Linux进程的创建函数fork()及其fork内核实现解析【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/zengyiwen/p/5755193.html
#include <unistd.h>pid_t fork(void);
/proc/sys/kernel/sched_child_runs_first
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <string.h>#include <errno.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <wait.h>int g_int = 1;//数据段的全局变量int main(){int local_int = 1;//栈上的局部变量int *malloc_int = malloc(sizeof(int));//通过malloc动态分配在堆上的变量*malloc_int = 1;pid_t pid = fork();if(pid == 0) /*子进程*/{local_int = 0;g_int = 0;*malloc_int = 0;fprintf(stderr,"[CHILD ] child change local global malloc value to 0\n");free(malloc_int);sleep(10);fprintf(stderr,"[CHILD ] child exit\n");exit(0);}else if(pid < 0){printf("fork failed (%s)",strerror(errno));return 1;}fprintf(stderr,"[PARENT] wait child exit\n");waitpid(pid,NULL,0);fprintf(stderr,"[PARENT] child have exit\n");printf("[PARENT] g_int = %d\n",g_int);printf("[PARENT] local_int = %d\n",local_int);printf("[PARENT] malloc_int = %d\n",local_int);free(malloc_int);return 0;}
[PARENT] wait child exit[CHILD ] child change local global malloc value to 0[CHILD ] child exit[PARENT] child have exit[PARENT] g_int = 1[PARENT] local_int = 1[PARENT] malloc_int = 1
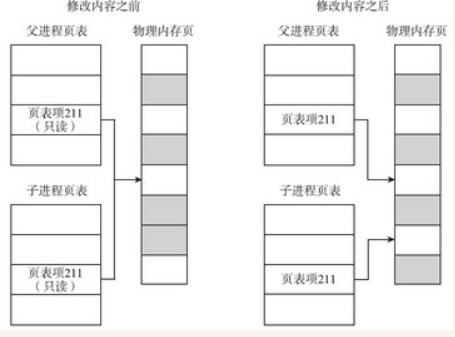
/*如果是写时拷贝, 那么无论是初始页表, 还是拷贝的页表, 都设置了写保护*后面无论父子进程, 修改页表对应位置的内存时, 都会触发page fault*/if (is_cow_mapping(vm_flags)) {ptep_set_wrprotect(src_mm, addr, src_pte);//设置为写保护pte = pte_wrprotect(pte);}
struct task_struct {...struct files_struct *files;...}
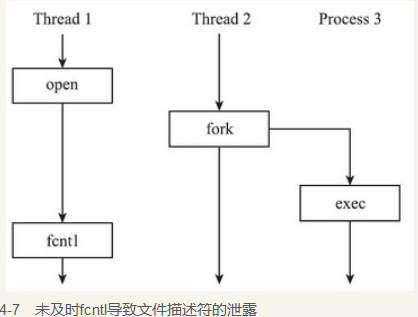
static int copy_files(unsigned long clone_flags,struct task_struct *tsk){struct files_struct *oldf, *newf;int error = 0;oldf = current->files;//获取父进程的文件结构体if (!oldf)goto out;/*创建线程和vfork, 都不用复制父进程的文件描述符, 增加引用计数即可*/if (clone_flags & CLONE_FILES) {atomic_inc(&oldf->count);goto out;}/*对于fork而言, 需要复制父进程的文件描述符*/newf = dup_fd(oldf, &error); //复制一份文件描述符if (!newf)goto out;tsk->files = newf;error = 0;out:return error;}
struct files_struct *dup_fd(struct files_struct *oldf,int *errorp){struct files_struct *newf;struct file **old_fds, **new_fds;int open_files, size, i;struct fdtable *old_fdt, *new_fdt;*errorp = -ENOMEM;newf = kmem_cache_alloc(files_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);if (!newf)goto out;
struct files_struct {atomic_t count;struct fdtable __rcu *fdt;struct fdtable fdtab;spinlock_t file_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;int next_fd;struct embedded_fd_set close_on_exec_init;struct embedded_fd_set open_fds_init;struct file __rcu * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];};struct fdtable //文件描述符表{unsigned int max_fds;struct file __rcu **fd; /* current fd array */fd_set *close_on_exec;fd_set *open_fds;struct rcu_head rcu;struct fdtable *next;};struct embedded_fd_set {unsigned long fds_bits[1];};
file类型指针的数组fd_array,也自带了两个大小为64的位图,其中open_fds_init位图用于记录文件的打开情况,close_on_exec_init位图用于记录文件描述符的FD_CLOSEXCE标志位是否置位。只要进程打开的文件个数小于64,file_struct结构体自带的指针数组和两个位图就足以满足需要。因此在分配了file_struct结构体后,内核会初始化file_struct自带的fdtable,代码如下所示:
atomic_set(&newf->count, 1);spin_lock_init(&newf->file_lock);newf->next_fd = 0;new_fdt = &newf->fdtab;new_fdt->max_fds = NR_OPEN_DEFAULT;new_fdt->close_on_exec = (fd_set *)&newf->close_on_exec_init;new_fdt->open_fds = (fd_set *)&newf->open_fds_init;new_fdt->fd = &newf->fd_array[0];new_fdt->next = NULL;

spin_lock(&oldf->file_lock);old_fdt = files_fdtable(oldf);open_files = count_open_files(old_fdt);/*如果父进程打开文件的个数超过NR_OPEN_DEFAULT*/while (unlikely(open_files > new_fdt->max_fds)) {spin_unlock(&oldf->file_lock); /* 如果不是自带的fdtable而是曾经分配的fdtable, 则需要先释放*/if (new_fdt != &newf->fdtab)__free_fdtable(new_fdt);/*创建新的fdtable*/new_fdt = alloc_fdtable(open_files - 1);if (!new_fdt) {*errorp = -ENOMEM;goto out_release;}/*如果超出了系统限制, 则返回EMFILE*/if (unlikely(new_fdt->max_fds < open_files)) {__free_fdtable(new_fdt);*errorp = -EMFILE;goto out_release;}spin_lock(&oldf->file_lock);old_fdt = files_fdtable(oldf);open_files = count_open_files(old_fdt);}
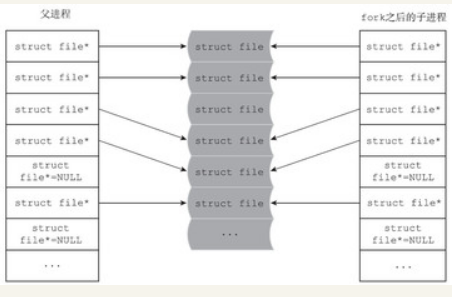
old_fds = old_fdt->fd;/*父进程的struct file 指针数组*/- new_fds = new_fdt->fd; /*子进程的struct file 指针数组*/
- /* 拷贝打开文件位图 */
- memcpy(new_fdt->open_fds->fds_bits,old_fdt->open_fds->fds_bits, open_files/8);
- /* 拷贝 close_on_exec位图 */
- memcpy(new_fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits,old_fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits, open_files/8);
- for (i = open_files; i != 0; i--) {
- struct file *f = *old_fds++;
- if (f) {
- get_file(f); /* f对应的文件的引用计数加1 */
- } else {
- FD_CLR(open_files - i, new_fdt->open_fds);
- }
- /* 子进程的struct file类型指针, *指向和父进程相同的struct file 结构体*/
- rcu_assign_pointer(*new_fds++, f);
- }
- spin_unlock(&oldf->file_lock);/* compute the remainder to be cleared */
- size = (new_fdt->max_fds - open_files) * sizeof(struct file *);
- /*将尚未分配到的struct file结构的指针清零*/
- memset(new_fds, 0, size);/*将尚未分配到的位图区域清零*/
- if (new_fdt->max_fds > open_files) {
- int left = (new_fdt->max_fds-open_files)/8;
- int start = open_files / (8 * sizeof(unsigned long));
memset(&new_fdt->open_fds->fds_bits[start], 0, left);memset(&new_fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits[start], 0, left);}rcu_assign_pointer(newf->fdt, new_fdt);return newf;out_release:kmem_cache_free(files_cachep, newf);out:return NULL;}
#include<stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>int glob = 88 ;int main(void) {int var;var = 88;pid_t pid;if ((pid = vfork()) < 0) {printf("vfork error");exit(-1);} else if (pid == 0) { /* 子进程 */var++;glob++;return 0;}printf("pid=%d, glob=%d, var=%d\n",getpid(), glob, var);return 0;}
Linux进程的创建函数fork()及其fork内核实现解析【转】的更多相关文章
- Linux进程的创建函数fork()及其fork内核实现解析
进程的创建之fork() Linux系统下,进程可以调用fork函数来创建新的进程.调用进程为父进程,被创建的进程为子进程. fork函数的接口定义如下: #include <unistd.h& ...
- linux 进程的创建
1. 进程号: 每个进程在被初始化的时候,系统都会为其分配一个唯一标识的进程id,称为进程号: 进程号的类型为pid_t,通过getpid()和getppid()可以获取当前进程号和当前进程的父进程的 ...
- linux进程学习-创建新进程
init进程将系统启动后,init将成为此后所有进程的祖先,此后的进程都是直接或间接从init进程“复制”而来.完成该“复制”功能的函数有fork()和clone()等. 一个进程(父进程)调用for ...
- linux进程解析--进程的创建
通常我们在代码中调用fork()来创建一个进程或者调用pthread_create()来创建一个线程,创建一个进程需要为其分配内存资源,文件资源,时间片资源等,在这里来描述一下linux进程的创建过程 ...
- Linux进程-进程的创建
今天学习了Linux的进程创建的基本原理,是基于0.11版本核心的.下面对其作一下简单的总结. 一.Linux进程在内存中的相关资源 很容易理解,Linux进程的创建过程就是内存中进程相关资源产生 ...
- Linux 进程,线程,线程池
在linux内核,线程与进程的区别很小,或者说内核并没有真正所谓单独的线程的概念,进程的创建函数是fork,而线程的创建是通过clone实现的. 而clone与fork都是调用do_fork(),差异 ...
- 撸代码--linux进程通信(基于共享内存)
1.实现亲缘关系进程的通信,父写子读 思路分析:1)首先我们须要创建一个共享内存. 2)父子进程的创建要用到fork函数.fork函数创建后,两个进程分别独立的执行. 3)父进程完毕写的内容.同一时候 ...
- Operating System-Process(1)什么是进程&&进程的创建(Creation)&&进程的终止(Termination)&&进程的状态(State)
本文阐述操作系统的核心概念之一:进程(Process),主要内容: 什么是进程 进程的创建(Creation) 进程的终止(Termination) 进程的状态(State) 一.什么是进程 1.1 ...
- 通过fork函数创建进程的跟踪,分析linux内核进程的创建
作者:吴乐 山东师范大学 <Linux内核分析>MOOC课程http://mooc.study.163.com/course/USTC-1000029000 一.实验过程 1.打开gdb, ...
随机推荐
- shell脚本如何获取当前时间
在shell脚本里常常需要获取系统时间来处理某项操作,linux的系统时间在shell里是可以直接调用系统变量的如: 获取今天时期:`date +%Y%m%d` 或 `date +%F` 或 $(da ...
- luogu 1066 引水入城(bfs+贪心)
90分,有一个点TLE.... 首先可以证明一个东西,如果从上面一排的某个点bfs一次到最下面一排的饮水点不是一个区间的话,那么最后一定所有饮水点不会被覆盖完的. 证明考虑反证法. 所以从上面一排的每 ...
- [codeforces743E]Vladik and cards
E. Vladik and cards time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- c# partial使用
1.有2个类 class1.cs ,class2.cs 2.这2个类里面都可以定义成这样 public partial class ClassAll { } 3.结果,里面的方法都是共享的,就像 ...
- 洛谷P4559 [JSOI2018]列队 【70分二分 + 主席树】
题目链接 洛谷P4559 题解 只会做\(70\)分的\(O(nlog^2n)\) 如果本来就在区间内的人是不用动的,区间右边的人往区间最右的那些空位跑,区间左边的人往区间最左的那些空位跑 找到这些空 ...
- Caffe框架详细梳理
protobuf是google公司开发的,并在Google内部久经考验的一个东西,在08年google把它贡献给了开源社区,随后便有越来越多的人使用它.protobuf是一个结构化信息传递的工具,主要 ...
- Httpclient与RestTemplate的比较(比httpClient更优雅的Restful URL访问)
一.HttpClient (一)HttpClient 客户端 1.HttpClient 是 apache 的开源,需要引入两个包:httpclient-4.2.4.jar 和 httpcore-4.2 ...
- 全表 or 索引
这一篇文章证实了以前对MySQL优化程序的工作原理. MySQL就像一个人一样,总是聪明的去选择当前最快的方式去查询,而不是像Oracle数据那样死板地根据规格去查询. 查询的要求在于快.而对于数据库 ...
- vmware中无法ping通主机的问题
虚拟机使用NAT方式运行一段时间后,发现无法ping通主机(物理机),显示错误如下 ipconfig如下 查看虚拟机中的网络连接,显示"未识别网络" 分析: 查看了网络上的一些资料 ...
- LeetCode-Max Points on a Line[AC源码]
package com.lw.leet3; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; imp ...
