前端(四):JavaScript面向对象之自定义对象
一、对象
1.字面量创建对象
var person = {
name: "sun",
age: 18,
work: function () {
console.log(this.name + "is working...");
},
address: {
home: "大屯里xxx路xxx小区xx单元xxx室",
phone: "123456789",
}
};
person.work();
console.log(person.address.home);
2.数据描述和存取描述设置
var person = {
age: 18,
address: {
home: "大屯里xxx路xxx小区xx单元xxx室",
phone: "123456789",
}
};
Object.defineProperties(person, {
name: {
value: "sun", // 该属性的值,可被读取
writable: true, // 表示能否修改属性的值,默认值为true
configurable: true, // 表示能否delete该属性并重新定义,直接在对象上定义的属性默认值为true
enumerable: true // 表示能否通过for-in枚举,直接在对象上定义的属性默认值为true
},
work: {
value: function(){
console.log(this.name + "is working...");
},
// 通过Object.defineProperty和Object.defineProperties定义属性,
// 如果没有声明writable、configurable、enumerable,它们的默认值都是false
}
});
person.work();
console.log(person.address.home);
3.get和set
var circle = {
value: 10,
get girth(){
return 2 * 3.14 * this.R
},
get area(){
return 3.4 * this.R * this.R
},
};
Object.defineProperty(circle, "R", {
get : function () {
return this.value;
},
set : function (val) {
console.log("半径被修改了!");
this.value = val;
}
});
circle.R = 100;
console.log("girth: " + circle.girth + "area: " + circle.area);
4.数据描述和存取描述检查
var circle = {
R: 10,
// __proto__: null,
get area(){
return 3.4 * this.R * this.R
},
};
Object.defineProperty(circle, "site", {
value: [0, 2.2, 4.1],
// enumerable: true, // 是否可配置(读取),不设置为true时,Object.keys(circle))和Object.values(circle))将获取不到该键值对
});
console.log("R" in circle); // 检查属性
console.log(circle.hasOwnProperty("R")); // 检查自有的属性
console.log(circle.propertyIsEnumerable("R")); // 检查属性是否是可枚举的
// Object对象的方法
console.log(Object.keys(circle));
console.log(Object.values(circle));
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(circle)); // 检查对象自身所有属性
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(circle, "R")); // 得到circle对象关于R属性的描述
二、prototype
1.prototype释义
- 每一次创建函数,解析器都会向函数中添加一个属性:prototype
- 如果函数作为普通函数调用prototype,没有任何作用
- 当该函数以构造函数的形式调用时,它会有一个隐含的属性__proto__指向其原型对象
- 每个实例有各自的__proto__指向原型对象的prototype, 也就是原型对象中的属性和方法被调用函数"共享"
- 当类的原型对象prototype指向的内存地址发生改变时,已创建实例的__proto__ !== prototype,也就是不会被覆盖。而新创建的实例仍然是__proto__ === prototyp
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// Person.prototype.gender = "male";
// Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
// return this.name + ", " + this.age + "years old."
// };
Person.prototype = {
gender: "male",
sayHello: function () {
return this.name + ", " + this.age + "years old."
}
};
var p1 = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
p1.sayHello();
console.log(Person.prototype);
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person);
2.prototype与__proto__
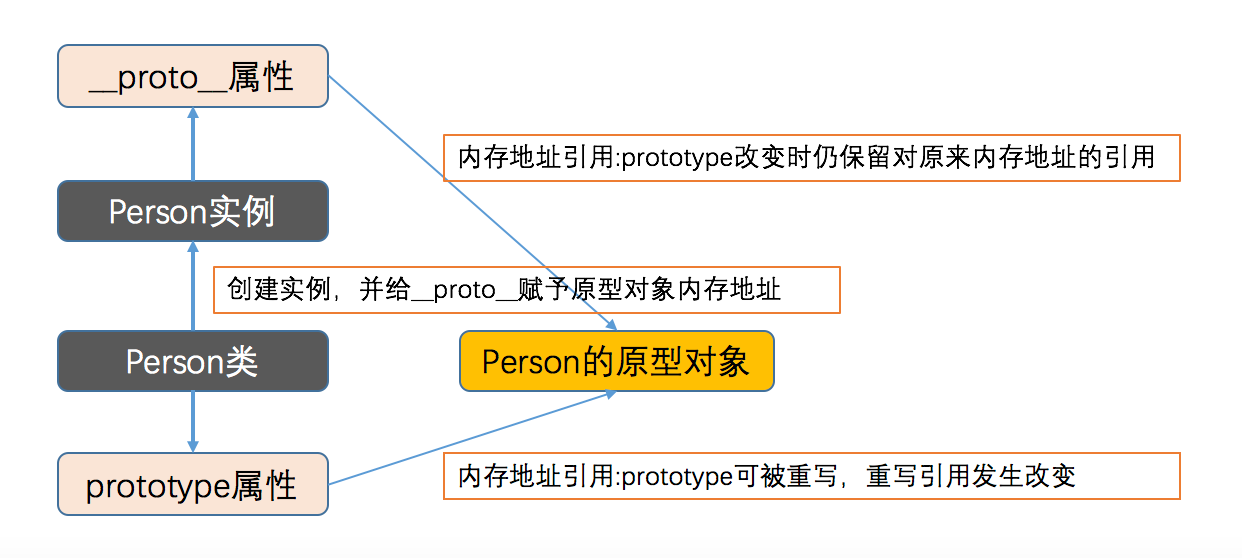
function Person() {}
var obj1 = { gender: "male"}; // 创建两个内存地址
var obj2 = { age: 200 };
Person.prototype = obj1;
var p1 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__ === Person.prototype);
console.log(p1.__proto__.gender);
console.log(Person.prototype);
Person.prototype = obj2;
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p2.__proto__.age);
console.log(Person.prototype);
console.log(p1.__proto__.age); // undefined
console.log(p2.__proto__.gender); // undefined
console.log(p1.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // false,表示当prototype指向的内存地址改变时,已经创建的实例对象的__proto__仍指向原来的内存地址
console.log(p2.__proto__ === Person.prototype);
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {name: "xxx", age: 100,};
var p1 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__.name);
Person.prototype = { price: 998,};
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p2.__proto__.price);
console.log(p1.__proto__.price); // undefined
console.log(p2.__proto__.name); // undefiend
console.log(p1.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // false, 原型对象的内存地址引用已发生改变
console.log(p1.__proto__.age); // __proto__指向的内存地址被保留
console.log(p2.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // true
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = { price: 60 };
var p1 = new Person();
Person.prototype = { price: 998};
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // 依然是false
console.log(p2.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // true
3.prototype之共享性
// prototype非常类似python中的静态属性和静态方法。每个实例都可以访问同一块内存空间。
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {price: 60}; var p1 = new Person();
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p1.__proto__.price);
console.log(p2.__proto__.price);
console.log(Person.prototype.price);
4.prototype之继承性
// 当访问实例对象的一个属性或方法时,它会先在对象自身中查找,如果有则直接使用;如果没有则在原型对象中继续查找,如果有则直接使用
function Person() {}
Person.prototype = {price: 60}; var p1 = new Person();
var p2 = new Person();
console.log(p1.price);
console.log(p2.price);
console.log(Person.prototype.price);
三、类
1.类的封装
// 字面量方法(工厂方法) -- 直接在var obj = {}内部写代码,缺点是只实例化一次
// 构造函数方法 -- 只用构造函数声明this,缺点是可扩展性差,数据重复
// 原型方法 -- 只用prototype声明共有的属性和方法,缺点是实例的数据相同,不满足多态
1.混合的构造函数/原型方法
// 最广泛的使用方法
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// prototype写在外面是为了保证其动态增加公共属性和方法
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + " years old."); // 把共有的属性和方法封装到prototype中
};
var p = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
p.sayHello();
// 我把它写给Person的属性,让父类也能够访问
function Person(name, age) {
Person.group = Person.prototype.group = "西天取经组";
Person.toString = Person.prototype.toString = function (){
console.log("Person: " + Person.group)
};
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + "years old.")
};
}
var person = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
console.log(person.constructor); // 检查构造器函数
console.log(person instanceof Person); // 检查是否为其原型类
person.sayHello();
Person.toString();
2.动态原型方法
// 也是常用的方法
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
if (typeof Person._initialized === "undefined"){
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + " years old.");
};
Person._initialized = true;
}
}
var p = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
p.sayHello();
3.混合工厂方法
// 混合工厂方法 -- 存在与工厂方法类似的问题,不建议使用
function Person(name, age) {
var obj = {};
obj.name = name;
obj.age = age;
obj.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + " years old.");
};
return obj
}
var p = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
p.sayHello();
4.再探讨类结构
function Person(name, age) {
// 静态属性
Person.group = "西天取经四人组,暗合金木水火土";
// 静态方法
Person.introduce = function () {
console.log("贫僧自东土大唐而来")
};
// 实例属性
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
// 实例方法,应该写在prototype中
this.say = function () {
console.log("hello, i'm " + this.name);
};
Person.prototype.introduce = Person.introduce; // 此时Person类和其实例都可以使用introduce方法
// 父类使用实例方法
Person.example = Person.prototype.example = function (self) {
self = self || this;
console.log(self.name + " " + self.age);
}
}
// 在python中,实例可以访问父类的属性和方法,父类也可以使用实例方法
// 在java和js中,实例不能调用父类的静态属性和静态方法,父类不能使用实例方法
// 如果想让实例和父类共享一个属性或者方法,就只能放到方法区并创建引用
var sun = new Person("孙悟空", 2000);
Person.introduce(); // 父类调用静态方法
sun.say();
sun.introduce(); // 实例调用静态方法
Person.example(sun); // 父类调用实例方法
sun.example(); // 子类调用实例方法
// 可见,prototype是父类和实例的沟通桥梁
2.自定义类
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sayHello = function () {
console.log(this.name + ", " + this.age + "years old.")
};
}
function New(Person) {
return function () {
var obj = {"__proto__": Person.prototype}; // 必须写在这里
Person.apply(obj, arguments); // arguments同this一样,是默认自带的关键字,用于存储传入的参数
return obj
}
}
var temp = New(Person);
var p1 = temp("孙悟空", 2000);
var p2 = temp("猪八戒", 1);
p1.sayHello();
p2.sayHello();
3.类的继承
1.拷贝继承字面量对象(实例)
var person = {
name: "Li",
age: 16,
address: {
home: "none",
city: "none",
},
say: function(){
console.log("hello, guy.")
}
};
var child = {gender:"female",};
function extendDeeply (p, c){
var c = c || {};
for (var prop in p) {
if (typeof p[prop] === "object") {
c[prop] = (p[prop].constructor === Array) ? [] : {};
extendDeeply(p[prop], c[prop]);
} else {
c[prop] = p[prop];
}
}
}
extendDeeply(person, child);
console.log(child);
child.say();
2.call和apply实现对象继承
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = {
home: "none",
city: "none",
}
}
Person.prototype.say = function () {
console.log("hello, guy.")
};
// 它继承的只是实例对象this,无法继承父类原型prototyp
function Child(name, age) {
Person.call(this, name, age);
this.gender = "female";
}
var child = new Child("Li", 16);
console.log(child);
// child.say(); 报错: child.say is not a function.
对象继承的缺点:只继承了实例对象的可访问的属性和方法,没有继承原型
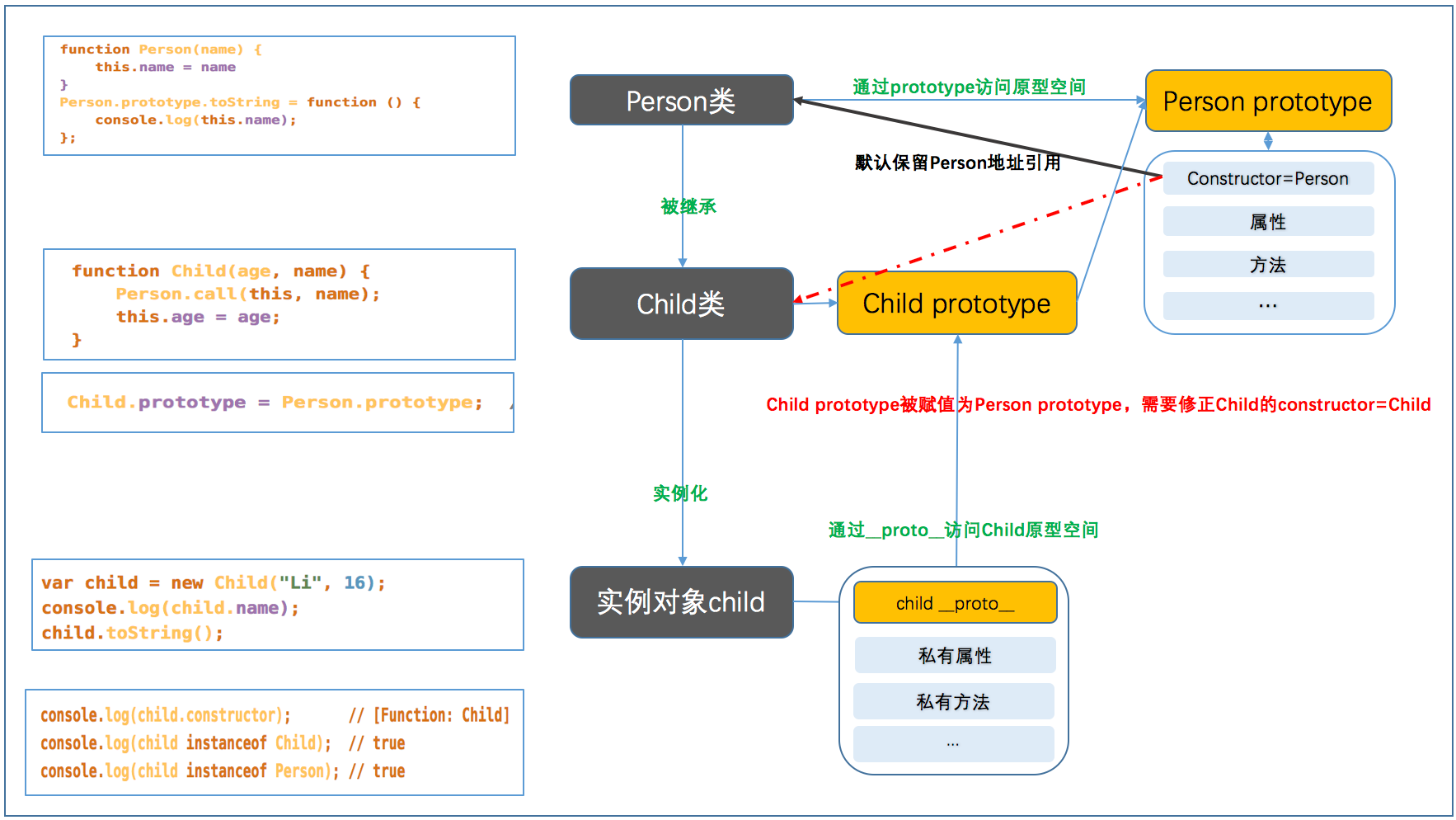
3.原型链继承
// 原型链继承
function Person() {}
Person.prototype.name = "Person";
Person.prototype.toString = function () {
console.log(this.name);
}; function Child(name, age) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
Child.prototype = Person.prototype;
Child.prototype.constructor = Child; var child = new Child("Li", 16);
console.log(child.name + " " + child.age);
child.toString();
// 其缺点是之继承了原型,没有继承实例
4.create实现类继承
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = {
home: "none",
city: "none",
}
}
Person.prototype.say = function () {
console.log("hello, guy.")
};
function Child(P, name, age) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = new P(name, age);
var c = new F();
return c;
}
Child.prototype.constructor = Child; // 无法修正
var child = new Child(Person, "Li", 16);
console.log(child);
console.log(child.name);
child.say();
console.log(child.constructor); // 结果为[Function: Person],构造器指向无法修正
console.log(child instanceof Child); // false
console.log(child instanceof Person); // true
5.Object.create实现类继承 -- 推荐的方式
// Object.create继承,实现原理和上面的create类似
// 1.创建父类
function Person() {}
Person.prototype.sayPerson = function () {
console.log("hello, Person.")
};
// 2.创建子类
function Child(gender) {this.gender = gender;} // 3.create继承
// Object.create的第二个参数是属性描述
Child.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype, {
name: {
value: "Li",
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
},
age: {
value: 16,
writable:true,
configurable:true,
enumerable:true,
},
}); // 重写子类prototype
Child.prototype.constructor = Child; // constructor 修正 // 4.在create之后写子类的prototype
Child.prototype.sayChild = function () {
console.log("hello, Child.")
}; var child = new Child("female");
console.log(child);
console.log(child.name + " " + child.age);
child.sayChild();
child.sayPerson();
5.组合继承 -- 推荐的方式
function Person(name, age) {
this.name =name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.toString = function () {
console.log(this.name + " " + this.age);
};
function Child(name, age, gender) {
Person.call(this, name, age);
this.gender = gender;
}
Child.prototype = new Person(); // new时不传参数,是为了只继承原型,即Child.prototype = Person.prototype
// Child.prototype = Person.prototype; // 两者等价
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
var child = new Child("Li", 16, "female");
console.log(child);
child.toString();
console.log(child instanceof Child); // true
console.log(child instanceof Person); // true
6.继承总结
js继承需要继承两部分内容:
- 一部分是父类构造函数中的this定义属性和方法,相当于继承初始化的数据
- 另一部分是父类的prototype,相当于继承实例方法
- 要实现this的继承,可以用call(apply);要实现prtotype的继承,可以用原型链
- 要实现两者的继承,可以用this+prototype的组合方式,Object.create本质上也是这种思路
7.prototype、constructor和__proto__在继承中的关系
前端(四):JavaScript面向对象之自定义对象的更多相关文章
- JavaScript 面向对象编程 · 理解对象
前言: 在我们深入 面向对象编程之前 ,让我们先理解一下Javascript的 对象(Object),我们可以把ECMAScript对象想象成散列表,其值无非就是一组名值对,其中值可以是数据 ...
- 重学前端--js是面向对象还是基于对象?
重学前端-面向对象 跟着winter老师一起,重新认识前端的知识框架 js面向对象或基于对象编程 以前感觉这两个在本质上没有什么区别,面向对象和基于对象都是对一个抽象的对象拥有一系列的行为和状态,本质 ...
- JavaScript 类的定义和引用 JavaScript高级培训 自定义对象
在Java语言中,我们可以定义自己的类,并根据这些类创建对象来使用,在Javascript中,我们也可以定义自己的类,例如定义User类.Hashtable类等等. 一,概述 在Java语言中 ...
- 前端(六):JavaScript面向对象之宿主对象
宿主对象即浏览器提供的对象,主要包括DOM对象和BOM对象. 一.DOM源起 1.SGML.XML和XHTML SGML(标准通用标记语言)是定义使用标签来表示数据的标记语言的语法. - 标签由一个小 ...
- 前端(五):JavaScript面向对象之内建对象
一.数据类型 js中数据类型分为两种,原始数据累次能够和引用数据类型. 1.原始数据类型 Undefined.Null.Boolean.Number.String是js中五种原始数据类型(primit ...
- JavaScript中创建自定义对象的方法
本文内容参考JavaScript高级程序设计(第3版)第6章:面向对象的程序设计 ECMA-262中把对象定义为:“无序属性的集合,其属性可以包含基本值.对象或者函数.”我所理解的就是对象就是一个结构 ...
- Javascript 中创建自定义对象的方法(设计模式)
Javascript 中创建对象,可以有很多种方法. Object构造函数/对象字面量: 抛开设计模式不谈,使用最基本的方法,就是先调用Object构造函数创建一个对象,然后给对象添加属性. var ...
- JavaScript面向对象之Windows对象
JavaScript之Window对象 首先我们先了解一个概念:事件. 事件,就是把一段代码设置好,满足条件时触发.或者说,事件是可以被 JavaScript 侦测到的行为. 网页中每个元素都可以触发 ...
- javascript面向对象(给对象添加属性和方法的方式)
1.在定义对象时,直接把属性和方法添加 <script type="text/JavaScript"> //给对象直接在定义时添加属性和方法 var g ...
随机推荐
- JS书籍推荐
JS书籍推荐 一.总结 一句话总结: 二.JS进阶书籍 第一阶段:<JavaScript DOM编程艺术> 看这本书之前,请先确认您对Javascript有个基本的了解,应该知道if el ...
- 微信小程序------联动选择器
picker 从底部弹起的滚动选择器,现支持五种选择器,通过mode来区分,分别是普通选择器,多列选择器,时间选择器,日期选择器,省市区选择器,默认是普通选择器. 先来看看效果图: 1:普通选择器 m ...
- wireshark初学者使用
介绍 Wireshark是一款网络封包分析软件,截取网络封包,显示其封包的详细信息.日常工作中用的比较多.在使用wireshark之前须了解常用的网络协议.如:tcp,http,ip,udp等.(其实 ...
- Log4j详细设置说明
1. 动态的改变记录级别和策略,即修改log4j.properties,不需要重启Web应用,这需要在web.xml中设置一下.2. 把log文件定在 /WEB-INF/logs/ 而不需要写绝对路径 ...
- 八、dbms_rls(实现精细访问控制)
1.概述 本报只适用于Oracle Enterprise Edition,它用于实现精细访问控制,并且精细访问控制是通过在SQL语句中动态增加谓词(WHERE子句)来实现的.通过使用ORACLE的精细 ...
- mysql主从复制跳过错误
mysql主从复制,经常会遇到错误而导致slave端复制中断,这个时候一般就需要人工干预,跳过错误才能继续 跳过错误有两种方式: 1.跳过指定数量的事务: mysql>slave stop; m ...
- iRSF快速简单易用的实现列表、排序、过滤功能
IRSF 是由javascript编写,iRSF快速简单易用的实现列表.排序.过滤功能(该三种操作以下简称为 RSF ). iRSF由三个类组成. iRSFSource 数据源 iRSFFilter ...
- 模式窗体中调用父页面js与非模式化调用非父页面的js方法
最近项目中使用模式窗体,遇到以下问题记录一下: 模式窗体:你必须关闭该窗体,才能操作其它窗体:比如说,必须按确定或取消,或者按关闭. 非模式窗体:不必关闭该窗体,就可转换到其它窗体上进行操作. 一:非 ...
- C与C++基础知识补遗
本随笔用来记载项目开发中遇到的以前没掌握的C/C++基础知识 void * buffer; 无类型指针,可以指向任何类型数据.ANSI标准规定无类型指针不能进行算法,而GNU规定无类型指针算法操作与c ...
- Android.mk编译的写法
更多Android.mk的 用法见 :http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/38705519 如何修改Android.mk 为Androi ...
