Spring事务管理(编码式、配置文件方式、注解方式)
1、事务(https://www.cnblogs.com/zhai1997/p/11710082.html)
(1)事务的特性:acdi
(2)事务的并发问题:丢失修改,脏读,不可重复读
(3)事务的隔离级别:1、2、4、8
2、Spring的事务管理
(1)Spring封装了事务管理的代码:打开事务、提交事务、回滚事务
在我们学习的不同阶段(JDBC、Hibernate),对事物处理的方法是不一样的,为了解决这个问题,Spring提供了一个接口,PlatformTransactionManager(平台事务管理器),
该接口可以根据不同的平台提供不同的方法来处理事务,
(2)Spring管理事务的属性
事务的隔离级别:1:读未提交、2:读已提交、4:可重复读、8:串行化
本次事务是否只读:true:只读
事务的传播行为:
PROPAGATION REQUIRED 支持当前事务,如果不存在就新建一个(默认)
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS 支持当前事务,如果不存在,就不使用事务
PROPAGATION MANDATORY 支持当前事务,如果不存在,抛出异常
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务,创建一个新的事务
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务
PROPAGATION_NEUER 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,抛出异常
PROPAGATION_NESTED 如果当前事务存在,则嵌套事务执行
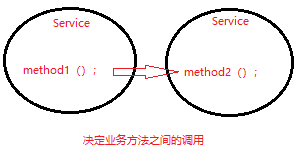
如果,事务method1调用事务method2,如果,method1没有开启事务,则method1需要先开启一个事务,method2也调用该事务,如果,method1,已经开启了一个事务,则method2直接用这个事务即可。
3、Spring管理事务的方式:编码式
(1)配置文件:
db.properties:
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///bank_transfer
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=root
applicationContext.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--指定要读取的配置文件的位置-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!--将连接池放入Spring容器-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<!--Dao-->
<bean name="accountDao" class="pers.zhb.dao.AccountDaoImp">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--Service-->
<bean name="accountserviceimp" class="pers.zhb.service.AccountServiceImp">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!--核心事务管理器,依赖于连接池-->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--事务模板对象-->
<bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
要确定好每个类之间的依赖关系。
(2) Dao层:
接口:
public interface AccountDao {
void increaseMoney(Integer id,Double money);
void decreaseMoney(Integer id,Double money);
}
实现类:
public class AccountDaoImp extends JdbcDaoSupport implements AccountDao{
@Override
public void increaseMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
String sql="update transfer set money=money+? where id = ?";
super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql,money,id);
}
@Override
public void decreaseMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
String sql="update transfer set money=money-? where id = ?";
super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql,money,id);
}
}
(3)Service层:
接口:
public interface AccountService {
void transfer(Integer from, Integer to,Double money);
}
实现类:
public class AccountServiceImp implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public void setTransactionTemplate(TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate) {
this.transactionTemplate = transactionTemplate;
}
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void transfer(final Integer from, final Integer to,final Double money) {
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {
accountDao.decreaseMoney(from,money);
int i=1/0;
accountDao.increaseMoney(to,money);
}
});
}
}
(4)测试类:
public static void main(String [] args){
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建容器对象
AccountServiceImp accountServiceImp =(AccountServiceImp)applicationContext.getBean("accountserviceimp");
accountServiceImp.transfer(1,2,12d);
}
在service层的方法中,故意制造了错误,再发生异常后未出现转账方钱减少而收款方前未增加的情况,即:钱的总数不会变。
4、Spring事务管理方式:xml配置aop事务
(1)导入约束:
导入tx、aop、context约束。
tx:配置事务通知
aop:配置aop
context:注解
(2)导包:
(3)Dao层的接口和实现类。
(4)Service层的接口和实现类,改层调用Dao层的两个转账方法。
(5)配置文件:
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///bank_transfer
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=root
该配置文件加jdbc前缀的目的是,与其他的功能的配置文件加以区别。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd "> <!--指定要读取的配置文件的位置-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!--将连接池放入Spring容器-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<!--Dao-->
<bean name="accountDao" class="pers.zhb.dao.AccountDaoImp">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--Service-->
<bean name="accountserviceimp" class="pers.zhb.service.AccountServiceImp">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!--核心事务管理器,依赖于连接池-->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--事务模板对象-->
<bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置事务通知-->
<tx:advice id="transactionInterceptor" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
</beans>
指出数据库相关的配置文件的位置。
读取配置文件中的数据,连接池被放入到了Spring容器。
将Dao层和Service层的对象放入到Spring容器中,其中Service层依赖于Dao层。
核心事务管理器,依赖于连接池。
事务模板对象,依赖于核心事务管理器。
配置事务通知:以方法为单位,isolation:隔离级别,propagation:传播行为,read-only:是否只读,是以方法为单位的。这里是将事务管理的通知(这里不用手动书写)织入到业务逻辑形成代理对象。
(6)测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String [] args){
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建容器对象
AccountServiceImp accountServiceImp =(AccountServiceImp)applicationContext.getBean("accountserviceimp");
accountServiceImp.transfer(1,2,12d);
}
}
5、Spring事务管理方式:注解
注解:
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly = false)
public void transfer(final Integer from, final Integer to,final Double money) {
accountDao.decreaseMoney(from,money);
accountDao.increaseMoney(to,money);
}
配置文件:
<!--指定要读取的配置文件的位置-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!--将连接池放入Spring容器-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<!--Dao-->
<bean name="accountDao" class="pers.zhb.dao.AccountDaoImp">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--Service-->
<bean name="accountserviceimp" class="pers.zhb.service.AccountServiceImp">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!--核心事务管理器,依赖于连接池-->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--事务模板对象-->
<bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 开启使用注解管理aop事务 -->
<tx:annotation-driven/>
<!--java.lang.ClassCastException: com.sun.proxy.$Proxy2 cannot be cast to...异常-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
</beans>
Spring事务管理(编码式、配置文件方式、注解方式)的更多相关文章
- 【核心核心】10.Spring事务管理【TX】XML+注解方式
转账案例环境搭建 1.引入JAR包 IOC的6个包 AOP的4个包 C3P0的1个包 MySQL的1个驱动包 JDBC的2个目标包 整合JUnit测试1个包 2.引入配置文件 log4j.proper ...
- Spring框架的事务管理之基于AspectJ的注解方式(重点掌握,最简单的方式)
1. 步骤一:恢复转账的开发环境(具体开发环境实现见:https://www.cnblogs.com/wyhluckdog/p/10137283.html)2. 步骤二:applicationCont ...
- Spring事务管理中的配置文件(三)
在开发中,遇到了sql语句报错,但是并没有回滚的情况. 经过几天的排查,终于找到了事务没有回滚的原因. 原来的项目用的是informix的数据库,原来针对事务回滚的机制都是好用的.我本地用的是mysq ...
- Spring 事务管理原理探究
此处先粘贴出Spring事务需要的配置内容: 1.Spring事务管理器的配置文件: 2.一个普通的JPA框架(此处是mybatis)的配置文件: <bean id="sqlSessi ...
- 事务管理(下) 配置spring事务管理的几种方式(声明式事务)
配置spring事务管理的几种方式(声明式事务) 概要: Spring对编程式事务的支持与EJB有很大的区别.不像EJB和Java事务API(Java Transaction API, JTA)耦合在 ...
- Spring事务管理详解_基本原理_事务管理方式
1. 事务的基本原理 Spring事务的本质其实就是数据库对事务的支持,使用JDBC的事务管理机制,就是利用java.sql.Connection对象完成对事务的提交,那在没有Spring帮我们管理事 ...
- Spring事务管理的三种方式
一 .第一种:全注解声明式事务 Xml代码 复制代码 收藏代码 .<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> .& ...
- Spring事务管理之几种方式实现事务
1.事务认识 大家所了解的事务Transaction,它是一些列严密操作动作,要么都操作完成,要么都回滚撤销.Spring事务管理基于底层数据库本身的事务处理机制.数据库事务的基础,是掌握Spring ...
- Spring事务管理之几种方式实现事务(转)
一:事务认识 大家所了解的事务Transaction,它是一些列严密操作动作,要么都操作完成,要么都回滚撤销.Spring事务管理基于底层数据库本身的事务处理机制.数据库事务的基础,是掌握Spring ...
随机推荐
- 区块链入门到实战(36)之Solidity – 运算符
Solidity – 算术运算符 Solidity 支持的算术运算符,如下表所示: 假设变量A的值为10,变量B的值为20. 序号 运算符与描述 1 + (加)求和例: A + B = 30 2 – ...
- CF1270B Interesting Subarray 题解
22:20下晚自习所以只打了10+min,然而这并不能成为我脑抽没一眼看出B题的借口,所以又掉回绿名了qwq.所以我还是太菜了. 题意分析 给出一个数列,要求找出一段连续的子数列满足这个子数列的最大值 ...
- h5c3
HTML5 第一天 一.什么是 HTML5 HTML5 的概念与定义 定义:HTML5 定义了 HTML 标准的最新版本,是对 HTML 的第五次重大修改,号称下一代的 HTML 两个概念: 是一个新 ...
- UnitTest单元测试框架解析【实用篇】
UnitTest是展开自动化测试的基础——这个框架很重要!首先我们先自己写一个测试类: 1.被测试类 Widthget.py: # coding: utf-8class Widthget: def _ ...
- HMM隐马尔可夫模型来龙去脉(二)
目录 前言 预备知识 一.估计问题 1.问题推导 2.前向算法/后向算法 二.序列问题 1.问题推导 2.维特比算法 三.参数估计问题 1.问题推导 2.期望最大化算法(前向后向算法) 总结 前言 H ...
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)解题总结
定义 深度优先搜索算法(Depth-First-Search),是搜索算法的一种.它沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支. 例如下图,其深度优先遍历顺序为 1->2->4-&g ...
- Mysql宽字节注入 ---学习笔记
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/niexinming/article/details/49109683 先补充一点背景:大 家都知道PHP在开启magic_quotes_gpc或者使 ...
- C++轻量级跨平台文件系统API
http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/experimental/fs https://www.starmessagesoftware.com/cpcclibrary htt ...
- 第四方 fast快捷支付封装
class Fastpay { protected $conf = [ 'appkey'=>'',//appkey 'key'=>'',//秘钥 ]; protected $http_ty ...
- 详细教程丨使用Prometheus和Thanos进行高可用K8S监控
本文转自Rancher Labs 介 绍 Prometheus高可用的必要性 在过去的几年里,Kubernetes的采用量增长了数倍.很明显,Kubernetes是容器编排的不二选择.与此同时,Pro ...
