Linux 线程 条件变量
//等待条件
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restric mutex); :把调用线程放到所等待条件的线程列表上
:对传进来已经加过锁的互斥量解锁
:线程进入休眠状态等待被唤醒
注:、2步为原子操作 //通知条件
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond); :通知指定条件已经满足
:等待线程重新锁定互斥锁
:等待线程需要重新测试条件是否满足
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h> using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::queue; #define N 100
#define ST 10 pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t ready = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; queue<int> que; void* threadProducer(void* arg)
{
while(true)
{
sleep(rand() % ST); cout << "Produce try in...\n";
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
cout << "Produce in!\n";
int source = rand() % N;
cout << "Produce " << source << endl;
que.push(source);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
cout << "Produce out\n"; pthread_cond_signal(&ready);
}
} void* threadConsumer(void* arg)
{
while(true)
{
sleep(rand() % ST); cout << "Consum try in...\n";
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
cout << "Consum in!\n";
while(que.empty())
{
pthread_cond_wait(&ready, &lock);
cout << "Consum from sleep\n";
}
cout << "Consum " << que.front() << endl;
que.pop();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
cout << "Consum out\n\n";
}
} int main(void)
{
pthread_t tProducer, tConsumer;
pthread_create(&tProducer, NULL, threadProducer, NULL);
pthread_create(&tConsumer, NULL, threadConsumer, NULL); pthread_join(tProducer, NULL);
pthread_join(tConsumer, NULL); exit();
}
生消

看到倒数的三四行,消费者进去了,发现没有数据了,则睡眠了,然后生产者进去生产了。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h> using std::cout;
using std::endl; pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t ready = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; int data = ; void* threadProducer(void* arg)
{
int i;
for(i = ; i < ; i++)
{
sleep(); if(i % != )
{
cout << "thread1:" << i << endl;
}
else
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
data = i;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock); pthread_cond_signal(&ready);
}
}
} void* threadConsumer(void* arg)
{
while(true)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
while(data == ) //no data
pthread_cond_wait(&ready, &lock);
cout <<"thread2:" << data << endl;
if(data == )
break;
else
data = ; //empty data
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
} int main(void)
{
pthread_t tProducer, tConsumer;
pthread_create(&tProducer, NULL, threadProducer, NULL);
pthread_create(&tConsumer, NULL, threadConsumer, NULL); pthread_join(tProducer, NULL);
pthread_join(tConsumer, NULL); exit();
}
3打印

程序大致这样:线程1中的循环,如果i不是3的倍数就自己打印了,如果是的话,把这个数放到一个地方(由于这个地方可以被线程2发现,所以要加锁访问),然后唤醒等待数据的线程2(如果线程2还没有在等待,那么这个唤醒则丢失,这是个bug,见下),线程2被唤醒后,消费了这个3的倍数,清空数据区。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h> using std::cout;
using std::endl; pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t ready = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; int data = ; void* threadProducer(void* arg)
{
int i;
for(i = ; i < ; i++)
{
sleep(); if(i % != )
{
cout << "thread1:" << i << endl;
}
else
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
data = i;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock); pthread_cond_signal(&ready);
}
}
} void* threadConsumer(void* arg)
{
sleep();
while(true)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
while(data == ) //no data
pthread_cond_wait(&ready, &lock);
cout <<"thread2:" << data << endl;
if(data == )
break;
else
data = ; //empty data
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
} int main(void)
{
pthread_t tProducer, tConsumer;
pthread_create(&tProducer, NULL, threadProducer, NULL);
pthread_create(&tConsumer, NULL, threadConsumer, NULL); pthread_join(tProducer, NULL);
pthread_join(tConsumer, NULL); exit();
}
bug
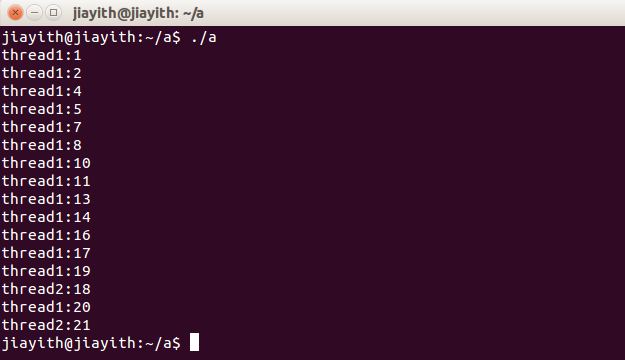
//下面是生产者 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock); //加锁访问临界区
/*在这里生产数据*/
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock); //解锁 pthread_cond_signal(&ready); //通知消费者 //下面是消费者 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock); //加锁访问临界区
while(没有待消费数据)
pthread_cond_wait(&ready, &lock); //睡在这里,等待被唤醒
/*被叫醒了,在这里消费数据*/
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock); //解锁
Linux 线程 条件变量的更多相关文章
- python线程条件变量Condition(31)
对于线程与线程之间的交互我们在前面的文章已经介绍了 python 互斥锁Lock / python事件Event , 今天继续介绍一种线程交互方式 – 线程条件变量Condition. 一.线程条件变 ...
- Linux Posix线程条件变量
生产者消费者模型 .多个线程操作全局变量n,需要做成临界区(要加锁--线程锁或者信号量) .调用函数pthread_cond_wait(&g_cond,&g_mutex)让这个线程锁在 ...
- Linux 多线程条件变量同步
条件变量是线程同步的另一种方式,实际上,条件变量是信号量的底层实现,这也就意味着,使用条件变量可以拥有更大的自由度,同时也就需要更加小心的进行同步操作.条件变量使用的条件本身是需要使用互斥量进行保护的 ...
- Linux:条件变量
条件变量: 条件变量本身不是锁!但它也可以造成线程阻塞.通常与互斥锁配合使用.给多线程提供一个会合的场所. 主要应用函数: pthread_cond_init函数 pthrea ...
- 笔记3 linux 多线程 条件变量+互斥锁
//cond lock #include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<pthread.h> struct test { ...
- Linux Qt使用POSIX多线程条件变量、互斥锁(量)
今天团建,但是文章也要写.酒要喝好,文要写美,方为我辈程序员的全才之路.嘎嘎 之前一直在看POSIX的多线程编程,上个周末结合自己的理解,写了一个基于Qt的用条件变量同步线程的例子.故此来和大家一起分 ...
- linux 互斥锁和条件变量
为什么有条件变量? 请参看一个线程等待某种事件发生 注意:本文是linux c版本的条件变量和互斥锁(mutex),不是C++的. mutex : mutual exclusion(相互排斥) 1,互 ...
- Linux 线程管理
解析1 LINUX环境下多线程编程肯定会遇到需要条件变量的情况,此时必然要使用pthread_cond_wait()函数.但这个函数的执行过程比较难于理解. pthread_cond_wait()的工 ...
- c++ 条件变量
.条件变量创建 静态创建:pthread_cond_t cond=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; 动态创建:pthread_cond _t cond; pthread_cond_i ...
随机推荐
- 信号之sigprocmask函数
一个进程的信号屏蔽字规定了当前阻塞而不能递送给该进程的信号集.调用函数sigprocmask可以检测或更改其信号屏蔽字,或者在一个步骤中同时执行这两个操作. #include <signal.h ...
- java中的链式编程
听到链式编程听陌生的,但是写出来就感觉其实很熟悉 package test; public class Test { String name; String phone; String mail; S ...
- iOS 10 推送必看(高阶1)
来源:徐不同 链接:http://www.jianshu.com/p/3d602a60ca4f iOS10 推送必看(基础篇) 虽然这篇文章比较长,也不好理解,但是还是建议大家收藏,以后用到的时候,可 ...
- TCP/IP协议原理与应用笔记22:静态和动态路由选择
1. 静态路由选择: Static routing 管理员手工设置 管理员手动更新 不能保证路由的一致性和及时性 管理性强 没有路由开销 小型.变化缓慢网络 2. 动态路由选择 Dynamic rou ...
- JavaScript中交换两个变量的值得三种做法(代码实现)
javascript在编程时经常会涉及到如何交换两个变量的值,例如常见的冒泡排序,快速排序等:下面我讲根据自己近期所学总结几种常见的交换两个变量值的方法: 方法一:借助第三方变量交换两个变量的值 va ...
- H5神器之canvas应用——网页修改保存图片
因为最近项目上的要求,需要在页面中可以对一张图片进行涂改和添加文字,然后再保存到(服务器)本地,因为也是第一次接触这方面的,然后爬网页啊爬网页,之后发现了一款adobe开发的一款插件,适合 Anroi ...
- Ubuntu下安装QT
环境 Ubuntu 9.10 qt4.7.3 gcc 4.4 Ubuntu中缺少 make 首先安装 sudo apt-get install make 如果不知道缺少啥,就按下面的装 1.sudo ...
- cordova在app内部指定浏览器打开链接插件:cordova-plugin-inappbrowser
原文网址:http://www.ncloud.hk/%E6%8A%80%E6%9C%AF%E5%88%86%E4%BA%AB/cordova-plugin-inappbrowser/ 要想App里边的 ...
- 第03篇. 标准Web项目Jetty9内嵌API简单启动
一直以来,想改变一些自己早已经习惯的事情. 到了一定年龄,便要学会寡言,每一句话都要有用,有重量. 喜怒不形于色,大事淡然,有自己的底线. --胖先生 昨天,简单的说了一下关于Jetty9的配置,大家 ...
- BZOJ 2819: Nim dfs序维护树状数组,倍增
1.随机选两个堆v,u,询问若在v到u间的路径上的石子堆中玩Nim游戏,是否有必胜策略,如果有,vfleaking将会考虑将这些石子堆作为初始局面之一,用来坑玩家.2.把堆v中的石子数变为k. 分析: ...
