HashMap,Hash优化与高效散列
OverView
Hash table based implementation of the Map interface. This implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits null values and the null key. (The HashMap class is roughly equivalent to Hashtable, except that it is unsynchronized and permits nulls.) This class makes no guarantees as to the order of the map; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant over time.
This implementation provides constant-time performance for the basic operations (get and put), assuming the hash function disperses the elements properly among the buckets. Iteration over collection views requires time proportional to the "capacity" of the HashMap instance (the number of buckets) plus its size (the number of key-value mappings). Thus, it's very important not to set the initial capacity too high (or the load factor too low) if iteration performance is important.
An instance of HashMap has two parameters that affect its performance: initial capacity and load factor. The capacity is the number of buckets in the hash table, and the initial capacity is simply the capacity at the time the hash table is created. The load factor is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to get before its capacity is automatically increased. When the number of entries in the hash table exceeds the product of the load factor and the current capacity, the hash table is rehashed (that is, internal data structures are rebuilt) so that the hash table has approximately twice the number of buckets.
As a general rule, the default load factor (.75) offers a good tradeoff between time and space costs. Higher values decrease the space overhead but increase the lookup cost (reflected in most of the operations of the HashMap class, including get and put). The expected number of entries in the map and its load factor should be taken into account when setting its initial capacity, so as to minimize the number of rehash operations. If the initial capacity is greater than the maximum number of entries divided by the load factor, no rehash operations will ever occur.
If many mappings are to be stored in a HashMap instance, creating it with a sufficiently large capacity will allow the mappings to be stored more efficiently than letting it perform automatic rehashing as needed to grow the table.
Note that this implementation is not synchronized. If multiple threads access a hash map concurrently, and at least one of the threads modifies the map structurally, it must be synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation that adds or deletes one or more mappings; merely changing the value associated with a key that an instance already contains is not a structural modification.) This is typically accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the map. If no such object exists, the map should be "wrapped" using the Collections.synchronizedMap method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental unsynchronized access to the map: Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));The iterators returned by all of this class's "collection view methods" are fail-fast: if the map is structurally modified at any time after the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator's own remove method, the iterator will throw a ConcurrentModificationException. Thus, in the face of concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined time in the future.
Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators throw ConcurrentModificationException on a best-effort basis. Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this exception for its correctness: the fail-fast behavior of iterators should be used only to detect bugs.
This class is a member of the Java Collections Framework.
Feild
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY 初始容量
The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
不论传入的initial capacity是多少,都会转化比他小且离他最近的2的幂
至于为什么是2的幂,呵呵呵呵,往下看
| default=16
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY 初始容量
元素个数永远不会超过这个上限,不论如何设置和扩展。
| MAXIMUM = 1<<30 = 2^29
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR 复制因子
当容量达到当前最大容量的多少时需要启动复制
| default = 0.75
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
threshold 复制门槛
当前容量超过(put时检查)threshold时,复制底层数据结果以扩展
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
modCount 修改计数
This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
the HashMap fail-fast
Hash
良好的hash保证,所有元素恰好落入数组的中(尽可能减少重复,以便减少指针移动次数)
当出现重复时,以链表的形式保存(新元素插入链表第一个!important)
| HashCode = Object.hashCode()
Magic
| 优化hash与更高效的散列算法
基于位的散列算法
//该方法返回此hash值应该储存在数组的下标
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
| PHP实现的测试代码
<?php
$arr = array();
$length = 10; //array length - 1
$data_length = 2001; //hashcode from 1 to 2002 for($i = 1; $i< $data_length; $i++) { if( !isset($arr[$i & $length]) ) {
$arr[$i & $length] = 1;
} else {
$arr[$i & $length]++;
}
} var_dump($arr);
case 1
| $length = 10
| $data_length = 2001
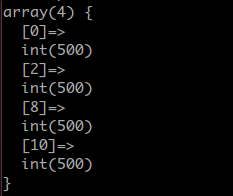
运行结果:
很巧的是,有的下标上居然没有落值,而有值得下标的值非常均匀
case 2
| $length = 7 = 2^3 - 1
| $data_length = 2001
实验一下数组长度为2的幂
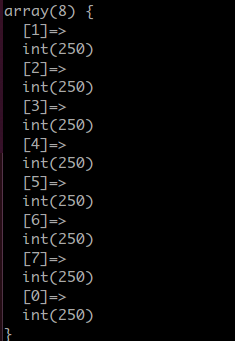
运行结果:
恰好均匀的落在了每一个上面
注意1<<n - 1 的所有位都是1,这样恰好可以保证从任意数恰好均匀落在所有位置上,原理等同于取余,但是限制是底数必须为2的幂,但是全是位操作 ![]()
优化Hash或抵制低效Hash
/**
* Applies a supplemental hash function to a given hashCode, which
* defends against poor quality hash functions. This is critical
* because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
*/
static int hash(int h) {
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
由于ForIndex方法的存在,为了避免出现低位相同的情况(低位相同会导致虽然高位不同的hashcode落在同样的下标上)
例如:原始数组3个(代表3个hash值),分别为 31,63,95,另外初始容量为16 = 2 ^ 4 = 10000
31=00000000000000000000000000011111
63=00000000000000000000000000111111
95=00000000000000000000000001011111
直接使用indexFor()结果如下
31=00000000000000000000000000011111 & 1111 = 1111 & 1111 = 15
63=00000000000000000000000000111111 & 1111 = 1111 & 1111 = 15
95=00000000000000000000000001011111 & 1111 = 1111 & 1111 = 15 //这说明质量低下的hash的低位总是相同,不适应indexFor
使用hash(),结果如下
31=00000000000000000000000000011111 => 00000000000000000000000000011110
63=00000000000000000000000000111111 => 00000000000000000000000000111100
95=00000000000000000000000001011111 => 00000000000000000000000001011010 //这样一来低位就不同了
00000000000000000000000000011110 & 1111 = 1110 & 1111 = 14
00000000000000000000000000111100 & 1111 = 1100 & 1111 = 12
00000000000000000000000001011010 & 1111 = 1010 & 1111 = 10
散列操作的主要目的是使在低位的散列码的差异明显,使得散列映射元件能够均匀地分布
Put & Get
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)
Hooks
init
初始化的时候的hook
/**
* Initialization hook for subclasses. This method is called
* in all constructors and pseudo-constructors (clone, readObject)
* after HashMap has been initialized but before any entries have
* been inserted. (In the absence of this method, readObject would
* require explicit knowledge of subclasses.)
*/
void init() {
}
remove & access
//Class.Entry /**
* This method is invoked whenever the value in an entry is
* overwritten by an invocation of put(k,v) for a key k that's already
* in the HashMap.
*/
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
} /**
* This method is invoked whenever the entry is
* removed from the table.
*/
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
HashMap,Hash优化与高效散列的更多相关文章
- HashMap的实现原理--链表散列
1. HashMap概述 HashMap是基于哈希表的Map接口的非同步实现.此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用null值和null键.此类不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变. ...
- Hash算法:双重散列
双重散列是线性开型寻址散列(开放寻址法)中的冲突解决技术.双重散列使用在发生冲突时将第二个散列函数应用于键的想法. 此算法使用: (hash1(key) + i * hash2(key)) % TAB ...
- 【Java集合学习】HashMap源码之“拉链法”散列冲突的解决
1.HashMap的概念 HashMap 是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射. HashMap 继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map.Cloneable.java.io ...
- java 散列与散列码探讨 ,简单HashMap实现散列映射表运行各种操作示列
java 散列与散列码探讨 ,简单HashMap实现散列映射表运行各种操作示列 package org.rui.collection2.maps; /** * 散列与散列码 * 将土拔鼠对象与预报对象 ...
- JDK1.8中对hashmap的优化
在Java编程语言中,最基本的结构就是两种,一个是数组,另外一个是模拟指针(引用),所有的数据结构都可以用这两个基本结构来构造的,HashMap也不例外.HashMap实际上是一个“链表散列”的数据结 ...
- 【数据结构】之散列链表(Java语言描述)
散列链表,在JDK中的API实现是 HashMap 类. 为什么HashMap被称为“散列链表”?这与HashMap的内部存储结构有关.下面将根据源码进行分析. 首先要说的是,HashMap中维护着的 ...
- Android数据加密之SHA安全散列算法
前言: 对于SHA安全散列算法,以前没怎么使用过,仅仅是停留在听说过的阶段,今天在看图片缓存框架Glide源码时发现其缓存的Key采用的不是MD5加密算法,而是SHA-256加密算法,这才勾起了我的好 ...
- 【Java-加密算法】对称加密、非对称加密、单向散列(转)
一提到加密,就会联想到数字签名,这两个经常被混淆的概念到底是什么呢? 加密:加密是一种以密码方式发送信息的方法.只有拥有正确密钥的人才能解开这个信息的密码.对于其他人来说,这个信息看起来就像是一系列随 ...
- JDK8;HashMap:再散列解决hash冲突 ,源码分析和分析思路
JDK8中的HashMap相对JDK7中的HashMap做了些优化. 接下来先通过官方的英文注释探究新HashMap的散列怎么实现 先不给源码,因为直接看源码肯定会晕,那么我们先从简单的概念先讲起 ...
随机推荐
- 为了更好更方便地活着——爱上private
刚开始接触OOP的时候,打心底里我不喜欢private与protected.我声明一个public然后不直接用它,不就跟private一样吗?在某些场合下,我还能偷偷地用一下public变量,这不是更 ...
- Vivado_MicroBlaze_问题及解决方法_汇总(不定时更新)
Vivado_MicroBlaze_问题及解决方法_汇总(不定时更新) 标签: Vivado 2015-07-03 14:35 4453人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 分类: 硬件(14) 版权声 ...
- 我的octopress配置
在github上用octopress搭建了自己的blog,octopress号称是"专门给黑客打造的博客(A blogging framework for 把hackers)",使 ...
- 【转】Selenium2 API详解
[转自]http://blog.csdn.net/wuxuehong0306/article/details/49762961 打开浏览器 Ø 打开firefox浏览器 WebDriver driv ...
- redis安装全过程
1. 从官网上下载redis. 2.安装gcc 3.进入./redis/src目录下make MALLOC =libc 4.遇到的问题 Redis简介: Redis是一个开源的使用ANSI C语言编写 ...
- C#多线程编程之:异步方法调用
异步方法 当一个线程调用方法后,直到方法执行完毕,线程才继续执行,这种方法被称为同步方法.然而,有些方法执行时间可能非常长,比如串口操作或访问网络,这样线程被阻塞,而无法响应用户的其他请求.这种情况通 ...
- laravel Hash密码 校对
laravel加密 是使用hash不可逆的,但是可以对加密后的密码进行校对 $data = $r->all();$id = $data['id'];$user_password = bcrypt ...
- PHP常用获取文件路径的函数集合整理
转自: http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_71ed1b870102vslg.html 我们在开发PHP项目过程中,经常会用到包含文件,所以有时候需要获取文件的相对路径或者绝 ...
- Devexpres下LookUpEdit绑定数据后会默认弹出数据框的解决办法
LookUpEdit绑定数据后会默认弹出数据框很不友好问题现象: 问题解决前的代码: lueManagement.Text = groupEntity.Name; 2 lueManagement.Ed ...
- eclipse 创建dynamic web project不能运行
按照李刚<轻量级java ee企业应用实战>第三版,第二章的配置,发现eclipse 创建dynamic web project不能运行,原来作者第二章时还不是在eclipse中开发的,只 ...
