深入理解 Vue 组件
深入理解 Vue 组件
组件使用中的细节点
使用 is 属性,解决组件使用中的bug问题
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>组件使用中的细节点</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="root">
<table>
<tbody>
<!-- H5编码规范要求,tbody内必须是tr,因此row组件不能用,会产生bug,
因此 is 关键字起到了很好的作用,将此时的 tr 标签等于我们创建的 row 子组件。
完美解决了既要使用组件永不会影响H5编码规范的问题
不仅仅是table标签,ul ol select 标签都有相同的问题。-->
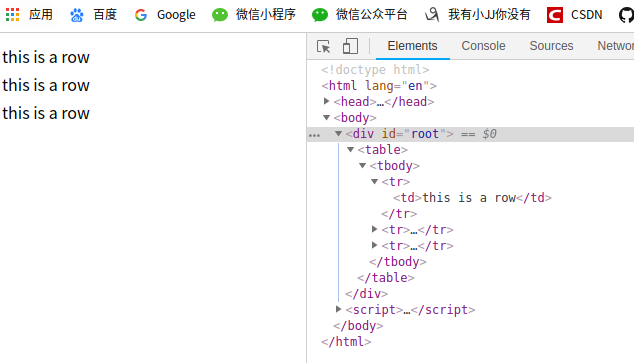
<tr is="row"></tr>
<tr is="row"></tr>
<tr is="row"></tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div> <script>
// 创建全局子组件
Vue.component('row',{
template:"<tr><td>this is a row</td></tr>"
}) var vm = new Vue({
el:"#root", })
</script>
</body> </html>
子组件定义data数据,data必须是个函数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="root">
<table>
<tbody>
<tr is="row"></tr>
<tr is="row"></tr>
<tr is="row"></tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<script>
// 子组件
Vue.component("row", {
// 子组件定义数据data的方法必须是一个函数返回,不能像根对象一样
data: function () {
return {
content: 'this is a row'
}
},
template: '<tr><td>{{content}}</td></tr>'
}) var vm = new Vue({
el: "#root",
})
</script>
</body> </html>
Vue中的 ref 引用的内容
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>ref</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 在vue当中,可以通过ref获取dom节点 -->
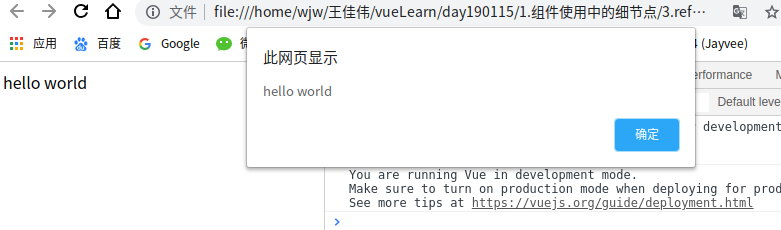
<div ref='hello' @click="handleClick">hello world</div>
</div>
<script> var vm = new Vue({
el: "#root",
methods: {
handleClick: function () {
// 获取dom中的内容
// this.$refs.hello 获取ref=hello的dom节点
alert(this.$refs.hello.innerHTML)
}
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
vue实现计数器功能
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>计数器功能</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="root">
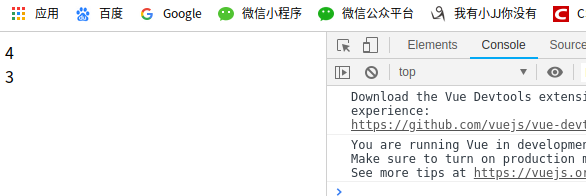
<counter ref='one' @change="handleChange"></counter>
<counter ref='two' @change="handleChange"></counter>
<!-- 求和 -->
<div>{{total}}</div>
</div>
<script>
// 子组件
Vue.component('counter', {
template: '<div @click="handleClick">{{number}}</div>',
data: function () {
return {
number: 0
}
},
methods: {
handleClick: function () {
this.number++
// 向外发送change事件
this.$emit('change')
}
}
}) var vm = new Vue({
el: "#root",
data: {
total: 0
},
methods: {
handleChange: function () {
this.total = this.$refs.one.number + this.$refs.two.number
// console.log(this.$refs.one.number)
// console.log(this.$refs.two.number)
}
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>

父子组件间传值
父组件向子组件传递数据
- 父组件通过属性的形式向子组件传递数据。
- 父组件可以随意的向子组件传递参数。
- 但是子组件绝对不能去修改父组件传进来的参数(单向数据流)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>父子间组件传值</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 父组件都是通过属性的形式向子组件传递数据 -->
<counter :count="1"></counter>
<counter :count="2"></counter>
</div> <script> // 局部组件
var counter = {
// props 表示子组件接受父组件的内容
props: ['count'],
data: function () {
return {
// 子组件自己的data number值
number:this.count
}
},
template: "<div @click='handleClick'>{{number}}</div>",
methods: {
// 点击累加方法
handleClick: function () {
// 父组件可以随意的向子组件传递参数
// 但是子组件绝对不能去修改父组件传进来的参数 单向数据流
// 因此修改自己的Number值
this.number++
},
}
} var vm = new Vue({
el: "#root",
// 注册局部组件.
components: {
counter: counter,
}
})
</script> </body> </html>
子组件向父组件传值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>父子间组件传值</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 父组件都是通过属性的形式向子组件传递数据 -->
<counter :count="3" @change="handleChange"></counter>
<counter :count="2" @change="handleChange"></counter>
<div>{{total}}</div>
</div> <script> // 局部组件
var counter = {
// props 表示子组件接受父组件的内容
props: ['count'],
data: function () {
return {
// 子组件自己的data number值
number:this.count
}
},
template: "<div @click='handleClick'>{{number}}</div>",
methods: {
// 点击累加方法
handleClick: function () {
// 父组件可以随意的向子组件传递参数
// 但是子组件绝对不能去修改父组件传进来的参数 单向数据流
// 因此修改自己的Number值
this.number++
// 向外触发事件,后可以跟参数
this.$emit('change',1)
},
}
} var vm = new Vue({
el: "#root",
data:{
total:5,
},
// 注册局部组件.
components: {
counter: counter,
},
methods:{
handleChange:function(step){
// step = 1 步长为2
// 求和等于默认值+点击一下的步长
this.total += step
}
}
})
</script> </body> </html>
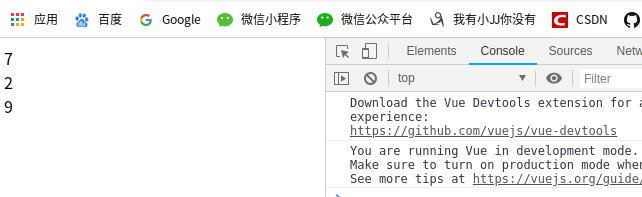
组件参数校验与非props特性
组件参数校验
组件参数校验是指:父组件向子组件传递参数的时候,子组件有权向父组件提出参数的形式和要求,并检验父组件传进的参数是否合乎要求。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>组件参数校验与非props特性</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- <child :content="123"></child> -->
<child content="123"></child>
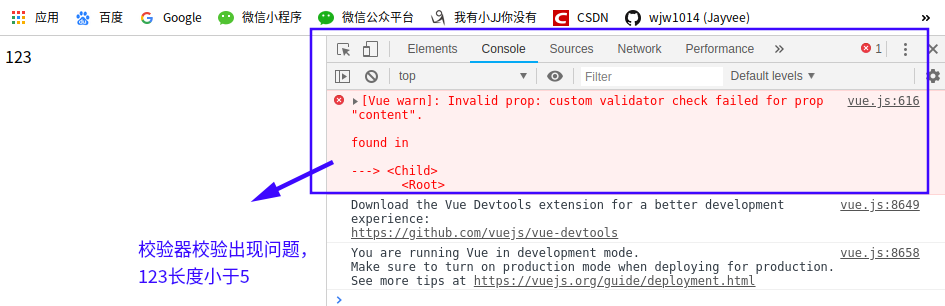
</div> <script> Vue.component('child',{
props:{
// content:String, // 子组件接收到的content数据,必须是一个字符串类型
// content:[Number,String] // 子组件接收到的content数据,要么是字符串,要么是数字
content:{ // 接收content
type:String, //类型type必须是string
// required:true, // 表示content必需传
// default:'default value', // 如果没有传进来,默认显示这个
validator:function(value){ // 校验器校验传入的内容长度必须大于5
return (value.length>5)
},
}
},
template:'<div>{{content}}</div>',
}) var vm = new Vue({
el:"#root", })
</script> </body>
</html>
非 Props 特性
Props 特性是指:当你的父组件使用子组件的时候通过属性向子组件传值的时候,恰好子组件里面声明了对父组件传递过来的属性的接收。
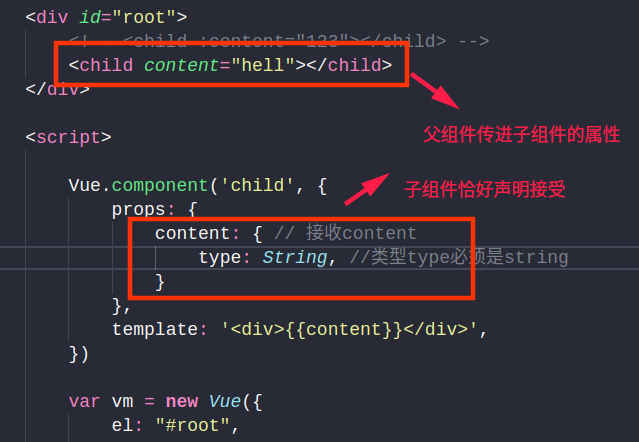
非Props 特性是指:父组件向子组件传递了一个属性,但是子组件并没有props接收的内容,也就是说,子组件并没有声明要接受父组件传递进来的属性。

非Props 特性特点一:如果子组件没人接收父组件传进的属性,则子组件不能使用父组件传进的值。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>非 Props 特性</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head> <body> <div id="root">
<!-- <child :content="123"></child> -->
<child content="hell"></child>
</div> <script> Vue.component('child', {
// props: {
// content: { // 接收content
// type: String, //类型type必须是string
// }
// }, // content 找不到,就会报错
template: '<div>{{content}}</div>',
}) var vm = new Vue({
el: "#root", })
</script>
</body> </html>
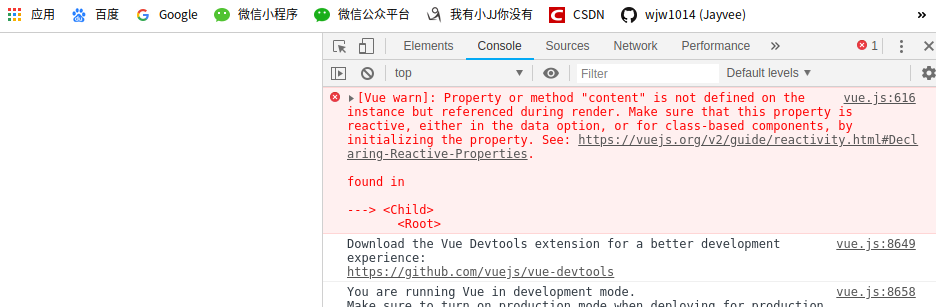
非Props 特性特点二:DOM中会保留父组件传递给子组件的属性标识
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>非 Props 特性</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head> <body> <div id="root">
<!-- <child :content="123"></child> -->
<child content="hell"></child>
</div> <script> Vue.component('child', {
// props: {
// content: { // 接收content
// type: String, //类型type必须是string
// }
// },
template: '<div>hello</div>', // content 找不到,就会报错
// template: '<div>{{content}}</div>',
}) var vm = new Vue({
el: "#root", })
</script>
</body> </html>

给组件绑定原生事件
很简单,在绑定事件的click后面加一个修饰符就行。
修饰符为 .native
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>给组件绑定原生事件</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body> <div id="root">
<!-- 原生点击事件 -->
<child @click.native="handleClick"></child>
</div> <script> Vue.component('child',{
template:'<div @click="handleChildClick">Child</div>',
}) var vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
methods:{
handleClick:function(){
alert('click')
}
}
})
</script> </body>
</html>

非父子组件间的传值
情景分析
我们可以把一个网页拆分成很多个部分,每个部分就是我们代码中是我一个组件,如下面的一张图:
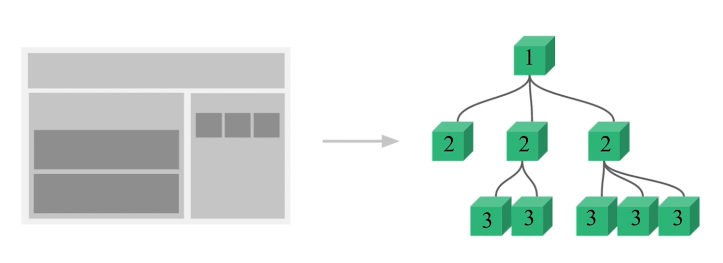
如果 1 2 层需要进行传值,则为父子组件之间的传值,通信方式在之前的内容讲到过。

如果 1 3 层进行传值,则为非父子组件间的传值,应该怎么办呢?
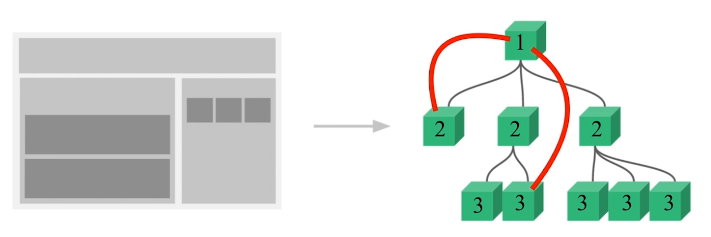
第一中方式:和父子组件间传值一样,一层一层的传递,第一层传给第二层,第二层在传给第三层,反之亦然。但是这种传值方式显然不方便太繁琐。
加入 3 3 层进行的非父子组件传值,又会是怎样的处理方法呢?

这种情况显然更加不适合层层传值,即第三层传给第二层,第二层传给第一层,第一层传给第二层,第二层传给第三层,累死了!代码变得非常的复杂。
非父子组件传值解决方法
第一种方法,我们可以使用 VUE 官方提供的一个数据层的框架,名字叫做 VUEX 来解决,但是使用有难度。
第二种方法,使用 发布订阅模式 来解决非父子组件的传值问题,在vue中叫做 总线机制 。
使用总线机制解决非父子组件传值问题
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>非父子组件间的传值(Bus|总线|发布订阅模式|观察者模式)</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<child content="Jayvee"></child>
<child content="Wong"></child>
</div> <script> Vue.prototype.bus = new Vue() Vue.component('child',{
data:function(){
return{
selfContent:this.content
}
},
template:'<div @click="handleClick">{{selfContent}}</div>',
props:{
content:String,
},
methods:{
handleClick:function(){
this.bus.$emit('change',this.selfContent)
}
},
mounted:function(){
var this_ = this
this.bus.$on('change',function(msg){
this_.selfContent = msg
})
}
}) var vm =new Vue({
el:"#root",
})
</script> </body>
</html>

VUE 中的插槽 - slot
父组件通过传值的方式向子组件添加标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>vue中的插槽(slot)</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<child content="<p>wjw</p>"></child>
</div> <script> Vue.component('child',{
props:['content'],
template:'<div><p>hello</p><div v-html="this.content"></div></div>'
}) var vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
}) </script> </body>
</html>

使用插槽
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>vue中的插槽(slot)</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<child>
<p>wjw</p>
</child>
</div> <script> Vue.component('child',{
template:'<div><p>hello</p><slot>默认内容</slot></div>'
}) var vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
}) </script> </body>
</html>

传入header和footer
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>vue中的插槽(slot)</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<body-content>
<div slot='header' class="header">header</div>
<div slot='footer' class="footer">footer</div>
</body-content>
</div> <script> Vue.component('body-content',{
template:`<div>
<slot name='header'></slot>
<div class="content">content</div>
<slot name='footer'></slot>
</div>`
}) var vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
}) </script> </body>
</html>

Vue中的作用域插槽
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>vue中的作用域插槽(slot)</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="root">
<child>
<template slot-scope="props">
<li>{{props.item}} -- hello</li>
</template>
</child>
</div> <script>
Vue.component('child', {
data: function () {
return {
list: [1, 2, 3, 4]
}
},
template: `<div>
<ul>
<slot v-for="item of list" :item=item></slot>
</ul>
</div>`
}) var vm = new Vue({
el: "#root",
})
</script> </body> </html>

Vue的动态组件与 v-once 指令
点击按钮实现两个组件显隐切换
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>VUE的动态组件与v-once指令</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<child-one v-if="type === 'child-one'"></child-one>
<child-two v-if="type === 'child-two'"></child-two>
<button @click="handleBtnClick">change</button>
</div> <script> Vue.component('child-one',{
template:"<div>child-one</div>"
}) Vue.component('child-two',{
template:"<div>child-two</div>"
}) var vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
type:'child-one'
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick:function(){
this.type = this.type === 'child-one'?'child-two':'child-one'
},
}
})
</script> </body>
</html>

动态组件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>VUE的动态组件与v-once指令</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- component是vue自带的,表示动态组件 -->
<component :is="type"></component>
<!-- <child-one v-if="type === 'child-one'"></child-one>
<child-two v-if="type === 'child-two'"></child-two> -->
<button @click="handleBtnClick">change</button>
</div> <script> Vue.component('child-one',{
template:"<div>child-one</div>"
}) Vue.component('child-two',{
template:"<div>child-two</div>"
}) var vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
type:'child-one'
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick:function(){
this.type = this.type === 'child-one'?'child-two':'child-one'
},
}
})
</script> </body>
</html>

V-once 节约性能,提高静态文件的展示效率
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>VUE的动态组件与v-once指令</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- component是vue自带的,表示动态组件 -->
<!-- <component :is="type"></component> -->
<child-one v-if="type === 'child-one'"></child-one>
<child-two v-if="type === 'child-two'"></child-two>
<button @click="handleBtnClick">change</button>
</div> <script> Vue.component('child-one',{
template:"<div v-once>child-one</div>"
}) Vue.component('child-two',{
template:"<div v-once>child-two</div>"
}) var vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
type:'child-one'
},
methods:{
handleBtnClick:function(){
this.type = this.type === 'child-one'?'child-two':'child-one'
},
}
})
</script> </body>
</html>

深入理解 Vue 组件的更多相关文章
- 不一样的角度理解Vue组件
什么是组件 以Java.C#等面向对象编程语言的角度去理解Vue组件,能够发现组件和面向对象编程的方式和风格很相似.一切事物皆为对象,通过面向对象的方式,将现实世界的事物抽象成对象,现实世界中的关系抽 ...
- 尝试用面向对象思维理解Vue组件
什么是组件 用面向对象的思维去理解Vue组件,可以将所有的事物都抽象为对象,而类或者说是组件,都具有属性和操作. 如抽取人类为组件,其基本的属性有姓名.年龄.国籍:基本的方法有吃饭.睡觉.跑步等. & ...
- 深入理解Vue组件3大核心概念
摘要: 搞懂Vue组件! 作者:浪里行舟 原文:详解vue组件三大核心概念 Fundebug经授权转载,版权归原作者所有. 前言 本文主要介绍属性.事件和插槽这三个vue基础概念.使用方法及其容易被忽 ...
- 深入理解--VUE组件中数据的存放以及为什么组件中的data必需是函数
1.组件中数据的存放 ***(重点)组件是一个单独模块的封装:这个模块有自己的HTML模板,也有data属性. 只是这个data属性必需是一个函数,而这个函数返回一个对象,这个对象里面存放着组件的数据 ...
- 怎样理解 Vue 组件中 data 必须为函数 ?
组件意在 复用 , 若为 对象, 则会相互干扰. 且 Vue 不允许此事发生, 规定必须为函数, 否则报错. 原理如下 对象 // 模拟创建组件 var Component= function() { ...
- 第四章、深入理解vue组件
4-1.使用组件的细节 a.使用is解决html出现bug 如下 table下面应该为tr,所以页面渲染的时候没有找到tr是有问题的,所以是有小bug,所以table中必须是tr b.改上面bug,t ...
- 深刻理解Vue中的组件
转载:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000010527064 --20更新: Vue2.6已经更新了关于内容插槽和作用域插槽的API和用法,为了不误导大家,我把插槽的内 ...
- 深入理解Vue父子组件通讯的属性和事件
在html中使用元素,会有一些属性,如class,id,还可以绑定事件,自定义组件也是可以的.当在一个组件中,使用了其他自定义组件时,就会利用子组件的属性和事件来和父组件进行数据交流. 父子组件之间的 ...
- vue组件最佳实践
看了老外的一篇关于组件开发的建议(强烈建议阅读英文原版),感觉不错翻译一下加深理解. 这篇文章制定一个统一的规则来开发你的vue程序,以至于达到一下目的. 1.让开发者和开发团队更容易发现一些事情. ...
随机推荐
- (已解决)Eclipse报错:Could not find XXX.apk. 没有Android项目命名. There is no android project named
可能是你把当前项目设置为library项目了,按以下步骤切换回普通项目: 选择 Project->Properties 在左边的列表中,选择 Android 取消钩中"Is Libra ...
- phpcs
phpcs(代码规范) https://juejin.im/post/5b18fdeb6fb9a01e573c3cb3 https://laravel-china.org/docs/psr/psr-2 ...
- redis的key越来越多,对速度是否有影响
---恢复内容开始--- redis存储key是用字典对象的,查询性能几乎和数量级无关,只要保证内存够用就可以了,如果内存不够,会把内存和swap空间交换,这种情况下就会很影响性能,会读取出现读取磁盘 ...
- netframework转core时文件响应流问题
做将framework webapi项目转成netcore平台上的webapi项目时,发现原来的返回文件响应流在netcore平台下失效.代码如下,返回pdf文件响应流,供前端显示 /// <s ...
- 《大话设计模式》c++实现 代理模式
代理模式 在代理模式(Proxy Pattern)中,一个类代表另一个类的功能.这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式. 在代理模式中,我们创建具有现有对象的对象,以便向外界提供功能接口. 介绍 意图:为其 ...
- python 文件写入错误
在保存网页文字到txt文件下时,出现如下错误 UnicodeEncodeError: 'gbk' codec can't encode character u'\xa9' in position 24 ...
- 原生js实现图片轮播效果
思路:设置父容器(一定宽度,一定高度,相对定位,子容器超出部分进行隐藏),子容器图片并排(浮动,绝对定位,每次点击进行相应的左或右偏移量) 1.html: <!DOCTYPE html> ...
- uvalive 3353 Optimal Bus Route Design
题意: 给出n个点,以及每个点到其他点的有向距离,要求设计线路使得每一个点都在一个环中,如果设计的线路拥有最小值,那么这个线路就是可选的.输出这个最小值或者说明最小线路不存在. 思路: 在DAG的最小 ...
- Qt5 信号重载
下面以最常用的QComboBox为例说明. [1]Qt4风格的connect 示例代码: connect(ui->comboBox, SIGNAL(activated(int index)), ...
- 电脑已连接wifi的密码查询
有时候,想登陆自己家的无线网络(尤其朋友来家里突然要连接无线网络),脑子刹那间一片空白想不起来密码,怎么办呢? 其实,我们可以通过电脑来查看网络的密码,现在分享如何在笔记本电脑上查看连接过的无线网络密 ...
