Spring中使用事务搭建转账环境 转账操作,
演示不使用事务出现异常情况
Dao层两个方法lessMoney()和moreMoney()
package com.swift;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class AccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
//少钱的方法
public void lessMoney(String from,double number) {
String sql="update account set money=money-? where username=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, number,from);
}
//多钱的方法
public void moreMoney(String to,double number) {
String sql="update account set money=money+? where username=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, number,to);
}
}
Service层调用两个方法
package com.swift;
public class AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void moneyTransfer(String from,String to,double number) {
accountDao.lessMoney(from,number);
int i=10/0;
accountDao.moreMoney(to,number);
}
}
但是两个操作减与加之间,如果出现异常,则会导致转账钱已经转了,但对方却没有到账的bug,可能服务器突然故障等引起
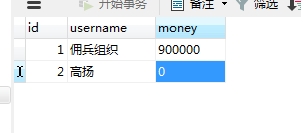
解决添加事务,出现异常进行回滚操作
下面使用配置文件的方法进行事务管理
没有改变的测试类
package com.swift; import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; @WebServlet("/test")
public class ServletTest extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public ServletTest() {
super();
} protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().append("Served at: ").append(request.getContextPath()); //使用JdbcTemplat的queryForObject方法
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("c3p0.xml");
AccountService accountService= (AccountService) context.getBean("accountService");
accountService.moneyTransfer("佣兵组织", "高扬", 100000);
} protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
} }
使用配置文件进行事务处理步骤如下:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <!-- c3p0连接池得到dataSource -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sw_database"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean> <!-- 第一步 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 注入dataSource -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean> <!-- 第二步 配置事务增强 -->
<tx:advice id="txadvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!-- 做事务操作 -->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 事务操作的方法匹配规则 -->
<tx:method name="money*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice> <!-- 第三步 配置切面 -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.swift.AccountService.*(..))" id="pointcut1"/>
<!-- 切面 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
</aop:config> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean> <bean id="accountDao" class="com.swift.AccountDao">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean> <bean id="accountService" class="com.swift.AccountService">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean> </beans>
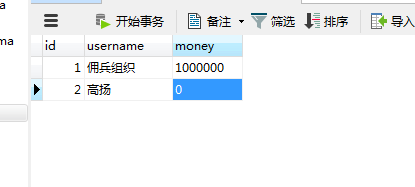
分三个步骤 管理 增强和切面
虽然还是会有异常,但是数据库中不会出错,不会钱转出了,却没有到账
工具类Account
package com.swift;
public class Account {
private int id;
private String username;
private String money;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(String money) {
this.money = money;
}
public Account(int id, String username, String money) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.money = money;
}
public Account() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", money=" + money + "]";
}
}
Spring事务中的传播行为如下:
Require:支持当前事务,如果没有事务,就建一个新的,这是最常见的;
Supports:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行;
Mandatory:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常;
RequiresNew:新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起;
NotSupported:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把事务挂起;
Never:以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
Nested:新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。与RequireNew的区别是与父事务相关,且有一个savepoint。
其中,Require、Supports、NotSupported、Never两个看文字也就能了解,就不多说了。而Mandatory是要求所有的操作必须在一个事务里,较Require来说,对事务要求的更加严格。
RequireNew:当一个Require方法A调用RequireNew方法B时,B方法会新new一个事务,并且这个事务和A事务没有关系,也就是说B方法出现异常,不会导致A的回滚,同理当B已提交,A再出现异常,B也不会回滚。
Nested:这个和RequireNew的区别是B方法的事务和A方法的事务是相关的。只有在A事务提交的时候,B事务都会提交。也就是说当A发生异常时,A、B事务都回滚,而当B出现异常时,B回滚,而A回滚到savepoint;
Spring事务的隔离级别,事务隔离级别如下:
Serializable:最严格的级别,事务串行执行,资源消耗最大;
Repeatable Read:保证了一个事务不会修改已经由另一个事务读取但未提交(回滚)的数据。
Read Committed:大多数主流数据库的默认事务等级,保证了一个事务不会读到另一个并行事务已经修改但未提交的数据。适用于大多数系统。
Read Uncommitted:保证了读取过程中不会读取到非法数据。
想要理解这四个级别,还需要知道三种不讨人喜欢的事情:
dirty reads:脏读,就是说事务A未提交的数据被事务B读走,如果事务A失败回滚,将导致B所读取的数据是错误的。
non-repeatable reads:不可重复读,就是说事务A中两处读取数据,第一次读时是100,然后事务B把值改成了200,事务A再读一次,结果就发现值变了,造成A事务数据混乱。
phantom read:幻读,和不可重复读相似,也是同一个事务中多次读不一致的问题。但是不可重复读的不一致是因为它所要取的数据集被改变了,而幻读所要读的数据不一致却不是他所要读的数据改变,而是它的条件数据集改变。比如:Select id where name="ppgogo*",第一次读去了6个符合条件的id,第二次读时,由于事务B把第一个贴的名字由"dd"改成了“ppgogo9”,结果取出来7个数据。
Spring中使用事务搭建转账环境 转账操作,的更多相关文章
- Spring中使用事务搭建转账环境方法二 相对简便的注解方法 ——配置文件注入对象属性需要setter方法 注解方法,不需要生成setter方法
XML配置文件代码如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns=" ...
- Spring中的事务操作
事务的特性 原子性:强调事务的不可分割. 一致性:事务的执行的前后数据的完整性保持一致. 隔离性:一个事务执行的过程中,不应该受到其他事务的干扰. 持久性:事务一旦结束,数据就持久化到数据库. 如果不 ...
- (转)Spring中的事务操作
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/70024364 事务的回顾 什么是事务 事务是逻辑上的一组操作,组成这组操作的各个逻辑单元,要么 ...
- Spring 中的事务操作、注解、以及 XML 配置
事务 事务全称叫数据库事务,是数据库并发控制时的基本单位,它是一个操作集合,这些操作要么不执行,要么都执行,不可分割.例如我们的转账这个业务,就需要进行数据库事务的处理. 转账中至少会涉及到两条 SQ ...
- Spring中@Transactional事务回滚
转载: Spring中@Transactional事务回滚 一.使用场景举例 在了解@Transactional怎么用之前我们必须要先知道@Transactional有什么用.下面举个栗子:比如一个部 ...
- SSM-Spring-23:概念《Spring中的事务是什么?》
------------吾亦无他,唯手熟尔,谦卑若愚,好学若饥------------- 本篇博客会详细讲述Spring中的事务,会展开来用语言解释,用于了解概念和准备面试 事务的概念: 一个或者一组 ...
- Spring中的事务管理
事务简介: 事务管理是企业级应用程序开发中必不可少的技术,用来确保数据的完整性和一致性 事务就是一系列的动作,它们被当作一个单独的工作单元.这些动作要么全部完成,要么全部不起作用 事务的四个关键属性( ...
- Spring中的事务管理详解
在这里主要介绍Spring对事务管理的一些理论知识,实战方面参考上一篇博文: http://www.cnblogs.com/longshiyVip/p/5061547.html 1. 事务简介: 事务 ...
- Spring,SpringMvc配置常见的坑,注解的使用注意事项,applicationContext.xml和spring.mvc.xml配置注意事项,spring中的事务失效,事务不回滚原因
1.Spring中的applicationContext.xml配置错误导致的异常 异常信息: org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Invalid ...
随机推荐
- [Xcode 实际操作]六、媒体与动画-(13)使用UIImageView制作帧动画
目录:[Swift]Xcode实际操作 本文将演示如何将导入的序列图片,转换为帧动画. 在项目导航区打开资源文件夹[Assets.xcassets] [+]->[Import]->选择图片 ...
- java实现对字符串和数字的冒泡排序
public static void sort(Object[] objects){ if(objects instanceof Number[]){ for (int i = 0; i < o ...
- js函数—隐形参数this
前言 this是函数中的隐形参数,它绑定的值取决于函数的调用位置. this的定义 <你不知道的js>中是这样说的:是函数体内的隐式参数,this就是记录函数调用上下文的一个属性.可以在函 ...
- axios 跨域配置
axios跨域设置 找到项目config文件夹下的index.js文件,将dev中的proxyTable项中添加配置 proxyTable: { '/api': { target: 'https:// ...
- jsp网站访问次数统计
JSP 点击量统计 有时候我们需要知道某个页面被访问的次数,这时我们就需要在页面上添加页面统计器,页面访问的统计一般在用户第一次载入时累加该页面的访问数上. 要实现一个计数器,您可以利用应用程序隐式对 ...
- vuex初使用(写的当然是最简单的应用啦)
关于vuex的简图 vuex文档:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh-cn/installation.html 一:npm安装 npm install vuex --save 在mai ...
- jQuery基础(1)
一.jQuery的介绍 1.为什么要使用jQuery? 在用js写代码时,会遇到一些问题,如下: 1)window.onload 事件有事件覆盖的问题,因此只能写一个事件: 2)代码容错性差: 3)浏 ...
- python之is 和 == 的区别//编码和解码
一.is 和 == 的区别: 1 .id() 内存地址 2. == 比较 #比较两边的值 3. is 比较 #比较的是内存地址 数字,字符串,有小数据池 #数字小 ...
- centos虚拟机安装指定版本docker
环境: centos 7.6+ docker-ce 17.03.2 安装依赖包 yum -y install yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 ...
- Java微信公众平台开发(十一)--微信JSSDK中Config配置
JSSDK曾经引爆前端以及后端的工程师,其魔性的力量毋庸置疑,在我们的技术眼里它的实现原理和根本是不能够被改变的,这篇文章就不对其js的实现做任何评价和解说了(因为我也不是很懂,哈哈),这里要说的是它 ...
