基于注解的简单SSH保存用户小案例
需求:搭建SSH框架环境,使用注解进行相关的注入(实体类的注解,AOP注解、DI注入),保存用户信息
效果:
一、导依赖包
二、项目的目录结构
三、web.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1"> <!--懒加载过滤器,解决懒加载问题-->
<filter>
<filter-name>openSession</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.support.OpenSessionInViewFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>openSession</filter-name>
<url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping> <!-- struts2的前端控制器 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>struts</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struts</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping> <!-- spring 创建监听器 -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener> <context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param> </web-app>
四、applicationContext.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:contex="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 打开注解扫描开关 -->
<contex:component-scan base-package="com.pri"/> <!-- 以下是属于hibernate的配置 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///ssh_demo1?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="user" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</bean> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<!--1、核心配置-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <!-- 2、可选配置-->
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.format_sql">true</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</prop>
</props>
</property>
<!-- 3、扫描映射文件 -->
<property name="packagesToScan" value="com.pri.domain"></property>
</bean> <!--开启事务控制-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager= "transactionManager"/>
</beans>
五、log4j.properties配置
#设置日志记录到控制台的方式
log4j.appender.std=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
#out以黑色字体输出,err以红色字体输出
log4j.appender.std.Target=System.err
log4j.appender.std.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.std.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
#设置日志记录到文件的方式
log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
#日志文件路径文件名
log4j.appender.file.File=mylog.log
#日志输出的格式
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
#日志输出的级别,以及配置记录方案,级别:error > warn > info>debug>trace
log4j.rootLogger=info, std, file
六、页面代码
index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>添加客户</h3>
<form action="${ pageContext.request.contextPath }/customerAction_save" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br/>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/><br/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>保存成功!</h1>
</body>
</html>
七、实体层代码
package com.pri.domain; import javax.persistence.*; @Entity
@Table(name = "customer")
public class Customer {
@Id
@Column(name = "userId")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer userId; @Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "age")
private Integer age; public Integer getUserId() {return userId; } public void setUserId(Integer userId) {this.userId = userId;} public String getName() {return name;} public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;} public Integer getAge() {return age;} public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}
}
八、action层代码
package com.pri.action; import com.pri.domain.Customer;
import com.pri.service.CustomerService;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven;
import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Action;
import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Namespace;
import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.ParentPackage;
import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotation.Result;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import javax.annotation.Resource; @Controller("customerAction")
@ParentPackage(value = "struts-default")
@Scope("prototype")
@Namespace(value = "/")
public class CustomerAction extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriven<Customer>{ private Customer customer; @Resource(name = "customerService")
private CustomerService customerService; @Override
public Customer getModel() {
if (customer == null ){
customer = new Customer();
}
return customer;
} @Action(value = "customerAction_save",
results = {@Result(name = SUCCESS,type = "redirect",location = "/success.jsp")})
public String save(){
customerService.save(customer);
return SUCCESS;
}
}
九、service层代码
package com.pri.service;
import com.pri.domain.Customer;
public interface CustomerService {
void save(Customer user);
}
//=======================================
package com.pri.service.impl;
import com.pri.domain.Customer;
import com.pri.dao.CustomerDao;
import com.pri.service.CustomerService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service("customerService")
@Transactional
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
@Resource(name = "customerDao")
private CustomerDao customerDao;
@Override
public void save(Customer customer) {
customerDao.save(customer);
}
}
十、dao层代码
package com.pri.dao;
import com.pri.domain.Customer;
public interface CustomerDao {
void save(Customer customer);
}
//==================================================================
package com.pri.dao.impl;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.support.HibernateDaoSupport;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Component("myHibernateDaoSupport")
public class MyHibernateDaoSupport extends HibernateDaoSupport {
@Resource(name = "sessionFactory")
public void setSuperSessionFactory(SessionFactory sessionFactory){
super.setSessionFactory(sessionFactory);
}
}
//=================================================
package com.pri.dao.impl;
import com.pri.dao.CustomerDao;
import com.pri.domain.Customer;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("customerDao")
public class CustomerDaoImpl extends MyHibernateDaoSupport implements CustomerDao {
@Override
public void save(Customer customer) {
getHibernateTemplate().save(customer);
}
}
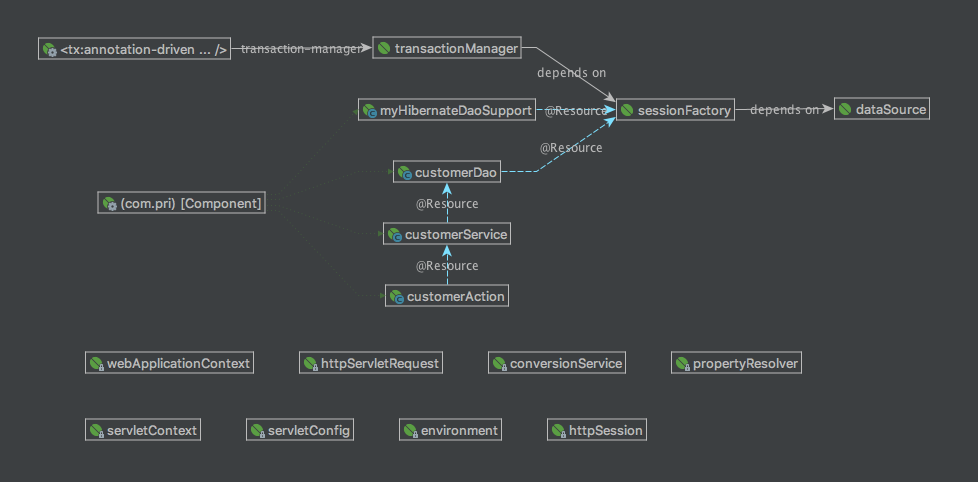
十一、Spring Beans Dependencies
基于注解的简单SSH保存用户小案例的更多相关文章
- Netty学习——基于netty实现简单的客户端聊天小程序
Netty学习——基于netty实现简单的客户端聊天小程序 效果图,聊天程序展示 (TCP编程实现) 后端代码: package com.dawa.netty.chatexample; import ...
- springboot+ehcache 基于注解实现简单缓存demo
1.加入maven依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactI ...
- jackson基于注解的简单使用
Jackson提供了一系列注解,方便对JSON序列化和反序列化进行控制,下面介绍一些常用的注解. 1.@JsonIgnore 此注解用于属性上,作用是进行JSON操作时忽略该属性. 2.@JsonFo ...
- 10 Spring框架--基于注解和xml的配置的应用案例
1.项目结构 2.基于xml配置的项目 <1>账户的业务层接口及其实现类 IAccountService.java package lucky.service; import lucky. ...
- Spring中基于注解的IOC(二):案例与总结
2.Spring的IOC案例 创建maven项目 导入依赖 pom.xml xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" ...
- Hibernate基于注解annotation的配置
Annotation在框架中是越来越受欢迎了,因为annotation的配置比起XML的配置来说方便了很多,不需要大量的XML来书写,方便简单了很多,只要几个annotation的配置,就可以完成我们 ...
- 菜鸟学SSH(十七)——基于注解的SSH将配置精简到极致
很早之前就想写一篇关于SSH整合的博客了,但是一直觉得使用SSH的时候那么多的配置文件,严重破坏了我们代码整体性,比如你要看两个实体的关系还得对照*.hbm.xml文件,要屡清一个Action可能需要 ...
- Servlet之保存用户偏好设置简单功能的实现
写在前面: 先来陈述一下为什么会有这样一个需求和这篇博文. 这是公司的一个项目,我们负责前端,后台服务由其他公司负责.该系统有一个系统偏好设置模块,用户可以设置系统的背景图片等系统样式,因为这是一个比 ...
- 8 -- 深入使用Spring -- 4...5 AOP代理:基于注解的“零配置”方式
8.4.5 基于注解的“零配置”方式 AspectJ允许使用注解定义切面.切入点和增强处理,而Spring框架则可识别并根据这些注解来生成AOP代理.Spring只是使用了和AspectJ 5 一样的 ...
随机推荐
- 3分钟解决MySQL 1032 主从错误(转)
转自 https://blog.51cto.com/suifu/1845457 3分钟解决MySQL 1032主从错误 Part1:写在最前 1032错误----现在生产库中好多数据,在从库误删了, ...
- ubuntu下apache2使用的简单总结
一. 修改apache2原80端口为90端口 1. 修改/etc/apache2/ports.conf, 将端口80改为90,443,改为444 2. 修改/etc/apache2/sites ...
- Java 设计模式之单利模式
一.首先介绍一下单例模式: 单例模式(Singleton),也叫单子模式,是一种常用的软件设计模式.在应用这个模式时,单例对象的类必须保证只有一个实例存在.许多时候整个系统只需要拥有一个的全局 ...
- eclipse安装SonarLint插件,sonarLint客户端的使用
一.在线安装sonarLint 打开eclipse里的help->Eclipse Marketplace,搜索“sonar”关键字,目前sonar的插件是sonarlint,如下图: 点击“In ...
- OO第二单元の小结
第二单元(线程与电梯问题)总结博客 三次作业的设计策略 第一次:本次作业只有一部电梯,而且不用捎带.因此,我一共设计了两个线程:一个负责管理输入,一个负责电梯运行.同时,我将调度队列设置为单例模式,里 ...
- AFNetworking 3.1.0 使用中某些知识点讲解
# POST / GET 请求 /*! 首先要知道,POST请求不能被缓存,只有 GET 请求能被缓存.因为从数学的角度来讲,GET 的结果是 幂等 的,就好像字典里的 key 与 value 就是 ...
- JQ 文件上传
var formData = new FormData(); var name = $("input").val(); formData.append("file&quo ...
- 03-树3 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example ...
- windows下python3.7.2内置venv虚拟环境下pyinstaller错误问题
起因 开发一直使用python -m venv .pyenv 方式创建虚拟环境,在利用pyinstaller打包发布应用时,出现错误 3178 INFO: Warnings written to C: ...
- Windows开发经验 - WinDbg
1. 远程调试 参考文章:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/debugger/remode-debugging-usi ...
