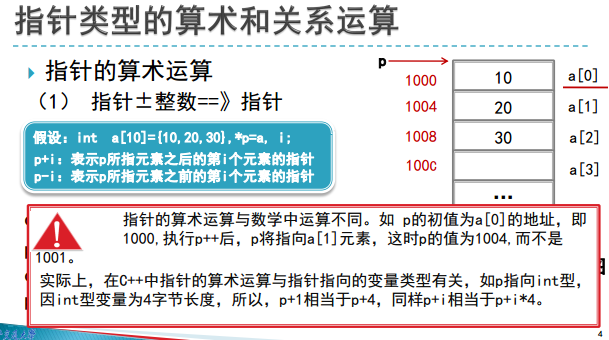
#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std; int main()
{
//int a[10]={10,20,30},*p=a,i;
int a[10]={10,20,30},i,*p;
p=a;
cout<<p<<" "<<*p<<endl;
p++;
cout<<p<<" "<<*p<<endl;
}
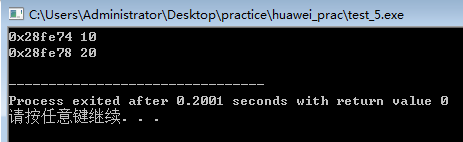

2、指针的关系运算

#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std; int main()
{
double x[5]={1,2,3,4,5.7},*p;
for(p=x;p<x+5;p++)
{
cout<<*p<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
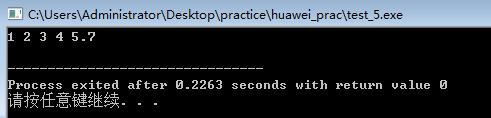


#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std; int main()
{
int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5},i; cout<<"a[i]:";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl; cout<<"*(a+i):";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<*(a+i)<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
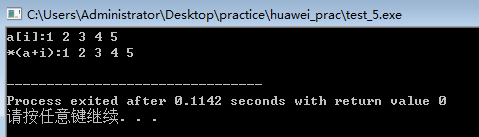
可以看到(a)是地址
#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std; int main()
{
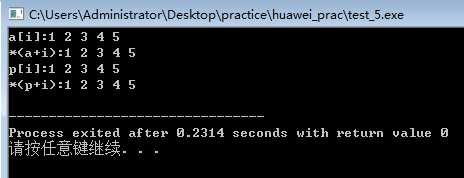
int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5},*p=a,i; cout<<"a[i]:";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl; cout<<"*(a+i):";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<*(a+i)<<" ";
cout<<endl; cout<<"p[i]:";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<p[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl; cout<<"*(p+i):";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<*(p+i)<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
3、二维数组

#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std; int main()
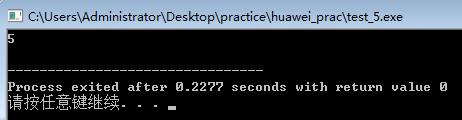
{
int a[2][2]={1,2,4,5},*p;
int max=a[0][0];
for(p=&a[0][0];p<&a[0][0]+4;p++)
{
if(max<*p)
max=*p;
}
cout<<max<<endl; }




#include<iostream>
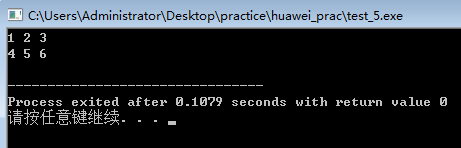
#include<string> using namespace std; int main()
{
int a[2][3]={1,2,3,4,5,6},(*p)[3];
for(p=a;p<a+2;p++)
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
cout<<*(*p+i)<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
} }


例子

#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std; char *strchr(char *str,char c)
{
while(*str!='\0')
{
if(*str==c)
return str;
str++;
}
return NULL;
}
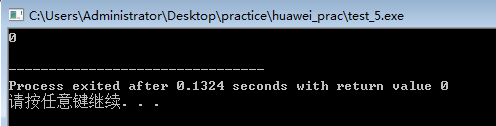
int main()
{
char *str="abcdefghij";
char *p;
p=strchr(str,'a');
if(p==NULL)
cout<<"Null";
else
cout<<p-str<<endl; }

#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std; char *strchr(char *str,char c)
{
while(*str!='\0')
{
if(*str==c)
return str;
str++;
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
char str[]="abcdefghij";
char *p;
p=strchr(str,'c');
if(p==NULL)
cout<<"Null";
else
cout<<p-str<<endl; }

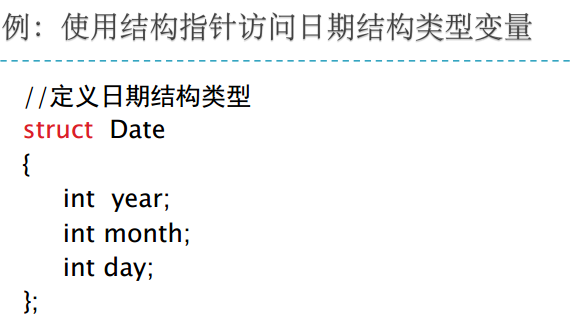
5、指针与结构体

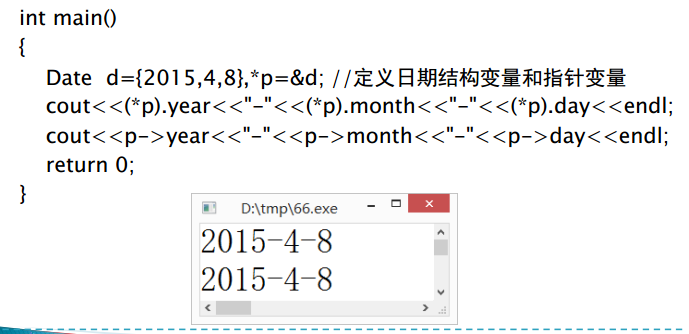
6、动态数组





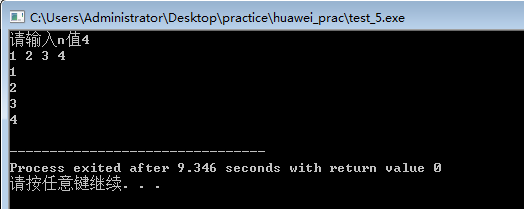
#include<iostream>
#include<string> using namespace std; int main()
{
int n,*p;
cout<<"请输入n值";
cin>>n;
p=new int[n];
if(p==NULL)
{
cout<<"空间申请失败";
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>p[i];
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
cout<<p[j]<<" "<<endl;
return 0; }
C++ 按址操作的更多相关文章
- RTTI、虚函数和虚基类的实现方式、开销分析及使用指导(虚函数的开销很小,就2次操作而已)
白杨 http://baiy.cn “在正确的场合使用恰当的特性” 对称职的C++程序员来说是一个基本标准.想要做到这点,首先要了解语言中每个特性的实现方式及其开销.本文主要讨论相对于传统 C 而言, ...
- C语言 结构体传值与传址分析
/********************************************************************** * 版权所有 (C)2017, Wang maochun ...
- 编译器开发系列--Ocelot语言5.表达式的有效性检查
本篇将对"1=3""&5"这样无法求值的不正确的表达式进行检查. 将检查如下这些问题.●为无法赋值的表达式赋值(例:1 = 2 + 2)●使用非法的函数 ...
- C++ 指向成员函数指针问题
成员函数指针与常规指针不同,一个指向成员变量的指针并不指向一个内存位置.通常最清晰的做法是将指向数据成员的指针看作为一个偏移量. class ru_m { public: typedef int (r ...
- char* 和char[]的区别
以下内容均来自互联网,系笔者汇总并总结. 1. 问题介绍 问题引入:在实习过程中发现了一个以前一直默认的错误,同样char *c = "abc"和char c[]="ab ...
- 【C】 04 - 表达式和语句
程序的生命力体现在它千变万化的行为,而再复杂的系统都是由最基本的语句组成的.C语句形式简单自由,但功能强大.从规范的角度学习C语法,一切显得简单而透彻,无需困扰于各种奇怪的语法. 1. 表达式(exp ...
- C++ 虚函数在基类与派生类对象间的表现及其分析
近来看了侯捷的<深入浅出MFC>,读到C++重要性质中的虚函数与多态那部分内容时,顿时有了疑惑.因为书中说了这么一句:使用“基类之指针”指向“派生类之对象”,由该指针只能调用基类所定义的函 ...
- drupal module 自定义
01 <?php function mytracer_menu() { $items = array(); $items['admin/config/mytracer'] = array( 't ...
- typeof、offsetof、container_of的解释
链表是内核最经典的数据结构之一,说到链表就不得不提及内核最经典(没有之一)的宏container_of. container_of似乎就是为链表而生的,它的主要作用是根据一个结构体变量中的一个域成员变 ...
随机推荐
- C/C++ 手动开O2
手动O2比赛不能用,平时玩玩就好 #pragma GCC optimize (2) #pragma G++ optimize (2)
- 【原创】为什么我的 Kafka 总是连接失败呢?
提出问题 近日助友 Docker 部署 Kafka 服务,服务日志启动正常,但客户端却无法连接 往日曾踩过此坑,然方法均源于博客,其语焉不详,不知为何不行,亦不知为何行,印象不甚深刻,耗费大量时间 为 ...
- 微信小程序结构目录、配置介绍、视图层(数据绑定,运算,列表渲染,条件渲染)
目录 一.小程序结构目录 1.1 小程序文件结构和传统web对比 1.2 基本的项目目录 二.配置介绍 2.1 配置介绍 2.2 全局配置app.json 2.3 page.json 三.视图层 3. ...
- JavaScript对象(二)
Part One:对象的三个特性 原型(prototype) 类(class) 可扩展性(extensible attribute) 1,b.isPrototypeOf(o) //判断b是不是o的 ...
- c:\Windows\system32\rundll32.exe Windows无法访问指定设备、路径或文件,你可能没有适当的权限访问该项目
非常懂如何修改权限的可以尝试,否则老老实实地重新注册的系统的.dll文件 重新注册方法如下: WIN+R下输入命令: cmd /c for %i in (%windir%\system32\*.dll ...
- SpringBoot图文教程15—项目异常怎么办?「跳转404错误页面」「全局异常捕获」
有天上飞的概念,就要有落地的实现 概念十遍不如代码一遍,朋友,希望你把文中所有的代码案例都敲一遍 先赞后看,养成习惯 SpringBoot 图文教程系列文章目录 SpringBoot图文教程1-Spr ...
- TP5使用Redis处理电商秒杀
本篇文章介绍了ThinkPHP使用Redis实现电商秒杀的处理方法,具有一定的参考价值,希望对学习ThinkPHP的朋友有帮助! TP5使用Redis处理电商秒杀 1.首先在TP5中创建抢购活动所需要 ...
- 关于OSS不再维护的一些讨论
FUSE for macOS 将不再维护 Fuse 是一款针对Mac OS的文件系统所开发的一款开源软件. 用于MacOS的FUSE软件包提供了多个API,用于为OS X 10.9至macOS 10. ...
- PDA程序开发的运行配置
前言:因为这个项目是公司一直在做的项目,所以只是简单说一下我从下载项目到成功运行的配置 开发工具:APICloud.雷神模拟器.Visusl studio vs配置: 1.svn下载后台代码后,修改w ...
- [CSP初赛] 组合数学的三个技巧以及从另一方面思考组合类问题
也不知道老师讲不讲 话说好久没有水博客了,看了一点\(python\)然后就去搞文化课了 正好网课讲到组合数学,然后觉得还蛮难的(其实是我变菜了),就想到了以前的\(csp\)的组合数学基础 果然被我 ...
