STL——容器(List)List 的数据元素插入和删除操作
push_back(elem);
//在容器尾部加入一个元素
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
10 cout << "初始遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
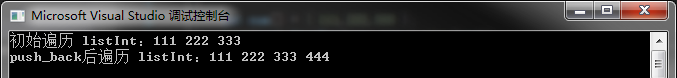
15 cout << endl;
16
17 listInt.push_back(444);
18 cout << "push_back后遍历 listInt:";
19 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
20 {
21 cout << *it << " ";
22 }
23 cout << endl;
24
25 return 0;
26 }
打印结果:
pop_back();
//删除容器中最后一个元素
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
10 cout << "初始遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16
17 listInt.pop_back();
18 cout << "pop_back 后遍历 listInt:";
19 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
20 {
21 cout << *it << " ";
22 }
23 cout << endl;
24
25 return 0;
26 }
打印结果:

push_front(elem);
//在容器开头插入一个元素
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
10 cout << "初始遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16
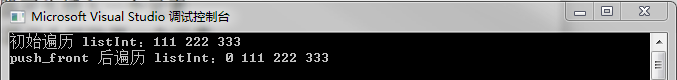
17 listInt.push_front(0);
18 cout << "push_front 后遍历 listInt:";
19 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
20 {
21 cout << *it << " ";
22 }
23 cout << endl;
24
25 return 0;
26 }
打印结果:
pop_front();
//从容器开头移除第一个元素
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
10 cout << "初始遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16
17 listInt.pop_front();
18 cout << "pop_front 后遍历 listInt:";
19 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
20 {
21 cout << *it << " ";
22 }
23 cout << endl;
24
25 return 0;
26 }
打印结果:

insert(pos, elem);
//在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置
这里需要注意一点,list 不可以随机存取元素,所以不支持 at.(position)函数与[]操作符。可以对其迭代器执行++和--,但是不能这样操作迭代器:it + 3
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
10 cout << "初始遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16
17
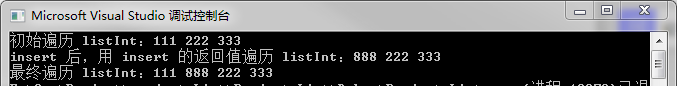
18 cout << "insert 后,用 insert 的返回值遍历 listInt:";
19 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.insert(++listInt.begin(), 888); it != listInt.end(); it++)
20 {
21 cout << *it << " ";
22 }
23 cout << endl;
24 cout << "最终遍历 listInt:";
25 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
26 {
27 cout << *it << " ";
28 }
29
30 return 0;
31 }
打印结果:
insert(pos, n, elem);
//在pos位置插入n个elem数据,返回新数据的第一个数据的位置(这个有没有返回值是编译器版本决定,早起版本的编译器没有返回值)
这里需要注意一点,list 不可以随机存取元素,所以不支持 at.(position)函数与[]操作符。可以对其迭代器执行++和--,但是不能这样操作迭代器:it + 3
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
10 cout << "初始遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16
17
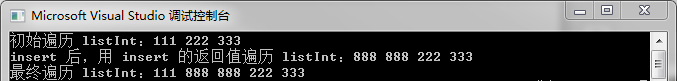
18 cout << "insert 后,用 insert 的返回值遍历 listInt:";
19 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.insert(++listInt.begin(), 2, 888); it != listInt.end(); it++)
20 {
21 cout << *it << " ";
22 }
23 cout << endl;
24 cout << "最终遍历 listInt:";
25 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
26 {
27 cout << *it << " ";
28 }
29
30 return 0;
31 }
打印结果:
insert(pos, beg, end);
//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,下面代码我举两种使用方法,一种是使用迭代器插入,另一种是插入数组
这里需要注意一点,list 不可以随机存取元素,所以不支持 at.(position)函数与[]操作符。可以对其迭代器执行++和--,但是不能这样操作迭代器:it + 3
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333 };
9 int num_1[] = { 666,777,888 };
10 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
11 list<int> listInt_A(2, 666);
12 cout << "初始遍历 listInt:";
13 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
14 {
15 cout << *it << " ";
16 }
17 cout << endl;
18
19
20 cout << "insert 后,用 insert 的返回值遍历 listInt:";
21 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.insert(++listInt.begin(), listInt_A.begin(), listInt_A.end()); it != listInt.end(); it++)
22 {
23 cout << *it << " ";
24 }
25
26 cout << endl;
27 cout << "最终遍历 listInt:";
28 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
29 {
30 cout << *it << " ";
31 }
32 cout << endl << endl;
33
34
35 //当然这里也可以插入数组
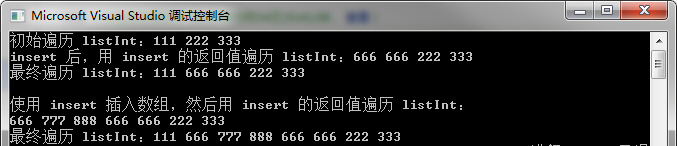
36 cout << "使用 insert 插入数组,然后用 insert 的返回值遍历 listInt:" << endl;
37 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.insert(++listInt.begin(), num_1, num_1 + size(num_1)); it != listInt.end(); it++)
38 {
39 cout << *it << " ";
40 }
41
42 cout << endl;
43 cout << "最终遍历 listInt:";
44 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
45 {
46 cout << *it << " ";
47 }
48
49 return 0;
50 }
打印结果:
clear();
//移除容器的所有数据
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
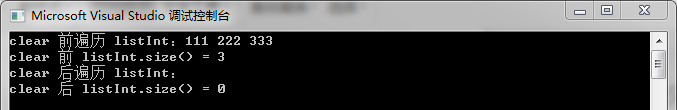
10 cout << "clear 前遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16 cout << "clear 前 listInt.size() = " << listInt.size() << endl;
17
18
19 listInt.clear();
20 cout << "clear 后遍历 listInt:";
21 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
22 {
23 cout << *it << " ";
24 }
25 cout << endl;
26 cout << "clear 后 listInt.size() = " << listInt.size() << endl;
27
28 return 0;
29 }
打印结果:
erase(beg, end);
//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333,444,555,666 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
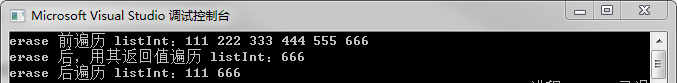
10 cout << "erase 前遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16
17
18 cout << "erase 后,用其返回值遍历 listInt:";
19 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.erase(++listInt.begin(), --listInt.end()); it != listInt.end(); it++)
20 {
21 cout << *it << " ";
22 }
23
24 cout << endl;
25 cout << "erase 后遍历 listInt:";
26 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
27 {
28 cout << *it << " ";
29 }
30
31 return 0;
32 }
打印结果:
erase(pos);
//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,333,444,555,666 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
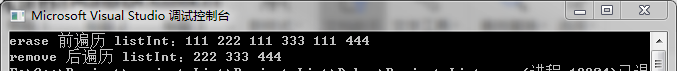
10 cout << "erase 前遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16
17
18 cout << "erase 后,用其返回值遍历 listInt:";
19 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.erase(++listInt.begin()); it != listInt.end(); it++)
20 {
21 cout << *it << " ";
22 }
23
24 cout << endl;
25 cout << "erase 后遍历 listInt:";
26 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
27 {
28 cout << *it << " ";
29 }
30
31 return 0;
32 }
打印结果:

remove(elem);
//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,111,333,111,444 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
10 cout << "erase 前遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16
17 listInt.remove(111);
18 cout << "remove 后遍历 listInt:";
19 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
20 {
21 cout << *it << " ";
22 }
23
24 return 0;
25 }
打印结果:
还有一种遍历删除法:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <list>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int num[] = { 111,222,111,333,111,444 };
9 list<int> listInt(num, num + size(num));
10 cout << "erase 前遍历 listInt:";
11 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
12 {
13 cout << *it << " ";
14 }
15 cout << endl;
16
17 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end();)
18 {
19 if (*it == 111)
20 {
21 it = listInt.erase(it);
22 }
23 else
24 {
25 it++;
26 }
27 }
28
29 cout << "erase 后遍历 listInt:";
30 for (list<int>::iterator it = listInt.begin(); it != listInt.end(); it++)
31 {
32 cout << *it << " ";
33 }
34
35 return 0;
36 }
打印结果:

======================================================================================================================
STL——容器(List)List 的数据元素插入和删除操作的更多相关文章
- [剑指offer]09用两个栈实现队列插入和删除操作,C++实现
原创博文,转载请注明出处! # 本文为牛客网<剑指offer>刷题笔记 1.题目 # 用两个栈实现队列的插入和删除操作 2.思路 栈服从先入后出的原则处理数据,队列服从先入先出的原则处理数 ...
- Java创建二叉搜索树,实现搜索,插入,删除操作
Java实现的二叉搜索树,并实现对该树的搜索,插入,删除操作(合并删除,复制删除) 首先我们要有一个编码的思路,大致如下: 1.查找:根据二叉搜索树的数据特点,我们可以根据节点的值得比较来实现查找,查 ...
- STL——容器(Map & multimap)的插入与迭代器
1. 容器(Map & multimap)的插入 map.insert(...); //往容器插入元素,返回pair<iterator,bool> map中插入元素的四种方式 ...
- jquery元素插入、删除、清空
1)jquery元素插入 <!--位置1--> <div id='test'> <!--位置2--> <div>测试</div> <! ...
- jquery元素插入、删除、清空、找父子级元素
1)jquery元素插入 <!--位置1--> <div id='test'> <!--位置2--> <div>测试</div> <! ...
- STL—— 容器(vector)数据插入insert()方法 的返回值
vector 容器下的 insert() 方法拥有返回值,由于insert() 方法拥有4种重载函数,他的返回值不尽相同. 第一种,插入单个元素后的返回值: 1 #include <iostre ...
- STL——容器(deque)deque 的插入 insert()
deque.insert(pos,elem); //在pos位置插入一个elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置. 1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <d ...
- Java BLOB 数据的插入与读取 操作
package com.lw.database; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import jav ...
- Thinkphp 数据的修改及删除操作
一.数据修改操作 save() 实现数据修改,返回受影响的记录条数 具体有两种方式实现数据修改,与添加类似(数组.AR方式) 1.数组方式: a) $goods = D(“Goods ...
随机推荐
- Elasticsearch 第八篇:数据类型 Array、Nested、Object 的设计与应用
h2.post_title { background-color: rgba(43, 102, 149, 1); color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 1); font-size: 1 ...
- Design Principle vs Design Pattern 设计原则 vs 设计模式
Design Principle vs Design Pattern设计原则 vs 设计模式 来源:https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/articles/differen ...
- 域渗透之ldap协议
LDAP(Light Directory Access Protocal)是一个基于X.500标准的轻量级目录访问协议,LDAP是支持跨平台的Internet协议,只需要通过LDAP做简单的配置就可以 ...
- ESP定律脱壳——NsPack3.x脱壳
首先进行查壳,NsPack 将程序拖入x64dbg 程序入口处标志性的push F8单步,发现仅有esp寄存器有变化 在esp上右键,在内存窗口查看,下硬件断点 F9运行程序,程序断在pop之后. 使 ...
- bWAPP----HTML Injection - Reflected (GET)
HTML Injection - Reflected (GET) 进入界面, html标签注入 这是核心代码 1 <div id="main"> 2 3 <h1& ...
- 他凭借这70份PDF,3170页文件,成功斩获了含BATJ所有的offer
前言 最近我一直在面试高级工程师,不管初级,高级,程序员,我想面试前,大家刷题一定是是少不了吧. 我也一样,我在网上找了很多面试题来看,最近又赶上跳槽的高峰期,好多粉丝,都问我要有没有最新面试题,索性 ...
- Stream流的这些操作,你得知道,对你工作有很大帮助
Stream流 Stream(流)是一个来自数据源的元素队列并支持聚合操作: 元素是特定类型的对象,形成一个队列. Java中的Stream并不会存储元素,而 是按需计算. 数据源 流的来源. 可以是 ...
- MindManager主题标记功能怎么使用
我们在使用MindManager制作思维导图的过程中,经常需要对主题的类别,优先程度等进行整理,毫无疑问,这是一项繁琐却又不得不做的工作.今天小编为大家带来了MindManager主题整理的一些小技巧 ...
- 从数据仓库双集群系统模式探讨,看GaussDB(DWS)的容灾设计
摘要:本文主要是探讨OLAP关系型数据库框架的数据仓库平台如何设计双集群系统,即增强系统高可用的保障水准,然后讨论一下GaussDB(DWS)的容灾应该如何设计. 当前社会.企业运行当中,大数据分析. ...
- Java基础教程——反射机制
Java反射机制 Java反射机制是Java语言的一个重要特性,使得Java语言具备"动态性": 在运行时获取任意一个对象所属的类的相关信息; 在运行时构造任意一个类的对象: 在运 ...
