从 RequireJs 源码剖析脚本加载原理
引言
俗话说的好,不喜欢研究原理的程序员不是好的程序员,不喜欢读源码的程序员不是好的 jser。这两天看到了有关前端模块化的问题,才发现 JavaScript 社区为了前端工程化真是煞费苦心。今天研究了一天前端模块化的问题,先是大概了解了下模块化的标准规范,然后了解了一下 RequireJs 的语法和使用方法,最后研究了下 RequireJs 的设计模式和源码,所以想记录一下相关的心得,剖析一下模块加载的原理。
一、认识 RequireJs
在开始之前,我们需要了解前端模块化,本文不讨论有关前端模块化的问题,有关这方面的问题可以参考阮一峰的系列文章 Javascript 模块化编程。
使用 RequireJs 的第一步:前往官网 http://requirejs.org/;
第二步:下载文件;

第三步:在页面中引入 requirejs.js 并设置 main 函数;
<script type="text/javascript" src="scripts/require.js" data-main="scripts/main.js"></script>
然后我们就可以在 main.js 文件里编程了,requirejs 采用了 main 函数式的思想,一个文件即为一个模块,模块与模块之间可以依赖,也可以毫无干系。使用 requirejs ,我们在编程时就不必将所有模块都引入页面,而是需要一个模块,引入一个模块,就相当于 Java 当中的 import 一样。
定义模块:
//直接定义一个对象
define({
color: "black",
size: "unisize"
});
//通过函数返回一个对象,即可以实现 IIFE
define(function () {
//Do setup work here return {
color: "black",
size: "unisize"
}
});
//定义有依赖项的模块
define(["./cart", "./inventory"], function(cart, inventory) {
//return an object to define the "my/shirt" module.
return {
color: "blue",
size: "large",
addToCart: function() {
inventory.decrement(this);
cart.add(this);
}
}
}
);
导入模块:
//导入一个模块
require(['foo'], function(foo) {
//do something
});
//导入多个模块
require(['foo', 'bar'], function(foo, bar) {
//do something
});
关于 requirejs 的使用,可以查看官网 API ,也可以参考 RequireJS 和 AMD 规范 ,本文暂不对 requirejs 的使用进行讲解。
二、main 函数入口
requirejs 的核心思想之一就是使用一个规定的函数入口,就像 C++ 的 int main(),Java 的 public static void main(),requirejs 的使用方式是把 main 函数缓存在 script 标签上。也就是将脚本文件的 url 缓存在 script 标签上。
<script type="text/javascript" src="scripts/require.js" data-main="scripts/main.js"></script>
初来乍到电脑同学一看,哇!script 标签难道还有什么不为人知的属性吗?吓得我赶紧打开了 W3C 查看相关 API,并为自己的 HTML 基础知识感到惭愧,可是遗憾的是 script 标签并没有相关的属性,甚至这都不是一个标准的属性,那么它到底是什么玩意呢?下面直接上一部分 requirejs 源码:
//Look for a data-main attribute to set main script for the page
//to load. If it is there, the path to data main becomes the
//baseUrl, if it is not already set.
dataMain = script.getAttribute('data-main');
实际上在 requirejs 中只是获取在 script 标签上缓存的数据,然后取出数据加载而已,也就是跟动态加载脚本是一样的,具体是怎么操作,在下面的讲解中会放出源码。
三、动态加载脚本
这一部分是整个 requirejs 的核心,我们知道在 Node.js 中加载模块的方式是同步的,这是因为在服务器端所有文件都存储在本地的硬盘上,传输速率快而且稳定。而换做了浏览器端,就不能这么干了,因为浏览器加载脚本会与服务器进行通信,这是一个未知的请求,如果使用同步的方式加载,就可能会一直阻塞下去。为了防止浏览器的阻塞,我们要使用异步的方式加载脚本。因为是异步加载,所以与模块相依赖的操作就必须得在脚本加载完成后执行,这里就得使用回调函数的形式。
我们知道,如果显示的在 HTML 中定义脚本文件,那么脚本的执行顺序是同步的,比如:
//module1.js
console.log("module1");
//module2.js
console.log("module2");
//module3.js
console.log("module3");
<script type="text/javascript" src="scripts/module/module1.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="scripts/module/module2.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="scripts/module/module3.js"></script>
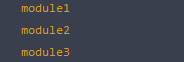
那么在浏览器端总是会输出:
但是如果是动态加载脚本的话,脚本的执行顺序是异步的,而且不光是异步的,还是无序的:
//main.js
console.log("main start"); var script1 = document.createElement("script");
script1.src = "scripts/module/module1.js";
document.head.appendChild(script1); var script2 = document.createElement("script");
script2.src = "scripts/module/module2.js";
document.head.appendChild(script2); var script3 = document.createElement("script");
script3.src = "scripts/module/module3.js";
document.head.appendChild(script3); console.log("main end");
使用这种方式加载脚本会造成脚本的无序加载,浏览器按照先来先运行的方法执行脚本,如果 module1.js 文件比较大,那么极其有可能会在 module2.js 和 module3.js 后执行,所以说这也是不可控的。要知道一个程序当中最大的 BUG 就是一个不可控的 BUG ,有时候它可能按顺序执行,有时候它可能乱序,这一定不是我们想要的。
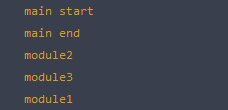
注意这里的还有一个重点是,"module" 的输出永远会在 "main end" 之后。这正是动态加载脚本异步性的特征,因为当前的脚本是一个 task ,而无论其他脚本的加载速度有多快,它都会在 Event Queue 的后面等待调度执行。这里涉及到一个关键的知识 — Event Loop ,如果你还对 JavaScript Event Loop 不了解,那么请先阅读这篇文章 深入理解 JavaScript 事件循环(一)— Event Loop。
四、导入模块原理
在上一小节,我们了解到,使用动态加载脚本的方式会使脚本无序执行,这一定是软件开发的噩梦,想象一下你的模块之间存在上下依赖的关系,而这时候他们的加载顺序是不可控的。动态加载同时也具有异步性,所以在 main.js 脚本文件中根本无法访问到模块文件中的任何变量。那么 requirejs 是如何解决这个问题的呢?我们知道在 requirejs 中,任何文件都是一个模块,一个模块也就是一个文件,包括主模块 main.js,下面我们看一段 requirejs 的源码:
/**
* Creates the node for the load command. Only used in browser envs.
*/
req.createNode = function (config, moduleName, url) {
var node = config.xhtml ?
document.createElementNS('http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml', 'html:script') :
document.createElement('script');
node.type = config.scriptType || 'text/javascript';
node.charset = 'utf-8';
node.async = true;
return node;
};
在这段代码中我们可以看出, requirejs 导入模块的方式实际就是创建脚本标签,一切的模块都需要经过这个方法创建。那么 requirejs 又是如何处理异步加载的呢?传说江湖上最高深的医术不是什么灵丹妙药,而是以毒攻毒,requirejs 也深得其精髓,既然动态加载是异步的,那么我也用异步来对付你,使用 onload 事件来处理回调函数:
//In the browser so use a script tag
node = req.createNode(config, moduleName, url); node.setAttribute('data-requirecontext', context.contextName);
node.setAttribute('data-requiremodule', moduleName); //Set up load listener. Test attachEvent first because IE9 has
//a subtle issue in its addEventListener and script onload firings
//that do not match the behavior of all other browsers with
//addEventListener support, which fire the onload event for a
//script right after the script execution. See:
//https://connect.microsoft.com/IE/feedback/details/648057/script-onload-event-is-not-fired-immediately-after-script-execution
//UNFORTUNATELY Opera implements attachEvent but does not follow the script
//script execution mode.
if (node.attachEvent &&
//Check if node.attachEvent is artificially added by custom script or
//natively supported by browser
//read https://github.com/requirejs/requirejs/issues/187
//if we can NOT find [native code] then it must NOT natively supported.
//in IE8, node.attachEvent does not have toString()
//Note the test for "[native code" with no closing brace, see:
//https://github.com/requirejs/requirejs/issues/273
!(node.attachEvent.toString && node.attachEvent.toString().indexOf('[native code') < 0) &&
!isOpera) {
//Probably IE. IE (at least 6-8) do not fire
//script onload right after executing the script, so
//we cannot tie the anonymous define call to a name.
//However, IE reports the script as being in 'interactive'
//readyState at the time of the define call.
useInteractive = true; node.attachEvent('onreadystatechange', context.onScriptLoad);
//It would be great to add an error handler here to catch
//404s in IE9+. However, onreadystatechange will fire before
//the error handler, so that does not help. If addEventListener
//is used, then IE will fire error before load, but we cannot
//use that pathway given the connect.microsoft.com issue
//mentioned above about not doing the 'script execute,
//then fire the script load event listener before execute
//next script' that other browsers do.
//Best hope: IE10 fixes the issues,
//and then destroys all installs of IE 6-9.
//node.attachEvent('onerror', context.onScriptError);
} else {
node.addEventListener('load', context.onScriptLoad, false);
node.addEventListener('error', context.onScriptError, false);
}
node.src = url;
注意在这段源码当中的监听事件,既然动态加载脚本是异步的的,那么干脆使用 onload 事件来处理回调函数,这样就保证了在我们的程序执行前依赖的模块一定会提前加载完成。因为在事件队列里, onload 事件是在脚本加载完成之后触发的,也就是在事件队列里面永远处在依赖模块的后面,例如我们执行:
require(["module"], function (module) {
//do something
});
那么在事件队列里面的相对顺序会是这样:

相信细心的同学可能会注意到了,在源码当中不光光有 onload 事件,同时还添加了一个 onerror 事件,我们在使用 requirejs 的时候也可以定义一个模块加载失败的处理函数,这个函数在底层也就对应了 onerror 事件。同理,其和 onload 事件一样是一个异步的事件,同时也永远发生在模块加载之后。
谈到这里 requirejs 的核心模块思想也就一目了然了,不过其中的过程还远不直这些,博主只是将模块加载的实现思想抛了出来,但 requirejs 的具体实现还要复杂的多,比如我们定义模块的时候可以导入依赖模块,导入模块的时候还可以导入多个依赖,具体的实现方法我就没有深究过了, requirejs 虽然不大,但是源码也是有两千多行的... ...但是只要理解了动态加载脚本的原理过后,其思想也就不难理解了,比如我现在就可以想到一个简单的实现多个模块依赖的方法,使用计数的方式检查模块是否加载完全:
function myRequire(deps, callback){
//记录模块加载数量
var ready = 0;
//创建脚本标签
function load (url) {
var script = document.createElement("script");
script.type = 'text/javascript';
script.async = true;
script.src = url;
return script;
}
var nodes = [];
for (var i = deps.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
nodes.push(load(deps[i]));
}
//加载脚本
for (var i = nodes.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
nodes[i].addEventListener("load", function(event){
ready++;
//如果所有依赖脚本加载完成,则执行回调函数;
if(ready === nodes.length){
callback()
}
}, false);
document.head.appendChild(nodes[i]);
}
}
实验一下是否能够工作:
myRequire(["module/module1.js", "module/module2.js", "module/module3.js"], function(){
console.log("ready!");
});
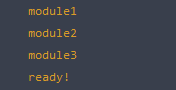
Yes, it's work!
总结
requirejs 加载模块的核心思想是利用了动态加载脚本的异步性以及 onload 事件以毒攻毒,关于脚本的加载,我们需要注意一下几点:
- 在 HTML 中引入 <script> 标签是同步加载;
- 在脚本中动态加载是异步加载,且由于被加载的脚本在事件队列的后端,因此总是会在当前脚本之后执行;
- 使用 onload 和 onerror 事件可以监听脚本加载完成,以异步的事件来处理异步的事件;
参考文献:
阮一峰 — RequireJS 和 AMD 规范
阮一峰 — Javascript 模块化编程
requirejs.org — requirejs api
从 RequireJs 源码剖析脚本加载原理的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot源码分析-配置文件加载原理
在Spring Boot源码分析-启动过程中我们进行了启动源码的分析,大致了解了整个Spring Boot的启动过程,具体细节这里不再赘述,感兴趣的同学可以自行阅读.今天让我们继续阅读源码,了解配置文 ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-资源加载
本章主要描述 MyBatis 资源加载模块中的 ClassLoaderWrapper 类和 Java 加载配置文件的三种方式. ClassLoaderWrapper 上一章的案例,使用 org.apa ...
- Mybatis源码解析(二) —— 加载 Configuration
Mybatis源码解析(二) -- 加载 Configuration 正如上文所看到的 Configuration 对象保存了所有Mybatis的配置信息,也就是说mybatis-config. ...
- 转 Spring源码剖析——核心IOC容器原理
Spring源码剖析——核心IOC容器原理 2016年08月05日 15:06:16 阅读数:8312 标签: spring源码ioc编程bean 更多 个人分类: Java https://blog ...
- 老李推荐:第14章9节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》 HierarchyViewer实现原理-遍历控件树查找控件
老李推荐:第14章9节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析> HierarchyViewer实现原理-遍历控件树查找控件 poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开发工程师的培训机构,以学员 ...
- 老李推荐:第14章3节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》 HierarchyViewer实现原理-HierarchyViewer实例化
老李推荐:第14章3节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析> HierarchyViewer实现原理-HierarchyViewer实例化 poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开发工程师的培 ...
- 老李推荐: 第14章2节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》 HierarchyViewer实现原理-HierarchyViewer架构概述
老李推荐: 第14章2节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析> HierarchyViewer实现原理-HierarchyViewer架构概述 HierarchyViewer库的引入让M ...
- 老李推荐:第14章1节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》 HierarchyViewer实现原理-面向控件编程VS面向坐标编程
老李推荐:第14章1节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析> HierarchyViewer实现原理-面向控件编程VS面向坐标编程 poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开发工程师的培训机 ...
- 老李推荐:第14章5节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》 HierarchyViewer实现原理-装备ViewServer-查询ViewServer运行状态
老李推荐:第14章5节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析> HierarchyViewer实现原理-装备ViewServer-查询ViewServer运行状态 poptest是国内唯一 ...
随机推荐
- TWaver 2D+GIS+3D的试用和在线Demo
TWaver 2D for HTML5试用下载: http://download.servasoft.com/dl/twaver/sssyuwyeriUR/k/twaver-html5-5.4.7.z ...
- jq、js中判断checkbox是否选中
最近在开发项目时用到checkbox复选框,其中遇到一个问题:在JQ中如何判断checkbox是否被选中呢?之前用JQ获取元素的属性用的都是attr(),但用在checkbox上却没有用,原因何在?? ...
- 点评阿里JAVA手册之编程规约(命名风格、常量定义、代码风格、控制语句、注释规约)
下载原版阿里JAVA开发手册 [阿里巴巴Java开发手册v1.2.0] 本文主要是对照阿里开发手册,注释自己在工作中运用情况. 本文难度系数为一星(★) 码出高效.码出质量. 代码的字里行间流淌的是 ...
- 一天搞定CSS:边框border--02
每一个标签都是一个盒子,具体见HTML教程 因此,每一个标签有大小,有边框 1.border样式:单一样式 2.border样式:复合样式 border: 粗细 类型 颜色: 3.border方向 4 ...
- 一位菜鸟的java 最基础笔记
java的特性 简单性(Simple). 结构体系中立(Architecture Neutral). 面向对象(Object Oriented). 易于移植(Portable). 分布式(Distri ...
- htm语言的语法基础及规则
HTML的主要语法是元素和标签.元素是符合DTD(文档类型定义)的文档组成部分,如title(文档标题).IMG(图象).table(表格)等等.元素名不区分大小写的.HTML用标签来规定元素的属性和 ...
- 常用数组、字符串方法总结&获取元素、DOM操作
字符串的方法.返回值.是否改变原字符串:1 charAt() 方法可返回指定位置的字符. 不改变原始字符串 JavaScript并没有一种有别于字符串类型的字符数据类型,返回的字符是长度为 1 的字符 ...
- Grunt压缩HTML和CSS
我的小伙伴们!我明明 在压缩图片之前发过一篇,关于Grunt压缩cCSS是和HTML的!但是不知道为什么,今天再一看.迷之消失了! 没办法.只好今天在写一次,从头开始!首先.我来介绍一下为什么要用构建 ...
- C# 并行任务——Parallel类
一.Parallel类 Parallel类提供了数据和任务的并行性: 二.Paraller.For() Paraller.For()方法类似于C#的for循环语句,也是多次执行一个任务.使用Paral ...
- 由 “无法使用从远程表选择的 lob 定位符” 错误而引导出来的一系列问题解决方案
周一上班遇到一个数据加工问题:无法使用从远程表选择的 lob 定位符,由于数据源表不是自己的,不能对源数据做修改,于是我打起了存储过程的主意 我们公司的存过是分三步走,第一层是同步源数据,第二层是对一 ...
