《机器学习Python实现_10_06_集成学习_boosting_gbdt分类实现》
一.利用回归树实现分类
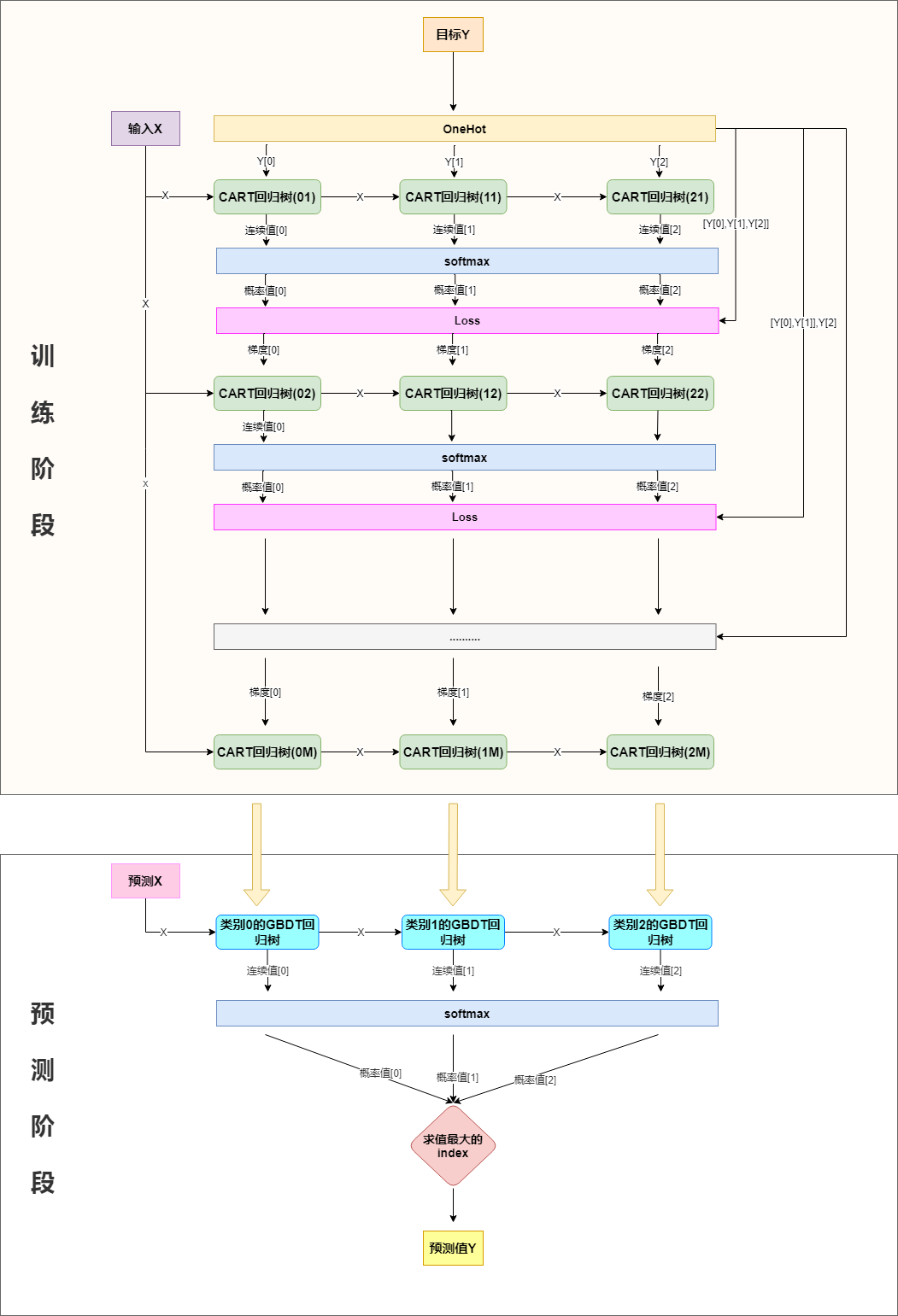
分类也可以用回归树来做,简单说来就是训练与类别数相同的几组回归树,每一组代表一个类别,然后对所有组的输出进行softmax操作将其转换为概率分布,然后再通过交叉熵或者KL一类的损失函数求每颗树相应的负梯度,指导下一轮的训练,以三分类为例,流程如下:
二.softmax+交叉熵损失,及其梯度求解
分类问题,一般会选择用交叉熵作为损失函数,下面对softmax+交叉熵损失函数的梯度做推导:
softmax函数在最大熵那一节已有使用,再回顾一下:
\]
交叉熵在logistic回归有介绍:
\]
将\(p_i\)替换为\(\frac{e^{y_i^{hat}}}{\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}}\)即是我们的损失函数:
=-\sum_{i=1}^n y_i(y_i^{hat}-log\sum_{j=1}^n e^{y_j^{hat}})\\
=log\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}-\sum_{i=1}^ny_iy_i^{hat}(由于是onehot展开,所以\sum_{i=1}^n y_i=1)
\]
计算梯度:
\]
所以,第一组回归树的拟合目标为\(y_1-\frac{e^{y_1^{hat}}}{\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}}\),第二组回归树学习的拟合目标为\(y_2-\frac{e^{y_2^{hat}}}{\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}}\),....,第\(n\)组回归树的拟合目标为\(y_n-\frac{e^{y_n^{hat}}}{\sum_{i=1}^n e^{y_i^{hat}}}\)
三.代码实现
import os
os.chdir('../')
from ml_models.tree import CARTRegressor
from ml_models import utils
import copy
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
class GradientBoostingClassifier(object):
def __init__(self, base_estimator=None, n_estimators=10, learning_rate=1.0):
"""
:param base_estimator: 基学习器,允许异质;异质的情况下使用列表传入比如[estimator1,estimator2,...,estimator10],这时n_estimators会失效;
同质的情况,单个estimator会被copy成n_estimators份
:param n_estimators: 基学习器迭代数量
:param learning_rate: 学习率,降低后续基学习器的权重,避免过拟合
"""
self.base_estimator = base_estimator
self.n_estimators = n_estimators
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
if self.base_estimator is None:
# 默认使用决策树桩
self.base_estimator = CARTRegressor(max_depth=2)
# 同质分类器
if type(base_estimator) != list:
estimator = self.base_estimator
self.base_estimator = [copy.deepcopy(estimator) for _ in range(0, self.n_estimators)]
# 异质分类器
else:
self.n_estimators = len(self.base_estimator)
# 扩展class_num组分类器
self.expand_base_estimators = []
def fit(self, x, y):
# 将y转one-hot编码
class_num = np.amax(y) + 1
y_cate = np.zeros(shape=(len(y), class_num))
y_cate[np.arange(len(y)), y] = 1
# 扩展分类器
self.expand_base_estimators = [copy.deepcopy(self.base_estimator) for _ in range(class_num)]
# 拟合第一个模型
y_pred_score_ = []
# TODO:并行优化
for class_index in range(0, class_num):
self.expand_base_estimators[class_index][0].fit(x, y_cate[:, class_index])
y_pred_score_.append(self.expand_base_estimators[class_index][0].predict(x))
y_pred_score_ = np.c_[y_pred_score_].T
# 计算负梯度
new_y = y_cate - utils.softmax(y_pred_score_)
# 训练后续模型
for index in range(1, self.n_estimators):
y_pred_score = []
for class_index in range(0, class_num):
self.expand_base_estimators[class_index][index].fit(x, new_y[:, class_index])
y_pred_score.append(self.expand_base_estimators[class_index][index].predict(x))
y_pred_score_ += np.c_[y_pred_score].T * self.learning_rate
new_y = y_cate - utils.softmax(y_pred_score_)
def predict_proba(self, x):
# TODO:并行优化
y_pred_score = []
for class_index in range(0, len(self.expand_base_estimators)):
estimator_of_index = self.expand_base_estimators[class_index]
y_pred_score.append(
np.sum(
[estimator_of_index[0].predict(x)] +
[self.learning_rate * estimator_of_index[i].predict(x) for i in
range(1, self.n_estimators - 1)] +
[estimator_of_index[self.n_estimators - 1].predict(x)]
, axis=0)
)
return utils.softmax(np.c_[y_pred_score].T)
def predict(self, x):
return np.argmax(self.predict_proba(x), axis=1)
#造伪数据
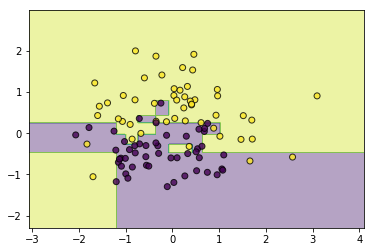
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
data, target = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_classes=2, n_informative=1, n_redundant=0,
n_repeated=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, class_sep=.5,random_state=21)
# 同质
classifier = GradientBoostingClassifier(base_estimator=CARTRegressor(),n_estimators=10)
classifier.fit(data, target)
utils.plot_decision_function(data, target, classifier)
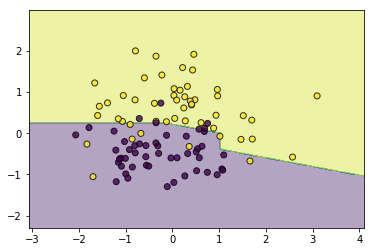
#异质
from ml_models.linear_model import LinearRegression
classifier = GradientBoostingClassifier(base_estimator=[LinearRegression(),LinearRegression(),LinearRegression(),CARTRegressor(max_depth=2)])
classifier.fit(data, target)
utils.plot_decision_function(data, target, classifier)
《机器学习Python实现_10_06_集成学习_boosting_gbdt分类实现》的更多相关文章
- 简单物联网:外网访问内网路由器下树莓派Flask服务器
最近做一个小东西,大概过程就是想在教室,宿舍控制实验室的一些设备. 已经在树莓上搭了一个轻量的flask服务器,在实验室的路由器下,任何设备都是可以访问的:但是有一些限制条件,比如我想在宿舍控制我种花 ...
- 利用ssh反向代理以及autossh实现从外网连接内网服务器
前言 最近遇到这样一个问题,我在实验室架设了一台服务器,给师弟或者小伙伴练习Linux用,然后平时在实验室这边直接连接是没有问题的,都是内网嘛.但是回到宿舍问题出来了,使用校园网的童鞋还是能连接上,使 ...
- 外网访问内网Docker容器
外网访问内网Docker容器 本地安装了Docker容器,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Docker容器? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Docker容器 ...
- 外网访问内网SpringBoot
外网访问内网SpringBoot 本地安装了SpringBoot,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地SpringBoot? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装Java 1 ...
- 外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB
外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB 本地安装了Elasticsearch,只能在局域网内访问其WEB,怎样从外网也能访问本地Elasticsearch? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Rails
外网访问内网Rails 本地安装了Rails,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Rails? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Rails 默认安装的Rails端口 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Memcached数据库
外网访问内网Memcached数据库 本地安装了Memcached数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Memcached数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网CouchDB数据库
外网访问内网CouchDB数据库 本地安装了CouchDB数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地CouchDB数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Cou ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网DB2数据库
外网访问内网DB2数据库 本地安装了DB2数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地DB2数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动DB2数据库 默认安装的DB2 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库
外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库 本地安装了OpenLDAP数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地OpenLDAP数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动 ...
随机推荐
- 看完我的笔记不懂也会懂----MarkDown使用指南
目录 语法 [TOC] 自动生成目录 1. 标题 2. 文本强调 3. 列表 4. 图片 5. 超链接 6. 文本引用 7. 分割线 8. 代码 9. 任务列表 (MPE专属) 10. 表格 11. ...
- react入个门
起步 react 特点 不使用模板 不是一个mvc框架 响应式 轻量级的js库 原理 虚拟dom 将dom抽象成js对象 diff算法 搭建开发环境 react.js 核心文件 react-dom.j ...
- 微信小程序onReachBottom第二次失效
当整个页面就是一个view包着一个轮播.一个横向scroll-view和一个纵向scroll-view onReachBottom方法只执行一次 解决方法:
- 【白话科普】CDN & 游戏加速器,两者是一个原理吗?
说起加速,大家可能就会联想到"游戏加速"之类的场景,而说到现在流行的云服务加速,则离不开 CDN 这个词.那么 CDN 和游戏加速器是同一种东西么?从效果上看两者都是为了" ...
- SHELL编程入门简介
一.SHELL软件概念和应用场景 1) 学习Linux技术,不是为了学习系统安装.命令操作.用户权限.配置IP.网络管理,学习Linux技术重点:基于Linux系统部署和维护各种应用软件.程序(Apa ...
- Servlet原理解析&使用指南
Servlet(Server Applet)全称Java Servlet,是用Java编写的服务器端程序.广义上指任何实现了Server接口的类,主要功能在于交互式地浏览和生成数据,生成动态Web内容 ...
- 聊一聊桥接(JSBridge)的原理
一.前言 如今的互联网时代也称移动互联网时代,基本上每个人每天都会花费大量时间在移动设备上,早期的移动端应用大都使用原生开发(android,ios),而现在的移动开发技术选型上基本都是混合开发(Hy ...
- swing实现QQ登录界面1.0( 实现了同一张图片只加载一次)、(以及实现简单的布局面板添加背景图片控件的标签控件和添加一个关闭按钮控件)
swing实现QQ登录界面1.0( 实现了同一张图片只加载一次).(以及实现简单的布局面板添加背景图片控件的标签控件和添加一个关闭按钮控件) 代码思路分析: 1.(同一张图片仅仅需要加载一次就够了,下 ...
- python3 多线程爬虫模板
原文:https://www.jianshu.com/p/06ae2373f560 1 import threading # 多线程模块 2 import queue # 队列模块 3 import ...
- [高精度]P1096 Hanoi 双塔问题
Hanoi 双塔问题 题目描述 给定A.B.C三根足够长的细柱,在A柱上放有2n个中间有孔的圆盘,共有n个不同的尺寸,每个尺寸都有两个相同的圆盘,注意这两个圆盘是不加区分的(下图为n=3的情形). 现 ...
