Codeforces Round #425 (Div. 2) Problem C Strange Radiation (Codeforces 832C) - 二分答案 - 数论
n people are standing on a coordinate axis in points with positive integer coordinates strictly less than 106. For each person we know in which direction (left or right) he is facing, and his maximum speed.
You can put a bomb in some point with non-negative integer coordinate, and blow it up. At this moment all people will start running with their maximum speed in the direction they are facing. Also, two strange rays will start propagating from the bomb with speed s: one to the right, and one to the left. Of course, the speed s is strictly greater than people's maximum speed.
The rays are strange because if at any moment the position and the direction of movement of some ray and some person coincide, then the speed of the person immediately increases by the speed of the ray.
You need to place the bomb is such a point that the minimum time moment in which there is a person that has run through point 0, and there is a person that has run through point 106, is as small as possible. In other words, find the minimum time moment t such that there is a point you can place the bomb to so that at time moment t some person has run through 0, and some person has run through point106.
The first line contains two integers n and s (2 ≤ n ≤ 105, 2 ≤ s ≤ 106) — the number of people and the rays' speed.
The next n lines contain the description of people. The i-th of these lines contains three integers xi, vi and ti (0 < xi < 106, 1 ≤ vi < s,1 ≤ ti ≤ 2) — the coordinate of the i-th person on the line, his maximum speed and the direction he will run to (1 is to the left, i.e. in the direction of coordinate decrease, 2 is to the right, i.e. in the direction of coordinate increase), respectively.
It is guaranteed that the points 0 and 106 will be reached independently of the bomb's position.
Print the minimum time needed for both points 0 and 106 to be reached.
Your answer is considered correct if its absolute or relative error doesn't exceed 10 - 6. Namely, if your answer is a, and the jury's answer is b, then your answer is accepted, if 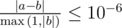 .
.
2 999
400000 1 2
500000 1 1
500000.000000000000000000000000000000
2 1000
400000 500 1
600000 500 2
400.000000000000000000000000000000
In the first example, it is optimal to place the bomb at a point with a coordinate of 400000. Then at time 0, the speed of the first person becomes 1000 and he reaches the point 106 at the time 600. The bomb will not affect on the second person, and he will reach the 0point at the time 500000.
In the second example, it is optimal to place the bomb at the point 500000. The rays will catch up with both people at the time 200. At this time moment, the first is at the point with a coordinate of 300000, and the second is at the point with a coordinate of 700000. Their speed will become 1500 and at the time 400 they will simultaneously run through points 0 and 106.
题目大意 数轴上有n个(每个人的位置大于0且小于106),每个人有一个朝向和一个最大速度。有一个神奇的炸弹,可以在一个非负整数点引爆(并不知道引爆的位置),并向两边射出速度s个单位每秒的光线(其速度严格大于人的速度),如果这个光线碰到人,且和人的朝向一样,那么人的最大速度会加上这个速度,引爆后所有人开始向他面向的方向全速奔跑(不考虑体力)。问最少需要多长时间使得点0和1e6被人到达了(不一定是同一个人)。
显然是二分答案。现在来思考判定。
当前二分的答案为mid,现在判断是否有人能够达到点0和1e6。
如果没有,就考虑一下用炸弹爆炸后的光线来加速。显然可以放炸弹的地方是一个区间(假设我们会算它,然后继续)。
然后判定的问题转化成判断两组区间,是否存在一对(在不同组内)的交集包含整点,这个就可以通过排序加二分查找解决,做法类似于codeforces 822C。
现在来思考如何计算这个区间(假定读者小学奥数学得还不错)
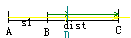
假定人在点B处,它的终点为C,在点A处放置炸弹,AB = s1, BC = dist,光线在点D处追上人,耗时t0,人的速度为v0,光线的速度为vs。所以有:
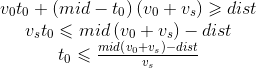
有了最大的追及时间就可以得到追及路程s1 = t0vs。
然后就可以交代码去codeforces了。
然而昨天晚上打比赛的时候,为了图快,没仔细读题,把题目大意读成所有人都离开(0, 1e6)的最少耗时,然而谜之Wrong Answer on pretest 3。还耗掉我一个小时,早知道该去切D题。
Code
/**
* Codeforces
* Problem#832C
* Accepted
* Time:155ms
* Memory:7400k
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#ifndef WIN32
#define Auto "%lld"
#else
#define Auto "%I64d"
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << ) - );
const signed long long llf = (signed long long)((1ull << ) - );
const double eps = 1e-;
const int binary_limit = ;
#define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b)
#define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b)
#define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c))
#define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c))
template<typename T>
inline boolean readInteger(T& u){
char x;
int aFlag = ;
while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != '-' && x != -);
if(x == -) {
ungetc(x, stdin);
return false;
}
if(x == '-'){
x = getchar();
aFlag = -;
}
for(u = x - ''; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << ) + (u << ) + x - '');
ungetc(x, stdin);
u *= aFlag;
return true;
} int opt = ;
typedef class Segment {
public:
double l;
double r; Segment(double l = 0.0, double r = 0.0):l(l), r(r) { } Segment getBing(Segment b) {
return Segment(max(l, b.l), min(r, b.r));
} boolean hasint() {
return (int)l != (int)r;
} boolean isResonable() {
return l <= r;
} boolean operator < (Segment b) const {
if(opt == ) {
if(l != b.l) return l < b.l;
return r < b.r;
}
if(r != b.r) return r < b.r;
return l < b.l;
} }Segment; boolean operator < (int x, Segment a) {
if(opt == ) {
return x < a.l;
}
return x < a.r;
} int n, s;
int pos[], spe[], ds[]; inline void init() {
readInteger(n);
readInteger(s);
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
readInteger(pos[i]);
readInteger(spe[i]);
readInteger(ds[i]);
}
} inline double calcS(double vs, double v0, double mid, double dist) {
double t0 = (mid * (v0 + vs) - dist) / vs;
return t0 * (vs - v0);
} /*
inline int ceil(double a) {
if(a == (int)a) return a;
return (int)a + 1;
}
*/ inline boolean check(double mid) {
double dist, t;
boolean f1 = false, f2 = false;
vector<Segment> v1, v2, v3;
for(int i = ; i <= n && (!f1 || !f2); i++) {
if(ds[i] == && !f1) {
dist = pos[i];
t = dist / spe[i];
if(t > mid) {
double s1 = calcS(s, spe[i], mid, dist);
if(s1 < ) continue;
v1.push_back(Segment(pos[i], pos[i] + s1));
v2.push_back(Segment(pos[i], pos[i] + s1));
} else f1 = true;
} else if(ds[i] == && !f2) {
dist = 1e6 - pos[i];
t = dist / spe[i];
if(t > mid) {
double s1 = calcS(s, spe[i], mid, dist);
if(s1 < ) continue;
v3.push_back(Segment(pos[i] - s1, pos[i]));
} else f2 = true;
}
}
if(f1 && f2) return true;
if(f1 && !v3.empty()) return true;
if(f2 && !v1.empty()) return true;
opt = ;
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end());
opt = ;
sort(v2.begin(), v2.end());
int sv1 = (signed)v1.size();
for(int i = , s; i < v3.size(); i++) {
Segment b = v3[i];
opt = ;
s = sv1 - (upper_bound(v1.begin(), v1.end(), (int)v3[i].r) - v1.begin());
opt = ;
s += upper_bound(v2.begin(), v2.end(), (int)ceil(v3[i].l)) - v2.begin();
if(s < sv1)
return true;
}
return false;
} inline void solve() {
int cnt = ;
double l = 0.0, r = 1e6;
while(l + eps < r && cnt <= binary_limit) {
double mid = (l + r) / ;
cnt++;
if(check(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid;
}
printf("%.9lf", r);
} int main() {
init();
solve();
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #425 (Div. 2) Problem C Strange Radiation (Codeforces 832C) - 二分答案 - 数论的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #425 (Div. 2) Problem D Misha, Grisha and Underground (Codeforces 832D) - 树链剖分 - 树状数组
Misha and Grisha are funny boys, so they like to use new underground. The underground has n stations ...
- Codeforces Round #425 (Div. 2) Problem B Petya and Exam (Codeforces 832B) - 暴力
It's hard times now. Today Petya needs to score 100 points on Informatics exam. The tasks seem easy ...
- Codeforces Round #425 (Div. 2) Problem A Sasha and Sticks (Codeforces 832A)
It's one more school day now. Sasha doesn't like classes and is always bored at them. So, each day h ...
- Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2) Problem D Palindromic characteristics (Codeforces 835D) - 记忆化搜索
Palindromic characteristics of string s with length |s| is a sequence of |s| integers, where k-th nu ...
- Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2) Problem C Star sky (Codeforces 835C) - 前缀和
The Cartesian coordinate system is set in the sky. There you can see n stars, the i-th has coordinat ...
- Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2) Problem A Key races (Codeforces 835 A)
Two boys decided to compete in text typing on the site "Key races". During the competition ...
- Codeforces Round #716 (Div. 2), problem: (B) AND 0, Sum Big位运算思维
& -- 位运算之一,有0则0 原题链接 Problem - 1514B - Codeforces 题目 Example input 2 2 2 100000 20 output 4 2267 ...
- Codeforces Round #425 (Div. 2) C - Strange Radiation
地址:http://codeforces.com/contest/832/problem/C 题目: C. Strange Radiation time limit per test 3 second ...
- Codeforces Round #425 (Div. 2)C
题目连接:http://codeforces.com/contest/832/problem/C C. Strange Radiation time limit per test 3 seconds ...
随机推荐
- django基础(一)
一.创建django程序 1.终端:django-admin startproject sitename 2.IDE创建Django程序时,本质上都是自动执行上述命令 常用命令: python man ...
- mybatis--parametertype的参数传递
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC ...
- 让bat以管理员权限运行
有的电脑是非管理员登录,运行程序时,需要提示是否运行运行.解决方法如下: @ echo off % % ver|find "5.">nul&&goto :Ad ...
- Lambda表达式语法
基础语法:‘->’Lambda操作符* 左侧:Lambda表达式的参数列表 对应接口中方法中的参数列表中的参数(比如nice1中MyPredict这个接口中的方法)* 右侧:Lambda表达式中 ...
- Exception in Spark
1: Exception in thread "main" org.apache.spark.SparkException: org.apache.spark.streaming. ...
- 2.匿名类,匿名类对象,private/protected/public关键字、abstract抽象类,抽象方法、final关键字的使用,多线程Thread类start方法原理
package com.bawei.multithread; //注意:模板方法我们通常使用抽象类或者抽象方法!这里我们为了方便在本类中使用就没有使用抽象类/抽象方法 public class Tem ...
- Unity AssetBoundle 打包流程
1.准备打包资源,给要打包的资源添加一个AssetBoundle名字 2.在Scripts文件夹下新建一个子文件夹,命名为Editor(注意名字不能写错),新建一个打包资源的C#类,命名为BuildA ...
- 取n到m行
取n到m行 . select top m * from tablename where id not in (select top n id from tablename order by id as ...
- Lua语言总结
[1]要退出交互模式和解释器,只需输入“os.exit()” [2]在交互模式执行程序块可以使用函数dofile,这个函数就可以立即执行一个文件.应用示例:dofile("f:/myLua/ ...
- Linux基础命令---检查密码文件pwck
pwck 检查用户密码文件“/etc/passwd”和“/etc/shadow”的完整性,将验证结果送到标砖输出.提示用户删除格式不正确或有其他不可更正错误的条目.检查以验证每个条目是否具有:正确的字 ...
