linux中文件内核数据结构
3.文件io
3.1 文件内核数据结构
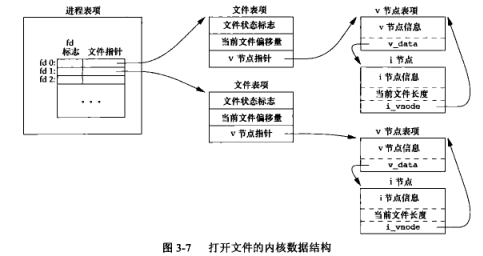
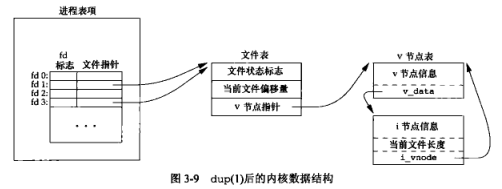
3.2 复制文件描述符的内核数据结构
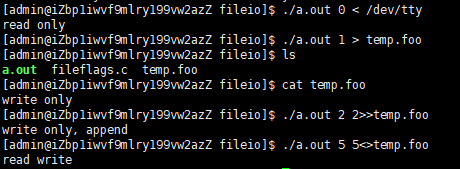
3.3 对指定的描述符打印文件标志
#include "apue.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int val;
if (argc != 2)
err_quit("usage: a.out <descriptor#>");
if ((val = fcntl(atoi(argv[1]), F_GETFL, 0)) < 0)
err_sys("fcntl error for fd %d", atoi(argv[1]));
switch (val & O_ACCMODE) {
case O_RDONLY:
printf("read only");
break;
case O_WRONLY:
printf("write only");
break;
case O_RDWR:
printf("read write");
break;
default:
err_dump("unknown access mode");
}
if (val & O_APPEND)
printf(", append");
if (val & O_NONBLOCK)
printf(", nonblocking");
if (val & O_SYNC)
printf(", synchronous writes");
#if !defined(_POSIX_C_SOURCE) && defined(O_FSYNC) && (O_FSYNC != O_SYNC)
if (val & O_FSYNC)
printf(", synchronous writes");
#endif
putchar('\n');
exit(0);
}
结果:
3.4 开启文件状态标志
#include "apue.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
void
set_fl(int fd, int flags) /* flags are file status flags to turn on */
{
int val;
if ((val = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL, 0)) < 0)
err_sys("fcntl F_GETFL error");
val |= flags; /* turn on flags */
if (fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, val) < 0)
err_sys("fcntl F_SETFL error");
}
如果将中间的一条语句修改如下(关闭文件标志):
val &= ~flags; //turn flags off
3.5 将标志输入复制到标准输出
#include "apue.h"
#define BUFFSIZE 4096
int
main(void)
{
int n;
char buf[BUFFSIZE];
//set_fl(STDOUT_FILENO,O_SYNC) //开启同步写标志
while ((n = read(STDIN_FILENO, buf, BUFFSIZE)) > 0)
if (write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n) != n)
err_sys("write error");
if (n < 0)
err_sys("read error");
exit(0);
}
程序运行时,设置O_SYNC会增加系统时间和时钟时间。
4.文件和目录
4.1 access函数的使用
#include "apue.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
err_quit("usage: a.out <pathname>");
if (access(argv[1], R_OK) < 0)
err_ret("access error for %s", argv[1]);
else
printf("read access OK\n");
if (open(argv[1], O_RDONLY) < 0)
err_ret("open error for %s", argv[1]);
else
printf("open for reading OK\n");
exit(0);
}

8.进程控制
8.1 fork函数实例
#include "apue.h"
int globvar = 6; /* external variable in initialized data */
char buf[] = "a write to stdout\n";
int
main(void)
{
int var; /* automatic variable on the stack */
pid_t pid;
var = 88;
if (write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, sizeof(buf)-1) != sizeof(buf)-1)
err_sys("write error");
printf("before fork\n"); /* we don't flush stdout */
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) {
err_sys("fork error");
} else if (pid == 0) { /* child */
globvar++; /* modify variables */
var++;
} else {
sleep(2); /* parent */
}
printf("pid = %ld, glob = %d, var = %d\n", (long)getpid(), globvar,
var);
exit(0);
}
运行结果

分析
为啥是
sizeof(buf)-1:
为什么出现有两次
before fork出现:

8.2 fork之后父子进程对文件的共享

8.3 vfork函数实例
#include "apue.h"
int globvar = 6; /* external variable in initialized data */
int
main(void)
{
int var; /* automatic variable on the stack */
pid_t pid;
var = 88;
printf("before vfork\n"); /* we don't flush stdio */
if ((pid = vfork()) < 0) {
err_sys("vfork error");
} else if (pid == 0) { /* child */
globvar++; /* modify parent's variables */
var++;
_exit(0); /* child terminates */
}
/* parent continues here */
printf("pid = %ld, glob = %d, var = %d\n", (long)getpid(), globvar,
var);
exit(0);
}
运行结果

linux中文件内核数据结构的更多相关文章
- linux中文件IO
一. linux常用文件IO接口 1.1. 文件描述符 1.1.1. 文件描述符的本质是一个数字,这个数字本质上是进程表中文件描述符表的一个表项,进程通过文件描述符作为index去索引查表得到文件表指 ...
- [转]Linux中文件权限目录权限的意义及权限对文件目录的意义
转自:http://www.jb51.net/article/77458.htm linux中目录与文件权限的意义 一.文件权限的意义 r:可以读这个文件的具体内容: w:可以编辑这个文件的内容,包括 ...
- LSOF查看linux中文件打开情况
如何查看linux中文件打开情况 前言 我们都知道,在linux下,“一切皆文件”,因此有时候查看文件的打开情况,就显得格外重要,而这里有一个命令能够在这件事上很好的帮助我们-它就是lsof. lin ...
- linux中文件压缩介绍
原文内容来自于LZ(楼主)的印象笔记,如出现排版异常或图片丢失等问题,可查看当前链接:https://app.yinxiang.com/shard/s17/nl/19391737/1c62bb7f-f ...
- linux中文件颜色,蓝色,白色等各自代表的含义
linux中文件颜色,蓝色,白色等各自代表的含义 绿色文件---------- 可执行文件,可执行的程序 红色文件-----------压缩文件或者包文件 蓝色文件----------目录 白色文件- ...
- [转载] linux中文件描述符fd和文件指针flip的理解
转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/Jezze/archive/2011/12/23/2299861.html 简单归纳:fd只是一个整数,在open时产生.起到一个索引的作用,进程通 ...
- linux中文件的三种time(atime,mtime,ctime)
linux下文件有3个时间的,分别是atime,mtime,ctime.有些博友对这3个时间还是比较迷茫和困惑的,我整理了下,写下来希望对博友们有所帮助. 1 这三个time的含义 简名 全名 中文名 ...
- linux中文件的时间戳
touch命令 touch用来创建新文件,或者修改时间戳. linux中的文件有三个时间点,利用stat命令查看: 1.atime:最后访问时间:文件最后一次被存取或执行的时间. 2.mtime:最后 ...
- Linux中文件压缩与解压
压缩与解压 compress 文件名 1 -v //详细信息 2 3 -d //等于 uncompress 默认只识别 .Z 如果使用别的后缀,会导致不识别,解压缩失败.也可以使用 -d -c 压缩包 ...
随机推荐
- Java | 字符串的使用 & 分析
字符串 字符串广泛应用 在 Java 编程中,在 Java 中字符串属于对象,在程序中所有的双引号字符串,都是String类的对象. 字符串的特点 1.字符串的内容永不可变. 2.正在是因为字符串的不 ...
- 前端-HTML标签
1.<p></p>段落标签 <p>别在最该拼搏的年纪选择稳定,世界上最大的不变是改变,只有每天进步,才能拥抱生命的无限可能!</p> 2.</b& ...
- web系统国际化思路
需求:php开发多个中文系统支持国际化 思路: 提炼各个系统中的中文字符,替换为资源key. 多媒体文件中的中文定位(图片中的中文,中文录音,中文视频,中文模板等). 统一翻译文字.准备资源文件. 各 ...
- 祝贺|合肥.NET俱乐部第二期技术沙龙活动圆满成功
热烈祝贺合肥.NET俱乐部第二期技术沙龙圆满成功,感恩参与活动的每一位小伙伴!正是因为有你们才促成了这次聚会的成功.现对此次活动进行简单回顾并附上精彩的活动图片,每一位参与活动者名单,以及此次活动讲师 ...
- 微信小程序云开发-云存储的应用-识别行驶证
一.准备工作 1.创建云函数identify 2.云函数identify中index.js代码 1 // 云函数入口文件 2 const cloud = require('wx-server-sdk' ...
- PAT乙级:1094 谷歌的招聘 (20分)
PAT乙级:1094 谷歌的招聘 (20分) 题干 2004 年 7 月,谷歌在硅谷的 101 号公路边竖立了一块巨大的广告牌(如下图)用于招聘.内容超级简单,就是一个以 .com 结尾的网址,而前面 ...
- C++第五十篇 -- 获取串口的描述信息
如何知道自己的电脑上有无串口呢? -- 手动 1. 查看电脑,看是否有串口器件(串口是一个九针的D型接口) 2. 在设备管理器上查看 乍一看,还以为是有两个串口,其实仔细看描述就知道,这是蓝牙虚拟串口 ...
- ts 学习笔记 - 类
目录 类 类的概念 类的用法 属性和方法 类的继承 存取器 静态属性 Typescript 中的用法 抽象类 类的类型 类与接口 类实现接口 接口继承接口 接口继承类 混合类型 类 类的概念 类 (c ...
- ifix 自动化(Automation)错误弹窗的解决方案
在先前ifix项目中添加了语音模块,然后概率性跳出自动化(Automation)错误弹窗,先前分析了很多种原因,从代码的冗余,编码等角度进行了优化,效果不是很理想,仍然会概率性出现.经过反反复复大约3 ...
- CSS 即将支持嵌套,SASS/LESS 等预处理器已无用武之地?
最近,有一则非常振奋人心的消息,CSS 即将原生支持嵌套 -- Agenda+ to publish FPWD of Nesting,表示 CSS 嵌套规范即将进入规范的 FWPD 阶段. 目前对应的 ...
