JVM Run-Time Data Areas--reference
http://www.programcreek.com/2013/04/jvm-run-time-data-areas/
This is my note of reading JVM specification. I draw a diagram which helps me understand.
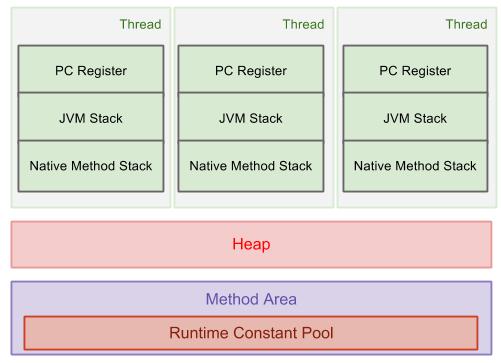
1. Data Areas for Each Individual Thread (not shared)
Data Areas for each individual thread include program counter register, JVM Stack, and Native Method Stack. They are all created when a new thread is created.
Program Counter Register: it is used to control each execution of each thread.
JVM Stack: It contains frames which is demonstrated in the diagram below.
Native Method Stack: it is used to support native methods, i.e., non-Java language methods.
2. Data Areas Shared by All Threads
All threads share Heap and Method Area.
Heap: it is the area that we most frequently deal with. It stores
arrays and objects, created when JVM starts up. Garbage Collection works
in this area.
Method Area: it stores run-time constant pool, field and method data, and methods and constructors code。
Runtime Constant Pool: It is a per-class or per-interface run-time
representation of the constant_pool table in a class file. It contains
several kinds of constants, ranging from numeric literals known at
compile-time to method and field references that must be resolved at
run-time.
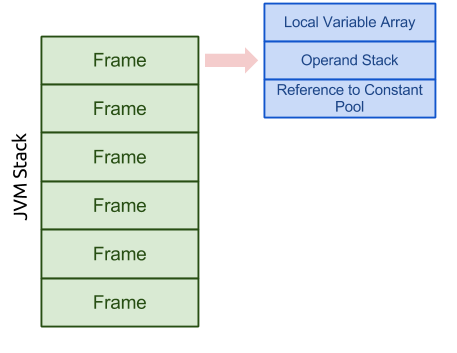
Stack contains Frames, and a frame is pushed to the stack when a
method is invoked. A frame contains local variable array, Operand Stack,
Reference to Constant Pool.
For more information, please go to the offical JVM specification site.
References:
1. JVM Specification – Run-Time Data Areas
2. Java Bytecode Fundamentals
JVM Run-Time Data Areas--reference的更多相关文章
- JVM Run-Time Data Areas.
Ref: JVM Run-Time Data Areas class SimpleThread extends Thread { public SimpleThread(String name) { ...
- Java Run-Time Data Areas
前言 本文主要介绍JVM的运行时数据区 来自Oracle文档 Java Virtual Machine Specification -- Chapter 2. The Structure of the ...
- Recover data from reference electrode via EEGLab 用EEGLab恢复参考电极数据
The data of scanning reference electrode will not show initially. Here is a summary of recovering it ...
- Java-JVM 运行时内存结构(Run-Time Data Areas)
Java 虚拟机定义了在程序执行期间使用的各种运行时数据区域. 其中一些数据区域所有线程共享,在 Java 虚拟机(JVM)启动时创建,仅在 Java 虚拟机退出时销毁. 还有一些数据区域是每个线程的 ...
- 深入理解JVM内幕(转)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/zhoudaxia/article/details/26454421/ 每个Java开发者都知道Java字节码是执行在JRE((Java Runtime ...
- 深入理解JVM内幕:从基本结构到Java 7新特性
转自:http://www.importnew.com/1486.html 每个Java开发者都知道Java字节码是执行在JRE((Java Runtime Environment Java运行时环境 ...
- JVM 内部原理(二)— 基本概念之字节码
JVM 内部原理(二)- 基本概念之字节码 介绍 版本:Java SE 7 每位使用 Java 的程序员都知道 Java 字节码在 Java 运行时(JRE - Java Runtime Enviro ...
- JVM 内部原理(一)— 概述
JVM 内部原理(一)- 概述 介绍 版本:Java SE 7 图中显示组件将会从两个方面分别解释.第一部分涵盖线程独有的组件,第二部分涵盖独立于线程的组件(即线程共享组件). 目录 线程独享(Thr ...
- Understanding JVM Internals---不得不转载呀
http://www.cubrid.org/blog/dev-platform/understanding-jvm-internals/ http://architects.dzone.com/art ...
随机推荐
- 只是误以为导入了maven依赖
背景: 之前用Spring Boot 开发了一个小项目,考虑将代码迁到Git服务器,由于之前没用过Git,在将代码正式签入Git服务器前, 我想先签入一个最简单的Spring Boot程序代码作为试验 ...
- tomcat异常 Socket bind failed: [730048]
tomcat从官网站点下载时须注意版本信息: zip格式为window压缩版. tar.gz为linux安装板. installer为window安装板. 解压后的各文件功能与作用: bin:用于放置 ...
- Flash Builder 4.6/4.7 注释以及字体大小修改
①修改字体颜色.粗体.斜体.下划线 英文版:windows-preferences-flex-editors-syntex coloring-ActionScript-Comment 汉化版:窗口—首 ...
- iis 部署webapi常见错误及解决方案
iis 部署webapi常见错误及解决方案 错误一: 原因:asp.net web api部署在Windows服务器上后,按照WebAPI定义的路由访问,老是出现404,但定义一个静态文件从站点访问, ...
- logstash--使用ngxlog收集windows日志
收集流程 1nxlog => 2logstash => 3elasticsearch 1. nxlog 使用模块 im_file 收集日志文件,开启位置记录功能 2. nxlog 使用模块 ...
- [ActionScript 3.0] AS向php发送二进制数据方法之——在URLRequest中构造HTTP协议发送数据
主类 HTTPSendPHP.as package { import com.JPEGEncoder.JPGEncoder; import com.fylib.httpRequest.HttpRequ ...
- 3. Javascript学习笔记——变量、内存、作用域
3. 变量.内存.作用域 3.1 基本类型和引用类型的值 ECMAScript 变量可能包含两种不同数据类型的值:基本类型值[Undefined.Null.Boolean.Number 和 Strin ...
- 更改Android编译软件版本(make/gcc/bision)
一.make版本 1.下载make的压缩包 ftp://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/make/ 2.解压,安装 cd make-x.x ./configuration sh build.sh su ...
- google浏览器安装不上的绝望经历
手贱把google的一些文件删除了,整个浏览器都没法打开 决定重装下,但是连卸载的功能都无法打开了 于是决定上网重新下载了个安装包,发现安装包都打不来 很绝望,查了很多资料 很多人说要删除注册表的东西 ...
- vue-cli项目启动遇到的坑
利用 npm init webpack projectname 之后 切换到项目所在文件夹下,执行命令 npm install ,一直非常慢,卡在那里基本不动. 最后是利用cnpm 安装成功的. 转载 ...
