HDU2196(SummerTrainingDay13-D tree dp)
Computer
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 30923 Accepted Submission(s): 3861
Problem Description
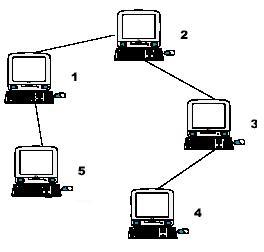
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
Input
Output
Sample Input
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
Sample Output
2
3
4
4
Author
//2017-09-13
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = ; int head[N], tot;
struct Edge{
int v, w, next;
}edge[N<<]; void init(){
tot = ;
memset(head, -, sizeof(head));
} void add_edge(int u, int v, int w){
edge[tot].v = v;
edge[tot].w = w;
edge[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
} //down[u][0]表示u节点往下走的最大距离,down[u][1]表示节点u往下走的次大距离
//up[u]表示节点u往上走的最大距离,son[u]表示u节点往下走的最大距离对应的儿子
int n, down[N][], up[N], son[N]; void dfs1(int u, int fa){
for(int i = head[u]; i != -; i = edge[i].next){
int v = edge[i].v, w = edge[i].w;
if(v == fa)continue;
dfs1(v, u);
if(down[v][]+w > down[u][]){//更新最大的情况
down[u][] = down[u][];
down[u][] = down[v][]+w;
son[u] = v;
}else if(down[v][]+w > down[u][])//只更新次大值的情况
down[u][] = down[v][] + w;
}
} void dfs2(int u, int fa){
for(int i = head[u]; i != -; i = edge[i].next){
int v = edge[i].v, w = edge[i].w;
if(v == fa)continue;
if(son[u] != v)
up[v] = max(up[u]+w, down[u][]+w);
else
up[v] = max(up[u]+w, down[u][]+w);
dfs2(v, u);
}
} int main()
{
//freopen("inputD.txt", "r", stdin);
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF){
init();
int v, w;
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%d%d", &v, &w);
add_edge(i, v, w);
add_edge(v, i, w);
}
memset(up, , sizeof(up));
memset(down, , sizeof(down));
dfs1(, );
dfs2(, );
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d\n", max(up[i], down[i][]));
} return ;
}
HDU2196(SummerTrainingDay13-D tree dp)的更多相关文章
- 96. Unique Binary Search Trees (Tree; DP)
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- HDU 4359——Easy Tree DP?——————【dp+组合计数】
Easy Tree DP? Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)To ...
- TYOI Day1 travel:Tree dp【处理重复走边】
题意: 给你一棵树,n个节点,每条边有长度. 然后有q组询问(u,k),每次问你:从节点u出发,走到某个节点的距离mod k的最大值. 题解: 对于无根树上的dp,一般都是先转成以1为根的有根树,然后 ...
- HDU 4359 Easy Tree DP?
Easy Tree DP? Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)To ...
- DP Intro - Tree DP Examples
因为上次比赛sb地把一道树形dp当费用流做了,受了点刺激,用一天时间稍微搞一下树形DP,今后再好好搞一下) 基于背包原理的树形DP poj 1947 Rebuilding Roads 题意:给你一棵树 ...
- Codeforces 442D Adam and Tree dp (看题解)
Adam and Tree 感觉非常巧妙的一题.. 如果对于一个已经建立完成的树, 那么我们可以用dp[ i ]表示染完 i 这棵子树, 并给从fa[ i ] -> i的条边也染色的最少颜色数. ...
- HDU5293(SummerTrainingDay13-B Tree DP + 树状数组 + dfs序)
Tree chain problem Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Other ...
- HDU3534(SummerTrainingDay13-C tree dp)
Tree Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submis ...
- Partial Tree(DP)
Partial Tree http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5534 Time Limit: / MS (Java/Others) Memory Li ...
随机推荐
- 背水一战 Windows 10 (90) - 文件系统: 获取 Package 中的文件, 可移动存储中的文件操作, “库”管理
[源码下载] 背水一战 Windows 10 (90) - 文件系统: 获取 Package 中的文件, 可移动存储中的文件操作, “库”管理 作者:webabcd 介绍背水一战 Windows 10 ...
- Linux和Windows下tomcat开机自启动设置
Linux下tomcat的开机自启动设置 1.修改系统文件rc.local:vi /etc/rc.d/rc.local rc.local是给用户自定义启动时需要执行的文件,和windows里面的“启动 ...
- OCP 12c考试题,062题库出现大量新题-第20道
choose three Your database is configured for ARCHIVELOG mode, and a daily full database backup is ta ...
- Android Studio 配置 androidAnnotations框架详细步骤
第一步:打开app的build.gradle文件 第二步:添加下面红色的部分 apply plugin: 'com.android.application' android { compileSdkV ...
- Java 中的 HttpServletRequest 和 HttpServletResponse 对象
HttpServletRequest对象详解 javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest是SUN制定的Servlet规范,是一个接口.表示请求,“HTTP请求协议”的完 ...
- Javascript百学不厌 - this
最近看了一本书,让自己的野路子走走正规路线 方法调用模式: 方法:当一个函数被保存为对象的一个属性时,我们称它为一个方法. var obj = { fun1: function() {this} // ...
- pdf.js显示合同签名问题
需求 pdf页面显示在ios11以下的环境,合同的签名印章或签字会显示不出 解决方案(初步处理参考下文引用,这里是后续具体做法) 现在通过使用pdf.js插件,参考下文,引入自己的代码 我把gener ...
- vsftpd3.0.3配置
2019.2.18更新 证实可用!!! 原文: 这两天测试在Ubuntu18.04上搭建一个ftp服务器,搜了一下大家都在用vsftpd,于是根据这个大佬的基础教程搭了一个,搭完一切正常,在windo ...
- 天了噜,Java 8 要停止维护了!
前些天的中兴事件,已经让国人意识到自己核心技术的不足,这次的 JDK 8 对企业停止免费更新更是雪上加霜.. 以下是 Oracle 官网提示的 JDK8 终止更新公告. 原文内容:Oracle wil ...
- C# TableLayoutPanel使用方法
一.利用TableLayoutPanel类展示表格,以10行5列为例 第1步:在前台创建一个panel,使TableLayoutPanel对象填充其内部. 第2步:创建TableLayoutPanel ...
