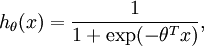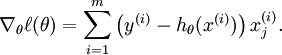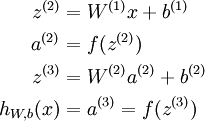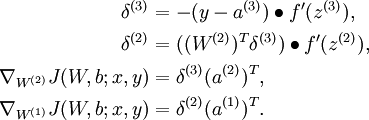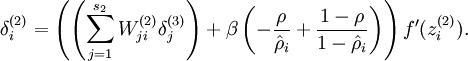Vectorized implementation
Vectorization
Vectorization refers to a powerful way to speed up your algorithms. Numerical computing and parallel computing researchers have put decades of work into making certain numerical operations (such as matrix-matrix multiplication, matrix-matrix addition, matrix-vector multiplication) fast. The idea of vectorization is that we would like to express our learning algorithms in terms of these highly optimized operations.
More generally, a good rule-of-thumb for coding Matlab/Octave is:
- Whenever possible, avoid using explicit for-loops in your code.
A large part of vectorizing our Matlab/Octave code will focus on getting rid of for loops, since this lets Matlab/Octave extract more parallelism from your code, while also incurring less computational overhead from the interpreter.
多用向量运算,别把向量拆成标量然后再循环
Logistic Regression Vectorization Example
Consider training a logistic regression model using batch gradient ascent. Suppose our hypothesis is
where we let
, so that
and
, and
is our intercept term. We have a training set
of
examples, and the batch gradient ascent update rule is
, where
is the log likelihood and
is its derivative.
We thus need to compute the gradient:
Further, suppose the Matlab/Octave variable y is a row vector of the labels in the training set, so that the variable y(i) is
.
Here's truly horrible, extremely slow, implementation of the gradient computation:
% Implementation
grad = zeros(n+,);
for i=:m,
h = sigmoid(theta'*x(:,i));
temp = y(i) - h;
for j=:n+,
grad(j) = grad(j) + temp * x(j,i);
end;
end;The two nested for-loops makes this very slow. Here's a more typical implementation, that partially vectorizes the algorithm and gets better performance:
% Implementation
grad = zeros(n+,);
for i=:m,
grad = grad + (y(i) - sigmoid(theta'*x(:,i)))* x(:,i);
end;
Neural Network Vectorization
Forward propagation
Consider a 3 layer neural network (with one input, one hidden, and one output layer), and suppose x is a column vector containing a single training example
. Then the forward propagation step is given by:
This is a fairly efficient implementation for a single example. If we have m examples, then we would wrap a for loop around this.
% Unvectorized implementation
for i=:m,
z2 = W1 * x(:,i) + b1;
a2 = f(z2);
z3 = W2 * a2 + b2;
h(:,i) = f(z3);
end;For many algorithms, we will represent intermediate stages of computation via vectors. For example, z2, a2, and z3 here are all column vectors that're used to compute the activations of the hidden and output layers. In order to take better advantage of parallelism and efficient matrix operations, we would like to have our algorithm operate simultaneously on many training examples. Let us temporarily ignore b1 and b2 (say, set them to zero for now). We can then implement the following:
% Vectorized implementation (ignoring b1, b2)
z2 = W1 * x;
a2 = f(z2);
z3 = W2 * a2;
h = f(z3)In this implementation, z2, a2, and z3 are all matrices, with one column per training example.
A common design pattern in vectorizing across training examples is that whereas previously we had a column vector (such as z2) per training example, we can often instead try to compute a matrix so that all of these column vectors are stacked together to form a matrix. Concretely, in this example, a2 becomes a s2 by m matrix (where s2 is the number of units in layer 2 of the network, and m is the number of training examples). And, the i-th column of a2 contains the activations of the hidden units (layer 2 of the network) when the i-th training example x(:,i) is input to the network.
% Inefficient, unvectorized implementation of the activation function
function output = unvectorized_f(z)
output = zeros(size(z))
for i=:size(z,),
for j=:size(z,),
output(i,j) = /(+exp(-z(i,j)));
end;
end;
end % Efficient, vectorized implementation of the activation function
function output = vectorized_f(z)
output = ./(+exp(-z)); % "./" is Matlab/Octave's element-wise division operator.
endFinally, our vectorized implementation of forward propagation above had ignored b1 and b2. To incorporate those back in, we will use Matlab/Octave's built-in repmat function. We have:
% Vectorized implementation of forward propagation
z2 = W1 * x + repmat(b1,,m);
a2 = f(z2);
z3 = W2 * a2 + repmat(b2,,m);
h = f(z3)repmat !!矩阵变形!!
Backpropagation
We are in a supervised learning setting, so that we have a training set
of m training examples. (For the autoencoder, we simply set y(i) = x(i), but our derivation here will consider this more general setting.)
we had that for a single training example (x,y), we can compute the derivatives as
Here,
denotes element-wise product. For simplicity, our description here will ignore the derivatives with respect to b(l), though your implementation of backpropagation will have to compute those derivatives too.
gradW1 = zeros(size(W1));
gradW2 = zeros(size(W2));
for i=:m,
delta3 = -(y(:,i) - h(:,i)) .* fprime(z3(:,i));
delta2 = W2'*delta3(:,i) .* fprime(z2(:,i)); gradW2 = gradW2 + delta3*a2(:,i)';
gradW1 = gradW1 + delta2*a1(:,i)';
end;This implementation has a for loop. We would like to come up with an implementation that simultaneously performs backpropagation on all the examples, and eliminates this for loop.
To do so, we will replace the vectors delta3 and delta2 with matrices, where one column of each matrix corresponds to each training example. We will also implement a function fprime(z) that takes as input a matrix z, and applies
element-wise.
Sparse autoencoder
When performing backpropagation on a single training example, we had taken into the account the sparsity penalty by computing the following:
也就是不要用循环一个样本一个样本的去更新参数,而是要将样本组织成矩阵的形式,应用矩阵运算,提高效率。
Vectorized implementation的更多相关文章
- DL三(向量化编程 Vectorized implementation)
向量化编程实现 Vectorized implementation 一向量化编程 Vectorization 1.1 基本术语 向量化 vectorization 1.2 向量化编程(Vectoriz ...
- 机器学习公开课笔记(4):神经网络(Neural Network)——表示
动机(Motivation) 对于非线性分类问题,如果用多元线性回归进行分类,需要构造许多高次项,导致特征特多学习参数过多,从而复杂度太高. 神经网络(Neural Network) 一个简单的神经网 ...
- 转载 Deep learning:一(基础知识_1)
前言: 最近打算稍微系统的学习下deep learing的一些理论知识,打算采用Andrew Ng的网页教程UFLDL Tutorial,据说这个教程写得浅显易懂,也不太长.不过在这这之前还是复习下m ...
- Deep learning:一(基础知识_1)
本文纯转载: 主要是想系统的跟tornadomeet的顺序走一遍deeplearning; 前言: 最近打算稍微系统的学习下deep learing的一些理论知识,打算采用Andrew Ng的网页教程 ...
- machine learning 之 Neural Network 1
整理自Andrew Ng的machine learning课程week 4. 目录: 为什么要用神经网络 神经网络的模型表示 1 神经网络的模型表示 2 实例1 实例2 多分类问题 1.为什么要用神经 ...
- Coursera Deep Learning 2 Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization - week1, Assignment(Regularization)
声明:所有内容来自coursera,作为个人学习笔记记录在这里. Regularization Welcome to the second assignment of this week. Deep ...
- Coursera机器学习+deeplearning.ai+斯坦福CS231n
日志 20170410 Coursera机器学习 2017.11.28 update deeplearning 台大的机器学习课程:台湾大学林轩田和李宏毅机器学习课程 Coursera机器学习 Wee ...
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning 课程笔记(第三周)浅层神经网络(Shallow neural networks)
3.1 神经网络概述(Neural Network Overview ) (神经网络中,我们要反复计算a和z,最终得到最后的loss function) 3.2 神经网络的表示(Neural Netw ...
- [UFLDL] Basic Concept
博客内容取材于:http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2012/06/24/2560261.html 参考资料: UFLDL wiki UFLDL St ...
随机推荐
- vue.js技巧小计
//删除数组索引方法01 del (index) { this.arr.splice(index ,1); } //删除数组索引方法01 del (index) { this.$delete(this ...
- GoldenGate 进程
GoldenGate进程 Manager进程 Manager进程是GoldenGate的控制进程,运行在源端和目标端上.它主要作用有以下几个方面:启动.监控.重启Goldengate的其他进程,报告错 ...
- HTML5的核心内容
开发者可以放心地使用html5的理由 兼容性.HTML5在老版本的浏览器可以正常运行,同时支持HTML5的新浏览器也能正常运行HTML4,用HTML4创建出来的网站不是必须全部重建的. 实用性.HTM ...
- Java基础学习总结(15)——java读取properties文件总结
一.java读取properties文件总结 在java项目中,操作properties文件是经常要做的,因为很多的配置信息都会写在properties文件中,这里主要是总结使用getResource ...
- Spring Cloud学习笔记【六】Hystrix 监控数据聚合 Turbine
上一篇我们介绍了使用 Hystrix Dashboard 来展示 Hystrix 用于熔断的各项度量指标.通过 Hystrix Dashboard,我们可以方便的查看服务实例的综合情况,比如:服务调用 ...
- COGS——T 2478. [HZOI 2016]简单的最近公共祖先
http://www.cogs.pro/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=2478 ★☆ 输入文件:easy_LCA.in 输出文件:easy_LCA.out 简单 ...
- 找出一堆数中最小的前K个数
描写叙述: 给定一个整数数组.让你从该数组中找出最小的K个数 思路: 最简洁粗暴的方法就是将该数组进行排序,然后取最前面的K个数就可以. 可是,本题要求的仅仅是求出最小的k个数就可以,用排序能够但显然 ...
- Android Design Support Library初探,NavigationView实践
前言 在前几天的IO大会上,Google带来了Android M,同时还有Android支持库的新一轮更新,其中更是增加一个全新的支持库Android Design Support Library,包 ...
- 21. 【intellij idea】Project Structure 讲解
转自:.https://www.cnblogs.com/zadomn0920/p/6196962.html 项目的左侧面板 项目设置->Project Project Settings -> ...
- Sql Server通用分页存储过程
Sql Server2005通用分页存储过程 CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[Common_GetPagedList] ( @TableName nvarchar(100), --表名 ...