谈谈Spring中的BeanPostProcessor接口
一、前言
这几天正在复习Spring的相关内容,在了解bean的生命周期的时候,发现其中涉及到一个特殊的接口——BeanPostProcessor接口。由于网上没有找到比较好的博客,所有最后花了好几个小时,通过Spring的官方文档对它做了一个大致的了解,下面就来简单介绍一下这个接口。
二、正文
2.1 BeanPostProcessor的功能
有时候,我们希望Spring容器在创建bean的过程中,能够使用我们自己定义的逻辑,对创建的bean做一些处理,或者执行一些业务。而实现方式有多种,比如自定义bean的初始化话方法等,而BeanPostProcessor接口也是用来实现类似的功能的。
如果我们希望容器中创建的每一个bean,在创建的过程中可以执行一些自定义的逻辑,那么我们就可以编写一个类,并让他实现BeanPostProcessor接口,然后将这个类注册到一个容器中。容器在创建bean的过程中,会优先创建实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的bean,然后,在创建其他bean的时候,会将创建的每一个bean作为参数,调用BeanPostProcessor的方法。而BeanPostProcessor接口的方法,即是由我们自己实现的。下面就来具体介绍一下BeanPostProcessor的使用。
2.2 BeanPostProcessor的使用
我们先看一看BeanPostProcessor接口的代码:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
// 注意这个方法名称关键的是before这个单词
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
// 注意这个方法名称关键的是after这个单词
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
}
可以看到,BeanPostProcessor接口只有两个抽象方法,由实现这个接口的类去实现(后面简称这两个方法为before和after),这两个方法有着相同的参数:
- bean:容器正在创建的那个
bean的引用; - beanName:容器正在创建的那个
bean的名称;
那这两个方法何时执行呢?这就涉及到Spring中,bean的生命周期了。下面引用《Spring实战》中的一张图,这张图表现了bean的生命周期,而Spring容器创建bean的具体过程,请参考这篇博客——简单谈谈Spring的IoC。
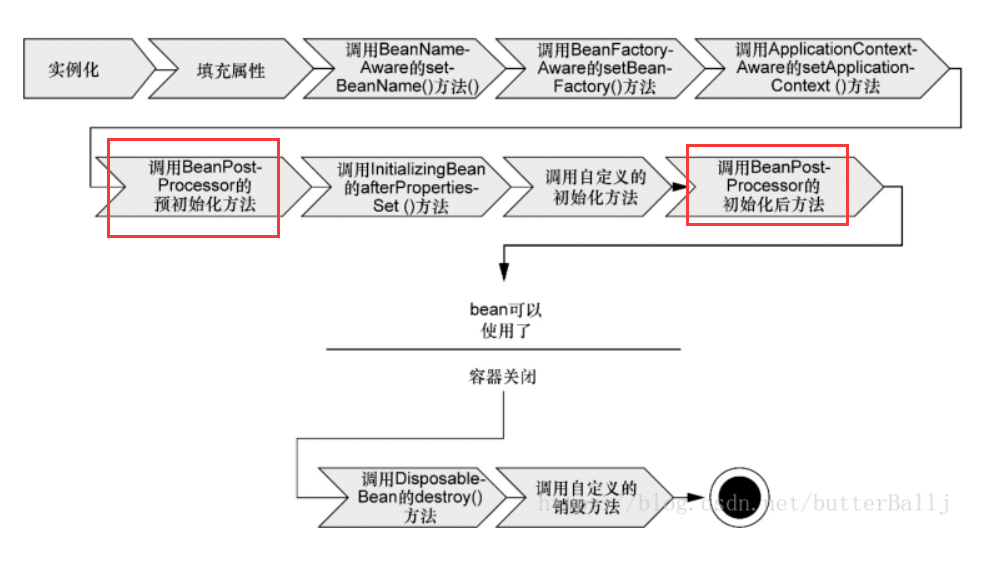
上图中标红的两个地方就是BeanPostProcessor中两个方法的执行时机。Spring容器在创建bean时,如果容器中包含了BeanPostProcessor的实现类对象,那么就会执行这个类的这两个方法,并将当前正在创建的bean的引用以及名称作为参数传递进方法中。这也就是说,BeanPostProcessor的作用域是当前容器中的所有bean(不包括一些特殊的bean,这个后面说)。
值得注意的是,我们可以在一个容器中注册多个不同的BeanPostProcessor的实现类对象,而bean在创建的过程中,将会轮流执行这些对象实现的before和after方法。那执行顺序如何确定呢?Spring提供了一个接口Ordered,我们可以让BeanPostProcessor的实现类实现这个Ordered接口,并实现接口的getOrder方法。这个方法的返回值是一个int类型,Spring容器会通过这个方法的返回值,对容器中的多个BeanPostProcessor对象进行从小到大排序,然后在创建bean时依次执行它们的方法。也就是说,getOrder方法返回值越小的BeanPostProcessor对象,它的方法将越先被执行。
2.3 一个简单的demo
下面就来写一个简单的demo,来看看BeanPostProcessor的效果。首先定义两个普通的bean,就叫User和Car吧:
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
// ... 省略getter和setter...
}
public class Car {
private int speed;
private double price;
// ... 省略getter和setter...
}
在定义一个BeanPostProcessor的实现类,重写接口的方法:
public class PostBean implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
// 输出信息,方便我们看效果
System.out.println("before -- " + beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
// 输出信息,方便我们看效果
System.out.println("after -- " + beanName);
return bean;
}
}
我们直接使用一个Java类作为Spring的配置,就不使用xml配置文件了。配置如下,在这个配置类中,声明了User、Car以及PostBean这三个bean的工厂方法,前两个是普通bean,而PostBean是实现BeanPostProcessor的bean:
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
// 在Spring中注册User这个bean
@Bean
public User user() {
return new User();
}
// 在Spring中注册Car这个bean
@Bean
public Car car() {
return new Car();
}
// 在Spring中注册PostBean这个bean,这个bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口
@Bean
public PostBean postBean() {
return new PostBean();
}
}
好,有了上面四个类,就可以开始测试了,下面是测试方法:
@Test
public void testConfig() {
ApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfig.class);
}
上面这个方法啥也不干,就是创建一个Spring的上下文对象,也就是Spring的IoC容器。这个容器将去加载BeanConfig这个类的配置,然后创建配置类中声明的对象。在创建User和Car的过程中,就会执行BeanPostProcessor实现类的方法。我们看看执行结果:
before -- org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
after -- org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
before -- org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
after -- org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
before -- car
after -- car
before -- user
after -- user
可以看到,BeanPostProcessor的before方法和after方法都被调用了四次,最后两次调用时,传入的参数正是我们自己定义的Bean——User和Car。那为什么调用了四次呢,明明我们只定义了两个普通bean。我们看上面的输出发现,前两次调用,传入的bean是Spring内部的组件。Spring在初始化容器的过程中,会创建一些自己定义的bean用来实现一些功能,而这些bean,也会执行我们注册进容器中的BeanPostProcessor实现类的方法。
2.4 使用BeanPostProcessor时容易踩的坑
BeanPostProcessor这个接口,在使用的过程中,其实还有许多的限制和坑点,若不了解的话,可能会让你对某些结果感到莫名其妙。下面我就来简单地说一说:
(一)BeanPostProcessor依赖的bean,不会执行BeanPostProcessor的方法
当我们在BeanPostProcessor的实现类中,依赖了其他的bean,那么被依赖的bean被创建时,将不会执行它所在的BeanPostProcessor实现类实现的方法,比如我们修改PostBean的实现,如下所示:
@Component
public class PostBean implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered {
// 让PostBean依赖User
@Autowired
private User user;
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
此时,容器在创建User这个bean时,不会执行PostBean实现的两个方法,因为由于PostBean依赖于user,所以user需要在PostBean之前创建完成,这也就意味着在user创建时,PostBean还未初始化完成,所以不会调用它的方法。
(二)BeanPostProcessor以及依赖的bean无法使用AOP
以下是Spring官方文档中的一段话:
Because AOP auto-proxying is implemented as a
BeanPostProcessoritself, neitherBeanPostProcessors nor the beans they reference directly are eligible for auto-proxying, and thus do not have aspects woven into them.
上面这段话的意思大致是说,Spring的AOP代理就是作为BeanPostProcessor实现的,所以我们无法对BeanPostProcessor的实现类使用AOP织入通知,也无法对BeanPostProcessor的实现类依赖的bean使用AOP织入通知。Spring的AOP实现我暂时还没有研究过,所以上面的说AOP作为BeanPostProcessor实现的意思我不是特别明白,但是我们现在只需要关注BeanPostProcessor以及它依赖的bean都无法使用AOP这一点。为了验证上面的说法,我稍微修改一下2.3中的例子,来测试一波。
首先,我们修改2.3中用到的PostBean和User这两个类,让PostBean依赖User这个类,同时为了输出更加地简单,我们将before和after方法中的println语句删了:
@Component
public class PostBean implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered {
// 让PostBean依赖User
@Autowired
private User user;
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
// 此方法用来测试AOP,作为切点
public void testAOP() {
System.out.println("Post Bean");
}
}
@Component
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
// ... 省略getter和setter...
// 此方法用来测试AOP,用作切点
public void testAOP() {
System.out.println("user bean");
}
}
然后,我们定义一个AOP的切面,在切面中将PostBean的testAOP方法作为切点,代码如下:
@Aspect
public class BeanPostProcessorAspect {
// 此方法织入PostBean的testAOP方法
@Before("execution(* cn.tewuyiang.pojo.PostBean.testAOP(..))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before1");
}
// 此方法织入User的testAOP方法
@Before("execution(* cn.tewuyiang.pojo.User.testAOP(..))")
public void before2() {
System.out.println("before2");
}
}
好,这就准备完毕,可以开始测试了。我们这次使用Spring注解扫描来配置bean以及为bean注入依赖,测试代码如下:
@Test
public void testConfig() {
ApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AutoConfig.class);
// 获取User这个bean,执行测试AOP的方法
User user = context.getBean(User.class);
user.testAOP();
// 获取PostBean这个bean,执行测试AOP的方法
PostBean bean = context.getBean(PostBean.class);
bean.testAOP();
}
输出如下:
user bean
post Bean
从输出中可以看到,使用AOP织入的前置通知没有执行,这也就验证了上面所说的,BeanPostProcessor的实现类以及实现类依赖的bean,无法使用AOP为其织入通知。但是这个限制具体有到什么程度,我也不是很确定,因为我使用xml配置依赖,以及上面使用注解扫描两种方式,AOP织入都没法使用,但是我在使用@Bean这种配置方式时,被依赖的bean却成功执行了通知。所以,关于此处提到的限制,还需要深入了解Spring容器的源码实现才能下定论。
(三)注册BeanPostProcessor的方式以及限制
我们如何将BeanPostProcessor注册到Spring容器中?方式主要有两种,第一种就是上面一直在用的,将其声明在Spring的配置类或xml文件中,作为普通的bean,让ApplicationContext对象去加载它,这样它就被自动注册到容器中了。而且Spring容器会对BeanPostProcessor的实现类做特殊处理,即会将它们挑选出来,在加载其他bean前,优先加载BeanPostProcessor的实现类。
还有另外一种方式就是使用ConfigurableBeanFactory接口的addBeanPostProcessor方法手动添加,ApplicationContext对象中组合了一个ConfigurableBeanFactory的实现类对象。但是这种方式添加BeanPostProcessor有一些缺点。首先,我们一创建Spring容器,在配置文件中配置的单例bean就会被加载,此时addBeanPostProcessor方法还没有执行,那我们手动添加的BeanPostProcessor也就无法作用于这些bean了,所以手动添加的BeanPostProcessor只能作用于那些延迟加载的bean,或者非单例bean。
还有一个就是,使用addBeanPostProcessor方式添加的BeanPostProcessor,Ordered接口的作用将失效,而是以注册的顺序执行。我们前面提过,Ordered接口用来指定多个BeanPostProcessor实现的方法的执行顺序。这是Spring官方文档中提到的:
While the recommended approach for
BeanPostProcessorregistration is throughApplicationContextauto-detection (as described above), it is also possible to register them programmatically against aConfigurableBeanFactoryusing theaddBeanPostProcessormethod. This can be useful when needing to evaluate conditional logic before registration, or even for copying bean post processors across contexts in a hierarchy. Note however thatBeanPostProcessors added programmatically do not respect theOrderedinterface. Here it is the order of registration that dictates the order of execution. Note also thatBeanPostProcessors registered programmatically are always processed before those registered through auto-detection, regardless of any explicit ordering.
(四)使用@Bean配置BeanPostProcessor的限制
如果我们使用Java类的方式配置Spring,并使用@Bean声明一个工厂方法返回bean实例,那么返回值的类型必须是BeanPostProcessor类型,或者等级低于BeanPostProcessor的类型。这里不好口头描述,直接看代码吧。以下是一个BeanPostProcessor的实现类,它实现了多个接口:
/**
* 此BeanPostProcessor的实现类,还实现了Ordered接口
*/
public class PostBean implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("before -- " + beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("after -- " + beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
我们在配置类中,声明PostBean可以有以下几种方式:
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
// 方式1:PostBean
@Bean
public PostBean postBean() {
return new PostBean();
}
// 方式2:返回值为BeanPostProcessor
@Bean
public BeanPostProcessor postBean() {
return new PostBean();
}
// 方式3:返回值为Ordered
@Bean
public Ordered postBean() {
return new PostBean();
}
}
以上三种方式都可以让Spring容器创建PostBean实例对象,因为PostBean实现了BeanPostProcessor和Ordered接口,所以它的对象也是这两种类型的对象。但是需要注意,上面三种方式中,只有第一种和第二种方式,会让Spring容器将PostBean当作BeanPostProcessor处理;而第三种方式,则会被当作一个普通Bean处理,实现BeanPostProcessor的两个方法都不会被调用。因为在PostBean的继承体系中,Ordered和BeanPostProcessor是同级别的,Spring无法识别出这个Ordered对象,也是一个BeanPostProcessor对象;但是使用PostBean却可以,因为PostBean类型就是BeanPostProcessor的子类型。所以,在使用@Bean声明工厂方法返回BeanPostProcessor实现类对象时,返回值必须是BeanPostProcessor类型,或者更低级的类型。Spring官方文档中,这一部分的内容如下:
Note that when declaring a
BeanPostProcessorusing an@Beanfactory method on a configuration class, the return type of the factory method should be the implementation class itself or at least theorg.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessorinterface, clearly indicating the post-processor nature of that bean. Otherwise, theApplicationContextwon’t be able to autodetect it by type before fully creating it. Since aBeanPostProcessorneeds to be instantiated early in order to apply to the initialization of other beans in the context, this early type detection is critical.
三、总结
以上就对BeanPostProcessor的功能、使用以及需要注意的问题做了一个大致的介绍。需要注意的是,上面所提到的问题,可能根据不同的情况,会有不同的结果,因为文档中的资料只是简单地提了几句,并不详细,上面的内容大部分都是我基于官方文档的描述,以及自己的测试得出,所以可能并不准确。还需要自己在实践中去尝试,或者阅读源码,才能彻底了解BeanPostProcessor的执行机制。
以上描述若存在错误或不足,希望能够提出来,因为这一部分内容,我也不太了解,所以希望有人帮忙指正。
四、参考
谈谈Spring中的BeanPostProcessor接口的更多相关文章
- spring中基础核心接口总结
spring中基础核心接口总结理解这几个接口,及其实现类就可以快速了解spring,具体的用法参考其他spring资料 1.BeanFactory最基础最核心的接口重要的实现类有:XmlBeanFac ...
- Spring中的BeanPostProcessor详解
Spring中的BeanPostProcessor详解 概述 BeanPostProcessor也称为Bean后置处理器,它是Spring中定义的接口,在Spring容器的创建过程中(具体为Bean初 ...
- 谈谈Spring中的对象跟Bean,你知道Spring怎么创建对象的吗?
本系列文章: 读源码,我们可以从第一行读起 你知道Spring是怎么解析配置类的吗? 配置类为什么要添加@Configuration注解? 推荐阅读: Spring官网阅读 | 总结篇 Spring杂 ...
- Spring中Aware相关接口原理
Spring中提供一些Aware相关接口,像是BeanFactoryAware. ApplicationContextAware.ResourceLoaderAware.ServletContextA ...
- spring中的aware接口
1.实现了相应的aware接口,这个类就获取了相应的资源. 2.spring中有很多aware接口,包括applicationContextAware接口,和BeanNameAware接口. 实现了这 ...
- Spring中的InitializingBean接口的使用
InitializingBean接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是继承该接口的类,在初始化bean的时候都会执行该方法. 测试,如下: imp ...
- spring中一些aware接口
Spring中提供一些Aware相关接口,像是BeanFactoryAware. ApplicationContextAware.ResourceLoaderAware.ServletContextA ...
- Spring 中的 MetaData 接口
什么是元数据(MetaData) 先直接贴一个英文解释: Metadata is simply data about data. It means it is a description and co ...
- 谈谈php中抽象类和接口的区别
php中抽象类和接口的区别 1) 概念 面向对象的三大概念:封装,继承,多态 把属性和方法封装起来就是类. 一个类的属性和方法被另外的类复制就是继承,PHP里面的任何类都可以被继承,被继 ...
随机推荐
- A 蚂蚁觅食
A. 蚂蚁觅食(一) 单点时限: 1.0 sec 内存限制: 512 MB 一只饥饿的小蚂蚁外出觅食,幸运的小蚂蚁发现了好多食物,但是它只有一次搬食物的机会.可因为力气太小了,它不能搬走重量超过自己体 ...
- mybatis 批量删除
mapper.xml: <update id="delete" parameterType="int"> delete from user_logi ...
- 运行一个nodejs服务,先发布为deployment,然后创建service,让集群外可以访问
问题来源 海口-老男人 17:42:43 就是我要运行一个nodejs服务,先发布为deployment,然后创建service,让集群外可以访问 旧报纸 17:43:35 也就是 你的需求为 一个a ...
- Matlab学习-(3)
1. 二维图 绘制完图形以后,可能还需要对图形进行一些辅助操作,以使图形意义更加明确,可读性更强. 1.1 图形标注 title(’图形名称’) (都放在单引号内)xlabel(’x轴说明’)ylab ...
- MVC-第一个简单的程序
来源于:https://www.cnblogs.com/miro/p/4030622.html 从空白开始,建立一个基本框架详细步骤 1,新建项目 NOTE:模板要选Empty,如果直接选MVC会产生 ...
- 进制之间转换——day_01
一.计算机文件大小单位 b = bit 位(比特) B = Byte 字节 1B = 8b #一个字节等于8位 简写 1Byte = 8 bit 1KB = 1024B 1MB = 1024KB 1G ...
- sqlliab7-8
less-7 https://www.jianshu.com/p/20d1282e6e1d ?id=0')) union select 1,'2','<?php @eval($_POST[&qu ...
- python爬虫+正则表达式实例爬取豆瓣Top250的图片
直接上全部代码 新手上路代码风格可能不太好 import requests import re from fake_useragent import UserAgent #### 用来伪造爬头部信息 ...
- tp5--开发规范
在日常开发的过程中,写代码都要有一定的规范,不然可读取就太差了,所以为了以后的维护.对接,好的代码规定是必须的. 以下是我自己对自己提出的要求: 全部: 1) 每个方法都要写好备注(@retrun作 ...
- php时间:获取上一个月,本月天数,下一个月
时间戳转日期 date() 日期转时间戳 strtotime() 当前时间戳time() 获取当前月的天数: $i=; $y=; echo date("t",strtotime(& ...
