Redis(九):主从复制的设计与实现解析
前面几篇我们已经完全理解了redis的基本功能的实现了。
但单靠基本功能实现,往往还是称不上优秀的项目的。毕竟,我们现在面对的都是复杂的环境,高并发的场景,大数据量的可能。
简而言之,现在的系统一般都需要支持分布式部署,不存在单点问题,才算是一个合格的系统。
而redis作为一个存储系统,单点问题肯定是不行的。
最简单的,就是起码得支持读写分离功能,因为我们面临的许多问题,一般是面对大量的查询问题。而要做到读写分离功能,就是要把主节点的数据同步到从节点上。从而可以让从节点接受读请求,以减轻主节点的读压力。
就让我们来分析下 Redis 是如何进行主从同步数据的吧!主从同步,换个名称也就是数据复制。
0. 主从复制的作用
数据冗余:主从复制实现了数据的热备份,是持久化之外的一种数据冗余方式。
故障恢复:当主节点出现问题时,可以由从节点提供服务,实现快速的故障恢复;实际上是一种服务的冗余。
负载均衡:在主从复制的基础上,配合读写分离,可以由主节点提供写服务,由从节点提供读服务(即写Redis数据时应用连接主节点,读Redis数据时应用连接从节点),分担服务器负载;尤其是在写少读多的场景下,通过多个从节点分担读负载,可以大大提高Redis服务器的并发量。
读写分离:可以用于实现读写分离,主库写、从库读,读写分离不仅可以提高服务器的负载能力,同时可根据需求的变化,改变从库的数量;
高可用基石:除了上述作用以外,主从复制还是哨兵和集群能够实施的基础,因此说主从复制是Redis高可用的基础。
1. Redis 主从复制简介
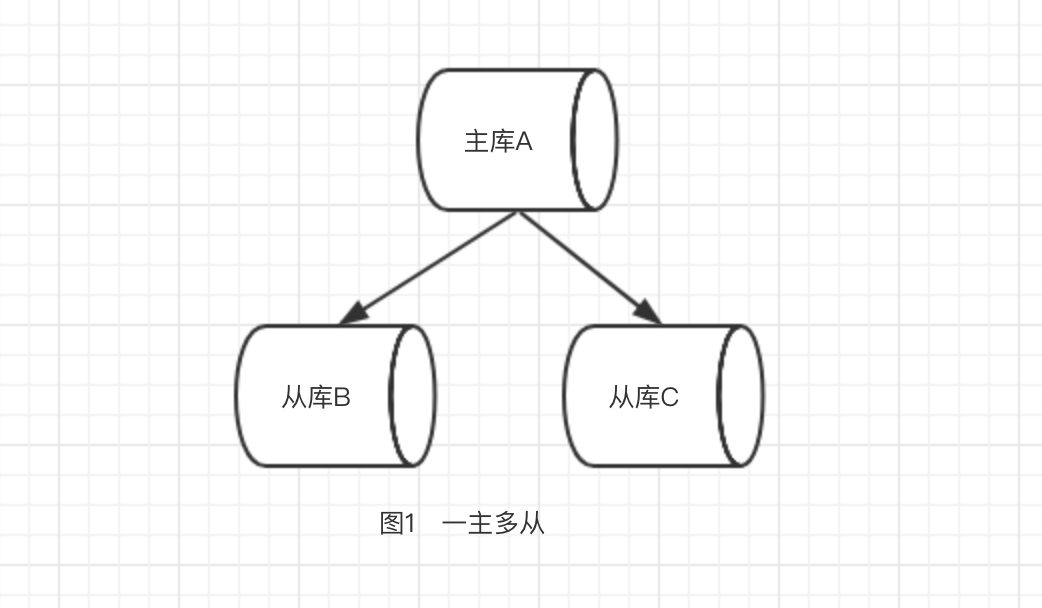
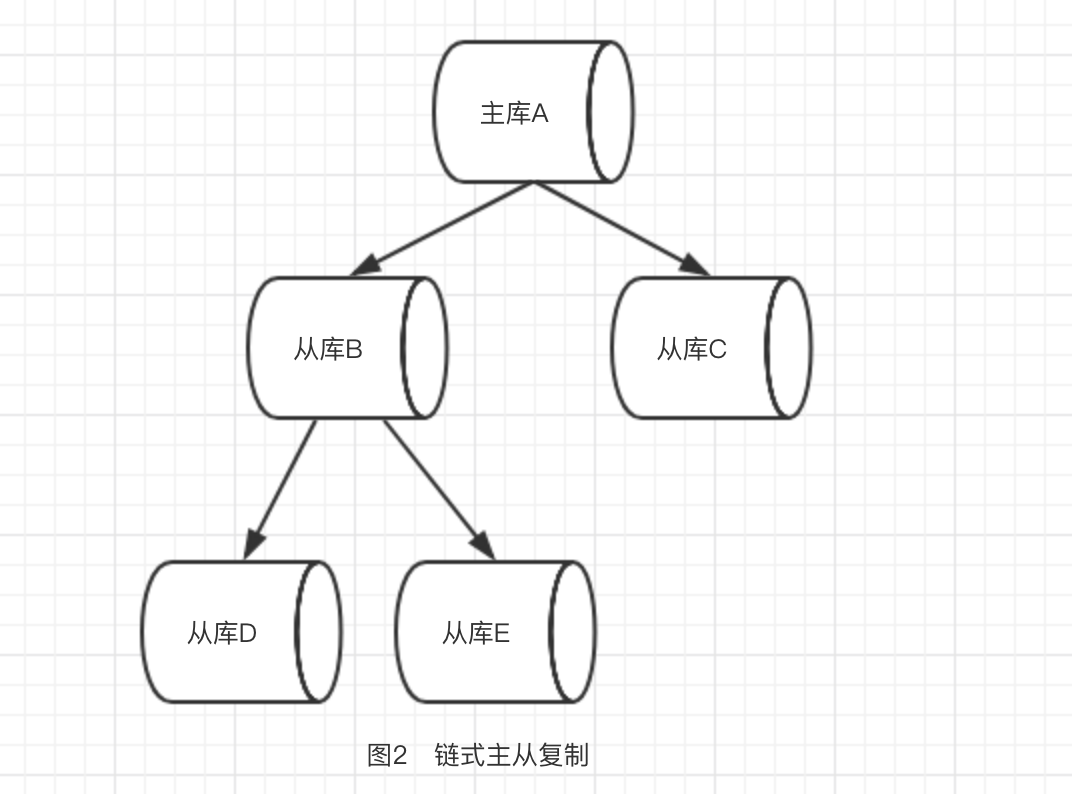
在主从复制中,数据库分为两类,一类是主库(master),另一类是同步主库数据的从库(slave)。主库可以进行读写操作,当写操作导致数据变化时会自动同步到从库。而从库一般是只读的(特定情况也可以写,通过参数slave-read-only指定),并接受来自主库的数据,一个主库可拥有多个从库,而一个从库只能有一个主库。这样就使得redis的主从架构有了两种模式:一类是一主多从如下图1,二类是“链式主从复制”--主->从->主-从如下图2。
2. Redis 主从复制的操作步骤简略说明
1. 首先,你得有至少2个redis server 实例,单机多实例或者多机多实例皆可。
2. 配置主从关系,使用 slaveof master_host master_port; (config rewrite 可直接写入配置文件,避免每次都重新写)
3. 验证主从配置,使用 info Replication;
上面的操作步骤是进行实时操作的,也可以直接将 master/slave 配置放到 redis.conf 中,启动时直接加载。
当master需要使用密码进行访问时,可以使用命令 masterauth 进行授权。
masterauth # 写到redis.conf配置文件中
config set masterauth # 通过命令行进行授权
3. 主要同步的实现原理
主从复制大致流程为:
1. slaveof 是我们的开启方法,它会将master信息写入到从节点;
2. 然后与master进行建立连接;
3. 然后master决定复制方式是全量同步还是部分同步;
4. master进行数据准备;
5. 将需要同步的发送给slave节点;
6. 从节点执行发送过来的数据;
但是,我们需要进行深入理解。
3.1. slaveof 命令源码解析
slaveof 为我们操作开启主从复制开启了入口,其接口定义如下:
{"slaveof",slaveofCommand,,"ast",,NULL,,,,,},
// 用法 slaveof <master_host> <master_port> 建立主从关系
// slaveof no one 取消主从同步
// replication.c
void slaveofCommand(client *c) {
/* SLAVEOF is not allowed in cluster mode as replication is automatically
* configured using the current address of the master node. */
if (server.cluster_enabled) {
addReplyError(c,"SLAVEOF not allowed in cluster mode.");
return;
} /* The special host/port combination "NO" "ONE" turns the instance
* into a master. Otherwise the new master address is set. */
// slaveof no one, 取消主从同步
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[1]->ptr,"no") &&
!strcasecmp(c->argv[2]->ptr,"one")) {
if (server.masterhost) {
// 取消当前的master关联,返回客户端目前状态信息,结束
replicationUnsetMaster();
sds client = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(),c);
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"MASTER MODE enabled (user request from '%s')",
client);
sdsfree(client);
}
} else {
long port; if ((getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[2], &port, NULL) != C_OK))
return; /* Check if we are already attached to the specified slave */
// 只能和一个 master 建立主从关系
if (server.masterhost && !strcasecmp(server.masterhost,c->argv[1]->ptr)
&& server.masterport == port) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"SLAVE OF would result into synchronization with the master we are already connected with. No operation performed.");
addReplySds(c,sdsnew("+OK Already connected to specified master\r\n"));
return;
}
/* There was no previous master or the user specified a different one,
* we can continue. */
// 设置master信息
replicationSetMaster(c->argv[1]->ptr, port);
// 输出client状态信息
sds client = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(),c);
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"SLAVE OF %s:%d enabled (user request from '%s')",
server.masterhost, server.masterport, client);
sdsfree(client);
}
addReply(c,shared.ok);
}
// 绑定新的master关联
/* Set replication to the specified master address and port. */
void replicationSetMaster(char *ip, int port) {
sdsfree(server.masterhost);
server.masterhost = sdsnew(ip);
server.masterport = port;
if (server.master) freeClient(server.master);
// slave 不进行阻塞客户端
disconnectAllBlockedClients(); /* Clients blocked in master, now slave. */
// 断开所有 slave 连接
disconnectSlaves(); /* Force our slaves to resync with us as well. */
// cacheMaster 丢弃
replicationDiscardCachedMaster(); /* Don't try a PSYNC. */
// 链式主从复制删除
freeReplicationBacklog(); /* Don't allow our chained slaves to PSYNC. */
// 断开正在连接slave请求
cancelReplicationHandshake();
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_CONNECT;
server.master_repl_offset = 0;
server.repl_down_since = 0;
}
// 取消master关联
/* Cancel replication, setting the instance as a master itself. */
void replicationUnsetMaster(void) {
if (server.masterhost == NULL) return; /* Nothing to do. */
sdsfree(server.masterhost);
server.masterhost = NULL;
if (server.master) {
if (listLength(server.slaves) == 0) {
/* If this instance is turned into a master and there are no
* slaves, it inherits the replication offset from the master.
* Under certain conditions this makes replicas comparable by
* replication offset to understand what is the most updated. */
server.master_repl_offset = server.master->reploff;
freeReplicationBacklog();
}
freeClient(server.master);
}
replicationDiscardCachedMaster();
cancelReplicationHandshake();
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_NONE;
} // blocked.c, 解除所有的阻塞客户端
/* Mass-unblock clients because something changed in the instance that makes
* blocking no longer safe. For example clients blocked in list operations
* in an instance which turns from master to slave is unsafe, so this function
* is called when a master turns into a slave.
*
* The semantics is to send an -UNBLOCKED error to the client, disconnecting
* it at the same time. */
void disconnectAllBlockedClients(void) {
listNode *ln;
listIter li; listRewind(server.clients,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *c = listNodeValue(ln); if (c->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED) {
addReplySds(c,sdsnew(
"-UNBLOCKED force unblock from blocking operation, "
"instance state changed (master -> slave?)\r\n"));
unblockClient(c);
c->flags |= CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY;
}
}
}
// networking.c, 断开所有的 slave 连接
/* Close all the slaves connections. This is useful in chained replication
* when we resync with our own master and want to force all our slaves to
* resync with us as well. */
void disconnectSlaves(void) {
while (listLength(server.slaves)) {
listNode *ln = listFirst(server.slaves);
freeClient((client*)ln->value);
}
}
// replication.c
/* Free a cached master, called when there are no longer the conditions for
* a partial resync on reconnection. */
void replicationDiscardCachedMaster(void) {
if (server.cached_master == NULL) return; serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Discarding previously cached master state.");
server.cached_master->flags &= ~CLIENT_MASTER;
freeClient(server.cached_master);
server.cached_master = NULL;
}
// replication.c
void freeReplicationBacklog(void) {
serverAssert(listLength(server.slaves) == 0);
zfree(server.repl_backlog);
server.repl_backlog = NULL;
}
// replication.c
/* This function aborts a non blocking replication attempt if there is one
* in progress, by canceling the non-blocking connect attempt or
* the initial bulk transfer.
*
* If there was a replication handshake in progress 1 is returned and
* the replication state (server.repl_state) set to REPL_STATE_CONNECT.
*
* Otherwise zero is returned and no operation is perforemd at all. */
int cancelReplicationHandshake(void) {
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_TRANSFER) {
replicationAbortSyncTransfer();
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_CONNECT;
} else if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_CONNECTING ||
slaveIsInHandshakeState())
{
undoConnectWithMaster();
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_CONNECT;
} else {
return 0;
}
return 1;
} // networking.c
/* Concatenate a string representing the state of a client in an human
* readable format, into the sds string 's'. */
sds catClientInfoString(sds s, client *client) {
char flags[16], events[3], *p;
int emask; p = flags;
if (client->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE) {
if (client->flags & CLIENT_MONITOR)
*p++ = 'O';
else
*p++ = 'S';
}
if (client->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) *p++ = 'M';
if (client->flags & CLIENT_MULTI) *p++ = 'x';
if (client->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED) *p++ = 'b';
if (client->flags & CLIENT_DIRTY_CAS) *p++ = 'd';
if (client->flags & CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY) *p++ = 'c';
if (client->flags & CLIENT_UNBLOCKED) *p++ = 'u';
if (client->flags & CLIENT_CLOSE_ASAP) *p++ = 'A';
if (client->flags & CLIENT_UNIX_SOCKET) *p++ = 'U';
if (client->flags & CLIENT_READONLY) *p++ = 'r';
if (p == flags) *p++ = 'N';
*p++ = '\0'; emask = client->fd == -1 ? 0 : aeGetFileEvents(server.el,client->fd);
p = events;
if (emask & AE_READABLE) *p++ = 'r';
if (emask & AE_WRITABLE) *p++ = 'w';
*p = '\0';
// 可变参数定义: sds sdscatfmt(sds s, char const *fmt, ...)
return sdscatfmt(s,
"id=%U addr=%s fd=%i name=%s age=%I idle=%I flags=%s db=%i sub=%i psub=%i multi=%i qbuf=%U qbuf-free=%U obl=%U oll=%U omem=%U events=%s cmd=%s",
(unsigned long long) client->id,
getClientPeerId(client),
client->fd,
client->name ? (char*)client->name->ptr : "",
(long long)(server.unixtime - client->ctime),
(long long)(server.unixtime - client->lastinteraction),
flags,
client->db->id,
(int) dictSize(client->pubsub_channels),
(int) listLength(client->pubsub_patterns),
(client->flags & CLIENT_MULTI) ? client->mstate.count : -1,
(unsigned long long) sdslen(client->querybuf),
(unsigned long long) sdsavail(client->querybuf),
(unsigned long long) client->bufpos,
(unsigned long long) listLength(client->reply),
(unsigned long long) getClientOutputBufferMemoryUsage(client),
events,
client->lastcmd ? client->lastcmd->name : "NULL");
}
所以,slaveof 只是做简单的验证,然后设置了下 master 信息,然后就返回了。那么是谁在做同步的工作呢?
其实同步任务是由 cron 任务运行的。
3.2. 如何执行同步任务?
因为复制是比较耗性能的东西,如果和用户线程共享处理过程的话,将可能引起并发性能的。所以,redis使用异步 cron 任务的形式实现主从复制功能。
// server.c, 初始化server,注册 cron
void initServer(void) {
...
/* Create out timers, that's our main way to process background
* operations. */
// 添加 serverCron 到 eventLoop 中,以便后续可以执行定时脚本
if (aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) {
serverPanic("Can't create event loop timers.");
exit(1);
}
...
} // ae.c, 添加时间事件
long long aeCreateTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long milliseconds,
aeTimeProc *proc, void *clientData,
aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc)
{
long long id = eventLoop->timeEventNextId++;
aeTimeEvent *te; te = zmalloc(sizeof(*te));
if (te == NULL) return AE_ERR;
te->id = id;
aeAddMillisecondsToNow(milliseconds,&te->when_sec,&te->when_ms);
te->timeProc = proc;
te->finalizerProc = finalizerProc;
te->clientData = clientData;
te->next = eventLoop->timeEventHead;
eventLoop->timeEventHead = te;
return id;
} // server.c, 主脚本运行入口, 每1秒运行1次
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
...
/* Replication cron function -- used to reconnect to master and
* to detect transfer failures. */
// 主从复制,连接 master,我们的入口
run_with_period(1000) replicationCron();
...
server.cronloops++;
return 1000/server.hz;
} // 重点入口: replicationCron()
// replication.c, 主从复制定时脚本
/* Replication cron function, called 1 time per second. */
void replicationCron(void) {
static long long replication_cron_loops = 0; /* Non blocking connection timeout? */
// 连接超时处理,取消重连
if (server.masterhost &&
(server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_CONNECTING ||
slaveIsInHandshakeState()) &&
(time(NULL)-server.repl_transfer_lastio) > server.repl_timeout)
{
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Timeout connecting to the MASTER...");
cancelReplicationHandshake();
} /* Bulk transfer I/O timeout? */
// 传输数据超时,取消重连
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_TRANSFER &&
(time(NULL)-server.repl_transfer_lastio) > server.repl_timeout)
{
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Timeout receiving bulk data from MASTER... If the problem persists try to set the 'repl-timeout' parameter in redis.conf to a larger value.");
cancelReplicationHandshake();
} /* Timed out master when we are an already connected slave? */
// slave 会话超时
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_CONNECTED &&
(time(NULL)-server.master->lastinteraction) > server.repl_timeout)
{
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"MASTER timeout: no data nor PING received...");
freeClient(server.master);
} /* Check if we should connect to a MASTER */
// 3.2.1. 初次设置master时,一定会进行连接处理
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_CONNECT) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Connecting to MASTER %s:%d",
server.masterhost, server.masterport);
if (connectWithMaster() == C_OK) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"MASTER <-> SLAVE sync started");
}
} /* Send ACK to master from time to time.
* Note that we do not send periodic acks to masters that don't
* support PSYNC and replication offsets. */
// 3.2.2. 每次定时任务执行,都会发生 ACK 给master
if (server.masterhost && server.master &&
!(server.master->flags & CLIENT_PRE_PSYNC))
replicationSendAck(); /* If we have attached slaves, PING them from time to time.
* So slaves can implement an explicit timeout to masters, and will
* be able to detect a link disconnection even if the TCP connection
* will not actually go down. */
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
robj *ping_argv[1]; /* First, send PING according to ping_slave_period. */
// 3.2.3. 发送 PING 请求
// 默认 repl_ping_slave_period: 10
if ((replication_cron_loops % server.repl_ping_slave_period) == 0) {
ping_argv[0] = createStringObject("PING",4);
replicationFeedSlaves(server.slaves, server.slaveseldb,
ping_argv, 1);
decrRefCount(ping_argv[0]);
} /* Second, send a newline to all the slaves in pre-synchronization
* stage, that is, slaves waiting for the master to create the RDB file.
* The newline will be ignored by the slave but will refresh the
* last-io timer preventing a timeout. In this case we ignore the
* ping period and refresh the connection once per second since certain
* timeouts are set at a few seconds (example: PSYNC response). */
// 3.2.4. 向以当前节点为master的slaves 发送空行数据
listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *slave = ln->value; if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START ||
(slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_END &&
server.rdb_child_type != RDB_CHILD_TYPE_SOCKET))
{
if (write(slave->fd, "\n", 1) == -1) {
/* Don't worry, it's just a ping. */
}
}
} /* Disconnect timedout slaves. */
// 断开连接超时的 slaves
if (listLength(server.slaves)) {
listIter li;
listNode *ln; listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *slave = ln->value; if (slave->replstate != SLAVE_STATE_ONLINE) continue;
if (slave->flags & CLIENT_PRE_PSYNC) continue;
if ((server.unixtime - slave->repl_ack_time) > server.repl_timeout)
{
serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Disconnecting timedout slave: %s",
replicationGetSlaveName(slave));
freeClient(slave);
}
}
} /* If we have no attached slaves and there is a replication backlog
* using memory, free it after some (configured) time. */
// 如果没有slave 跟随当前节点,一段时间后将backlog 释放掉
if (listLength(server.slaves) == 0 && server.repl_backlog_time_limit &&
server.repl_backlog)
{
time_t idle = server.unixtime - server.repl_no_slaves_since; if (idle > server.repl_backlog_time_limit) {
freeReplicationBacklog();
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"Replication backlog freed after %d seconds "
"without connected slaves.",
(int) server.repl_backlog_time_limit);
}
} /* If AOF is disabled and we no longer have attached slaves, we can
* free our Replication Script Cache as there is no need to propagate
* EVALSHA at all. */
if (listLength(server.slaves) == 0 &&
server.aof_state == AOF_OFF &&
listLength(server.repl_scriptcache_fifo) != 0)
{
replicationScriptCacheFlush();
} /* If we are using diskless replication and there are slaves waiting
* in WAIT_BGSAVE_START state, check if enough seconds elapsed and
* start a BGSAVE.
*
* This code is also useful to trigger a BGSAVE if the diskless
* replication was turned off with CONFIG SET, while there were already
* slaves in WAIT_BGSAVE_START state. */
if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1) {
time_t idle, max_idle = 0;
int slaves_waiting = 0;
int mincapa = -1;
listNode *ln;
listIter li; listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *slave = ln->value;
if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START) {
idle = server.unixtime - slave->lastinteraction;
if (idle > max_idle) max_idle = idle;
slaves_waiting++;
mincapa = (mincapa == -1) ? slave->slave_capa :
(mincapa & slave->slave_capa);
}
}
// 3.2.5. 如果有等待同步的slave, 且等待时间超过 server.repl_diskless_sync_delay, 默认是: 5s
if (slaves_waiting && max_idle > server.repl_diskless_sync_delay) {
/* Start a BGSAVE. Usually with socket target, or with disk target
* if there was a recent socket -> disk config change. */
startBgsaveForReplication(mincapa);
}
} /* Refresh the number of slaves with lag <= min-slaves-max-lag. */
// 刷新本节点的 从健康节点 数量,以便在需要确保多少节点时才进行写入的场景判定
refreshGoodSlavesCount();
replication_cron_loops++; /* Incremented with frequency 1 HZ. */
}
以上,就是整个主从复制的主体框架了。且以上代码包含了两种角色的运行机制。1: master 的运行; 2. slave 的运行;
slave 的运行过程如下:
1. 从节点每秒运行一次定时任务;
2. 当定时任务发现存在新的主节点后,会调用 connectWithMaster() 尝试与master节点建立网络连接;
3. 建立连接后,由 syncWithMaster() 进行处理后续同步事务;
4. 各种连接超时释放处理;
master 的运行过程如下:
1. 各种连接超时释放处理;
2. 定期进行 PING slave 操作;
3. 向slave写入一个空行,相当于ping操作与slave续租期;
4. 清理连接超时的slaves, 如果一个slave也没有, 则直接把backlog释放掉;
5. 如果未开启磁盘持久化操作,且有等待同步的slaves, 则主动开启一个 bgsave;
从上面的框架中,可以说大部分时候都是在处理各种异常问题和续期问题,但是实际最重要的一个连接master操作却只有一行代码。那么slave连接master之后,是如何进行后续的同步的呢?好像这个定时任务的运行并没有太大的作用呢!
3.3. 从节点如何处理同步操作?
从节点是整个同步操作的操控者,整个同步可以说都是其主导的。从上一节的过程,我们可以看到,只有一个连接master的只剩,所以必定许多工作要这里完成。
实际上,slave连接到master的请求实现,基于 epoll 模型的异步操作,所以,在主框架中,我们只看到一个连接操作。因为连接完成后的操作,是异步执行的。 先总览一个时序图,然后再细分源码:
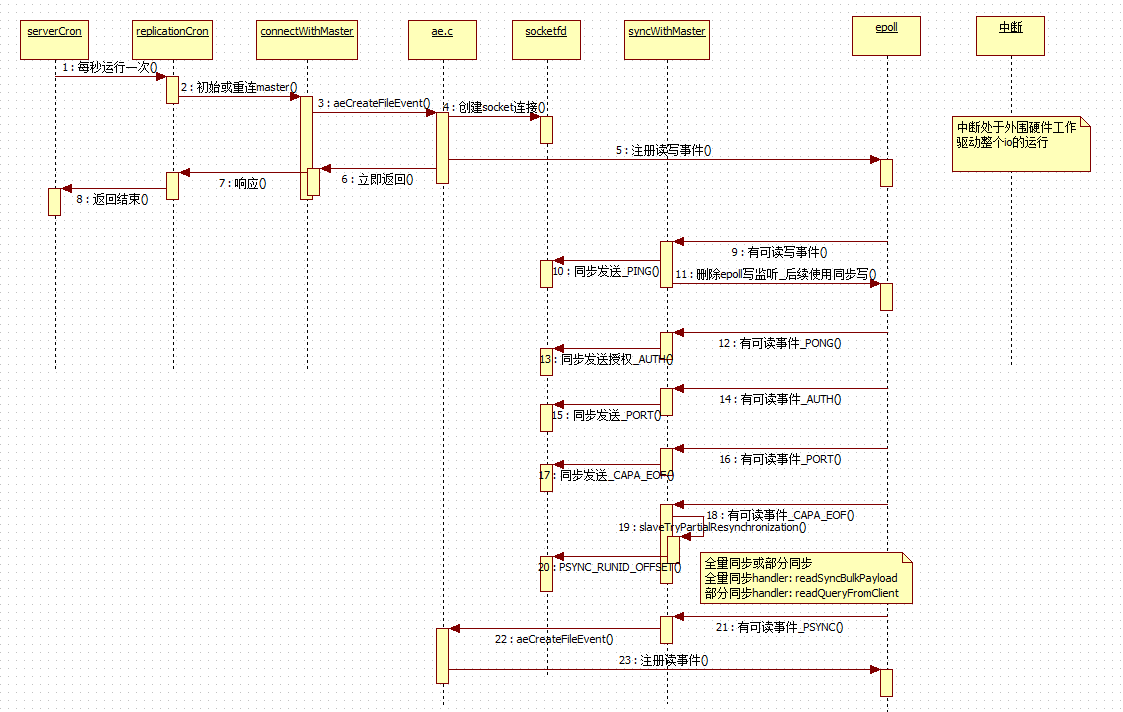
可以看到,epoll 模型在这其中起到了很大作用,将许多同步工作转换为了异步,避免了阻塞。
// replication.c, 连接请求到 master 节点
int connectWithMaster(void) {
int fd;
// 创建socket fd
fd = anetTcpNonBlockBestEffortBindConnect(NULL,
server.masterhost,server.masterport,NET_FIRST_BIND_ADDR);
if (fd == -1) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Unable to connect to MASTER: %s",
strerror(errno));
return C_ERR;
}
// 使用epoll模型进行异步连接
// 连接成功后,由 syncWithMaster 进行事件处理
// 关注 读写事件
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE|AE_WRITABLE,syncWithMaster,NULL) ==
AE_ERR)
{
close(fd);
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Can't create readable event for SYNC");
return C_ERR;
} server.repl_transfer_lastio = server.unixtime;
server.repl_transfer_s = fd;
// 状态变更,以便下次不会再进行连接
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_CONNECTING;
return C_OK;
}
// anet.c, 建立一个非阻塞的socket连接
int anetTcpNonBlockBestEffortBindConnect(char *err, char *addr, int port,
char *source_addr)
{
// ANET_CONNECT_BE_BINDING 代表将进行重试尽可能建立连接
return anetTcpGenericConnect(err,addr,port,source_addr,
ANET_CONNECT_NONBLOCK|ANET_CONNECT_BE_BINDING);
}
// 与master连接成功后,由 syncWithMaster 进行处理后续事务
// replication.c
void syncWithMaster(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
char tmpfile[256], *err = NULL;
int dfd, maxtries = 5;
int sockerr = 0, psync_result;
socklen_t errlen = sizeof(sockerr);
UNUSED(el);
UNUSED(privdata);
UNUSED(mask); /* If this event fired after the user turned the instance into a master
* with SLAVEOF NO ONE we must just return ASAP. */
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_NONE) {
close(fd);
return;
} /* Check for errors in the socket. */
if (getsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ERROR, &sockerr, &errlen) == -1)
sockerr = errno;
if (sockerr) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Error condition on socket for SYNC: %s",
strerror(sockerr));
goto error;
} /* Send a PING to check the master is able to reply without errors. */
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_CONNECTING) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Non blocking connect for SYNC fired the event.");
/* Delete the writable event so that the readable event remains
* registered and we can wait for the PONG reply. */
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_WRITABLE);
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PONG;
/* Send the PING, don't check for errors at all, we have the timeout
* that will take care about this. */
// 发送一个 PING 出去,检查 master 是否可以响应
err = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_WRITE,fd,"PING",NULL);
if (err) goto write_error;
return;
} /* Receive the PONG command. */
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PONG) {
// 同步读取PING结果
err = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_READ,fd,NULL); /* We accept only two replies as valid, a positive +PONG reply
* (we just check for "+") or an authentication error.
* Note that older versions of Redis replied with "operation not
* permitted" instead of using a proper error code, so we test
* both. */
// 没有权限且提示不是请授权类的提示,则发生错误
// 没有调用 auth 前
// -NOAUTH, 代表未授权, 可以进入下一步授权操作
if (err[0] != '+' &&
strncmp(err,"-NOAUTH",7) != 0 &&
strncmp(err,"-ERR operation not permitted",28) != 0)
{
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Error reply to PING from master: '%s'",err);
sdsfree(err);
goto error;
} else {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"Master replied to PING, replication can continue...");
}
sdsfree(err);
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_SEND_AUTH;
} /* AUTH with the master if required. */
// 需要输入master密码状态
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_SEND_AUTH) {
if (server.masterauth)
// 发送授权命令
// AUTH master_password
err = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_WRITE,fd,"AUTH",server.masterauth,NULL);
if (err) goto write_error;
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_AUTH;
return;
} else {
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_SEND_PORT;
}
} /* Receive AUTH reply. */
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_AUTH) {
// 授权响应,读取结果
// 授权成功响应 +OK, 其他授权失败
err = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_READ,fd,NULL);
if (err[0] == '-') {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Unable to AUTH to MASTER: %s",err);
sdsfree(err);
goto error;
}
sdsfree(err);
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_SEND_PORT;
} /* Set the slave port, so that Master's INFO command can list the
* slave listening port correctly. */
// 发送端口号给master, 以便master可以列举出所有slave的端口号
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_SEND_PORT) {
sds port = sdsfromlonglong(server.port);
// 发送本节点的端口给 master
// 命令: REPLCONF listening-port port
err = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_WRITE,fd,"REPLCONF",
"listening-port",port, NULL);
sdsfree(port);
if (err) goto write_error;
sdsfree(err);
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PORT;
return;
} /* Receive REPLCONF listening-port reply. */
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PORT) {
err = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_READ,fd,NULL);
/* Ignore the error if any, not all the Redis versions support
* REPLCONF listening-port. */
// 忽略失败情况,影响不大,只是个展示问题,且并非所有版本都支持该命令
if (err[0] == '-') {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"(Non critical) Master does not understand "
"REPLCONF listening-port: %s", err);
}
sdsfree(err);
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_SEND_CAPA;
} /* Inform the master of our capabilities. While we currently send
* just one capability, it is possible to chain new capabilities here
* in the form of REPLCONF capa X capa Y capa Z ...
* The master will ignore capabilities it does not understand. */
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_SEND_CAPA) {
// 发送命令: REPLCONF capa eof
err = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_WRITE,fd,"REPLCONF",
"capa","eof",NULL);
if (err) goto write_error;
sdsfree(err);
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_CAPA;
return;
} /* Receive CAPA reply. */
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_CAPA) {
err = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_READ,fd,NULL);
/* Ignore the error if any, not all the Redis versions support
* REPLCONF capa. */
if (err[0] == '-') {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"(Non critical) Master does not understand "
"REPLCONF capa: %s", err);
}
sdsfree(err);
// 可以进行数据同步了 PSYNC
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_SEND_PSYNC;
} /* Try a partial resynchonization. If we don't have a cached master
* slaveTryPartialResynchronization() will at least try to use PSYNC
* to start a full resynchronization so that we get the master run id
* and the global offset, to try a partial resync at the next
* reconnection attempt. */
if (server.repl_state == REPL_STATE_SEND_PSYNC) {
// 尝试进行部分同步, 可能为 全量同步、部分同步、或者命令不支持
// PSYNC_WAIT_REPLY, PSYNC_CONTINUE, PSYNC_FULLRESYNC, PSYNC_NOT_SUPPORTED
if (slaveTryPartialResynchronization(fd,0) == PSYNC_WRITE_ERROR) {
err = sdsnew("Write error sending the PSYNC command.");
goto write_error;
}
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PSYNC;
return;
} /* If reached this point, we should be in REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PSYNC. */
if (server.repl_state != REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PSYNC) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"syncWithMaster(): state machine error, "
"state should be RECEIVE_PSYNC but is %d",
server.repl_state);
goto error;
}
// 读取 PSYNC 结果
// PSYNC_WAIT_REPLY, PSYNC_CONTINUE, PSYNC_FULLRESYNC, PSYNC_NOT_SUPPORTED
psync_result = slaveTryPartialResynchronization(fd,1);
if (psync_result == PSYNC_WAIT_REPLY) return; /* Try again later... */ /* Note: if PSYNC does not return WAIT_REPLY, it will take care of
* uninstalling the read handler from the file descriptor. */ if (psync_result == PSYNC_CONTINUE) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE, "MASTER <-> SLAVE sync: Master accepted a Partial Resynchronization.");
return;
} /* PSYNC failed or is not supported: we want our slaves to resync with us
* as well, if we have any (chained replication case). The mater may
* transfer us an entirely different data set and we have no way to
* incrementally feed our slaves after that. */
// 不能使用 PSYNC 进行同步,断开当前节点的 slaves
// 不允许链式主从
disconnectSlaves(); /* Force our slaves to resync with us as well. */
freeReplicationBacklog(); /* Don't allow our chained slaves to PSYNC. */ /* Fall back to SYNC if needed. Otherwise psync_result == PSYNC_FULLRESYNC
* and the server.repl_master_runid and repl_master_initial_offset are
* already populated. */
if (psync_result == PSYNC_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Retrying with SYNC...");
// 不支持 PSYNC, 降级为 SYNC
if (syncWrite(fd,"SYNC\r\n",6,server.repl_syncio_timeout*1000) == -1) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"I/O error writing to MASTER: %s",
strerror(errno));
goto error;
}
} /* Prepare a suitable temp file for bulk transfer */
// 准备从rdb文件中读取数据,最多重试5次(共5s)
// 临时文件名: temp-<1560888xxx>.<pid>.rdb
while(maxtries--) {
snprintf(tmpfile,256,
"temp-%d.%ld.rdb",(int)server.unixtime,(long int)getpid());
dfd = open(tmpfile,O_CREAT|O_WRONLY|O_EXCL,0644);
if (dfd != -1) break;
sleep(1);
}
if (dfd == -1) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Opening the temp file needed for MASTER <-> SLAVE synchronization: %s",strerror(errno));
goto error;
} /* Setup the non blocking download of the bulk file. */
// 使用 epoll 模型进行异步接收master传送过来的rdb文件
// 由 readSyncBulkPayload 函数进行结果处理
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd, AE_READABLE,readSyncBulkPayload,NULL)
== AE_ERR)
{
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Can't create readable event for SYNC: %s (fd=%d)",
strerror(errno),fd);
goto error;
}
// 保存同步状态
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_TRANSFER;
server.repl_transfer_size = -1;
server.repl_transfer_read = 0;
server.repl_transfer_last_fsync_off = 0;
server.repl_transfer_fd = dfd;
server.repl_transfer_lastio = server.unixtime;
server.repl_transfer_tmpfile = zstrdup(tmpfile);
return; error:
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE|AE_WRITABLE);
close(fd);
server.repl_transfer_s = -1;
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_CONNECT;
return; write_error: /* Handle sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_WRITE) errors. */
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Sending command to master in replication handshake: %s", err);
sdsfree(err);
goto error;
}
整个连接成功之后的处理过程还是比较繁杂的,主要逻辑就在 syncWithMaster,主要是在各个状态之间的转换,尤其头疼,不过幸好都是流水式的一步步下来。
1. REPL_STATE_CONNECTING: 待连接状态. slave 发送 PING命令进行主动连接, 然后将状态置为 REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PONG;
2. REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PONG: 待master响应状态. slave同步等待结果(其实一般会立即获取到,因为epoll已经准备好,才会调用此状态),判断是否PING正常后, 将状态置为 REPL_STATE_SEND_AUTH;
3. REPL_STATE_SEND_AUTH: 等待授权状态. slave 发送 auth passwd 给master后, 将状态置为 REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_AUTH;
4. REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_AUTH: 等待授权响应状态. slave同步等待结果, 判断授权通过后, 将状态置为 REPL_STATE_SEND_PORT;
5. REPL_STATE_SEND_PORT: 待发送端口状态. slave发送自身的服务端口给master以便master展示使用, 然后将状态置为 REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PORT;
6. REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PORT: 等待端口发送结果. 不论结果如何, 直接将状态置为 REPL_STATE_SEND_CAPA;
7. REPL_STATE_SEND_CAPA: 等待发送capa命令状态. 发送 REPLCONF capa eof 后, 将状态置为 REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_CAPA;
8. REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_CAPA: 等待capa命令发送结果. 不论结果如何, 将状态置为 REPL_STATE_SEND_PSYNC;
9. REPL_STATE_SEND_PSYNC: 等待PSYNC同步命令状态. 尝试使用PSYNC进行部分复制,结果可能是全量复制或部分复制,也可能使用其他版本命令执行, 将状态置为 REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PSYNC;
10. REPL_STATE_RECEIVE_PSYNC: 等待PSYNC结果. 这是真正接收数据的时候, 是终态, 根据上一次命令的请求方式,接收相应结果进一步处理;
11. 重新注册一个 epoll 事件,用于接收master传输过来的数据,处理方法为 readSyncBulkPayload();
接下来,我们先看看尝试部分时都做了哪些事,因为这决定了是使用全量复制还是部分复制:
// 尝试进行部分同步
// replication.c
int slaveTryPartialResynchronization(int fd, int read_reply) {
char *psync_runid;
char psync_offset[32];
sds reply; /* Writing half */
// 第一次调用时, read_reply=0, 即是写动作
// 向 master 写入 PSYNC psync_runid psync_offset
// 即是每次都拉取一部分数据吧
if (!read_reply) {
/* Initially set repl_master_initial_offset to -1 to mark the current
* master run_id and offset as not valid. Later if we'll be able to do
* a FULL resync using the PSYNC command we'll set the offset at the
* right value, so that this information will be propagated to the
* client structure representing the master into server.master. */
server.repl_master_initial_offset = -1;
// 如果已经建立了连接,则 psync_runid, psync_offset 都是可预知的
// 否则 psync_runid = "?", psync_offset="-1";
if (server.cached_master) {
psync_runid = server.cached_master->replrunid;
snprintf(psync_offset,sizeof(psync_offset),"%lld", server.cached_master->reploff+1);
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Trying a partial resynchronization (request %s:%s).", psync_runid, psync_offset);
} else {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Partial resynchronization not possible (no cached master)");
psync_runid = "?";
memcpy(psync_offset,"-1",3);
} /* Issue the PSYNC command */
// 首次发送命令 PSYNC ? -1
// 后续使用实际的信息 PSYNC psync_runid psync_offset
reply = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_WRITE,fd,"PSYNC",psync_runid,psync_offset,NULL);
if (reply != NULL) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Unable to send PSYNC to master: %s",reply);
sdsfree(reply);
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE);
return PSYNC_WRITE_ERROR;
}
return PSYNC_WAIT_REPLY;
} /* Reading half */
// 读取 PSYNC 的结果
reply = sendSynchronousCommand(SYNC_CMD_READ,fd,NULL);
if (sdslen(reply) == 0) {
/* The master may send empty newlines after it receives PSYNC
* and before to reply, just to keep the connection alive. */
sdsfree(reply);
return PSYNC_WAIT_REPLY;
} aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE);
// +FULLRESYNC 代表需要进行全量复制,否则进行部分复制
// +FULLRESYNC runid offset
if (!strncmp(reply,"+FULLRESYNC",11)) {
char *runid = NULL, *offset = NULL; /* FULL RESYNC, parse the reply in order to extract the run id
* and the replication offset. */
runid = strchr(reply,' ');
if (runid) {
runid++;
offset = strchr(runid,' ');
if (offset) offset++;
}
// runid 长度为 40
if (!runid || !offset || (offset-runid-1) != CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Master replied with wrong +FULLRESYNC syntax.");
/* This is an unexpected condition, actually the +FULLRESYNC
* reply means that the master supports PSYNC, but the reply
* format seems wrong. To stay safe we blank the master
* runid to make sure next PSYNCs will fail. */
memset(server.repl_master_runid,0,CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE+1);
} else {
memcpy(server.repl_master_runid, runid, offset-runid-1);
server.repl_master_runid[CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE] = '\0';
server.repl_master_initial_offset = strtoll(offset,NULL,10);
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Full resync from master: %s:%lld",
server.repl_master_runid,
server.repl_master_initial_offset);
}
/* We are going to full resync, discard the cached master structure. */
// 全量同步,重置master缓存
replicationDiscardCachedMaster();
sdsfree(reply);
return PSYNC_FULLRESYNC;
}
// 部分复制的情况下,只会返回 +CONTINUE
if (!strncmp(reply,"+CONTINUE",9)) {
/* Partial resync was accepted, set the replication state accordingly */
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"Successful partial resynchronization with master.");
// 立即将结果释放,那什么时候处理结果呢?
sdsfree(reply);
// 实际上通过该方法同步数据的
replicationResurrectCachedMaster(fd);
// 继续使用 部分同步
return PSYNC_CONTINUE;
} /* If we reach this point we received either an error since the master does
* not understand PSYNC, or an unexpected reply from the master.
* Return PSYNC_NOT_SUPPORTED to the caller in both cases. */
// PSYNC 不支持,因处理为降级版本
if (strncmp(reply,"-ERR",4)) {
/* If it's not an error, log the unexpected event. */
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Unexpected reply to PSYNC from master: %s", reply);
} else {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"Master does not support PSYNC or is in "
"error state (reply: %s)", reply);
}
sdsfree(reply);
replicationDiscardCachedMaster();
return PSYNC_NOT_SUPPORTED;
}
通过上面的过程,我们可以看清了整个与master是如何协调进行同步的,主要依赖于 PSYNC 的返回值决定。也可以看到,全量同步功能时,注册了一个可读事件的监听,具体处理使用 readSyncBulkPayload 进行承载。
3.4. 全量同步数据的实现方式
通过前面的分析,我们看到全量同时时,注册了一个FileEvent事件,依赖于epoll实现异步操作。具体处理由 readSyncBulkPayload() 进行处理。它负责异步读取master 同步过来的数据,写入aof文件,加载到slave的数据库中。具体如下:
// replication.c
/* Asynchronously read the SYNC payload we receive from a master */
#define REPL_MAX_WRITTEN_BEFORE_FSYNC (1024*1024*8) /* 8 MB */
void readSyncBulkPayload(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
char buf[4096];
ssize_t nread, readlen;
off_t left;
UNUSED(el);
UNUSED(privdata);
UNUSED(mask); /* Static vars used to hold the EOF mark, and the last bytes received
* form the server: when they match, we reached the end of the transfer. */
static char eofmark[CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE];
static char lastbytes[CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE];
static int usemark = 0; /* If repl_transfer_size == -1 we still have to read the bulk length
* from the master reply. */
// 先读取数据长度
if (server.repl_transfer_size == -1) {
if (syncReadLine(fd,buf,1024,server.repl_syncio_timeout*1000) == -1) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"I/O error reading bulk count from MASTER: %s",
strerror(errno));
goto error;
} if (buf[0] == '-') {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"MASTER aborted replication with an error: %s",
buf+1);
goto error;
} else if (buf[0] == '\0') {
/* At this stage just a newline works as a PING in order to take
* the connection live. So we refresh our last interaction
* timestamp. */
server.repl_transfer_lastio = server.unixtime;
return;
} else if (buf[0] != '$') {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Bad protocol from MASTER, the first byte is not '$' (we received '%s'), are you sure the host and port are right?", buf);
goto error;
} /* There are two possible forms for the bulk payload. One is the
* usual $<count> bulk format. The other is used for diskless transfers
* when the master does not know beforehand the size of the file to
* transfer. In the latter case, the following format is used:
*
* $EOF:<40 bytes delimiter>
*
* At the end of the file the announced delimiter is transmitted. The
* delimiter is long and random enough that the probability of a
* collision with the actual file content can be ignored. */
if (strncmp(buf+1,"EOF:",4) == 0 && strlen(buf+5) >= CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE) {
usemark = 1;
memcpy(eofmark,buf+5,CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE);
memset(lastbytes,0,CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE);
/* Set any repl_transfer_size to avoid entering this code path
* at the next call. */
server.repl_transfer_size = 0;
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"MASTER <-> SLAVE sync: receiving streamed RDB from master");
} else {
usemark = 0;
// 读取数据长度, 写入 server.repl_transfer_size, 后续判断是否取完整数据
server.repl_transfer_size = strtol(buf+1,NULL,10);
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"MASTER <-> SLAVE sync: receiving %lld bytes from master",
(long long) server.repl_transfer_size);
}
return;
} /* Read bulk data */
if (usemark) {
readlen = sizeof(buf);
} else {
left = server.repl_transfer_size - server.repl_transfer_read;
readlen = (left < (signed)sizeof(buf)) ? left : (signed)sizeof(buf);
} nread = read(fd,buf,readlen);
if (nread <= 0) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"I/O error trying to sync with MASTER: %s",
(nread == -1) ? strerror(errno) : "connection lost");
cancelReplicationHandshake();
return;
}
server.stat_net_input_bytes += nread; /* When a mark is used, we want to detect EOF asap in order to avoid
* writing the EOF mark into the file... */
int eof_reached = 0; if (usemark) {
/* Update the last bytes array, and check if it matches our delimiter.*/
// 更新 最后几个字符
if (nread >= CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE) {
memcpy(lastbytes,buf+nread-CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE,CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE);
} else {
int rem = CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE-nread;
memmove(lastbytes,lastbytes+nread,rem);
memcpy(lastbytes+rem,buf,nread);
}
if (memcmp(lastbytes,eofmark,CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE) == 0) eof_reached = 1;
} server.repl_transfer_lastio = server.unixtime;
// 将数据写入到 temp rdb 文件中
if (write(server.repl_transfer_fd,buf,nread) != nread) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Write error or short write writing to the DB dump file needed for MASTER <-> SLAVE synchronization: %s", strerror(errno));
goto error;
}
server.repl_transfer_read += nread; /* Delete the last 40 bytes from the file if we reached EOF. */
if (usemark && eof_reached) {
if (ftruncate(server.repl_transfer_fd,
server.repl_transfer_read - CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE) == -1)
{
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Error truncating the RDB file received from the master for SYNC: %s", strerror(errno));
goto error;
}
} /* Sync data on disk from time to time, otherwise at the end of the transfer
* we may suffer a big delay as the memory buffers are copied into the
* actual disk. */
// 缓冲达到一定值后,直接刷盘
// REPL_MAX_WRITTEN_BEFORE_FSYNC: 8M
if (server.repl_transfer_read >=
server.repl_transfer_last_fsync_off + REPL_MAX_WRITTEN_BEFORE_FSYNC)
{
off_t sync_size = server.repl_transfer_read -
server.repl_transfer_last_fsync_off;
rdb_fsync_range(server.repl_transfer_fd,
server.repl_transfer_last_fsync_off, sync_size);
server.repl_transfer_last_fsync_off += sync_size;
} /* Check if the transfer is now complete */
// 传输完成
if (!usemark) {
if (server.repl_transfer_read == server.repl_transfer_size)
eof_reached = 1;
} if (eof_reached) {
// 直接将临时 rdb 文件改名为正式的 rdb 文件,从而实现数据替换
if (rename(server.repl_transfer_tmpfile,server.rdb_filename) == -1) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Failed trying to rename the temp DB into dump.rdb in MASTER <-> SLAVE synchronization: %s", strerror(errno));
cancelReplicationHandshake();
return;
}
serverLog(LL_NOTICE, "MASTER <-> SLAVE sync: Flushing old data");
// 清空原来的数据,刷入新数据
signalFlushedDb(-1);
emptyDb(
-1,
server.repl_slave_lazy_flush ? EMPTYDB_ASYNC : EMPTYDB_NO_FLAGS,
replicationEmptyDbCallback);
/* Before loading the DB into memory we need to delete the readable
* handler, otherwise it will get called recursively since
* rdbLoad() will call the event loop to process events from time to
* time for non blocking loading. */
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,server.repl_transfer_s,AE_READABLE);
serverLog(LL_NOTICE, "MASTER <-> SLAVE sync: Loading DB in memory");
// 重新载入 rdb 文件,从而完成同步操作
if (rdbLoad(server.rdb_filename) != C_OK) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Failed trying to load the MASTER synchronization DB from disk");
cancelReplicationHandshake();
return;
}
/* Final setup of the connected slave <- master link */
zfree(server.repl_transfer_tmpfile);
close(server.repl_transfer_fd);
// 设置 master 信息,以便下次直接使用
replicationCreateMasterClient(server.repl_transfer_s);
serverLog(LL_NOTICE, "MASTER <-> SLAVE sync: Finished with success");
/* Restart the AOF subsystem now that we finished the sync. This
* will trigger an AOF rewrite, and when done will start appending
* to the new file. */
if (server.aof_state != AOF_OFF) {
int retry = 10;
// 重新关联 aof 文件,以便后续写入aof正常
stopAppendOnly();
while (retry-- && startAppendOnly() == C_ERR) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Failed enabling the AOF after successful master synchronization! Trying it again in one second.");
sleep(1);
}
if (!retry) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"FATAL: this slave instance finished the synchronization with its master, but the AOF can't be turned on. Exiting now.");
exit(1);
}
}
} return; error:
cancelReplicationHandshake();
return;
}
以上就是全量复制功能实现了,大体步骤为:
1. 先读取整体数据长度;(肯定是master发来的数据了)
2. 依次读取就绪数据,将其定入临时aof文件 temp-<unixtime>.<pid>.aof;
3. 达到一定缓冲数量后,强制刷盘;
4. master 传输完成后,slave将临时aof文件重命名为正式的aof文件;
5. slave 清空原来db数据;
6. 禁用aof文件的监听,载入新的aof数据,重新开启监听;
7. aof 先停止再启动,重新关联新文件;
3.5. 部分复制的实现
前面我们看到有个 slaveTryPartialResynchronization(), 是做部分同步检测的,但是它只会返回几个状态,好像返回后都没有做什么后续处理。只有全量同步时,我们看到了如上逻辑。那么部分同步是如何实现的呢?其中有个 +CONTINUE 的状态值得我们注意:
...
// 部分复制的情况下,只会返回 +CONTINUE
if (!strncmp(reply,"+CONTINUE",9)) {
/* Partial resync was accepted, set the replication state accordingly */
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"Successful partial resynchronization with master.");
// 立即将结果释放,那什么时候处理结果呢?
sdsfree(reply);
// 实际上通过该方法同步数据的
replicationResurrectCachedMaster(fd);
// 继续使用 部分同步
return PSYNC_CONTINUE;
}
...
就这上面这个,返回 CONTINUE 后,外部逻辑只是返回,所以肯定是 replicationResurrectCachedMaster() 做了处理。而这个处理,应该是读取后续的数据没错了!
// replication.c, 使用 cacheMaster 做 PSYNC 处理复制数据
/* Turn the cached master into the current master, using the file descriptor
* passed as argument as the socket for the new master.
*
* This function is called when successfully setup a partial resynchronization
* so the stream of data that we'll receive will start from were this
* master left. */
void replicationResurrectCachedMaster(int newfd) {
server.master = server.cached_master;
server.cached_master = NULL;
server.master->fd = newfd;
server.master->flags &= ~(CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY|CLIENT_CLOSE_ASAP);
server.master->authenticated = 1;
server.master->lastinteraction = server.unixtime;
server.repl_state = REPL_STATE_CONNECTED; /* Re-add to the list of clients. */
listAddNodeTail(server.clients,server.master);
// 添加file事件,epoll事件, 由 readQueryFromClient 进行事件处理
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, newfd, AE_READABLE,
readQueryFromClient, server.master)) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Error resurrecting the cached master, impossible to add the readable handler: %s", strerror(errno));
freeClientAsync(server.master); /* Close ASAP. */
} /* We may also need to install the write handler as well if there is
* pending data in the write buffers. */
// 如果有待发送数据,建立一个 写的 fileEvent 事件
if (clientHasPendingReplies(server.master)) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, newfd, AE_WRITABLE,
sendReplyToClient, server.master)) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Error resurrecting the cached master, impossible to add the writable handler: %s", strerror(errno));
freeClientAsync(server.master); /* Close ASAP. */
}
}
}
// 接下来,我们查看下 当master发送数据过来时,部分复制是如何实现的
// networking.c, 从 master 中读取数据, privdata = server.master
void readQueryFromClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
client *c = (client*) privdata;
int nread, readlen;
size_t qblen;
UNUSED(el);
UNUSED(mask);
// PROTO_IOBUF_LEN: 1024*16
// PROTO_MBULK_BIG_ARG: 1024*32
readlen = PROTO_IOBUF_LEN;
/* If this is a multi bulk request, and we are processing a bulk reply
* that is large enough, try to maximize the probability that the query
* buffer contains exactly the SDS string representing the object, even
* at the risk of requiring more read(2) calls. This way the function
* processMultiBulkBuffer() can avoid copying buffers to create the
* Redis Object representing the argument. */
if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK && c->multibulklen && c->bulklen != -1
&& c->bulklen >= PROTO_MBULK_BIG_ARG)
{
int remaining = (unsigned)(c->bulklen+2)-sdslen(c->querybuf); if (remaining < readlen) readlen = remaining;
} qblen = sdslen(c->querybuf);
if (c->querybuf_peak < qblen) c->querybuf_peak = qblen;
c->querybuf = sdsMakeRoomFor(c->querybuf, readlen);
// 读取请求命令
nread = read(fd, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen);
if (nread == -1) {
if (errno == EAGAIN) {
return;
} else {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Reading from client: %s",strerror(errno));
freeClient(c);
return;
}
} else if (nread == 0) {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Client closed connection");
freeClient(c);
return;
} sdsIncrLen(c->querybuf,nread);
c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime;
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) c->reploff += nread;
server.stat_net_input_bytes += nread;
// 超出最大限制,不处理
if (sdslen(c->querybuf) > server.client_max_querybuf_len) {
sds ci = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(),c), bytes = sdsempty(); bytes = sdscatrepr(bytes,c->querybuf,64);
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Closing client that reached max query buffer length: %s (qbuf initial bytes: %s)", ci, bytes);
sdsfree(ci);
sdsfree(bytes);
freeClient(c);
return;
}
// 处理 querybuf 数据, 其实就和普通的客户端写请求一样的处理方式
processInputBuffer(c);
}
处理master 部分同步过来的数据,重新在 slave 执行一次即可,基于epoll的事件监听,可以持续处理同步数据。
所以,部分复制,其实就是重新在slave端执行与master相同的请求就好了。这个processInputBuffer()过程在前面的文章已经介绍过。
3.6. PSYNC 命令实现原理
从上面可以看出,PSYNC是整个主从复制过程的重要操作,那么 PSYNC 都是怎么实现的呢?大体上应该是一个范围查找响应的过程,但是细节必然很多。我们可以先自己想想,要处理的点大概有哪些呢?
1. 第一次调用时,即 PSYNC ? -1 如何处理?
2. 后续调用时 即 PSYNC psync_runid psync_offset 如何处理?
3. 响应结构是如何的?比如如何响应+CONTINUE?
我们就通过源码来解答这些问题吧!
首先是 PSYNC 的定义: 可以看到,sync 和 psync 居然是一样的实现?
// 差别是 sync 的参数只有一个,而 psync 的参数是3个
{"sync",syncCommand,1,"ars",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
{"psync",syncCommand,3,"ars",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
具体实现:
// 用法: PSYNC run_id offset
// replication.c
/* SYNC and PSYNC command implemenation. */
void syncCommand(client *c) {
/* ignore SYNC if already slave or in monitor mode */
// SYNC 命令只能调用成功一次,后续就直接忽略了
if (c->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE) return; /* Refuse SYNC requests if we are a slave but the link with our master
* is not ok... */
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_state != REPL_STATE_CONNECTED) {
addReplyError(c,"Can't SYNC while not connected with my master");
return;
} /* SYNC can't be issued when the server has pending data to send to
* the client about already issued commands. We need a fresh reply
* buffer registering the differences between the BGSAVE and the current
* dataset, so that we can copy to other slaves if needed. */
// 还有输出未完成时不能再进行处理
if (clientHasPendingReplies(c)) {
addReplyError(c,"SYNC and PSYNC are invalid with pending output");
return;
} serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Slave %s asks for synchronization",
replicationGetSlaveName(c)); /* Try a partial resynchronization if this is a PSYNC command.
* If it fails, we continue with usual full resynchronization, however
* when this happens masterTryPartialResynchronization() already
* replied with:
*
* +FULLRESYNC <runid> <offset>
*
* So the slave knows the new runid and offset to try a PSYNC later
* if the connection with the master is lost. */
// 事实上,psync 和 sync 的实现还是区别对待的
// psync 将会优先尝试部分复制
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[0]->ptr,"psync")) {
// 部分复制将不会重置 flags, 即每次 psync 都会成功运行
if (masterTryPartialResynchronization(c) == C_OK) {
server.stat_sync_partial_ok++;
return; /* No full resync needed, return. */
} else {
char *master_runid = c->argv[1]->ptr; /* Increment stats for failed PSYNCs, but only if the
* runid is not "?", as this is used by slaves to force a full
* resync on purpose when they are not albe to partially
* resync. */
if (master_runid[0] != '?') server.stat_sync_partial_err++;
}
} else {
/* If a slave uses SYNC, we are dealing with an old implementation
* of the replication protocol (like redis-cli --slave). Flag the client
* so that we don't expect to receive REPLCONF ACK feedbacks. */
c->flags |= CLIENT_PRE_PSYNC;
}
// 以下为全量复制
/* Full resynchronization. */
server.stat_sync_full++; /* Setup the slave as one waiting for BGSAVE to start. The following code
* paths will change the state if we handle the slave differently. */
c->replstate = SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START;
if (server.repl_disable_tcp_nodelay)
anetDisableTcpNoDelay(NULL, c->fd); /* Non critical if it fails. */
c->repldbfd = -1;
// 添加slave 到master的从节点集合中, 设置 SLAVE 标识,表示已执行过 SYNC 操作
c->flags |= CLIENT_SLAVE;
listAddNodeTail(server.slaves,c); /* CASE 1: BGSAVE is in progress, with disk target. */
// 如果 rdb 存储已在进行中,即 BGSAVE 已经在运行
// 此种是对于后来进行主从同步的客户端,只需告知正在运行 BGSAVE 即可
if (server.rdb_child_pid != -1 &&
server.rdb_child_type == RDB_CHILD_TYPE_DISK)
{
/* Ok a background save is in progress. Let's check if it is a good
* one for replication, i.e. if there is another slave that is
* registering differences since the server forked to save. */
client *slave;
listNode *ln;
listIter li; listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
slave = ln->value;
if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_END) break;
}
/* To attach this slave, we check that it has at least all the
* capabilities of the slave that triggered the current BGSAVE. */
if (ln && ((c->slave_capa & slave->slave_capa) == slave->slave_capa)) {
/* Perfect, the server is already registering differences for
* another slave. Set the right state, and copy the buffer. */
copyClientOutputBuffer(c,slave);
replicationSetupSlaveForFullResync(c,slave->psync_initial_offset);
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Waiting for end of BGSAVE for SYNC");
} else {
/* No way, we need to wait for the next BGSAVE in order to
* register differences. */
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Waiting for next BGSAVE for SYNC");
} /* CASE 2: BGSAVE is in progress, with socket target. */
} else if (server.rdb_child_pid != -1 &&
server.rdb_child_type == RDB_CHILD_TYPE_SOCKET)
{
/* There is an RDB child process but it is writing directly to
* children sockets. We need to wait for the next BGSAVE
* in order to synchronize. */
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Waiting for next BGSAVE for SYNC"); /* CASE 3: There is no BGSAVE is progress. */
} else {
// master 不持久化方式下,不启动 bgsave
if (server.repl_diskless_sync && (c->slave_capa & SLAVE_CAPA_EOF)) {
/* Diskless replication RDB child is created inside
* replicationCron() since we want to delay its start a
* few seconds to wait for more slaves to arrive. */
if (server.repl_diskless_sync_delay)
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Delay next BGSAVE for SYNC");
} else {
/* Target is disk (or the slave is not capable of supporting
* diskless replication) and we don't have a BGSAVE in progress,
* let's start one. */
// 主动开启一个后台 BGSAVE
if (startBgsaveForReplication(c->slave_capa) != C_OK) return;
}
}
// 如果是第一个 slave, 则创建backlog
if (listLength(server.slaves) == 1 && server.repl_backlog == NULL)
createReplicationBacklog();
// 最后,直接return, 说明响应没有一个统一的格式,各自情况各自判断就好
return;
} // 3.6.1. 后台 BGSAVE 的触发
// replication.c
/* Start a BGSAVE for replication goals, which is, selecting the disk or
* socket target depending on the configuration, and making sure that
* the script cache is flushed before to start.
*
* The mincapa argument is the bitwise AND among all the slaves capabilities
* of the slaves waiting for this BGSAVE, so represents the slave capabilities
* all the slaves support. Can be tested via SLAVE_CAPA_* macros.
*
* Side effects, other than starting a BGSAVE:
*
* 1) Handle the slaves in WAIT_START state, by preparing them for a full
* sync if the BGSAVE was succesfully started, or sending them an error
* and dropping them from the list of slaves.
*
* 2) Flush the Lua scripting script cache if the BGSAVE was actually
* started.
*
* Returns C_OK on success or C_ERR otherwise. */
int startBgsaveForReplication(int mincapa) {
int retval;
int socket_target = server.repl_diskless_sync && (mincapa & SLAVE_CAPA_EOF);
listIter li;
listNode *ln; serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Starting BGSAVE for SYNC with target: %s",
socket_target ? "slaves sockets" : "disk"); if (socket_target)
// 直接向socket中写入数据同步
retval = rdbSaveToSlavesSockets();
else
// 存储到磁盘rdb 文件中
retval = rdbSaveBackground(server.rdb_filename); /* If we failed to BGSAVE, remove the slaves waiting for a full
* resynchorinization from the list of salves, inform them with
* an error about what happened, close the connection ASAP. */
if (retval == C_ERR) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"BGSAVE for replication failed");
listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *slave = ln->value; if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START) {
slave->flags &= ~CLIENT_SLAVE;
listDelNode(server.slaves,ln);
addReplyError(slave,
"BGSAVE failed, replication can't continue");
slave->flags |= CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY;
}
}
return retval;
} /* If the target is socket, rdbSaveToSlavesSockets() already setup
* the salves for a full resync. Otherwise for disk target do it now.*/
if (!socket_target) {
listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *slave = ln->value;
// 依次响应 slave 端 +FULLRESYNC <master_runid> <master_offset>
if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START) {
replicationSetupSlaveForFullResync(slave,
getPsyncInitialOffset());
}
}
} /* Flush the script cache, since we need that slave differences are
* accumulated without requiring slaves to match our cached scripts. */
// lua 脚本相关,略
if (retval == C_OK) replicationScriptCacheFlush();
return retval;
}
// rdb.c, 后台保存数据到 filename 中
int rdbSaveBackground(char *filename) {
pid_t childpid;
long long start; if (server.rdb_child_pid != -1) return C_ERR; server.dirty_before_bgsave = server.dirty;
server.lastbgsave_try = time(NULL); start = ustime();
// 使用fork() 创建子进程进行 bgsave
// 所以,bgsave 应该是个很耗内存的事
if ((childpid = fork()) == 0) {
int retval; /* Child */
// fork() 出的子进程执行此代码区域
closeListeningSockets(0);
redisSetProcTitle("redis-rdb-bgsave");
// 所以,整个耗时的操作都在 rdbSave() 中了
retval = rdbSave(filename);
if (retval == C_OK) {
size_t private_dirty = zmalloc_get_private_dirty(); if (private_dirty) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"RDB: %zu MB of memory used by copy-on-write",
private_dirty/(1024*1024));
}
}
// 执行完rdbSave()后,直接退出子进程
// 此处的退出操作,并不会清理进程 I/O 缓冲,以便将来方便使用
exitFromChild((retval == C_OK) ? 0 : 1);
} else {
/* Parent */
// 父进程执行此代码区域
server.stat_fork_time = ustime()-start;
server.stat_fork_rate = (double) zmalloc_used_memory() * 1000000 / server.stat_fork_time / (1024*1024*1024); /* GB per second. */
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("fork",server.stat_fork_time/1000);
if (childpid == -1) {
server.lastbgsave_status = C_ERR;
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Can't save in background: fork: %s",
strerror(errno));
return C_ERR;
}
// 记录子进程信息
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Background saving started by pid %d",childpid);
server.rdb_save_time_start = time(NULL);
server.rdb_child_pid = childpid;
server.rdb_child_type = RDB_CHILD_TYPE_DISK;
// bgsave 期间禁止dict进行扩容
updateDictResizePolicy();
return C_OK;
}
return C_OK; /* unreached */
}
// replication.c, 响应客户端需要进行全量复制
/* Send a FULLRESYNC reply in the specific case of a full resynchronization,
* as a side effect setup the slave for a full sync in different ways:
*
* 1) Remember, into the slave client structure, the offset we sent
* here, so that if new slaves will later attach to the same
* background RDB saving process (by duplicating this client output
* buffer), we can get the right offset from this slave.
* 2) Set the replication state of the slave to WAIT_BGSAVE_END so that
* we start accumulating differences from this point.
* 3) Force the replication stream to re-emit a SELECT statement so
* the new slave incremental differences will start selecting the
* right database number.
*
* Normally this function should be called immediately after a successful
* BGSAVE for replication was started, or when there is one already in
* progress that we attached our slave to. */
int replicationSetupSlaveForFullResync(client *slave, long long offset) {
char buf[128];
int buflen; slave->psync_initial_offset = offset;
slave->replstate = SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_END;
/* We are going to accumulate the incremental changes for this
* slave as well. Set slaveseldb to -1 in order to force to re-emit
* a SLEECT statement in the replication stream. */
server.slaveseldb = -1; /* Don't send this reply to slaves that approached us with
* the old SYNC command. */
if (!(slave->flags & CLIENT_PRE_PSYNC)) {
buflen = snprintf(buf,sizeof(buf),"+FULLRESYNC %s %lld\r\n",
server.runid,offset);
if (write(slave->fd,buf,buflen) != buflen) {
freeClientAsync(slave);
return C_ERR;
}
}
return C_OK;
}
// rdb.c, 子进程bgsave 数据过程
/* Save the DB on disk. Return C_ERR on error, C_OK on success. */
int rdbSave(char *filename) {
char tmpfile[256];
FILE *fp;
rio rdb;
int error = 0;
// 先使用临时文件写数据,然后再更名为 rdb正式文件
snprintf(tmpfile,256,"temp-%d.rdb", (int) getpid());
fp = fopen(tmpfile,"w");
if (!fp) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Failed opening .rdb for saving: %s",
strerror(errno));
return C_ERR;
} rioInitWithFile(&rdb,fp);
// rdbSaveRio 主dump数据的关键实现
if (rdbSaveRio(&rdb,&error) == C_ERR) {
errno = error;
goto werr;
} /* Make sure data will not remain on the OS's output buffers */
if (fflush(fp) == EOF) goto werr;
if (fsync(fileno(fp)) == -1) goto werr;
if (fclose(fp) == EOF) goto werr; /* Use RENAME to make sure the DB file is changed atomically only
* if the generate DB file is ok. */
if (rename(tmpfile,filename) == -1) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Error moving temp DB file on the final destination: %s", strerror(errno));
unlink(tmpfile);
return C_ERR;
}
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"DB saved on disk");
server.dirty = 0;
server.lastsave = time(NULL);
server.lastbgsave_status = C_OK;
return C_OK; werr:
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Write error saving DB on disk: %s", strerror(errno));
fclose(fp);
unlink(tmpfile);
return C_ERR;
}
// replication.c, 针对第一个进行主从复制的 slave, 需要触发 backlog 的初始化
void createReplicationBacklog(void) {
serverAssert(server.repl_backlog == NULL);
server.repl_backlog = zmalloc(server.repl_backlog_size);
server.repl_backlog_histlen = 0;
server.repl_backlog_idx = 0;
/* When a new backlog buffer is created, we increment the replication
* offset by one to make sure we'll not be able to PSYNC with any
* previous slave. This is needed because we avoid incrementing the
* master_repl_offset if no backlog exists nor slaves are attached. */
server.master_repl_offset++; /* We don't have any data inside our buffer, but virtually the first
* byte we have is the next byte that will be generated for the
* replication stream. */
server.repl_backlog_off = server.master_repl_offset+1;
} // 3.6.2. 部分复制时的处理方式
// replication.c, 部分复制尝试
/* This function handles the PSYNC command from the point of view of a
* master receiving a request for partial resynchronization.
*
* On success return C_OK, otherwise C_ERR is returned and we proceed
* with the usual full resync. */
int masterTryPartialResynchronization(client *c) {
long long psync_offset, psync_len;
char *master_runid = c->argv[1]->ptr;
char buf[128];
int buflen; /* Is the runid of this master the same advertised by the wannabe slave
* via PSYNC? If runid changed this master is a different instance and
* there is no way to continue. */
// run_id 发生了变化,则需要重新同步
if (strcasecmp(master_runid, server.runid)) {
/* Run id "?" is used by slaves that want to force a full resync. */
if (master_runid[0] != '?') {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Partial resynchronization not accepted: "
"Runid mismatch (Client asked for runid '%s', my runid is '%s')",
master_runid, server.runid);
} else {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Full resync requested by slave %s",
replicationGetSlaveName(c));
}
goto need_full_resync;
} /* We still have the data our slave is asking for? */
if (getLongLongFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[2],&psync_offset,NULL) !=
C_OK) goto need_full_resync;
// offset 超出范围,使用全量同步
if (!server.repl_backlog ||
psync_offset < server.repl_backlog_off ||
psync_offset > (server.repl_backlog_off + server.repl_backlog_histlen))
{
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"Unable to partial resync with slave %s for lack of backlog (Slave request was: %lld).", replicationGetSlaveName(c), psync_offset);
if (psync_offset > server.master_repl_offset) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Warning: slave %s tried to PSYNC with an offset that is greater than the master replication offset.", replicationGetSlaveName(c));
}
goto need_full_resync;
} /* If we reached this point, we are able to perform a partial resync:
* 1) Set client state to make it a slave.
* 2) Inform the client we can continue with +CONTINUE
* 3) Send the backlog data (from the offset to the end) to the slave. */
c->flags |= CLIENT_SLAVE;
c->replstate = SLAVE_STATE_ONLINE;
c->repl_ack_time = server.unixtime;
c->repl_put_online_on_ack = 0;
listAddNodeTail(server.slaves,c);
/* We can't use the connection buffers since they are used to accumulate
* new commands at this stage. But we are sure the socket send buffer is
* empty so this write will never fail actually. */
// 响应客户端 +CONTINUE
buflen = snprintf(buf,sizeof(buf),"+CONTINUE\r\n");
if (write(c->fd,buf,buflen) != buflen) {
freeClientAsync(c);
return C_OK;
}
// 输出部分同步的数据
psync_len = addReplyReplicationBacklog(c,psync_offset);
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"Partial resynchronization request from %s accepted. Sending %lld bytes of backlog starting from offset %lld.",
replicationGetSlaveName(c),
psync_len, psync_offset);
/* Note that we don't need to set the selected DB at server.slaveseldb
* to -1 to force the master to emit SELECT, since the slave already
* has this state from the previous connection with the master. */ refreshGoodSlavesCount();
return C_OK; /* The caller can return, no full resync needed. */ need_full_resync:
/* We need a full resync for some reason... Note that we can't
* reply to PSYNC right now if a full SYNC is needed. The reply
* must include the master offset at the time the RDB file we transfer
* is generated, so we need to delay the reply to that moment. */
return C_ERR;
}
// replication.c, 根据偏移量响应从节点数据
/* Feed the slave 'c' with the replication backlog starting from the
* specified 'offset' up to the end of the backlog. */
long long addReplyReplicationBacklog(client *c, long long offset) {
long long j, skip, len; serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] Slave request offset: %lld", offset); if (server.repl_backlog_histlen == 0) {
serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] Backlog history len is zero");
return 0;
} serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] Backlog size: %lld",
server.repl_backlog_size);
serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] First byte: %lld",
server.repl_backlog_off);
serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] History len: %lld",
server.repl_backlog_histlen);
serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] Current index: %lld",
server.repl_backlog_idx); /* Compute the amount of bytes we need to discard. */
// 重点就是 计算出需要同步的点
skip = offset - server.repl_backlog_off;
serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] Skipping: %lld", skip); /* Point j to the oldest byte, that is actaully our
* server.repl_backlog_off byte. */
j = (server.repl_backlog_idx +
(server.repl_backlog_size-server.repl_backlog_histlen)) %
server.repl_backlog_size;
serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] Index of first byte: %lld", j); /* Discard the amount of data to seek to the specified 'offset'. */
j = (j + skip) % server.repl_backlog_size; /* Feed slave with data. Since it is a circular buffer we have to
* split the reply in two parts if we are cross-boundary. */
len = server.repl_backlog_histlen - skip;
serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] Reply total length: %lld", len);
while(len) {
long long thislen =
((server.repl_backlog_size - j) < len) ?
(server.repl_backlog_size - j) : len; serverLog(LL_DEBUG, "[PSYNC] addReply() length: %lld", thislen);
addReplySds(c,sdsnewlen(server.repl_backlog + j, thislen));
len -= thislen;
j = 0;
}
return server.repl_backlog_histlen - skip;
} //3.6.3. 全量复制时如何响应客户端
// 因为前面我们看到只是响应了一个 FULLRESYNC <master_runid> <master_offset> 的标识而已
// 实际上,这也是一个后台脚本在运行时处理的
// replication.c,
/* This function is called at the end of every background saving,
* or when the replication RDB transfer strategy is modified from
* disk to socket or the other way around.
*
* The goal of this function is to handle slaves waiting for a successful
* background saving in order to perform non-blocking synchronization, and
* to schedule a new BGSAVE if there are slaves that attached while a
* BGSAVE was in progress, but it was not a good one for replication (no
* other slave was accumulating differences).
*
* The argument bgsaveerr is C_OK if the background saving succeeded
* otherwise C_ERR is passed to the function.
* The 'type' argument is the type of the child that terminated
* (if it had a disk or socket target). */
void updateSlavesWaitingBgsave(int bgsaveerr, int type) {
listNode *ln;
int startbgsave = 0;
int mincapa = -1;
listIter li; listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *slave = ln->value; if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START) {
startbgsave = 1;
mincapa = (mincapa == -1) ? slave->slave_capa :
(mincapa & slave->slave_capa);
}
// 当bgsave 完成后, replstate 将变为 SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_END
// 代表可以进行发送 rdb 文件了
// 同样,基于epoll io模型,进行高效发送文件
else if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_END) {
struct redis_stat buf; /* If this was an RDB on disk save, we have to prepare to send
* the RDB from disk to the slave socket. Otherwise if this was
* already an RDB -> Slaves socket transfer, used in the case of
* diskless replication, our work is trivial, we can just put
* the slave online. */
if (type == RDB_CHILD_TYPE_SOCKET) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"Streamed RDB transfer with slave %s succeeded (socket). Waiting for REPLCONF ACK from slave to enable streaming",
replicationGetSlaveName(slave));
/* Note: we wait for a REPLCONF ACK message from slave in
* order to really put it online (install the write handler
* so that the accumulated data can be transfered). However
* we change the replication state ASAP, since our slave
* is technically online now. */
slave->replstate = SLAVE_STATE_ONLINE;
slave->repl_put_online_on_ack = 1;
slave->repl_ack_time = server.unixtime; /* Timeout otherwise. */
} else {
if (bgsaveerr != C_OK) {
freeClient(slave);
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"SYNC failed. BGSAVE child returned an error");
continue;
}
if ((slave->repldbfd = open(server.rdb_filename,O_RDONLY)) == -1 ||
redis_fstat(slave->repldbfd,&buf) == -1) {
freeClient(slave);
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"SYNC failed. Can't open/stat DB after BGSAVE: %s", strerror(errno));
continue;
}
slave->repldboff = 0;
slave->repldbsize = buf.st_size;
slave->replstate = SLAVE_STATE_SEND_BULK;
slave->replpreamble = sdscatprintf(sdsempty(),"$%lld\r\n",
(unsigned long long) slave->repldbsize); aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,slave->fd,AE_WRITABLE);
// 注册一个写事件到 epoll 中,由 sendBulkToSlave 进行具体的发送逻辑
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, slave->fd, AE_WRITABLE, sendBulkToSlave, slave) == AE_ERR) {
freeClient(slave);
continue;
}
}
}
}
if (startbgsave) startBgsaveForReplication(mincapa);
}
// replication.c, 发送 rdb 文件到从节点
void sendBulkToSlave(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
client *slave = privdata;
UNUSED(el);
UNUSED(mask);
char buf[PROTO_IOBUF_LEN];
ssize_t nwritten, buflen; /* Before sending the RDB file, we send the preamble as configured by the
* replication process. Currently the preamble is just the bulk count of
* the file in the form "$<length>\r\n". */
if (slave->replpreamble) {
nwritten = write(fd,slave->replpreamble,sdslen(slave->replpreamble));
if (nwritten == -1) {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE,"Write error sending RDB preamble to slave: %s",
strerror(errno));
freeClient(slave);
return;
}
server.stat_net_output_bytes += nwritten;
sdsrange(slave->replpreamble,nwritten,-1);
if (sdslen(slave->replpreamble) == 0) {
sdsfree(slave->replpreamble);
slave->replpreamble = NULL;
/* fall through sending data. */
} else {
return;
}
} /* If the preamble was already transfered, send the RDB bulk data. */
lseek(slave->repldbfd,slave->repldboff,SEEK_SET);
buflen = read(slave->repldbfd,buf,PROTO_IOBUF_LEN);
if (buflen <= 0) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Read error sending DB to slave: %s",
(buflen == 0) ? "premature EOF" : strerror(errno));
freeClient(slave);
return;
}
if ((nwritten = write(fd,buf,buflen)) == -1) {
if (errno != EAGAIN) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Write error sending DB to slave: %s",
strerror(errno));
freeClient(slave);
}
return;
}
slave->repldboff += nwritten;
server.stat_net_output_bytes += nwritten;
// 一次次地写入socket中,直到传输完成
if (slave->repldboff == slave->repldbsize) {
close(slave->repldbfd);
slave->repldbfd = -1;
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,slave->fd,AE_WRITABLE);
putSlaveOnline(slave);
}
}
PSYNC 也是主从同步的重要命令,它决定是全量复制还是部分复制。全量复制时,得决定是否开启 BGSAVE 操作;而部分复制时则只需把offset后的数据发送回slave即可完成数据同步。
4. 如何持续同步?
也叫增量同步。前面我们看这么多东西,其实也只做到了初次的全量复制和部分复制功能。那么第一次复制之后呢,后续又是如何持续同步的呢?
想想前面,既然有一个定时任务一直在运行,由它来实现可能是个不错的想法。从节点一直向其发送ping命令,而master节点则一直将自身的数据写入slave中,从而完成持续同步。
事实上,每个写动作,都会有一个事件传播的操作。而这个操作里,就会有一个检测 slave 情况的设定,而非cron去处理。就是 replicationFeedSlaves():
// 将命令传播给slaves
// 触发的场景如: 很多写操作, 特别的:某个key过期,
// replication.c
void replicationFeedSlaves(list *slaves, int dictid, robj **argv, int argc) {
listNode *ln;
listIter li;
int j, len;
char llstr[LONG_STR_SIZE]; /* If there aren't slaves, and there is no backlog buffer to populate,
* we can return ASAP. */
if (server.repl_backlog == NULL && listLength(slaves) == 0) return; /* We can't have slaves attached and no backlog. */
serverAssert(!(listLength(slaves) != 0 && server.repl_backlog == NULL)); /* Send SELECT command to every slave if needed. */
if (server.slaveseldb != dictid) {
robj *selectcmd; /* For a few DBs we have pre-computed SELECT command. */
if (dictid >= 0 && dictid < PROTO_SHARED_SELECT_CMDS) {
selectcmd = shared.select[dictid];
} else {
int dictid_len; dictid_len = ll2string(llstr,sizeof(llstr),dictid);
selectcmd = createObject(OBJ_STRING,
sdscatprintf(sdsempty(),
"*2\r\n$6\r\nSELECT\r\n$%d\r\n%s\r\n",
dictid_len, llstr));
} /* Add the SELECT command into the backlog. */
if (server.repl_backlog) feedReplicationBacklogWithObject(selectcmd); /* Send it to slaves. */
listRewind(slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *slave = ln->value;
if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START) continue;
addReply(slave,selectcmd);
} if (dictid < 0 || dictid >= PROTO_SHARED_SELECT_CMDS)
decrRefCount(selectcmd);
}
server.slaveseldb = dictid; /* Write the command to the replication backlog if any. */
if (server.repl_backlog) {
char aux[LONG_STR_SIZE+3]; /* Add the multi bulk reply length. */
aux[0] = '*';
len = ll2string(aux+1,sizeof(aux)-1,argc);
aux[len+1] = '\r';
aux[len+2] = '\n';
feedReplicationBacklog(aux,len+3); for (j = 0; j < argc; j++) {
long objlen = stringObjectLen(argv[j]); /* We need to feed the buffer with the object as a bulk reply
* not just as a plain string, so create the $..CRLF payload len
* and add the final CRLF */
aux[0] = '$';
len = ll2string(aux+1,sizeof(aux)-1,objlen);
aux[len+1] = '\r';
aux[len+2] = '\n';
feedReplicationBacklog(aux,len+3);
feedReplicationBacklogWithObject(argv[j]);
feedReplicationBacklog(aux+len+1,2);
}
} /* Write the command to every slave. */
listRewind(server.slaves,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *slave = ln->value; /* Don't feed slaves that are still waiting for BGSAVE to start */
// 只有初始化完成后的从节点,才会推送同步写操作
if (slave->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_WAIT_BGSAVE_START) continue; /* Feed slaves that are waiting for the initial SYNC (so these commands
* are queued in the output buffer until the initial SYNC completes),
* or are already in sync with the master. */ /* Add the multi bulk length. */
addReplyMultiBulkLen(slave,argc); /* Finally any additional argument that was not stored inside the
* static buffer if any (from j to argc). */
for (j = 0; j < argc; j++)
addReplyBulk(slave,argv[j]);
}
}
写操作的命令传播,是在 call() 调用实际的数据操作里统一封装的,避免了到处写相同的代码。
// server.c, 执行命令核心方法包装
// 调用如: processCommand().call(c,CMD_CALL_FULL); 会以最大能力处理命令
/* Call() is the core of Redis execution of a command.
*
* The following flags can be passed:
* CMD_CALL_NONE No flags.
* CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG Check command speed and log in the slow log if needed.
* CMD_CALL_STATS Populate command stats.
* CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF Append command to AOF if it modified the dataset
* or if the client flags are forcing propagation.
* CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL Send command to salves if it modified the dataset
* or if the client flags are forcing propagation.
* CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE Alias for PROPAGATE_AOF|PROPAGATE_REPL.
* CMD_CALL_FULL Alias for SLOWLOG|STATS|PROPAGATE.
*
* The exact propagation behavior depends on the client flags.
* Specifically:
*
* 1. If the client flags CLIENT_FORCE_AOF or CLIENT_FORCE_REPL are set
* and assuming the corresponding CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF/REPL is set
* in the call flags, then the command is propagated even if the
* dataset was not affected by the command.
* 2. If the client flags CLIENT_PREVENT_REPL_PROP or CLIENT_PREVENT_AOF_PROP
* are set, the propagation into AOF or to slaves is not performed even
* if the command modified the dataset.
*
* Note that regardless of the client flags, if CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF
* or CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL are not set, then respectively AOF or
* slaves propagation will never occur.
*
* Client flags are modified by the implementation of a given command
* using the following API:
*
* forceCommandPropagation(client *c, int flags);
* preventCommandPropagation(client *c);
* preventCommandAOF(client *c);
* preventCommandReplication(client *c);
*
*/
void call(client *c, int flags) {
long long dirty, start, duration;
int client_old_flags = c->flags;
...
/* Call the command. */
dirty = server.dirty;
start = ustime();
c->cmd->proc(c);
duration = ustime()-start;
dirty = server.dirty-dirty;
if (dirty < 0) dirty = 0;
...
// 此处将需要传播的命令传播到 slave
/* Propagate the command into the AOF and replication link */
if (flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE &&
(c->flags & CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP) != CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP)
{
int propagate_flags = PROPAGATE_NONE; /* Check if the command operated changes in the data set. If so
* set for replication / AOF propagation. */
if (dirty) propagate_flags |= (PROPAGATE_AOF|PROPAGATE_REPL); /* If the client forced AOF / replication of the command, set
* the flags regardless of the command effects on the data set. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_REPL) propagate_flags |= PROPAGATE_REPL;
if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_AOF) propagate_flags |= PROPAGATE_AOF; /* However prevent AOF / replication propagation if the command
* implementatino called preventCommandPropagation() or similar,
* or if we don't have the call() flags to do so. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PREVENT_REPL_PROP ||
!(flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL))
propagate_flags &= ~PROPAGATE_REPL;
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PREVENT_AOF_PROP ||
!(flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF))
propagate_flags &= ~PROPAGATE_AOF; /* Call propagate() only if at least one of AOF / replication
* propagation is needed. */
// 如果需要传播命令,则调用 propagate(), propagate 会决定写 AOF 或者 slaves
if (propagate_flags != PROPAGATE_NONE)
propagate(c->cmd,c->db->id,c->argv,c->argc,propagate_flags);
} /* Restore the old replication flags, since call() can be executed
* recursively. */
c->flags &= ~(CLIENT_FORCE_AOF|CLIENT_FORCE_REPL|CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP);
c->flags |= client_old_flags &
(CLIENT_FORCE_AOF|CLIENT_FORCE_REPL|CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP);
...
server.stat_numcommands++;
}
/* Propagate the specified command (in the context of the specified database id)
* to AOF and Slaves.
*
* flags are an xor between:
* + PROPAGATE_NONE (no propagation of command at all)
* + PROPAGATE_AOF (propagate into the AOF file if is enabled)
* + PROPAGATE_REPL (propagate into the replication link)
*
* This should not be used inside commands implementation. Use instead
* alsoPropagate(), preventCommandPropagation(), forceCommandPropagation().
*/
void propagate(struct redisCommand *cmd, int dbid, robj **argv, int argc,
int flags)
{
// 写 AOF 文件
if (server.aof_state != AOF_OFF && flags & PROPAGATE_AOF)
feedAppendOnlyFile(cmd,dbid,argv,argc);
// 写slave
if (flags & PROPAGATE_REPL)
replicationFeedSlaves(server.slaves,dbid,argv,argc);
}
其实整个同步过程并不太复杂,大体就是建立连接然后复制数据然后恢复数据的过程,只是要实现的时候,代码还是不会太少。
当然,这里面会有很多要注意的点:
1. 如何不影响性能?
2. 如何保证低延迟?
3. 如何安全地复制?
4. 如何检测异常?
5. 如何保证高可用性?
Redis(九):主从复制的设计与实现解析的更多相关文章
- redis的主从复制配置
redis的主从复制配置 一. 原理 Redis的主从复制功能非常强大,一个master可以拥有多个slave,而一个slave又可以拥有多个slave,如此下去,形成了强大的多级服务器集群架 ...
- Redis的字典(dict)rehash过程源代码解析
Redis的内存存储结构是个大的字典存储,也就是我们通常说的哈希表.Redis小到能够存储几万记录的CACHE,大到能够存储几千万甚至上亿的记录(看内存而定),这充分说明Redis作为缓冲的强大.Re ...
- Redis基础学习(五)—Redis的主从复制
一.概述 Redis的主从复制策略是通过其持久化的rdb文件来实现的,其过程是先dump出rdb文件,将rdb文件全量传输给slave,然后再将dump后的操作实时同步到slave中.让从服务 ...
- Redis的主从复制与Redis Sentinel哨兵机制
1 Redis的主从复制 1.1 什么是主从复制 持久化保证了即使redis服务重启也不会丢失数据,因为redis服务重启后会将硬盘上持久化的数据恢复到内存中,但是当redis服务器的硬盘损 ...
- 浅谈:redis的主从复制 + 哨兵模式
浅谈:redis的主从复制 + 哨兵模式 主从模式 在谈论redis的主从复制之前,我们先回想下mysql的主从搭建过程,第一步呢首先要在主库服务器中修改my.cnf,开启一下bin_log功能, ...
- Redis总结(三)Redis 的主从复制
接着上一篇,前面两篇我总结了<Redis总结(一)Redis安装>和<Redis总结(二)C#中如何使用redis> 所以这一篇,会讲讲Redis 的主从复制以及C#中如何调用 ...
- 实现Redis的主从复制配置
实现Redis的主从复制配置比较简单,而且容易明白. 下图是要配置的主从复制结构图: 1.说明 Redis主从复制中一个主服务可以有多个从服务,一个从服务可以有多个从服务. 配置比较简单,只需要更改r ...
- redis的主从复制部署和使用
reids一种key-value的缓存数据库目前非常流行的被使用在很多场景,比如在数据库读写遇到瓶颈时缓存且读写分离会大大提升这块的性能,下面我就说说redis的主从复制 首先需要启动多个redis实 ...
- redis实现主从复制-单机测试
一.redis实现主从复制-单机测试1.安装redis tar -zxvf redis-2.8.4.tar.gzcd redis-2.8.4make && make install2. ...
随机推荐
- Java并发-几种常见的锁
这几天在忙着投提前批内推,前面看的好多东西没有总结,正好这两天补上顺带复习一下 synchronized:Java之重型锁
- 能快速理解Java_集合类_的文章
目录 @ 这篇文章是我学习完Java集合类做的笔记和总结,如果你想认真细读这篇文章,请做好受虐的准备(建议电脑看),因为这篇文章有点长,ヽ(ー_ー)ノ. 如果在看我这篇文章过程中,发现了错误,望指点. ...
- centos7 安装jdk8和maven3
centos7 安装jdk8和maven3 标签(空格分隔): java,linux jdk 第一种安装: yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk /usr/lib/jvm/ 默 ...
- MapGIS文件如何压缩存盘
经过多次编辑修改的MapGIS数据,含有大量逻辑上已删除的节点或图元,数据冗余复杂, 在转换过程前应注意一定要采用压缩存盘方式处理,目的是确保编辑状态已删除的数据真正从物理存储层删除,以确保数据的精简 ...
- Scala实践2
一.Scala基本类型和操作 1.1 基本类型 Scala的基本类型与Java基本类型相同,都是byte.short.int.long.char.string.float.double.boolea ...
- 2019-2020春江云暖你先知,CAE/EDA/高校等CloudHPC领域年均复合增长率超21%
原创: 灵魂工作室 速石科技 我猜,我们是最早和你说春天来了的人. 一年前,我们还在小心谨慎地定义着Cloud HPC,一脸娇羞地拿Novartis 诺华制药在5年前做的案例当作标杆. 不久前,Hyp ...
- Scala 学习(3)之「类——基本概念1」
类 小提示:可以通过:paste进入 Scala 的多行模式,输入对应的代码块之后,按ctrl + D退出多行模式,然后再调用刚才输入的函数或者方法进行测试 //定义类,包含 field 以及方法 c ...
- woj - 将一个问题转换为背包问题
Problem 1538 - B - Stones II Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536KB Total Submit: 428 Accepte ...
- 切蛋糕(贪心 or 优先队列)
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/80/D来源:牛客网 最可爱的applese生日啦,他准备了许多个质量不同的蛋糕,想请一些同学来参加他的派对为他庆生,为 ...
- Nginx作为web静态资源服务器——防盗链
基于http_refer防盗链配置模块 Syntax:valid_referers none | blocked | server_names | string ...; Default:—— C ...
