socker TCP UDP BIO NIO
BIO: Java 1.4 以前只有之中方式。
bio:阻塞式IO, 一个 socker 连接占用一个 线程。如果 IO 阻塞,会在传输速度限制,这个线程也会一直等待在这里,等待从socker 的 IO 流 中读写数据。
Java 基于 socker 的 连接方式都是 BIO,都是阻塞式的IO。
TCP:
server:
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(20000);
while( true ) {
Socket socket = ss.accept();
List<String> datas = IOUtils.readLines( socket.getInputStream() );
System.out.println( datas.get(0) );
socket.close(); }
cilent:
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 20000);
IOUtils.write("hello", socket.getOutputStream() );
socket.getOutputStream().flush();
socket.getOutputStream().close();
socket.close();
原理图: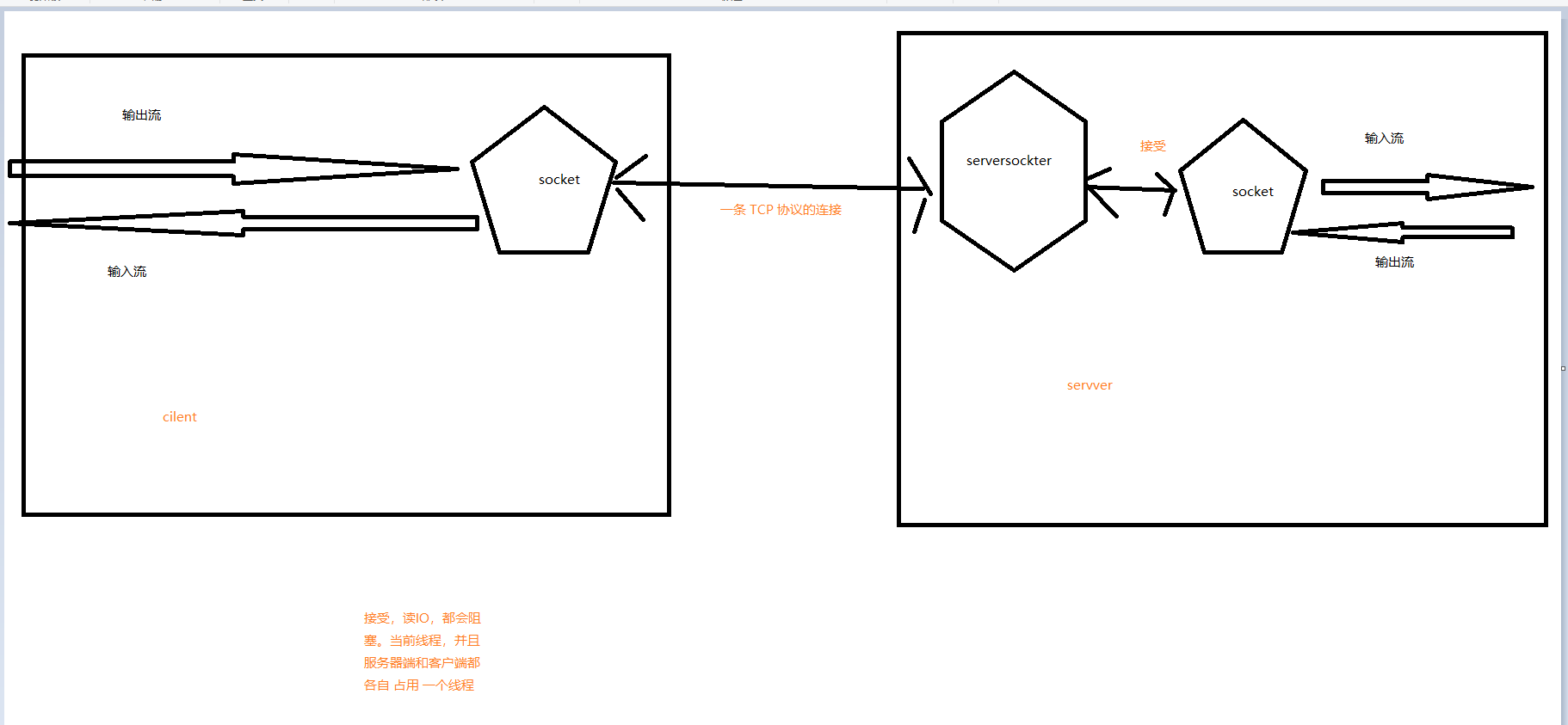
UDP:
server:
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(20000);
while( true ) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
ds.receive( dp );
System.out.println( new String(dp.getData()) );
}
client:
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
String data = "hello";
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(data.getBytes(),data.length(),InetAddress.getLocalHost(),20000);
ds.send(dp);
NIO: Java 1.4 以后支持的IO方式
NIO: 非阻塞式的IO, NIO 不再是 传统socker 方式。 一个 IO请求过来,会有一个线程,来处理这个IO请求,但是如果这个IO阻塞,那么这个线程会被处理别的 IO请求的 的事情。如果阻塞的IO的操作完成(完成一个块数据写入缓冲区),那么就会有一个线程分配过来处理这部分数据。
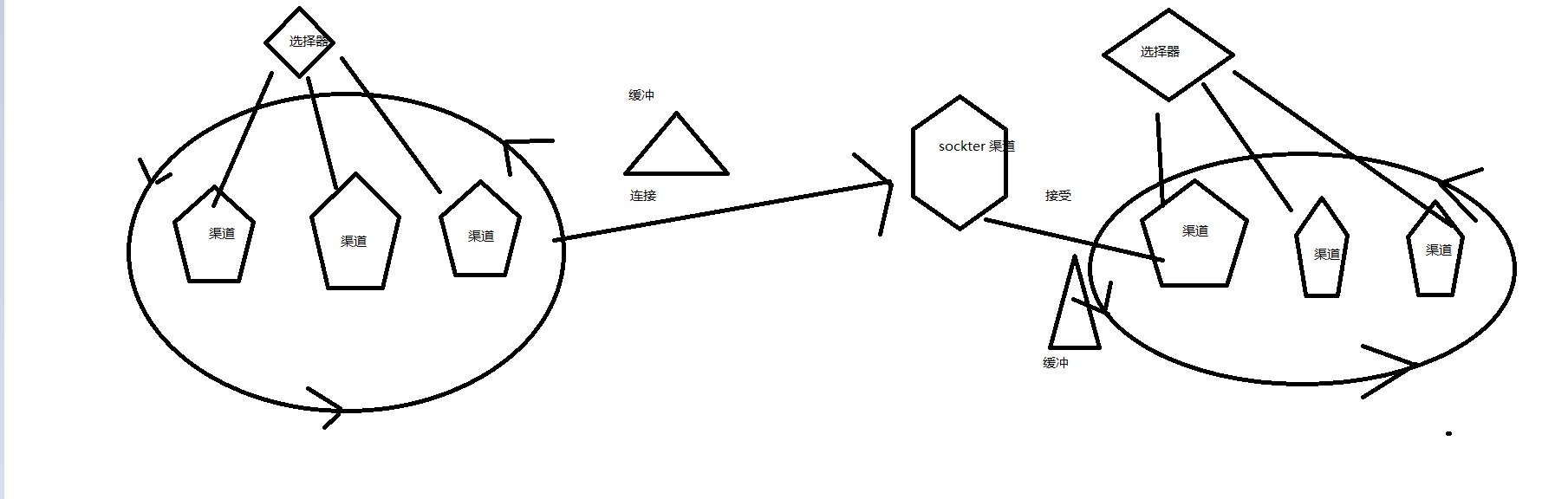
selecter: NIO 不再是 传统socke的概念。 socker 一个 连接,就固定一个 线程来处理,并且这个线程值服务这个 socker。但是 NIO 改变了这种IO 模型, selecter 里面跑着一个独立的线程,这个线程管理 一些渠道( channel , 有点 类似 socker ),如果 某个
渠道的 数据准备好了,那么 selecter 就会分配一个线程来 读写 这个channet 的数据。
buffer: 前面 一直强调 当数据准备好了,什么样才叫数据准备好了? socker 方式的 io 模式是一个 字节 一个字节读写的。 NIO 是通过 一块一块读写的( 一块就是 多个字节 ),但是这个这个 一块数据是 需要 一个临时存放区域的,这就是buffer 。当一个 块 数据满了以后,就分配 线程 来执行这个请求。
channel: 相当于以前的 流的 概念,可以 李杰成一个管道。BIO 一个连接一个线程,并且在socker结束以前一直占用着这个线程。NIO 是一个 也是一个连接一个线程。但是这个线程不会一直 等待这个 连接的IO操作。
例子代码:
server:
package comcxygg.test.nio; import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.UUID; public class NioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 开启一个服务端
* 设置为非阻塞
* 绑定端口号
*/
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080)); System.out.println("serverSocketChannel:" + serverSocketChannel.hashCode() );
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//UUID->客户端连接
Map<String,SocketChannel> clientMap = new HashMap<>(); while (true) {
selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
selectionKeys.forEach(selectionKey -> { try {
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
/**
* 服务端接收到连接
* 保存接收到的客户端连接
*/
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
System.out.println("server:" + server.hashCode() ); SocketChannel socketChannel = server.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
String key = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
clientMap.put(key,socketChannel);
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress()+"连接上了服务器");
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
/**
* 读取客户端消息
* 转发到所有客户端
*/
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); System.out.println( "服务器端socketChannel:" + socketChannel.hashCode());
try {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = socketChannel.read(buffer); if (len > 0) {
buffer.flip();
Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
String receiveMsg = String.valueOf(charset.decode(buffer).array());
String key = null;
for (Map.Entry<String,SocketChannel> entry : clientMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() == socketChannel) {
key = entry.getKey();
break;
}
}
String sendMsg = key + ":" + receiveMsg;
System.out.println(sendMsg);
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
writeBuffer.put(sendMsg.getBytes());
writeBuffer.flip();
clientMap.get(key).write( writeBuffer );
/* for (Map.Entry<String,SocketChannel> entry : clientMap.entrySet()) {
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
writeBuffer.put(sendMsg.getBytes());
writeBuffer.flip();
entry.getValue().write(writeBuffer);
}*/
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();//java.io.IOException: 远程主机强迫关闭了一个现有的连接。
socketChannel.close();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
selectionKeys.clear();
} }
}
client:
package comcxygg.test.nio; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class NioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 开启一个客户端
* 设置为非阻塞
* 连接到服务器
*/
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",8080)); Selector selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); System.out.println( "socketChannel:" + socketChannel.hashCode() ); while (true) {
selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
for (SelectionKey selectionKey : selectionKeys) {
if (selectionKey.isConnectable()) {
/**
* 客户端已连接
* 开启一个线程监听控制台输入
*/
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
System.out.println( "client1:" + client.hashCode() );
if (client.isConnectionPending()) {
client.finishConnect();
}
client.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
System.out.println(socketChannel.getLocalAddress()+"连上了服务器");
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
executor.submit(()->{
try {
while (true) {
writeBuffer.clear();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line = reader.readLine();
writeBuffer.put(line.getBytes());
writeBuffer.flip();
client.write(writeBuffer);
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) { /**
* 打印服务端消息
*/
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
System.out.println( "client2:" + client.hashCode() );
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = client.read(readBuffer);
System.out.println(new String(readBuffer.array(),0,len));
}
}
selectionKeys.clear();
}
}
}
BIO 图:
NIO 的 UDP 协议使用:
别的基本一样 只是 渠道使用的 DatagramChannel 。
socker TCP UDP BIO NIO的更多相关文章
- 拿搬东西来解释udp tcpip bio nio aio aio异步
[群主]雷欧纳德简单理解 tcpip是有通信确认的面对面通信 有打招呼的过程 有建立通道的过程 有保持通道的确认 有具体传输udp是看到对面的人好像在对面等你 就往对面扔东西[群主]雷欧 ...
- Netty5序章之BIO NIO AIO演变
Netty5序章之BIO NIO AIO演变 Netty是一个提供异步事件驱动的网络应用框架,用以快速开发高性能.高可靠的网络服务器和客户端程序.Netty简化了网络程序的开发,是很多框架和公司都在使 ...
- Netty序章之BIO NIO AIO演变
Netty序章之BIO NIO AIO演变 Netty是一个提供异步事件驱动的网络应用框架,用以快速开发高性能.高可靠的网络服务器和客户端程序.Netty简化了网络程序的开发,是很多框架和公司都在使用 ...
- BIO & NIO & NIO常见框架
BIO & NIO BIO - Blocking IO - 同步式阻塞式IO --- UDP/TCP NIO - New IO - 同步式非阻塞式IO AIO - Asynchronous ...
- tomcat bio nio apr 模式性能测试
转自:tomcat bio nio apr 模式性能测试与个人看法 11.11活动当天,服务器负载过大,导致部分页面出现了不可访问的状态.那后来主管就要求调优了,下面是tomcat bio.nio.a ...
- I/O模型系列之三:IO通信模型BIO NIO AIO
一.传统的BIO 网络编程的基本模型是Client/Server模型,也就是两个进程之间进行相互通信,其中服务端提供位置信息(绑定的IP地址和监听端口),客户端通过连接操作向服务端监听的地址发起连接请 ...
- BIO,NIO与AIO的区别
Java NIO : 同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个请求一个线程,即客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接有I/O请求时才启动一个线程进行处理.Java AIO(NIO.2 ...
- 【netty】(1)---BIO NIO AIO演变
BIO NIO AIO演变 Netty是一个提供异步事件驱动的网络应用框架,用以快速开发高性能.高可靠的网络服务器和客户端程序.Netty简化了网络程序的开发,是很多框架和公司都在使用的技术. Net ...
- Java提供了哪些IO方式?IO, BIO, NIO, AIO是什么?
IO一直是软件开发中的核心部分之一,而随着互联网技术的提高,IO的重要性也越来越重.纵观开发界,能够巧妙运用IO,不但对于公司,而且对于开发人员都非常的重要.Java的IO机制也是一直在不断的完善,以 ...
随机推荐
- loj2494 [hnoi2018]寻宝游戏
题意:给你n个元素的数组a.你可以在每个元素之前添加and和or的符号.每次询问最后变成r有多少种添号情况. n<=1000,m<=5000,q<=1000. 标程: #includ ...
- sql中on的连接条件与where的区别
left join [表名] on [条件] where [条件] --on表示连接条件 --where表示对结果的过滤条件 两者不尽相同,使用时需注意 例如: select * from tabl ...
- ThinkPHP模型基础类提供的连贯操作方法
ThinkPHP模型基础类提供的连贯操作方法(也有些框架称之为链式操作),可以有效的提高数据存取的代码清晰度和开发效率,并且支持所有的CURD操作. 直线电机哪家好 使用也比较简单, 假如我们现在要查 ...
- 洛谷 2915 [USACO08NOV]奶牛混合起来Mixed Up Cows
一道水状压,然而不知道是不是太久没做过dp了,我盯着它二十分钟才反应过来.... 还把数组开小了WA了一发QAQ //Twenty #include<algorithm> #include ...
- Python GUI文本编辑器
使用Python编写一个简单的文本编辑器,需要展示一个用户界面,功能包括打开.保存文本文件. 使用tkinter库来编写GUI. #简单GUI文本编辑器 from tkinter import * f ...
- <每日一题>题目25:快速排序
''' 快速排序:分而治之,一分为二进行排序 ''' import cProfile import random def quick_sort(nums): if len(nums) <= 1: ...
- 基于neighborhood models(item-based) 的个性化推荐系统
文章主要介绍的是koren 08年发的论文[1], 2.2neighborhood models部分内容(其余部分会陆续补充上来). koren论文中用到netflix 数据集, 过于大, 在普通的 ...
- C# 判断当前请求是GET、还是POST ?
方法一: HttpContext.Current.Request.RequestType == "POST" //当前请求为:POST 方法二: if(Request.Serv ...
- selenium简单应用
文章引用自:https://wenku.baidu.com/view/d5c296c75727a5e9846a6182.html 例子:
- java连接SQLserver数据库模板代码
package cn.mldn.lxh.dbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; public class Dat ...
