springboot学习笔记-6 springboot整合RabbitMQ
一 RabbitMQ的介绍
RabbitMQ是消息中间件的一种,消息中间件即分布式系统中完成消息的发送和接收的基础软件.这些软件有很多,包括ActiveMQ(apache公司的),RocketMQ(阿里巴巴公司的,现已经转让给apache).
消息中间件的工作过程可以用生产者消费者模型来表示.即,生产者不断的向消息队列发送信息,而消费者从消息队列中消费信息.具体过程如下:
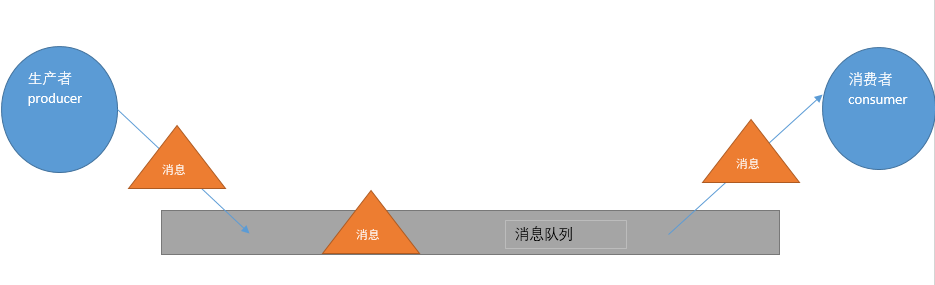
从上图可看出,对于消息队列来说,生产者,消息队列,消费者是最重要的三个概念,生产者发消息到消息队列中去,消费者监听指定的消息队列,并且当消息队列收到消息之后,接收消息队列传来的消息,并且给予相应的处理.消息队列常用于分布式系统之间互相信息的传递.
对于RabbitMQ来说,除了这三个基本模块以外,还添加了一个模块,即交换机(Exchange).它使得生产者和消息队列之间产生了隔离,生产者将消息发送给交换机,而交换机则根据调度策略把相应的消息转发给对应的消息队列.那么RabitMQ的工作流程如下所示:
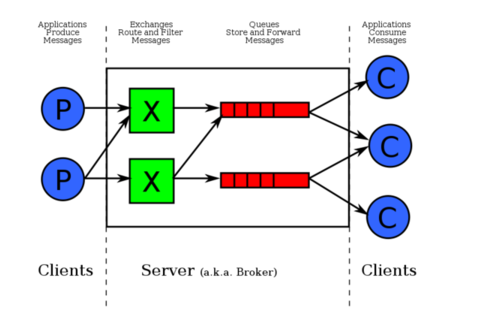
紧接着说一下交换机.交换机的主要作用是接收相应的消息并且绑定到指定的队列.交换机有四种类型,分别为Direct,topic,headers,Fanout.
Direct是RabbitMQ默认的交换机模式,也是最简单的模式.即创建消息队列的时候,指定一个BindingKey.当发送者发送消息的时候,指定对应的Key.当Key和消息队列的BindingKey一致的时候,消息将会被发送到该消息队列中.
topic转发信息主要是依据通配符,队列和交换机的绑定主要是依据一种模式(通配符+字符串),而当发送消息的时候,只有指定的Key和该模式相匹配的时候,消息才会被发送到该消息队列中.
headers也是根据一个规则进行匹配,在消息队列和交换机绑定的时候会指定一组键值对规则,而发送消息的时候也会指定一组键值对规则,当两组键值对规则相匹配的时候,消息会被发送到匹配的消息队列中.
Fanout是路由广播的形式,将会把消息发给绑定它的全部队列,即便设置了key,也会被忽略.
二.SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ(Direct模式)
SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ非常简单!感觉SpringBoot真的极大简化了开发的搭建环境的时间..这样我们程序员就可以把更多的时间用在业务上了,下面开始搭建环境:
首先创建两个maven工程,这是为了模拟分布式应用系统中,两个应用之间互相交流的过程,一个发送者(Sender),一个接收者(Receiver)
紧接着,配置pom.xml文件,注意其中用到了springboot对于AMQP(高级消息队列协议,即面向消息的中间件的设计)
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.7</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
<scope>true</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加springboot对amqp的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
紧接着,我们编写发送者相关的代码.首先毫无疑问,要书写启动类:
@SpringBootApplication
public class App{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
接着在application.properties中,去编辑和RabbitMQ相关的配置信息,配置信息的代表什么内容根据键就能很直观的看出了.这里端口是5672,不是15672...15672是管理端的端口!
spring.application.name=spirng-boot-rabbitmq-sender
spring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=guest
spring.rabbitmq.password=guest
随后,配置Queue(消息队列).那注意由于采用的是Direct模式,需要在配置Queue的时候,指定一个键,使其和交换机绑定.
@Configuration
public class SenderConf {
@Bean
public Queue queue() {
return new Queue("queue");
}
}
接着就可以发送消息啦!在SpringBoot中,我们使用AmqpTemplate去发送消息!代码如下:
@Component
public class HelloSender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate template; public void send() {
template.convertAndSend("queue","hello,rabbit~");
}
}
编写测试类!这样我们的发送端代码就编写完了~
@SpringBootTest(classes=App.class)
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class TestRabbitMQ { @Autowired
private HelloSender helloSender; @Test
public void testRabbit() {
helloSender.send();
}
}
接着我们编写接收端.接收端的pom文件,application.properties(修改spring.application.name),Queue配置类,App启动类都是一致的!这里省略不计.主要在于我们需要配置监听器去监听绑定到的消息队列,当消息队列有消息的时候,予以接收,代码如下:
@Component
public class HelloReceive { @RabbitListener(queues="queue") //监听器监听指定的Queue
public void processC(String str) {
System.out.println("Receive:"+str);
} }
接下来就可以测试啦,首先启动接收端的应用,紧接着运行发送端的单元测试,接收端应用打印出来接收到的消息,测试即成功!
需要注意的地方,Direct模式相当于一对一模式,一个消息被发送者发送后,会被转发到一个绑定的消息队列中,然后被一个接收者接收!
实际上RabbitMQ还可以支持发送对象:当然由于涉及到序列化和反序列化,该对象要实现Serilizable接口.HelloSender做出如下改写:
public void send() {
User user=new User(); //实现Serializable接口
user.setUsername("hlhdidi");
user.setPassword("123");
template.convertAndSend("queue",user);
}
HelloReceiver做出如下改写:
@RabbitListener(queues="queue") //监听器监听指定的Queue
public void process1(User user) { //用User作为参数
System.out.println("Receive1:"+user);
}
三.SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ(Topic转发模式)
首先我们看发送端,我们需要配置队列Queue,再配置交换机(Exchange),再把队列按照相应的规则绑定到交换机上:
@Configuration
public class SenderConf { @Bean(name="message")
public Queue queueMessage() {
return new Queue("topic.message");
} @Bean(name="messages")
public Queue queueMessages() {
return new Queue("topic.messages");
} @Bean
public TopicExchange exchange() {
return new TopicExchange("exchange");
} @Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage(@Qualifier("message") Queue queueMessage, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessage).to(exchange).with("topic.message");
} @Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessages(@Qualifier("messages") Queue queueMessages, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessages).to(exchange).with("topic.#");//*表示一个词,#表示零个或多个词
}
}
而在接收端,我们配置两个监听器,分别监听不同的队列:
@RabbitListener(queues="topic.message") //监听器监听指定的Queue
public void process1(String str) {
System.out.println("message:"+str);
}
@RabbitListener(queues="topic.messages") //监听器监听指定的Queue
public void process2(String str) {
System.out.println("messages:"+str);
}
好啦!接着我们可以进行测试了!首先我们发送如下内容:

方法的第一个参数是交换机名称,第二个参数是发送的key,第三个参数是内容,RabbitMQ将会根据第二个参数去寻找有没有匹配此规则的队列,如果有,则把消息给它,如果有不止一个,则把消息分发给匹配的队列(每个队列都有消息!),显然在我们的测试中,参数2匹配了两个队列,因此消息将会被发放到这两个队列中,而监听这两个队列的监听器都将收到消息!那么如果把参数2改为topic.messages呢?显然只会匹配到一个队列,那么process2方法对应的监听器收到消息!
四.SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ(Fanout Exchange形式)
那前面已经介绍过了,Fanout Exchange形式又叫广播形式,因此我们发送到路由器的消息会使得绑定到该路由器的每一个Queue接收到消息,这个时候就算指定了Key,或者规则(即上文中convertAndSend方法的参数2),也会被忽略!那么直接上代码,发送端配置如下:
@Configuration
public class SenderConf { @Bean(name="Amessage")
public Queue AMessage() {
return new Queue("fanout.A");
} @Bean(name="Bmessage")
public Queue BMessage() {
return new Queue("fanout.B");
} @Bean(name="Cmessage")
public Queue CMessage() {
return new Queue("fanout.C");
} @Bean
FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange("fanoutExchange");//配置广播路由器
} @Bean
Binding bindingExchangeA(@Qualifier("Amessage") Queue AMessage,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(AMessage).to(fanoutExchange);
} @Bean
Binding bindingExchangeB(@Qualifier("Bmessage") Queue BMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(BMessage).to(fanoutExchange);
} @Bean
Binding bindingExchangeC(@Qualifier("Cmessage") Queue CMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(CMessage).to(fanoutExchange);
} }
发送端使用如下代码发送:

接收端监听器配置如下:
@Component
public class HelloReceive {
@RabbitListener(queues="fanout.A")
public void processA(String str1) {
System.out.println("ReceiveA:"+str1);
}
@RabbitListener(queues="fanout.B")
public void processB(String str) {
System.out.println("ReceiveB:"+str);
}
@RabbitListener(queues="fanout.C")
public void processC(String str) {
System.out.println("ReceiveC:"+str);
} }
运行测试代码,发现三个监听器都接收到了数据,测试成功!
springboot学习笔记-6 springboot整合RabbitMQ的更多相关文章
- springboot 学习之路 20 (整合RabbitMQ)
整合RabbitMQ: 我的操作系统是window7 ,所以在整合ribbotMQ之前需要先安装rabbitMq服务:安装步骤请参考:window下安装RabbitMQ 这个详细介绍了安装步骤,请按 ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(4)----SpringBoot中freemarker、thymeleaf的使用
1. freemarker引擎的使用 如果你使用的是idea或者eclipse中安装了sts插件,那么在新建项目时就可以直接指定试图模板 如图: 勾选freeMarker,此时springboot项目 ...
- springboot学习笔记-5 springboot整合shiro
shiro是一个权限框架,具体的使用可以查看其官网 http://shiro.apache.org/ 它提供了很方便的权限认证和登录的功能. 而springboot作为一个开源框架,必然提供了和sh ...
- 【转】SpringBoot学习笔记(7) SpringBoot整合Dubbo(使用yml配置)
http://blog.csdn.net/a67474506/article/details/61640548 Dubbo是什么东西我这里就不详细介绍了,自己可以去谷歌 SpringBoot整合Dub ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(16)----SpringBoot整合Swagger2
Swagger 是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成,描述,调用和可视化RESTful风格的web服务 http://swagger.io Springfox的前身是swagger-springmvc,是 ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(11)-----SpringBoot中使用rabbitmq,activemq消息队列和rest服务的调用
1. activemq 首先引入依赖 pom.xml文件 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId& ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(9)----SpringBoot中使用关系型数据库以及事务处理
在实际的运用开发中,跟数据库之间的交互是必不可少的,SpringBoot也提供了两种跟数据库交互的方式. 1. 使用JdbcTemplate 在SpringBoot中提供了JdbcTemplate模板 ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(6) SpringBoot数据缓存Cache [Guava和Redis实现]
https://blog.csdn.net/a67474506/article/details/52608855 Spring定义了org.springframework.cache.CacheMan ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(15)----SpringBoot使用Druid
直接访问Druid官网wiki,有详细教程,地址如下: SpringBoot支持Druid地址:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/tree/master/druid-s ...
随机推荐
- Git如何合并分支代码
如果是在IDEA中使用Git,可以直接合并代码. 我当前的开发分支,是feature/bing,现在我需要合并分支 feature/xxs 上的代码,这个过程只需要在IDEA中完成. 1.更新代码,会 ...
- day11 高阶函数 函数式编程
高阶函数,满足 接收函数作为参数或者返回有函数 函数可以当做参数传递给另一个函数 def foo(n): print(n) def bar(name): print("my name is ...
- P3312 [SDOI2014]数表
啊啊啊我昨天怎么没写题解wwww 补昨日题解... 题目链接 : https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P3312 也是莫反 我要把fft留到今天写 [和zyn小 ...
- 在 Linux 上安装配置 BitTorrent Sync [转]
背景介绍:目前我们线上的前端服务器数量比较多,超过200多台,每次发布新应用的时候,都是将软件包放在一台专门的Push服务器上,再由所有的前端服务器通过rsync自动同步.但随着前端服务器的数量越来越 ...
- luogu2336 喵星球上的点名 (SA+二分答案+树状数组)
离散化一下然后把姓名串和询问串都放一起做SA 和bzoj3277串类似地,满足某一询问的后缀(就是和这个询问对应的后缀的LCP>=这个询问长度的后缀)的排名也是一个区间,把这个区间二分出来即可 ...
- luogu2607/bzoj1040 [ZJOI2008]骑士 (基环树形dp)
N个点,每个点发出一条边,那么这个图的形状一定是一个基环树森林(如果有重边就会出现森林) 那我做f[0][x]和f[1][x]分别表示对于x子树,x这个点选还是不选所带来的最大价值 然后就变成了这好几 ...
- 在任意位置获取应用程序CONTEXT
Android程序中访问资源时需要提供Context,一般来说只有在各种component中(Activity, Provider等等)才能方便的使用api来获取Context, 而在某些工具类中要获 ...
- SqlServer存储过程详解
SqlServer存储过程详解 1.创建存储过程的基本语法模板: if (exists (select * from sys.objects where name = 'pro_name')) dro ...
- Luogu 1312 【NOIP2011】玛雅游戏 (搜索)
Luogu 1312 [NOIP2011]玛雅游戏 (搜索) Description Mayan puzzle 是最近流行起来的一个游戏.游戏界面是一个7行5列的棋盘,上面堆放着一些方块,方块不能悬空 ...
- CF 1000
水爆了...... 当然不是题目水,而是我水. 第一题,看完题目我稍微惊了一下,有点难度(并不). 开个map,先加后减,统计正数即可. 第二题,看完我冷汗就流下来了,有点难啊,这是B难度? 趴床上推 ...
