邮件发送模型及其Python应用实例
SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
制定:
First:RFC 788 in 1981
Last:RFC 5321 in 2008
端口:
TCP 25(SMTP), TCP 465/587(SMTP_SSL)
功能:
用户客户端:
发送消息:SMTP
接收和管理消息:POP3、IMAP
邮件服务器:
发送和接收消息:SMTP
说明:
SMTP仅定义了消息传输格式(如消息发送者参数),而非消息内容(如消息头和消息体)。
邮件发送模型
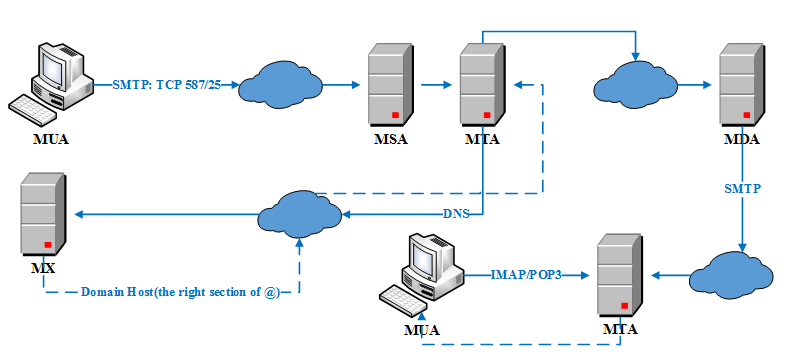
流程描述:
(1) 使用SMTP协议,通过MUA(Mail User Agent)提交邮件到MSA(Mail Submission Agent),然后MSA递送邮件到MTA(Mail Transfer Agent)[通常而言,MSA和MTA是同一邮件服务器上的两个不同例程,其也被称为SMTP服务器]。
(2) MTA通过DNS在MX(Mail Exchanger Record)上查询接收者的邮件服务器。
(3) MTA发送邮件到目标邮件服务器MTA,其间可能是两个MTA直接通信,或者经过多个SMTP服务器,最终到达MDA(Mail Delivery Agent)。
(4) MDA直接递送或者通过SMTP协议,将邮件递送到本地MTA。
(5) 终端应用程序通过IMAP/POP3协议接收和管理邮件。
SMTP协议
SMTP由3部分构成:
- MAIL:建立发送者地址。
- RCPT:建立接收者地址。
- DATA:标志邮件内容的开始。邮件内容由两部分构成:邮件头和以空行分割的邮件体。DATA是一组命令,服务器需要做两次回复:第一次回复表明其准备好接收邮件,第二次回复表明其接收/拒绝整个邮件。
一个简单的SMTP发送示例(主要为了说明SMTP的3个部分),如sender给receiver1和receiver2发送邮件:
S:表示SMTP服务器 C:表示SMTP客户端
客户端C建立TCP连接后,服务端S通过greeting建立会话(附带服务器的FQDN(Fully Qualified Domain Name)),客户端C通过HELLO响应会话(附带客户端的FQDN)。
# 建立会话
S: 220 smtp.example.com ESMTP Postfix
C: HELO client.example.org
S: 250 Hello client.example.org, I am glad to meet you # 发送消息
C: MAIL FROM:<sender@example.org>
S: 250 Ok
C: RCPT TO:<receiver1@example.com>
S: 250 Ok
C: RCPT TO:<receiver2@example.com>
S: 250 Ok
C: DATA
S: 354 End data with <CR><LF>.<CR><LF>
C: From: "Sender Example" <sender@example.org>
C: To: "Receiver1 Example" <receiver1@example.com>
C: Cc: receiver2@example.com
C: Date: Tue, 15 January 2008 16:02:43 -0500
C: Subject: Test message
C:
C: Hello Receiver1.
C: This is a test message with 5 header fields and 4 lines in the message body.
C: Your friend,
C: Sender
C: .
S: 250 Ok: queued as 12345
C: QUIT
S: 221 Bye
{The server closes the connection}
Python邮件模块
python中邮件发送使用smtplib模块,其一般流程为:初始化连接->发送邮件->退出。其中包含的类有SMTP,SMTP_SSL,LMTP。如上SMTP中的会话示例在python中对应的部分如下:
C: HELO client.example.org --- SMTP.helo([hostname]): 使用HELO向SMTP服务器标识自己。
S: 250 Hello client.example.org, I am glad to meet you
--- SMTP.verify(address):服务器用来验证地址的有效性,返回一个元组(250,相关地址)或者(>=400, 错误消息字符串)。
C: MAIL FROM:<sender@example.org> --- low-level methods: mail()
C: RCPT TO:<receiver1@example.com> --- low-level methods: rcpt()
C: DATA --- low-level methods: data()
C: QUIT --- SMTP.quit(): 终止会话,关闭连接。
Python Email Demos
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import print_function
from __future__ import with_statement __author__ = 'xxx'
__all__ = ['BTEmail'] import smtplib
import sys
import os
import time
import mimetypes
from email import encoders
from email.header import Header
from email.utils import parseaddr, formataddr
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
from email.mime.image import MIMEImage
from email.mime.audio import MIMEAudio
from email.mime.base import MIMEBase # ----- The following information should be in the configuration file.
from_addr = 'xxx@sina.com'
to_addrs = ['yyy@126.com', 'zzz@163.com']
cc_addrs = ['xxx@sina.com', 'www@qq.com']
bcc_addrs = []
username = 'xxx@sina.com'
password = '---'
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ class BTEmail(object):
def __init__(self, host='smtp.sina.com', port=465, username=None, password=None):
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.username = username
self.password = password @classmethod
def _format_addr(cls, envolope_string):
# parseaddr() only parses single address or string.
(name, addr) = parseaddr(envolope_string)
return formataddr((\
Header(name, 'utf-8').encode(),\
addr.encode('utf-8') if isinstance(addr, unicode) else addr)) @classmethod
def construct_msg(cls, contentfile, contenttype='html', charset='utf-8',
attach_flag=False, attachpath=None):
with open(contentfile, 'rb') as fp:
content = MIMEText(fp.read(), contenttype, charset) if not attach_flag:
msg = content
else:
# Construct root container.
msg = MIMEMultipart()
# Attach mail contents to the container.
msg.attach(content) # Attach attachments to the container.
for filename in os.listdir(attachpath):
item = os.path.join(attachpath, filename)
if not os.path.isfile(item):
continue
# Guess the content type based on the file's extension.
(ctype, encoding) = mimetypes.guess_type(item)
if ctype is None or encoding is not None:
ctype = 'application/octet-stream'
(maintype, subtype) = ctype.split('/', 1) # Load and encode attachments.
"""
# Use MIMEBase class construct attachments.
with open(item, 'rb') as fp:
attachment = MIMEBase(_maintype=maintype, _subtype=subtype)
attachment.set_payload(fp.read())
encoders.encode_base64(attachment)
"""
# Use concrete type class construct attachments.
if maintype == 'text':
with open(item, 'rb') as fp:
attachment = MIMEText(fp.read(), _subtype=subtype)
elif maintype == 'image':
with open(item, 'rb') as fp:
attachment = MIMEImage(fp.read(), _subtype=subtype)
elif maintype == 'audio':
with open(item, 'rb') as fp:
attachment = MIMEAudio(fp.read(), _subtype=subtype)
else:
with open(item, 'rb') as fp:
attachment = MIMEBase(_maintype=maintype, _subtype=subtype)
attachment.set_payload(fp.read())
encoders.encode_base64(attachment) # Set attachment header.
attachment.add_header('Content-Disposition', 'attachment', filename=filename)
msg.attach(attachment)
return msg @classmethod
def make_envolope(cls, msg, from_addr, to_addrs, subject='A Simple SMTP Demo'):
if msg:
msg['From'] = cls._format_addr(u'BT<%s>' % from_addr)
# msg['To'] should be a string, not a list.
msg['To'] = ','.join(to_addrs)
msg['Cc'] = ','.join(cc_addrs)
msg['Bcc'] = ','.join(bcc_addrs)
msg['Subject'] = Header(u'主题<%s>' % subject, 'utf-8').encode() def send_mail(self, from_addr, to_addrs, msg):
smtp_server = smtplib.SMTP_SSL()
try:
#smtp_server.set_debuglevel(True) RECONNECT = 10 # Reconnect times.
for i in xrange(RECONNECT):
try:
smtp_server.connect(self.host, self.port)
except smtplib.SMTPConnectError:
if i < RECONNECT:
print('Connecting to smtp server...')
time.sleep(6)
continue
else:
sys.exit('Can not connect to smtp server.')
except smtplib.SMTPServerDisconnected:
sys.exit('SMTP server is lost.')
else:
break try:
smtp_server.starttls()
except smtplib.SMTPException:
print('SMTP server does not support the STARTTLS extension.') try:
smtp_server.login(username, password)
except smtplib.SMTPAuthenticationError:
print('Username or Password is incorrect.') try:
refusal_dict = smtp_server.sendmail(from_addr, to_addrs, msg.as_string())
except smtplib.SMTPSenderRefused:
sys.exit('SMTP server does not accept the %s.' % from_addr)
except smtplib.SMTPDataError:
sys.exit('SMTP server replied with an unexpected error code .')
else:
if refusal_dict:
print('*****SMTP server rejects the following recipients:*****')
print(list(refusal_dict.items()))
print('*******************************************************')
finally:
smtp_server.quit() def main():
# Send text/plain email.
"""
email_obj = BTEmail(host='smtp.sina.com', port=465, username=username, password=password)
msg = email_obj.construct_msg(r'content\mail.txt', 'plain', 'utf-8')
email_obj.make_envolope(msg, from_addr, to_addrs, subject='This is a plain text mail.')
email_obj.send_mail(from_addr, to_addrs + cc_addrs, msg)
""" # Send text/html email.
"""
email_obj = BTEmail(host='smtp.sina.com', port=465, username=username, password=password)
msg = email_obj.construct_msg(r'content\mail.html', 'html', 'utf-8')
email_obj.make_envolope(msg, from_addr, to_addrs, subject='This is a html mail.')
email_obj.send_mail(from_addr, to_addrs + cc_addrs, msg)
""" # Send email with attachments.
email_obj = BTEmail(host='smtp.sina.com', port=465, username=username, password=password)
msg = email_obj.construct_msg(r'content\mail.html', 'html', 'utf-8', attach_flag=True, attachpath=r'attachment')
email_obj.make_envolope(msg, from_addr, to_addrs, subject='A html mail with attachments.')
email_obj.send_mail(from_addr, to_addrs + cc_addrs, msg) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
邮件发送模型及其Python应用实例的更多相关文章
- python学习笔记(SMTP邮件发送)
想着给框架添加邮件发送功能.所以整理下python下邮件发送功能 首先python是支持邮件的发送.内置smtp库.支持发送纯文本.HTML及添加附件的邮件 之后是邮箱.像163.qq.新浪等邮箱默认 ...
- .NET开发邮件发送功能的全面教程(含邮件组件源码)
今天,给大家分享的是如何在.NET平台中开发“邮件发送”功能.在网上搜的到的各种资料一般都介绍的比较简单,那今天我想比较细的整理介绍下: 1) 邮件基础理论知识 2) ...
- .NET开发邮件发送功能
.NET开发邮件发送功能 今天,给大家分享的是如何在.NET平台中开发“邮件发送”功能.在网上搜的到的各种资料一般都介绍的比较简单,那今天我想比较细的整理介绍下: 1) 邮件基础理论知 ...
- python SMTP邮件发送(转载)
Python SMTP发送邮件 SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)即简单邮件传输协议,它是一组用于由源地址到目的地址传送邮件的规则,由它来控制信件的中转方式. py ...
- Python 邮件发送
python发送各类邮件的主要方法 python中email模块使得处理邮件变得比较简单,今天着重学习了一下发送邮件的具体做法,这里写写自己的的心得,也请高手给些指点. 一.相关模块介绍 ...
- python实现邮件发送完整代码(带附件发送方式)
实例一:利用SMTP与EMAIL实现邮件发送,带附件(完整代码) __author__ = 'Administrator'#coding=gb2312 from email.Header import ...
- python实现邮件发送
实例补充: #**************************利用STMP自动发送邮件******************************import smtplibsmtp = smtp ...
- python初级实战-----关于邮件发送问题
python发邮件需要掌握两个模块的用法,smtplib和email,这俩模块是python自带的,只需import即可使用.smtplib模块主要负责发送邮件,email模块主要负责构造邮件. sm ...
- python学习笔记(SMTP邮件发送:带附件)
博主有段时间没有更新博客了 先整理一个之前整理过的SMTP邮件发送,这次是带附件的功能 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf_8 -*- from email ...
随机推荐
- pip换国内源
pip换国内源 1.国内常用源 阿里云 http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ 中国科技大学 https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu. ...
- unity3d动态操作组件
利用范型,动态操作组件(添加或删除) e.AddComponent<CubeTranslate> ();//动态添加组件 Destroy (e.GetComponent<CubeTr ...
- angular绑定数据 使用循环输出列表数据
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <script sr ...
- Rabbitmq消息队列(六) 主题交换机
1.简介 前面学习了有选择性的接收消息,但是却没有办法基于多个标准来接收消息.为了实现这个目的,接下来我们学习如何使用另一种更复杂的交换机 —— 主题交换机. 2.主题交换机 发送到主题交换机(top ...
- unity, particle play once and destroy
粒子播放一次后销毁: //ref: http://answers.unity3d.com/questions/219609/auto-destroying-particle-system ...
- 并且需要用websocket实时接收数据 VS 组件ng2websocket的
chart.service.ts: import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { WebSocketService } from './we ...
- PMON
PMON是一个兼有BIOS和boot loader部分功能的开放源码软件,多用于嵌入式系统. 与BIOS相比功能不足,与常见的bootloader 相比,功能要丰富的多.基于龙芯的系统采用 pmon ...
- nginx vhosts rewrite 独立文件的方式出现
[root@web01 /]# cat /app/server/nginx/conf/nginx.conf user www www; worker_processes ; error_log /ap ...
- gpg: symbol lookup error
今天使用sudo apt-get 安装包的时候,出现gpg错误,如下: gpg: symbol lookup error: /usr/local/lib/libreadline.so.6: undef ...
- iOS网络访问之使用AFNetworking
AFNetworking是IOS上常用的第三方网络访问库,我们可以在github上下载它,同时github上有它详细的使用说明,最新的AFNetworing2.0与1.0有很大的变化,这里仅对2.0常 ...
