hdoj--1950--Bridging signals(二分查找+LIS)
Bridging signals
Time Limit: 5000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1280 Accepted Submission(s): 832
each other all over the place. At this late stage of the process, it is too
expensive to redo the routing. Instead, the engineers have to bridge the signals, using the third dimension, so that no two signals cross. However, bridging is a complicated operation, and thus it is desirable to bridge as few signals as possible. The call
for a computer program that finds the maximum number of signals which may be connected on the silicon surface without rossing each other, is imminent. Bearing in mind that there may be housands of signal ports at the boundary of a functional block, the problem
asks quite a lot of the programmer. Are you up to the task?
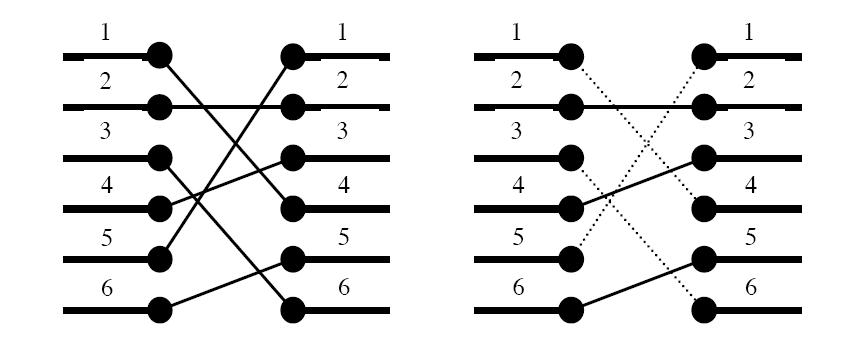
Figure 1. To the left: The two blocks' ports and their signal mapping (4,2,6,3,1,5). To the right: At most three signals may be routed on the silicon surface without crossing each other. The dashed signals must be bridged.
A typical situation is schematically depicted in figure 1. The ports of the two functional blocks are numbered from 1 to p, from top to bottom. The signal mapping is described by a permutation of the numbers 1 to p in the form of a list of p unique numbers
in the range 1 to p, in which the i:th number pecifies which port on the right side should be connected to the i:th port on the left side.
Two signals cross if and only if the straight lines connecting the two ports of each pair do.
functional blocks. Then follow p lines, describing the signal mapping: On the i:th line is the port number of the block on the right side which should be connected to the i:th port of the block on the left side.
4
6
4
2
6
3
1
5
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
1
8
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
9
5
8
9
2
3
1
7
4
6
3
9
1
4
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MIN -1000000
#define MAX 100001
int a[MAX];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int l,r,mid,top=0,m;
a[0]=MIN;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&m);
if(a[top]<m)
a[++top]=m;
else
{
l=1;r=top;
while(l<=r)
{
mid=(l+r)/2;
if(a[mid]<m)
l=mid+1;
else
r=mid-1;
}
a[l]=m;
}
}
printf("%d\n",top);
}
return 0;
}
hdoj--1950--Bridging signals(二分查找+LIS)的更多相关文章
- hdoj 1950 Bridging signals【二分求最大上升子序列长度】【LIS】
Bridging signals Time Limit: 5000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- HDU 1950 Bridging signals(LIS)
最长上升子序列(LIS)的典型变形,O(n^2)的动归会超时.LIS问题可以优化为nlogn的算法. 定义d[k]:长度为k的上升子序列的最末元素,若有多个长度为k的上升子序列,则记录最小的那个最末元 ...
- Poj 1631 Bridging signals(二分+DP 解 LIS)
题意:题目很难懂,题意很简单,求最长递增子序列LIS. 分析:本题的最大数据40000,多个case.用基础的O(N^2)动态规划求解是超时,采用O(n*log2n)的二分查找加速的改进型DP后AC了 ...
- hdu 1950 Bridging signals 求最长子序列 ( 二分模板 )
Bridging signals Time Limit: 5000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- (hdu)1950 Bridging signals(最长上升子序列)
Problem Description 'Oh no, they've done it again', cries the chief designer at the Waferland chip f ...
- HDU 1950 Bridging signals【最长上升序列】
解题思路:题目给出的描述就是一种求最长上升子序列的方法 将该列数an与其按升序排好序后的an'求出最长公共子序列就是最长上升子序列 但是这道题用这种方法是会超时的,用滚动数组优化也超时, 下面是网上找 ...
- poj 1631 Bridging signals (二分||DP||最长递增子序列)
Bridging signals Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 9234 Accepted: 5037 ...
- nyoj--214--单调递增子序列(二)(二分查找+LIS)
单调递增子序列(二) 时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:4 描述 给定一整型数列{a1,a2...,an}(0<n<=100000),找出单调递增最长子序 ...
- HDU 1950 Bridging signals (LIS,O(nlogn))
题意: 给一个数字序列,要求找到LIS,输出其长度. 思路: 扫一遍+二分,复杂度O(nlogn),空间复杂度O(n). 具体方法:增加一个数组,用d[i]表示长度为 i 的递增子序列的最后一个元素, ...
随机推荐
- 从乐视和小米“最火电视”之战 看PR传播策略
今年的双11够热闹.一方面,阿里.京东.国美.苏宁等电商巨头卯足了劲儿.试图在双11期间斗个你死我活,剑拔弩张的气势超过了以往不论什么一场双11:还有一方面.不少硬件厂商.家电企业也来凑双11 ...
- UESTC--1263--The Desire of Asuna(贪心)
The Desire of Asuna Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65535KB 64bit IO Format: %lld & %llu Su ...
- Oracle RAC 全局等待事件 gc current block busy 和 gc cr multi block request 说明--转载(http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/article/details/7777511)
一.RAC 全局等待事件说明 在RAC环境中,和全局调整缓存相关的最常见的等待事件是global cache cr request,global cache busy和equeue. 当一个进程访问需 ...
- ORACLE查询闪回
在Oracle中如果错误地提交了修改操作,然后想查看修改前的值,这时候可以使用查询闪回(query flashback). 查询闪回可以根据根据一个时间值或者系统变更号(SCN)进行. 执行闪回操作, ...
- leetcode 系列文章目录
leetcode 系列文章目录 0. 两数之和1. 两数相加 2. 无重复字符的最长子串 3. 寻找两个有序数组的中位数 4. 最长回文子串 5. Z 字形变换 6. 整数反转 7. 字符串转换整数 ...
- 9.自己实现linux中的tree
运行效果: 代码: #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include < ...
- TCP和UDP的具体区别
TCP和UDP的最完整的区别 TCP UDP TCP与UDP基本区别: 1.基于连接与无连接 2.TCP要求系统资源较多,UDP较少: 3.UDP程序结构较简单 4.流模式(TCP)与数据报模式(UD ...
- node操作mysql插入数据异常,incorrect string value
产生的原因 我在创建表的时候,并没有设定字符编码,所以,默认的字符编码是 latin1 在我插入数据的时候,我的一个字段name设定的是varchar(20) 其实,这时的编码就是 latin1 所以 ...
- http接口服务方结合策略模式实现总结
在项目中,我们经常会使用到http+xml的接口,而且不仅仅的是一个,可能会有多个http的接口需要实时的交互.但是http接口的接收消息的公共部分是一样的,只有每个接口的报文解析和返回报文是不同的, ...
- SpringMVC(六)POJO类作为 @RequestMapping方法的参数
Command or form objects to bind request parameters to bean properties (via setters) or directly to f ...
