cf446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
4 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of
Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation
F1 = 1; F2 = 1; Fn = Fn - 1 + Fn - 2 (n > 2).
DZY loves Fibonacci numbers very much. Today DZY gives you an array consisting of n integers: a1, a2, ..., an.
Moreover, there are mqueries, each query has one of the two types:
- Format of the query "1 l r". In reply to the query, you need to add Fi - l + 1 to
each element ai,
where l ≤ i ≤ r. - Format of the query "2 l r". In reply to the query you should output the value of
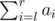 modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).
modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).
Help DZY reply to all the queries.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 300000).
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) —
initial array a.
Then, m lines follow. A single line describes a single query in the format given in the statement. It is guaranteed that for each query inequality 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n holds.
For each query of the second type, print the value of the sum on a single line.
4 4
1 2 3 4
1 1 4
2 1 4
1 2 4
2 1 3
17
12
After the first query, a = [2, 3, 5, 7].
For the second query, sum = 2 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 17.
After the third query, a = [2, 4, 6, 9].
For the fourth query, sum = 2 + 4 + 6 = 12.
题意是给定一个数列,要求支持两种操作:1是在区间[l,r]上的所有数依次加上斐波那契数列的前(r-l+1)项;2是区间求和
显然很容易看出这是线段树。
区间求和是很简单的,关键是线段树节点的标记怎么打
和普通的区间加减的标记不同,加减标记可以直接在左右节点上修改。但是加斐波那契数不行。因为假设当前这一段要加上斐波那契数列[l1 , r1],它的左儿子的标记是[l2 , r2]。那么下传的时候直接改成[l1+l2 , r1+r2]绝对不行。
所以我们必须考虑怎样转移标记。
突破口应该还是在斐波那契数本身上。由于斐波那契数的性质a[i]=a[i-1]+a[i-2],我们可以猜想[l , r] = [l-1 , r-1] + [l-2 , r-2],并很容易证明这是正确的。
不只是这样,对于区间[l , r],令len=r - l + 1 ,则[l , r]一定可以表示为 t1 * [1 , len] + t2 * [2 , len+1]。因为[l , r] = [l-1 , r-1] + [l-2 , r-2], [l-1 , r-1] = [l-2 , r-2] + [l-3 , r-3]……这样无限递归下去,容易看出只有l != 1且l != 2时存在区间[l-2 , r-2]。那么[l , r]一定可以变为若干[l-1 , r-1]和[l-2 , r-2]的和。当然变化时区间长度len=r-l+1显然是不会变的。所以对于一个节点,我们只要知道一个len=r-l+1,然后无论有多么复杂的斐波那契数的区间加在一起,总可以用t1、t2表示。这样就很好写pushdown了。
然而还有一个问题需要我们解决,那就是求出对于给定的l(只要知道l就可以了。至于为什么请自行脑补),[l , r] = 多少[l-1 , r-1] + 多少[l-2 , r-2]。
假设我们用二元组(t1,t2)可以表示l,那么很容易写出前几项:
1=(1 , 0)……[1 , len]=0 * [2 , len+1] + 1 * [1 , len]
2=(0 , 1)……[2 , len+1]=1 * [2 , len+1] + 0 * [1 , len]
3=(1 , 1)……[3 , len+2]=1 * [2 , len+1] + 1 * [1 , len]
4=(1 , 2)……[4 , len+3]=1 * [2 , len+1] + 2 * [1 , len]
5=(2 , 3)……[5 , len+4]=2 * [2 , len+1] + 3 * [1 , len]
……(发现规律了吧!以下就不列举了)
那么我们直接预处理出对于l的t1、t2,方便调用。最后该怎么搞就怎么搞
(对了在这里说一下,为什么t1、t2在递归的时候也可以取模?因为假设我们求一个区间的和,令s[]表示斐波那契数的前缀和取模,令t1=T1+mod , t2=T2+mod。那么区间和是t1 * s[len] + t2 * (s[len+1]-s[1]),拆开来就是T1 * s[len] + T2 * (s[len+1]-s[1]) + mod * (s[len]+s[len+1]-s[1]),对mod取模之后显然就是T1 * s[len] + T2 * (s[len+1]-s[1])。所以取模之后是一样的)
但是,这样常数好像巨大!所以我第十个点就T了
先贴个代码吧
#include<cstdio>
#define LL long long
#define mod 1000000009
struct trees{
int l,r,ls,rs;
long long tot,t1,t2;
}tree[800001];
inline int read()
{
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int n,m,opr,x,y,treesize;
int a[210001];
int F[310001];
int s[310001];
int sF[310001];
int F1[310001];
int F2[310001];
inline void update(int k)
{
tree[k].tot=tree[tree[k].ls].tot+tree[tree[k].rs].tot;
while (tree[k].tot>mod) tree[k].tot-=mod;
}
inline void pushdown(int k)
{
int l=tree[k].l,r=tree[k].r;
LL t1=tree[k].t1,t2=tree[k].t2;
tree[k].t1=0;tree[k].t2=0;
if (r==l)return;
int len=r-l+1,llen=len-(len>>1),ls=tree[k].ls,rs=tree[k].rs;
tree[ls].tot+=t1*sF[llen]+t2*(sF[llen+1]-1);
tree[ls].tot%=mod;
tree[ls].t1+=t1;
while (tree[ls].t1>mod) tree[ls].t1-=mod;
tree[ls].t2+=t2;
while (tree[ls].t2>mod) tree[ls].t2-=mod;
tree[rs].tot+=t1*(sF[len]-sF[llen])+t2*(sF[len+1]-sF[llen+1]);
tree[rs].tot%=mod;
tree[rs].t1=(tree[rs].t1+t1*F1[llen+1]+t2*F1[llen+2])%mod;
tree[rs].t2=(tree[rs].t2+t1*F2[llen+1]+t2*F2[llen+2])%mod;
update(k);
}
inline void buildtree(int l,int r)
{
if (l>r) return;
int now=++treesize;
tree[now].l=l;
tree[now].r=r;
if (l==r)return;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
tree[now].ls=treesize+1;
buildtree(l,mid);
tree[now].rs=treesize+1;
buildtree(mid+1,r);
update(now);
}
inline void change(int now,int x,int y,LL t1,LL t2)
{
if(tree[now].t1||tree[now].t2)pushdown(now);
t1%=mod;t2%=mod;
int l=tree[now].l,r=tree[now].r,len=r-l+1;
if (x==l&&y==r)
{
tree[now].t1=t1;
tree[now].t2=t2;
tree[now].tot+=t1*sF[len]+t2*(sF[len+1]-1);
tree[now].tot%=mod;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if (mid>=y)change(tree[now].ls,x,y,t1,t2);
else if(mid<x)change(tree[now].rs,x,y,t1,t2);
else
{
change(tree[now].ls,x,mid,t1,t2);
int rest=mid-x+2;
change(tree[now].rs,mid+1,y,t1*F1[rest]+t2*F1[rest+1],t1*F2[rest]+t2*F2[rest+1]);
}
update(now);
}
inline long long ask(int now,int x,int y)
{
if(tree[now].t1||tree[now].t2)pushdown(now);
int l=tree[now].l,r=tree[now].r;
if (l==x&&r==y)return tree[now].tot;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if (mid>=y)return ask(tree[now].ls,x,y);
else if (mid<x)return ask(tree[now].rs,x,y);
else return ask(tree[now].ls,x,mid)+ask(tree[now].rs,mid+1,y);
}
int main()
{
//freopen("cf.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("cf.out","w",stdout);
n=read();m=read();
F[1]=F[2]=sF[1]=F1[1]=F2[2]=1;sF[2]=2;
for (int i=3;i<=n+3;++i)
{
F[i]=(F[i-1]+F[i-2])%mod;
sF[i]=(sF[i-1]+F[i])%mod;
F1[i]=(F1[i-1]+F1[i-2])%mod;
F2[i]=(F2[i-1]+F2[i-2])%mod;
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
a[i]=read();
s[i]=s[i-1]+a[i];
}
buildtree(1,n);
for (int i=1;i<=m;++i)
{
opr=read();x=read();y=read();
if (opr==1)change(1,x,y,1,0);
if (opr==2)printf("%lld\n",(ask(1,x,y)%mod+s[y]-s[x-1])%mod);
}
return 0;
}
可以看出pushdown是有多长……但是确实有太多东西要处理,而且我已经加了一些常数优化,比如取模的时候改成减法,这样速度快一点点。还有在pushdown之前加一行判断,只有在t1、t2至少有一个不为0的时候才值得标记下传。但这样n=m=30w的数据还是会爆。
最后我去看了一下A的人的代码是如何写的。也不班门弄斧了,附代码:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#define lson (2*id)
#define rson (2*id+1)
using namespace std;
const __int64 p=1000000009;
const __int64 q1=691504013,q2=308495997;
const __int64 k=276601605;
int n,Q;
__int64 a[300005],p1[300005],p2[300005];
__int64 sp1[300005],sp2[300005];
struct tree
{
int l,r,len;
__int64 s1,s2,first1,first2;
}tr[1200005];
void build(int l,int r,int id)
{
tr[id].l=l;
tr[id].r=r;
tr[id].len=r-l+1;
tr[id].first2=tr[id].first1=0;
tr[id].s1=tr[id].s2=0;
if(l!=r)
{
int mid=(tr[id].l+tr[id].r)/2;
build(l,mid,lson);
build(mid+1,r,rson);
}
}
void pushdown(int id)
{
if(tr[id].first1!=0)
{
__int64 t=tr[id].first1;
tr[id].first1=0;
tr[lson].s1=(tr[lson].s1+t*sp1[tr[lson].len-1])%p;
tr[lson].first1=(tr[lson].first1+t)%p;
tr[rson].s1=(tr[rson].s1+t*p1[tr[lson].len]%p*sp1[tr[rson].len-1])%p;
tr[rson].first1=(tr[rson].first1+t*p1[tr[lson].len])%p;
}
if(tr[id].first2!=0)
{
__int64 t=tr[id].first2;
tr[id].first2=0;
tr[lson].s2=(tr[lson].s2+t*sp2[tr[lson].len-1])%p;
tr[lson].first2=(tr[lson].first2+t)%p;
tr[rson].s2=(tr[rson].s2+t*p2[tr[lson].len]%p*sp2[tr[rson].len-1])%p;
tr[rson].first2=(tr[rson].first2+t*p2[tr[lson].len])%p;
}
}
void update(int l,int r,int id,int x)
{
if(tr[id].l>=l&&tr[id].r<=r)
{
int y=tr[id].l-l+x;
tr[id].s1=(tr[id].s1+k*p1[y]%p*sp1[tr[id].len-1]%p)%p;
tr[id].s2=(tr[id].s2+k*p2[y]%p*sp2[tr[id].len-1]%p)%p;
tr[id].first1=(tr[id].first1+k*p1[y])%p;
tr[id].first2=(tr[id].first2+k*p2[y])%p;
return ;
}
pushdown(id);
int mid=(tr[id].l+tr[id].r)/2;
if(l<=mid) update(l,r,lson,x);
if(r>mid) update(l,r,rson,x);
tr[id].s1=(tr[lson].s1+tr[rson].s1)%p;
tr[id].s2=(tr[lson].s2+tr[rson].s2)%p;
}
__int64 query(int l,int r,int id)
{
if(tr[id].l>=l&&tr[id].r<=r) return ((tr[id].s1-tr[id].s2)+p)%p;
pushdown(id);
int mid=(tr[id].l+tr[id].r)/2;
__int64 ans1=0,ans2=0;
if(l<=mid) ans1=query(l,r,lson);
if(r>mid) ans2=query(l,r,rson);
return (ans1+ans2)%p;
}
void init()
{
p1[0]=p2[0]=1;
sp1[0]=sp2[0]=1;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&Q);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
p1[i]=p1[i-1]*q1%p;
p2[i]=p2[i-1]*q2%p;
sp1[i]=(sp1[i-1]+p1[i])%p;
sp2[i]=(sp2[i-1]+p2[i])%p;
}
}
int main()
{
init();
a[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%I64d",&a[i]);
a[i]+=a[i-1];
}
build(1,n,1);
while(Q--)
{
int op,l,r;
scanf("%d%d%d",&op,&l,&r);
if(op==1) update(l,r,1,1);
else
{
__int64 v1=query(l,r,1),v2=((a[r]-a[l-1])+p)%p;
printf("%I64d\n",(v1+v2)%p);
}
}
return 0;
}
好不容易找到一个像样的线段树……
从代码中发现他的一个显而易见的一个优化:因为是不断加数字进去,所以直接用线段树维护加入的数,而原来的数直接用前缀和处理询问。
但是我看了很久也没看懂前面定义的大常数是什么意思……
如果哪位神犇一眼看出了这有什么用,请不要“不屑于”回答……
cf446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers的更多相关文章
- 【思维题 线段树】cf446C. DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
我这种maintain写法好zz.考试时获得了40pts的RE好成绩 In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is de ...
- CF446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 线段树 + 数学
有两个性质需要知道: $1.$ 对于任意的 $f[i]=f[i-1]+f[i-2]$ 的数列,都有 $f[i]=fib[i-2]\times f[1]+fib[i-1]\times f[2]$ 其中 ...
- 「CF446C」 DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
「CF446C」 DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 这里提供一种优美的根号分治做法. 首先,我们考虑一种不太一样的暴力.对于一个区间加斐波那契数的操作 \([a,b]\),以及一 ...
- codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(数学 or 数论+线段树)(两种方法)
In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation F1 ...
- Codeforces 446-C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 同余 线段树 斐波那契数列
C. DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- Codeforces Round #FF 446 C. DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
參考:http://www.cnblogs.com/chanme/p/3843859.html 然后我看到在别人的AC的方法里还有这么一种神方法,他预先设定了一个阈值K,当当前的更新操作数j<K ...
- Codeforces446C - DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
Portal Description 给出一个\(n(n\leq3\times10^5)\)个数的序列,进行\(m(m\leq3\times10^5)\)次操作,操作有两种: 给区间\([L,R]\) ...
- [CodeForces - 447E] E - DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
E DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is define ...
- ACM学习历程—Codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(线段树 && 数论)
Description In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence ...
随机推荐
- 【剑指offer】面试题37:两个链表的第一个公共结点
题目: 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点. 思路: 由链表的定义知是单链表.对于单链表,如果两个链表有公共结点,则两个链表必然是像Y型相交.则先计算出各个链表的长度,让长链表的头指针先走多出来的 ...
- thinkphp连接mysql5.5版本数据库
//数据库配置信息 'DB_TYPE' => 'mysqli', // 数据库类型 'DB_HOST' => 'localhost', // 服务器地址 'DB_NAME' => ' ...
- EL表达式 functions String处理函数
01.uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions" prefix="fn" %> 02.上面的 uri 根据 ...
- CSS3实现三角形
很多时候我们用到三角形这个效果: 我们可以用CSS3实现这个效果,怎去做呢?先阐述一下原理,我们定义一个空的div,设置这个div宽高为0,给这个div加上一个100px边框(这里是方便观察),得到的 ...
- 优化移动体验的HTML5技巧
简介 连轴转的刷新,不断变向的页面转换,以及tap事件的周期性的延迟仅仅是现在移动web环境令人头疼事情的一小部分.开发者正试图尽可能的靠近原生应用,但却经常被各种兼容问题,系统复位,和僵化的框架打乱 ...
- android中使用哪种方式解析XML比較好
SAX是一个用于处理XML事件驱动的"推"模型. 长处是一种解析速度快而且占用内存少的xml解析器,它须要哪些数据再载入和解析哪些内容. 缺点是它不会记录标签的关系.而要让你的应用 ...
- AssemblyInfo.cs文件的作用
在asp.net中有一个配置文件AssemblyInfo.cs主要用来设定生成的有关程序集的常规信息dll文件的一些參数,以下是默认的AssemblyInfo.cs文件的内容详细介绍 //是否符合公共 ...
- 老漏洞easy击:CVE-2012 0158占顶!
watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQvaXF1c2hp/font/5a6L5L2T/fontsize/400/fill/I0JBQkFCMA==/d ...
- Ubuntu中设置静态IP和DNS(转载)
原文地址:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_669421480102v3bb.html VMware 中使用网络,对虚拟机设置静态IP:在Ubuntu中设置静态IP共两步: ...
- OC基础 点语法的使用
OC基础 点语法的使用 1.创建一个Student类继承于NSObject,Student.h文件 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface ...
