Codeforces Round #439 (Div. 2) Problem E (Codeforces 869E) - 暴力 - 随机化 - 二维树状数组 - 差分
Adieu l'ami.
Koyomi is helping Oshino, an acquaintance of his, to take care of an open space around the abandoned Eikou Cram School building, Oshino's makeshift residence.
The space is represented by a rectangular grid of n × m cells, arranged into n rows and m columns. The c-th cell in the r-th row is denoted by (r, c).
Oshino places and removes barriers around rectangular areas of cells. Specifically, an action denoted by "1 r1 c1 r2 c2" means Oshino's placing barriers around a rectangle with two corners being (r1, c1) and (r2, c2) and sides parallel to squares sides. Similarly, "2 r1 c1 r2 c2" means Oshino's removing barriers around the rectangle. Oshino ensures that no barriers staying on the ground share any common points, nor do they intersect with boundaries of the n × m area.
Sometimes Koyomi tries to walk from one cell to another carefully without striding over barriers, in order to avoid damaging various items on the ground. "3 r1 c1 r2 c2" means that Koyomi tries to walk from (r1, c1) to (r2, c2) without crossing barriers.
And you're here to tell Koyomi the feasibility of each of his attempts.
The first line of input contains three space-separated integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 2 500, 1 ≤ q ≤ 100 000) — the number of rows and columns in the grid, and the total number of Oshino and Koyomi's actions, respectively.
The following q lines each describes an action, containing five space-separated integers t, r1, c1, r2, c2 (1 ≤ t ≤ 3, 1 ≤ r1, r2 ≤ n, 1 ≤ c1, c2 ≤ m) — the type and two coordinates of an action. Additionally, the following holds depending on the value of t:
- If t = 1: 2 ≤ r1 ≤ r2 ≤ n - 1, 2 ≤ c1 ≤ c2 ≤ m - 1;
- If t = 2: 2 ≤ r1 ≤ r2 ≤ n - 1, 2 ≤ c1 ≤ c2 ≤ m - 1, the specified group of barriers exist on the ground before the removal.
- If t = 3: no extra restrictions.
For each of Koyomi's attempts (actions with t = 3), output one line — containing "Yes" (without quotes) if it's feasible, and "No" (without quotes) otherwise.
5 6 5
1 2 2 4 5
1 3 3 3 3
3 4 4 1 1
2 2 2 4 5
3 1 1 4 4
No
Yes
2500 2500 8
1 549 1279 1263 2189
1 303 795 1888 2432
1 2227 622 2418 1161
3 771 2492 1335 1433
1 2017 2100 2408 2160
3 48 60 798 729
1 347 708 1868 792
3 1940 2080 377 1546
No
Yes
No
For the first example, the situations of Koyomi's actions are illustrated below.
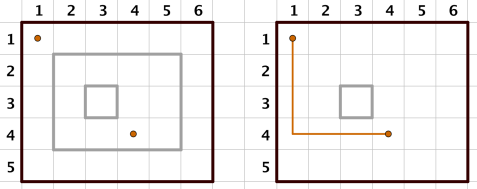
题目大意 在一个m×n的方格板上,操作1将一个矩形区域的边界上加上一圈障碍,操作2将一个矩形区域的边界上的障碍移除,操作3询问两点是否能不越过障碍互相到达。题目保证任意两圈矩形障碍不会有公共点(边界上)。
题目可以看成每次从平面中分割出一个小平面或者将一个平面复原,然后询问两个点是否在同一平面内。
于是常用套路打标记。
Solution 1 暴力差分
每次修改操作暴力每行进行差分。
当然这个差分得稍微改一下,前者用一个独一无二的正数,后者用一个负数。
查询的时候进行由那一行首往后扫描,如果遇到正数就压入栈,遇到负数就弹处栈顶。
最终栈顶就是这个点所在平面的标号。由于开始是在最外面的平面,所以首先在栈中加入一个元素。
然后判断一下两个点是否在同一平面就行了。
如果代码比较丑,请卡常数。
(最坏的时间复杂度是O(nq),虽然觉得不可思议,但它就是过了。。)
Code
/**
* Codeforces
* Problem#869E
* Accepted
* Time: 1934ms
* Memory: 24600k
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; int n, m, q;
int top = ;
int sta[];
int mp[][]; inline void init() {
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &q);
} int getSign(int x, int y) {
top = ;
sta[] = ;
for(int i = ; i <= y; i++) {
if(mp[x][i] > )
sta[++top] = mp[x][i];
else if(mp[x][i] < )
top--;
}
return sta[top];
} inline void solve() {
int opt, x1, y1, x2, y2;
while(q--) {
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &opt, &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
switch(opt) {
case :
for(int i = x1; i <= x2; i++)
mp[i][y1] = q, mp[i][y2 + ] = -;
break;
case :
for(int i = x1; i <= x2; i++)
mp[i][y1] = , mp[i][y2 + ] = ;
break;
case :
top = ;
puts((getSign(x1, y1) == getSign(x2, y2)) ? ("Yes") : ("No"));
break;
}
}
} int main() {
init();
solve();
return ;
}
The Untended Antiquity(Brute force)
Solution 2 随机化标号
思想仍然是差分,这次思考能不能想普通的差分一样做,可以扔进某个数据结构维护前缀和。
是不是可以前面 + 标号,右边的后一个 - 标号?很遗憾这么做是错误的。
比如一处+1 +2,而另一处是+3,显然它们不在一个平面内,但是这个算法会认为它们在一个平面内。
那怎么办呢?rand啊!没人知道它的标号是什么,可以通过两次rand得到一个30位的数,这样几乎不可能被卡掉。
Code
/**
* Codeforces
* Problem#869E
* Accepted
* Time: 109ms
* Memory: 49300k
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//#define lowbit(_x) (_x & (-_x))
#define ll long long
#define pii pair<int, int> int n, m, q;
int top = ;
ll f[][];
map< pair< pii, pii >, int> g; inline int lowbit(int x) {
return x & -x;
} inline void init() {
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &q);
} inline int rd() {
return rand() << | rand();
} inline void add(int x, int y, int val) {
for(; x <= n + ; x += lowbit(x))
for(int j = y; j <= m + ; j += lowbit(j))
f[x][j] += val;
} inline ll getSum(int x, int y) {
ll rt = ;
for(; x; x -= lowbit(x))
for(int j = y; j; j -= lowbit(j))
rt += f[x][j];
return rt;
} template<typename V, typename K>
pair<V, K> makepair(V a, K b) {
return pair<V, K>(a, b);
} inline void solve() {
srand((unsigned) time (NULL));
for(int i = ; i <= ; i++)
srand(rd());
int opt, x1, y1, x2, y2, v;
while(q--) {
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &opt, &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
switch(opt) {
case :
v = rd();
g[makepair(pii(x1, y1), pii(x2, y2))] = v;
add(x2 + , y2 + , v), add(x1, y1, v);
add(x1, y2 + , -v), add(x2 + , y1, -v);
break;
case :
v = g[makepair(pii(x1, y1), pii(x2, y2))];
add(x2 + , y2 + , -v), add(x1, y1, -v);
add(x1, y2 + , v), add(x2 + , y1, v);
break;
case :
// cerr << getSum(x1, y1) << " " << getSum(x2, y2) << endl;
puts((getSum(x1, y1) == getSum(x2, y2)) ? ("Yes") : ("No"));
break;
}
}
} int main() {
init();
solve();
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #439 (Div. 2) Problem E (Codeforces 869E) - 暴力 - 随机化 - 二维树状数组 - 差分的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #439 (Div. 2) Problem C (Codeforces 869C) - 组合数学
— This is not playing but duty as allies of justice, Nii-chan! — Not allies but justice itself, Onii ...
- Codeforces Round #439 (Div. 2) Problem B (Codeforces 869B)
Even if the world is full of counterfeits, I still regard it as wonderful. Pile up herbs and incense ...
- Codeforces Round #439 (Div. 2) Problem A (Codeforces 869A) - 暴力
Rock... Paper! After Karen have found the deterministic winning (losing?) strategy for rock-paper-sc ...
- Codeforces Round #198 (Div. 1) D. Iahub and Xors 二维树状数组*
D. Iahub and Xors Iahub does not like background stories, so he'll tell you exactly what this prob ...
- Codeforces 707 E. Garlands (二维树状数组)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/707/E 给你nxm的网格,有k条链,每条链上有len个节点,每个节点有一个值. 有q个操作,操作ask问 ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) E. Garlands 二维树状数组 暴力
E. Garlands 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/E Description Like all children, Ale ...
- Codeforces Round #369 (Div. 2) A. Bus to Udayland【字符串/二维字符数组求连起来的座位并改为其他字符】
A. Bus to Udayland time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- HDU5465/BestCoder Round #56 (div.2) 二维树状数组
Clarke and puzzle 问题描述 克拉克是一名人格分裂患者.某一天,有两个克拉克(aa和bb)在玩一个方格游戏. 这个方格是一个n*mn∗m的矩阵,每个格子里有一个数c_{i, j}ci ...
- Codeforces #590 D 二维树状数组
题意 给一个10^5之内的字符串(小写字母)时限2s 输入n,有n个操作 (n<10^5) 当操作是1的时候,输入位置x和改变的字母 当操作是2的时候,输入区间l和r,有多少不同的字母 思路 ...
随机推荐
- servlet的请求转发与重定向
重定向: Spring的重定向 spring的请求转发:
- MFC 运行报错:Debug Assertion Failed! dbgheap.c
对话框已调用DestroyWindow 时,在调用delete this导致
- 001-http协议-请求报文以及服务器响应状态
Http协议的几个概念: 1.连接(Connection):浏览器和服务器之间传输数据的通道. 一般请求完毕就关闭,http不保持连接.不保持连接会降低处理速度(因为建立连接速度很慢),保持连接的话就 ...
- python windows 安装pandas,numpy....
用cmd进入python的安装目录的sripts文件夹下,输入pip install pandas 等它自己下载安装完成,提示
- 提高Linux运维效率的30个命令行常用快捷键
提高Linux运维效率的30个命令行常用快捷键 表4-1 30个常用快捷键 快捷键 功能说明 最有用快捷键 tab 命令或路径等的补全键,Linux最有用快捷键* 移动光标快捷键 Ctrl+a 光标 ...
- 了解MQ
一.了解RocketMQ? rocketMQ是阿里开源的一款十分优秀的消息队列,rocketMQ具有很多其他消息队列不具有的特性,更重要的是rocketMQ是用java开发的学习成本较低,并且经历了双 ...
- jQuery-设计模式
[目录] 一.选择网页元素 二.改变结果集 三.链式操作 四.元素的操作:取值和赋值 五.元素的操作:移动 六.元素的操作:复制.删除和创建 七.工具方法 八.事件操作 九.特殊效果 [正文] 一.选 ...
- (转)Hashtable与ConcurrentHashMap区别
ConcurrentHashMap融合了hashtable和hashmap二者的优势. hashtable是做了同步的,hashmap未考虑同步.所以hashmap在单线程情况下效率较高.hashta ...
- SQL 跟据出生日期求年龄
最近做项目时遇到一个问题. 跟据人员的生日与当前日期进行比较求出该人员实际年龄.这个看上去比较简单的问题,其实不细心去看也会有很多问题. 先看第一种: 一张人员信息表里有一人生日(Birthday)列 ...
- Mysql版本java问题(com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver和com.mysql.jdbc.Driver)
老版本com.mysql.jdbc.Driver已弃用 String url1 = "jabc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test"; String url1 ...
