Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) A B C 水 模拟 贪心
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
There are n integers b1, b2, ..., bn written in a row. For all i from 1 to n, values ai are defined by the crows performing the following procedure:
- The crow sets ai initially 0.
- The crow then adds bi to ai, subtracts bi + 1, adds the bi + 2 number, and so on until the n'th number. Thus,ai = bi - bi + 1 + bi + 2 - bi + 3....
Memory gives you the values a1, a2, ..., an, and he now wants you to find the initial numbers b1, b2, ..., bn written in the row? Can you do it?
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of integers written in the row.
The next line contains n, the i'th of which is ai ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the value of the i'th number.
Print n integers corresponding to the sequence b1, b2, ..., bn. It's guaranteed that the answer is unique and fits in 32-bit integer type.
5
6 -4 8 -2 3
2 4 6 1 3
5
3 -2 -1 5 6
1 -3 4 11 6
In the first sample test, the crows report the numbers 6, - 4, 8, - 2, and 3 when he starts at indices 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively. It is easy to check that the sequence 2 4 6 1 3 satisfies the reports. For example, 6 = 2 - 4 + 6 - 1 + 3, and - 4 = 4 - 6 + 1 - 3.
In the second sample test, the sequence 1, - 3, 4, 11, 6 satisfies the reports. For example, 5 = 11 - 6 and 6 = 6.
题意:a,b序列满足ai = bi - b(i + 1) + b(i + 2) - b(i + 3)....
给你a序列 输出b序列
题解:观察样咧很容易得出b[i]=a[i]+a[i+1];
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n;
ll a[];
ll b[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%I64d",&a[i]);
b[n]=a[n];
for(int i=n-;i>=;i--)
b[i]=a[i]+a[i+];
cout<<b[];
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
cout<<" "<<b[i];
cout<<endl;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Memory is performing a walk on the two-dimensional plane, starting at the origin. He is given a string s with his directions for motion:
- An 'L' indicates he should move one unit left.
- An 'R' indicates he should move one unit right.
- A 'U' indicates he should move one unit up.
- A 'D' indicates he should move one unit down.
But now Memory wants to end at the origin. To do this, he has a special trident. This trident can replace any character in s with any of 'L', 'R', 'U', or 'D'. However, because he doesn't want to wear out the trident, he wants to make the minimum number of edits possible. Please tell Memory what is the minimum number of changes he needs to make to produce a string that, when walked, will end at the origin, or if there is no such string.
The first and only line contains the string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 100 000) — the instructions Memory is given.
If there is a string satisfying the conditions, output a single integer — the minimum number of edits required. In case it's not possible to change the sequence in such a way that it will bring Memory to to the origin, output -1.
RRU
-1
UDUR
1
RUUR
2
In the first sample test, Memory is told to walk right, then right, then up. It is easy to see that it is impossible to edit these instructions to form a valid walk.
In the second sample test, Memory is told to walk up, then down, then up, then right. One possible solution is to change s to "LDUR". This string uses 1 edit, which is the minimum possible. It also ends at the origin.
题意:给你一个串4个方向用4个字母表示 形成路径 要求要从起点最终回到起点 问你最少需要更改多少字母(某次的方向)
使得满足条件 回到起点。
题解:对于当前路径 判断起点与终点间的曼哈顿距离为dis
dis%2!=0则无论怎么更改都不能回到起点 (每更改一次方向都会使得距离变化2)
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
char s[];
int main()
{
cin>>s;
int len=strlen(s);
int xx=,yy=;
for(int i=; i<len; i++)
{
if(s[i]=='L')
xx--;
if(s[i]=='R')
xx++;
if(s[i]=='U')
yy++;
if(s[i]=='D')
yy--;
}
if((abs(xx)+abs(yy))%)
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
else
cout<<(abs(xx)+abs(yy))/<<endl;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Memory is now interested in the de-evolution of objects, specifically triangles. He starts with an equilateral triangle of side length x, and he wishes to perform operations to obtain an equilateral triangle of side length y.
In a single second, he can modify the length of a single side of the current triangle such that it remains a non-degenerate triangle (triangle of positive area). At any moment of time, the length of each side should be integer.
What is the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y?
The first and only line contains two integers x and y (3 ≤ y < x ≤ 100 000) — the starting and ending equilateral triangle side lengths respectively.
Print a single integer — the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y if he starts with the equilateral triangle of side length x.
6 3
4
8 5
3
22 4
6
In the first sample test, Memory starts with an equilateral triangle of side length 6 and wants one of side length 3. Denote a triangle with sides a, b, and c as (a, b, c). Then, Memory can do 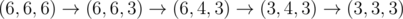 .
.
In the second sample test, Memory can do 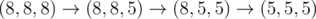 .
.
In the third sample test, Memory can do: 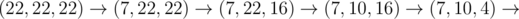
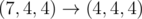 .
.
题意:给你x,y分别为初始等边三角形的边长和目标等边三角形的边长(x>y) 每次只能变化一条边,并且中间三角形为非退化三角形也就是必须是合法的三角形
问你最少的变化次数
题解:逆向思维 由y变到x 贪心使得 某条边增量尽可能大 并且能行成三角形 统计次数
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int x,y;
int a[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
a[]=y;a[]=y;a[]=y;
int ans=;
while(a[]!=x||a[]!=x||a[]!=x)
{
sort(a,a+);
if(a[]+a[]->=x)
a[]=x;
else
a[]=a[]+a[]-;
ans++;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) A B C 水 模拟 贪心的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #375 (Div. 2) A B C 水 模拟 贪心
A. The New Year: Meeting Friends time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes in ...
- Codeforces Round #277 (Div. 2) A B C 水 模拟 贪心
A. Calculating Function time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stand ...
- Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) A , B , C 水,水,贪心
A. Memory and Crow time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces Round #376 (Div. 2) A B C 水 模拟 并查集
A. Night at the Museum time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- Codeforces Round #288 (Div. 2) C. Anya and Ghosts 模拟 贪心
C. Anya and Ghosts time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces Round #392 (Div. 2) A B C 水 模拟 暴力
A. Holiday Of Equality time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) B. Interesting drink (模拟)
Interesting drink 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/B Description Vasiliy likes to res ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) A. Beru-taxi (水题)
Beru-taxi 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/A Description Vasiliy lives at point (a, b ...
- Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem(水.......没做出来)+C题
Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem A. Sweet Problem time limit per test 1 second memory ...
随机推荐
- 其他窗体赋值给comboBox实现值的回显,并使赋的值处于选中状态(根据text获取selectedindex)
Form1 发货单位的这个下拉框comboBox1已经绑定数据库test表的name字段,里面有很多单位名称 比如有:甲公司.乙公司... 1.Form1的comboBox1首先绑定数据库的数据表te ...
- 理解ROS rqt_console和 roslaunch
1.使用rqt_console和roslaunch 这篇教程将介绍使用rqt_console和rqt_logger_level来调试以及使用roslaunch一次启动许多nodes.如果你使用ROS ...
- 【个人使用.Net类库】(2)Log日志记录类
开发接口程序时,要保证程序稳定运行就要时刻监控接口程序发送和接收的数据,这就需要一个日志记录的类将需要的信息记录在日志文件中,便于自己维护接口程序.(Web系统也是如此,只是对应的日志实现比这个要复杂 ...
- poj 2536 GopherII(二分图匹配)
Description The gopher family, having averted the canine threat, must face a new predator. The are n ...
- [网络技术]网关 路由器 OSI
tracert 1.网关与路由 关键的区别:网关是这样一个网络节点:以两个不同协议搭建的网络可以通过它进行通信.路由器是这样一种设备:它能在计算机网络间收发数据包,同时创建一个覆盖网络(overlay ...
- JavaScript之document对象使用
1.document 对象常用的有三种: A.document.getElementById:通过html元素的Id,来获取html对象.适用于单个的html元素. B.document.getEle ...
- 微软TechEd2013大会将在北京、上海召开!
微软TechEd2013大会将在北京.上海召开 大家期盼已久的微软TechEd2013大会终于到来了! 我公司依旧是微软公司指定票商 ,继续为您提供最最优质的售前咨询.最最完善的售后服务! 微软Tec ...
- 《day15---多线程安全问题_JDK1.5的锁机制》
//15同步问题的分析案例以及解决思路 //两个客户到一个银行去存钱,每个客户一次存100,存3次. //问题,该程序是否有安全问题,如果有,写出分析过程,并定于解决方案. /* 发现运行结果: su ...
- hdu1005 矩阵
//Accepted hdu1005 0MS 248K #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream&g ...
- poj2193
//Accepted 368K 532MS //线性dp //dp[i][j]表示前i位最后一个是j的排列数 //dp[i][j]=sum(dp[i-1][h]) h*2<=j #include ...
