HDU 4923 (贪心+证明)
Room and Moor
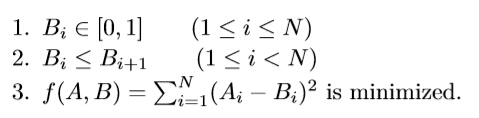
For each test case:
The first line contains a single integer N (1<=N<=100000), which denotes the length of A and B.
The second line consists of N integers, where the ith denotes Ai.
4 9 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 9 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 4 0 0 1 1 4 0 1 1 1
1.428571 1.000000 0.000000 0.000000
题意:不多说了。
sl: 其实就是一个贪心的思想。
网上讲解很多。比赛时没搞出来。。。呵呵了。
1 // by caonima
2 // hehe
3 #include <cstdio>
4 #include <cstring>
5 #include <stack>
6 #include <queue>
7 #include <vector>
8 #include <algorithm>
9 using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1e6+;
struct node {
int one,zero;
double val;
}v[MAX];
stack<node> ans;
int a[MAX];
void init() {
while(!ans.empty()) ans.pop();
}
int main() {
int cas,n;
scanf("%d",&cas);
while(cas--) {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) {
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
a[n+]=;
int L=,R=n;
while(a[L]==) L++;
while(a[R]==) R--;
if(L>=R) printf("0.000000\n");
else {
int id=;
for(int i=L;i<=R;) {
int cnt0=,cnt1=;
while(a[i]==) {
cnt1++; i++;
}
while(a[i]==) {
cnt0++; i++;
}
v[id].one=cnt1; v[id].zero=cnt0;
v[id++].val=(double) cnt1/(double)(cnt0+cnt1);
}
init();
for(int i=;i<id;i++) {
if(ans.empty()) ans.push(v[i]);
else {
node vn=ans.top();
if(vn.val<=v[i].val) ans.push(v[i]);
else {
node t=v[i];
while(true) {
node vx=ans.top();
if(vx.val>t.val) {
t.one+=vx.one; t.zero+=vx.zero;
t.val=(double) t.one/(double)(t.one+t.zero);
ans.pop();
}
else {
ans.push(t);
break;
}
if(ans.empty()) {
ans.push(t);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
double res=;
while(!ans.empty()) {
node vn=ans.top();
ans.pop();
res+=vn.val*vn.val*vn.zero+(-vn.val)*(-vn.val)*vn.one;
}
printf("%.6lf\n",res);
}
}
84 }
HDU 4923 (贪心+证明)的更多相关文章
- HDU 4923 Room and Moor (单调栈)
题意: 给你一个A数列,让你求一个单调递增的B数列(0<=bi<=1),使得sum{(ai-bi)^2}最小. 思路: 很明显,如果A = 0...01...1,那么bi=ai即可. 可以 ...
- HDU 4802 && HDU 4803 贪心,高精 && HDU 4804 轮廓线dp && HDU 4805 计算几何 && HDU 4811 (13南京区域赛现场赛 题目重演A,B,C,D,J)
A.GPA(HDU4802): 给你一些字符串对应的权重,求加权平均,如果是N,P不计入统计 GPA Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory ...
- HDU 4923 Room and Moor
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4923 解题报告:给出一个长度为n的只包含0和1的序列,是否存在一个序列Bi满足一下条件: 1. ...
- Hdu 5289-Assignment 贪心,ST表
题目: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5289 Assignment Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) ...
- hdu 4803 贪心/思维题
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4803 话说C++还卡精度么? G++ AC C++ WA 我自己的贪心策略错了 -- 就是尽量下键,然后上 ...
- hdu 1735(贪心) 统计字数
戳我穿越:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1735 对于贪心,二分,枚举等基础一定要掌握的很牢,要一步一个脚印走踏实 这是道贪心的题目,要有贪心的意 ...
- hdu 4923 单调栈
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4923 给定一个序列a,元素由0,1组成,求一个序列b,元素在0~1之间,并且保证递增.输出最小的∑(ai−bi) ...
- hdu 4974 贪心
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4974 n个人进行选秀,有一个人做裁判,每次有两人进行对决,裁判可以选择为两人打分,可以同时加上1分,或者单独为一 ...
- hdu 4982 贪心构造序列
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4982 给定n和k,求一个包含k个不相同正整数的集合,要求元素之和为n,并且其中k-1的元素的和为完全平方数 枚举 ...
随机推荐
- 使用 typescript 和 canvas 重构snow效果
前言:之前做过一个 snow 效果,但是是直接用 HTML 做的点击此处查看 ,几个星期前,我用 typescript 和 canvas 重构了一下, snow效果是一个很简单的效果,但是用来练手还是 ...
- redis之简单动态字符串(SDS)
O(N):时间复杂度 N的值越大 时间复杂度随N的平方增大 O(1):就是说N很大的时候,复杂度基本不增长了.基本就是常量了. 在Redis数据库里 包含字符串值的键值对 在底层都是由SDS实现的. ...
- array_column() 函数[二维数组转为一维数组]
array_column() 函数 输出数组中某个键值的集合[二维数组转为一位数组] <?php // 表示由数据库返回的可能记录集的数组 $a = array( array( 'id' =&g ...
- EditText(4)常用属性详解
常用的属性: 显示密码 通过设置EditText的setTransformationMethod()方法来实现隐藏密码或这显示密码. editText.setTransformationMethod( ...
- 程序 从存储卡 内存卡 迁移到 SD卡
程序 从存储卡 内存卡 迁移到 SD卡 如果你想移动其他软件,在应用市场界面,点击“管理 > 应用搬家”,点击需要转移的应用旁边的“移至SD卡”即可.
- 初识mybatis之入门案例
我也是自学了一下,在idea中基于maven的mybatis的配置.有什么不对的地方,请指正,谢谢. 1.1咋们先来配置测试一下,配置mybatis的图解: 1.2 pom.xml需要mybatis的 ...
- 25 C#类的继承
继承是面向对象编程的一个重要特性.任何类都可以从另一个类中继承,这就是说,这个类拥有它继承的类的所有成员.在OOP 中,被继承的类称为父类(也称为基类).注意,C#中的对象仅能直接派生于一个基类,当然 ...
- Objective-C设计模式——适配器Adapter(接口适配)
适配器模式 适配器模式通俗来讲,其实就是对客户端添加新的类但却不修改客户端和新的类的接口.此时我们需要自己来实现适配,在适配器模式中有Target对象,即客户端所需要的接口对象,Adaptee对象,即 ...
- Typora——自定义设置
Typora提供自定义设置,在偏好设置里面,有一个主题文件夹,如果对界面的样式进行设定,可以添加一个css文件,命名规范是 github.user.css,下面代码会对h1~h4进行自动序列化 bod ...
- 7z.exe 命令行压缩文件排除文件(exclude filenames) 手记
命令行使用格式:Usage: 7z <command> [<switches>...] <archive_name> [<file_names>...] ...
