Kernel Methods for Deep Learning
@article{cho2009kernel,
title={Kernel Methods for Deep Learning},
author={Cho, Youngmin and Saul, Lawrence K},
pages={342--350},
year={2009}}
引
这篇文章介绍了一种新的核函数, 其启发来自于神经网络的运算.
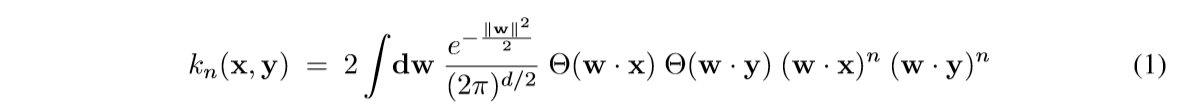
其中\(\Theta(z)=\frac{1}{2}(1+\mathrm{sign}(z))\).
主要内容
主要性质, 公式(1)可以表示成:
\tag{2}
\]
其中:
\tag{3}
\]
\tag{4}
\]
特别的:
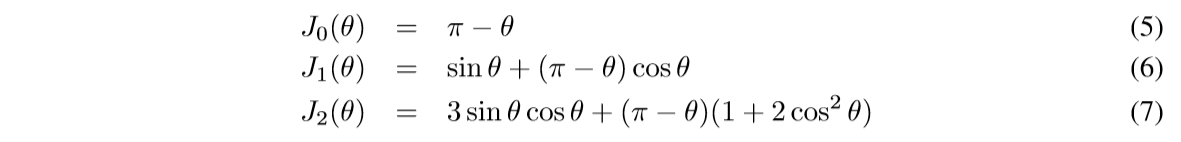
其证明如下:
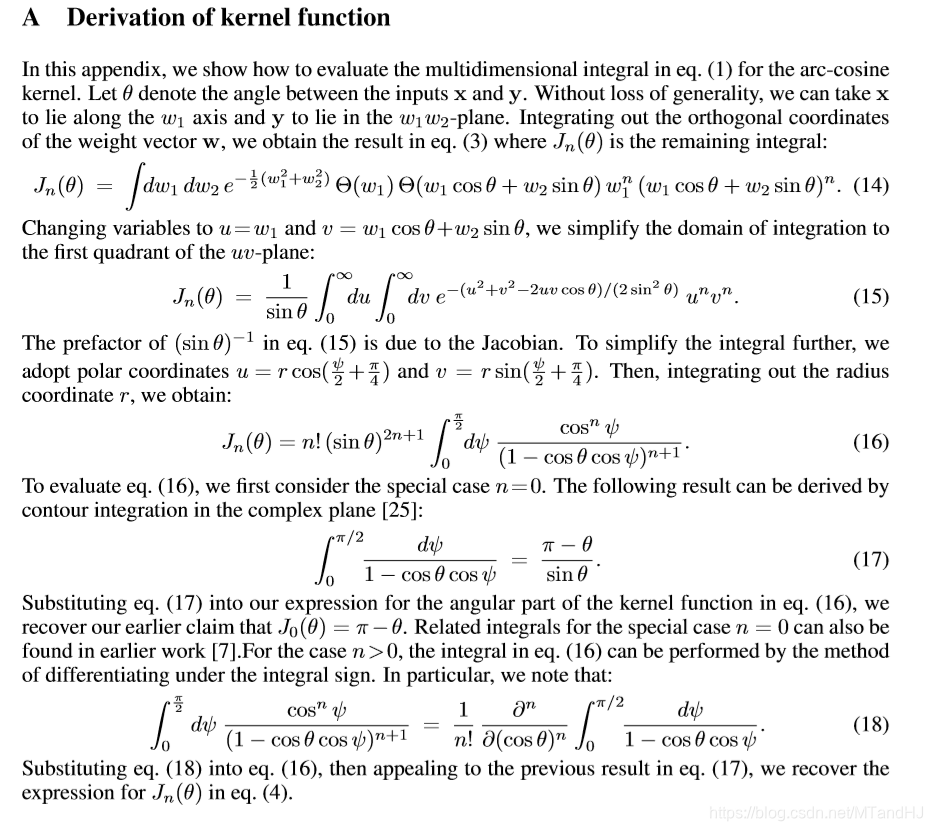
第(17)的证明我没有推, 因为 contour integration 暂时不了解.
细心的读者可能会发现, 最后的结果是\(\frac{\partial^n}{\partial(\cos \theta)^n}\), 注意对于一个函数\(f(\cos \theta)\), 我们可以令\(g(\theta) = f(\cos \theta)\)则:
\]
又
\]
便得结论.
与深度学习的联系
如果我们把注意力集中在某一层, 假设输入为\(\mathbf{x}\), 输出为:
\]
其中\(g(z) = \Theta(z) z^n\)是激活函数, 不同的n有如下的表现:
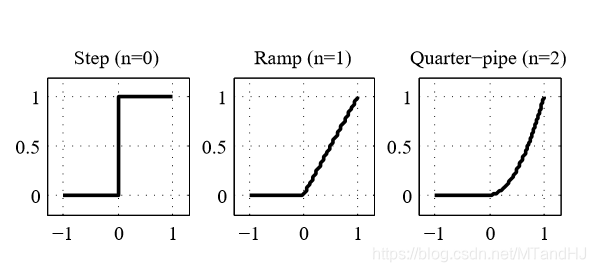
\(n=1\)便是我们熟悉的ReLU.
考虑俩个输入\(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y}\)所对应的输出\(\mathbf{f}(\mathbf{x}),\mathbf{f}(\mathbf{y})\)的内积:
\]
如果每个权重\(W_{ij}\)都服从标准正态分布, 则:
\]
实验
实验失败了, 代码如下.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.svm import NuSVC
"""
Arc_cosine kernel
"""
class Arc_cosine:
def __init__(self, n=1):
self.n = n
self.own_kernel = self.kernels(n)
def kernel0(self, x, y):
norm_x = np.linalg.norm(x)
norm_y = np.linalg.norm(y)
cos_value = x @ y / (norm_x *
norm_y)
angle = np.arccos(cos_value)
return 1 - angle / np.pi
def kernel1(self, x, y):
norm_x = np.linalg.norm(x)
norm_y = np.linalg.norm(y)
cos_value = x @ y / (norm_x *
norm_y)
angle = np.arccos(cos_value)
sin_value = np.sin(angle)
return (norm_x * norm_y) ** self.n * \
(sin_value + (np.pi - angle) *
cos_value) / np.pi
def kernel2(self, x, y):
norm_x = np.linalg.norm(x)
norm_y = np.linalg.norm(y)
cos_value = x @ y / (norm_x *
norm_y)
angle = np.arccos(cos_value)
sin_value = np.sin(angle)
return (norm_x * norm_y) ** self.n * \
3 * sin_value * cos_value + \
(np.pi - angle) * (1 + 2 * cos_value ** 2)
def kernels(self, n):
if n is 0:
return self.kernel0
elif n is 1:
return self.kernel1
elif n is 2:
return self.kernel2
else:
raise ValueError("No such kernel, n should be "
"0, 1 or 2")
def kernel(self, X, Y):
m = X.shape[0]
n = Y.shape[0]
C = np.zeros((m, n))
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
C[i, j] = self.own_kernel(
X[i], Y[j]
)
return C
def __call__(self, X, Y):
return self.kernel(X, Y)
在俩个数据上进行SVM, 数据如下:
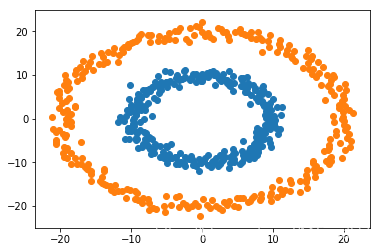
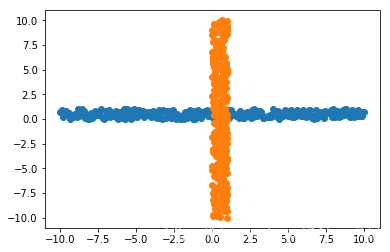
在SVM上跑:
'''
#生成圈圈数据
def generate_data(circle, r1, r2, nums=300):
variance = 1
rs1 = np.random.randn(nums) * variance + r1
rs2 = np.random.randn(nums) * variance + r2
angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, nums)
data1 = (rs1 * np.sin(angles) + circle[0],
rs1 * np.cos(angles) + circle[1])
data2 = (rs2 * np.sin(angles) + circle[0],
rs2 * np.cos(angles) + circle[1])
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'x':data1[0], 'y': data1[1],
'label':np.ones(nums)})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'x':data2[0], 'y': data2[1],
'label':-np.ones(nums)})
return df1, df2
'''
#生成十字数据
def generate_data(left, right, down, up,
circle=(0., 0.), nums=300):
variance = 1
y1 = np.random.rand(nums) * variance + circle[1]
x2 = np.random.rand(nums) * variance + circle[0]
x1 = np.linspace(left, right, nums)
y2 = np.linspace(down, up, nums)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(
{'x': x1,
'y': y1,
'label':np.ones_like(x1)}
)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(
{'x': x2,
'y': y2,
'label':-np.ones_like(x2)}
)
return df1, df2
def pre_test(left, right, func, nums=100):
x1, y1 = left
x2, y2 = right
x = np.linspace(x1, x2, nums)
y = np.linspace(y1, y2, nums)
X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y)
m, n = X.shape
Z = func(np.vstack((X.reshape(1, -1),
Y.reshape(1, -1))).T).reshape(m, n)
return X, Y, Z
df1, df2 = generate_data(-10, 10, -10, 10)
df = df1.append(df2)
classifer2 = NuSVC(kernel=Arc_cosine(n=1))
classifer2.fit(df.iloc[:, :2], df['label'])
X, Y, Z = pre_test((-10, -10), (10, 10), classifer2.predict)
plt.contourf(X, Y, Z)
plt.show()
预测结果均为:
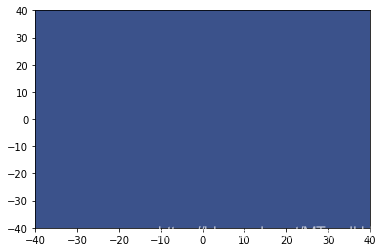
而在一般的RBF上, 结果都是很好的:

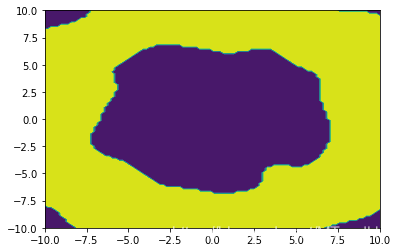
在多项式核上也ok:

如果有人能发现代码中的错误,请务必指正.
Kernel Methods for Deep Learning的更多相关文章
- (转) Ensemble Methods for Deep Learning Neural Networks to Reduce Variance and Improve Performance
Ensemble Methods for Deep Learning Neural Networks to Reduce Variance and Improve Performance 2018-1 ...
- 深度学习的集成方法——Ensemble Methods for Deep Learning Neural Networks
本文主要参考Ensemble Methods for Deep Learning Neural Networks一文. 1. 前言 神经网络具有很高的方差,不易复现出结果,而且模型的结果对初始化参数异 ...
- Paper List ABOUT Deep Learning
Deep Learning 方向的部分 Paper ,自用.一 RNN 1 Recurrent neural network based language model RNN用在语言模型上的开山之作 ...
- Deep Learning方向的paper
转载 http://hi.baidu.com/chb_seaok/item/6307c0d0363170e73cc2cb65 个人阅读的Deep Learning方向的paper整理,分了几部分吧,但 ...
- Kernel Functions for Machine Learning Applications
In recent years, Kernel methods have received major attention, particularly due to the increased pop ...
- Deep Learning and the Triumph of Empiricism
Deep Learning and the Triumph of Empiricism By Zachary Chase Lipton, July 2015 Deep learning is now ...
- How To Improve Deep Learning Performance
如何提高深度学习性能 20 Tips, Tricks and Techniques That You Can Use ToFight Overfitting and Get Better Genera ...
- My deep learning reading list
My deep learning reading list 主要是顺着Bengio的PAMI review的文章找出来的.包括几本综述文章,将近100篇论文,各位山头们的Presentation.全部 ...
- Deep Learning关于Vision的Reading List
最近开始学习深度学习了,加油! 下文转载自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_bda0d2f10101fpp4.html 主要是顺着Bengio的PAMI review的文 ...
随机推荐
- API接口设计之token、timestamp、sign 具体架构与实现(APP/小程序,传输安全)
Java生鲜电商平台-API接口设计之token.timestamp.sign 具体设计与实现 说明:在实际的业务中,难免会跟第三方系统进行数据的交互与传递,那么如何保证数据在传输过程中的安全呢(防窃 ...
- android:textAppearance解析
Android的系统自带的文字外观设置及实际显示效果图 android:textAppearancexml布局里面设置文字的外观: 如"android:textAppearance=&quo ...
- jenkins之邮箱设置
- maven内存溢出解决方法
maven内存溢出(InvocationTargetException: PermGen space) 解决方案:maven脚本:mvn.bat文件@REM set MAVEN_OPTS=-Xdebu ...
- 【Python】【Module】time
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_ __author__ = 'Alex Li' import time # print(time.clock()) #返回处理器时间,3.3开始已废弃 , 改成了 ...
- react中在hooks方法useEffect中加载异步数据
useEffect( ()=>{ (async function getPipeList(value:any) { let result= await GetPipeList(value); s ...
- 基于Kubernetes的hpa实现pod实例数量的自动伸缩
Pod 是在 Kubernetes 体系中,承载用户业务负载的一种资源.Pod 们运行的好坏,是用户们最为关心的事情.在业务流量高峰时,手动快速扩展 Pod 的实例数量,算是玩转 Kubernetes ...
- Mysql从头部署多个版本
目录 一.环境准备 二.下载安装包 三.Mysql-5.6单独部署 四.Mysql-5.7单独部署 五.添加到多版本控制 六.muliti使用 一.环境准备 系统:centos7.3一台 软件版本:m ...
- Jenkins凭证管理
目录 一.简介 二.管理凭证 三.常用凭证 保密文本 账号密码 保密文件 账号秘钥 四.优雅使用凭证 保密文本 账号密码 保密文件 五.凭证插件 集成HashiCorp Vault pipeline ...
- TSN(时间敏感网络)测试、仿真、分析平台应用攻略
前言 在汽车领域,近几年车内网络通讯方式的变革诉求,期望能够有更高的数据传输速率,以及保证实时性的通讯方式引入.例如对于ADAS而言,传统的CAN总线已经远远不能满足其对通讯的要求,而基于车载以太网的 ...
