标准模板库(STL)学习指南之vector向量
拷贝构造函数和重载的赋值操作符)
三.必须包含的头文件#include <vector>
capacity返回vector能容纳的元素最大数量。如果插入元素时,元素个数超过capacity,
需要重新配置内部存储器。
->构造、拷贝和析构

->非变动操作
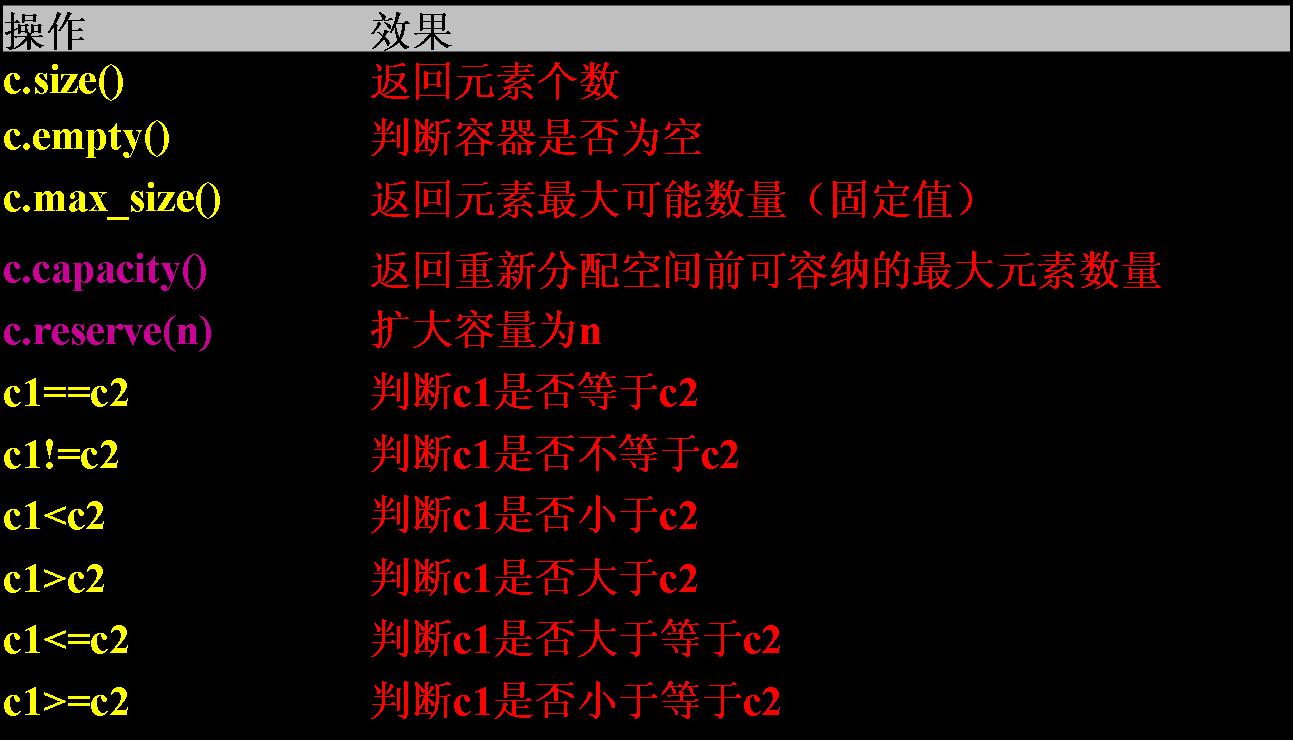
eg.

vector<int> v1(10);
cout << "The capacity of v1 is " << v1.capacity() << endl;
cout << "The size of v1 is " << v1.size() << endl;
vector<int> v2;
v2.reserve(20);
cout << "The capacity of v2 is " << v2.capacity() << endl;
cout << "The size of v2 is " << v2.size() << endl;
output :
The capacity of v1 is 10
The size of v1 is 10
The capacity of v2 is 20
The size of v2 is 0

->赋值操作

所有的赋值操作都有可能调用元素类型的默认构造函数,拷贝构造函数,赋值操作符和析构函数
如:
eg.

vector<int> v;
v.assign( 10, 42 );
for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v.size(); i++ ) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
OutPut :
42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42
vector<int> v1;
for( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) {
v1.push_back( i );
}
vector<int> v2;
v2.assign( v1.begin(), v1.end() );
for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++ ) {
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
output :
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9

元素存取

下面的操作是错误的:
std::vector<T> v;//empty
eg.

string str;
while( cin >> str ) words.push_back(str);
sort( words.begin(), words.end() );
cout << "In alphabetical order, the first word is '" << words.front() << "'." << endl;
假设输入是: now is the time for all good men to come to the aid of their country
output:
In alphabetical order, the first word is 'aid'.
vector<int> v;
for( int i = 0; i < 5; i++ ) {
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << "The first element is " << v.front()
<< " and the last element is " << v.back() << endl;
output:
The first element is 0 and the last element is 4

迭代器相关函数

使用迭代器时应注意:
迭代器持续有效,除非发生以下两种情况:
eg.

vector<string> words;
string str;
while( cin >> str ) words.push_back(str);
for( vector<string>::const_iterator iter = words.begin();
iter != words.end(); ++iter ) {
cout << *iter << endl;
}
假设输入是 : hey mickey you're so fine
output:
hey
mickey
you're
so
fine

插入(insert)元素

eg.

vector<char> alphaVector;
for( int i=0; i < 10; i++ ) {
alphaVector.push_back( i + 'A' );
}
// Insert four C's into the vector
vector<char>::iterator theIterator = alphaVector.begin();
alphaVector.insert( theIterator, 4, 'C' );
// Display the vector
for( theIterator = alphaVector.begin(); theIterator != alphaVector.end(); ++theIterator ) {
cout << *theIterator;
}
output:
CCCCABCDEFGHIJ
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back( 0 );
v1.push_back( 1 );
v1.push_back( 2 );
v1.push_back( 3 );
vector<int> v2;
v2.push_back( 5 );
v2.push_back( 6 );
v2.push_back( 7 );
v2.push_back( 8 );
cout << "Before, v2 is: ";
for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++ ) {
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v2.insert( v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end() );
cout << "After, v2 is: ";
for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++ ) {
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
output :
Before, v2 is: 5 6 7 8
After, v2 is: 5 6 7 8 0 1 2 3


eg.

vector<char> alphas;
for( int i=0; i < 10; i++ ) {
static const char letters[] = "ABCDEFGHIJ";
alphas.push_back( letters[i] );
}
vector<char>::size_type size = alphas.size();
vector<char>::iterator startIterator;
vector<char>::iterator tempIterator;
for( vector<char>::size_type i=0; i < size; i++ ) {
startIterator = alphas.begin();
alphas.erase( startIterator );
// Display the vector
for( tempIterator = alphas.begin(); tempIterator != alphas.end(); ++tempIterator ) {
cout << *tempIterator;
}
cout << endl;
}
output:
BCDEFGHIJ
CDEFGHIJ
DEFGHIJ
EFGHIJ
FGHIJ
GHIJ
HIJ
IJ
J
vector<char> alphas;
for( int i=0; i < 10; i++ ) {
static const char letters[] = "ABCDEFGHIJ";
alphas.push_back( letters[i] );
}
// display the complete vector
for( vector<char>::size_type i = 0; i < alphas.size(); i++ ) {
cout << alphas[i];
}
cout << endl;
// use erase to remove all but the first two and last three elements
// of the vector
alphas.erase( alphas.begin()+2, alphas.end()-3 );
// display the modified vector
for( vector<char>::size_type i = 0; i < alphas.size(); i++ ) {
cout << alphas[i];
}
cout << endl;
output:
ABCDEFGHIJ
ABHIJ
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<char> alphas;
for( int i=0; i < 10; i++ ) {
static const char letters[] = "ABCDEFGHIJ";
alphas.push_back( letters[i] );
}
vector<char>::iterator iter = alphas.begin();
while( iter != alphas.end() )
{
if (*iter == 'B' || *iter == 'D')
iter = alphas.erase( iter );
else
++iter;
}
copy(alphas.begin(), alphas.end(), ostream_iterator<char>(cout, ""));
cout << endl;
}
output :
ACEFGHIJ

转载自:http://www.cppblog.com/MiYu/archive/2010/08/31/125459.html
作者:ACShiryu
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/ACShiryu/
若非注明,本博客文章均为原创,版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
该文章也同步发布在我的新浪微博中-ACShiryu's weibo,欢迎收听。
标准模板库(STL)学习指南之vector向量的更多相关文章
- 标准模板库(STL)学习探究之vector容器
标准模板库(STL)学习探究之vector容器 C++ Vectors vector是C++标准模板库中的部分内容,它是一个多功能的,能够操作多种数据结构和算法的模板类和函数库.vector之所以被 ...
- 标准模板库(STL)学习指南之sort排序
对于程序员来说,数据结构是必修的一门课.从查找到排序,从链表到二叉树,几乎所有的算法和原理都需要理解,理解不了也要死记硬背下来.幸运的是这些理论都已经比较成熟,算法也基本固定下来,不需要你再去花费心思 ...
- 标准模板库(STL)学习指南之List链表
本文转载自天极网,原文地址:http://www.yesky.com/255/1910755.shtml.转载请注明 什么是STL呢?STL就是Standard Template Library,标准 ...
- 标准模板库(STL)学习指南之priority_queue优先队列
转载自CSDN博客:http://blog.csdn.net/suwei19870312/article/details/5294016 priority_queue 调用 STL里面的 make_h ...
- 标准模板库(STL)学习指南之set集合
set是关联容器.其键值就是实值,实值就是键值,不可以有重复,所以我们不能通过set的迭代器来改变set的元素的值,set拥有和list相同的特性:当对他进行插入和删除操作的时候,操作之前的迭代器依然 ...
- 标准模板库(STL)学习指南之map映射
转载自CSDN博客:http://blog.csdn.net/bat603/article/details/1456141 Map是STL的一个关联容器,它提供一对一(其中第一个可以称为关键字,每个关 ...
- 标准模板库(STL)学习探究之stack
标准模板库(STL)学习探究之stack queue priority_queue list map/multimap dequeue string
- 标准模板库(STL)学习探究之Multimap容器
C++ Multimaps和maps很相似,但是MultiMaps允许重复的元素.(具体用法请参考map容器) 函数列表: begin() 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 cle ...
- C++的标准模板库STL中实现的数据结构之顺序表vector的分析与使用
摘要 本文主要借助对C++的标准模板库STL中实现的数据结构的学习和使用来加深对数据结构的理解.即联系数据结构的理论分析和详细的应用实现(STL),本文是系列总结的第一篇,主要针对线性表中的顺序表(动 ...
随机推荐
- 【BZOJ5016】[Snoi2017]一个简单的询问 莫队
[BZOJ5016][Snoi2017]一个简单的询问 Description 给你一个长度为N的序列ai,1≤i≤N和q组询问,每组询问读入l1,r1,l2,r2,需输出 get(l,r,x)表示计 ...
- A/B(逆元)
A/B Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submiss ...
- 九度OJ 1339:ACM (排序)
时间限制:1 秒 内存限制:32 兆 特殊判题:否 提交:712 解决:379 题目描述: 今年的ACM世界总决赛快要开始了,需要有一个排名算法来对每支队伍进行现场排名.ACM组委会把这个任务交给了你 ...
- spring mvc 基本原理
在web.xml配置spring mvc入口servlet: <servlet> <servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name&g ...
- GIT笔记:GITHUB教程【官方自译版】
GIT笔记:将项目发布到GITHUB GITHUB是什么 GitHub是版本控制和协作的代码托管平台.它可以让你和其他人在任何地方一起工作. 1.创建一个新的仓库 存储库通常用于组织单个项目.存储库可 ...
- Java多线程系列 JUC锁06 Condition条件
Condition介绍 Condition中提供了一组类似于Object中的监视器方法.与Lock配合可以完成等待通知模式. Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Cond ...
- 奥森图标和CSS特殊字体使用方法
作为第一篇博文,写这个 我快要被气炸,好吧,废话不说了 昨天在项目中发现有很多这些Awesome图标 也在网上找了下Font Awesome下载后这些文件,现在的版本是4.2,Font Awesome ...
- 斯坦福机器学习视频笔记 Week3 逻辑回归与正则化 Logistic Regression and Regularization
我们将讨论逻辑回归. 逻辑回归是一种将数据分类为离散结果的方法. 例如,我们可以使用逻辑回归将电子邮件分类为垃圾邮件或非垃圾邮件. 在本模块中,我们介绍分类的概念,逻辑回归的损失函数(cost fun ...
- <a href
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEnco ...
- 【转】HTTP方法
[转]HTTP方法 掌握HTTP虽然不是必须的,但是如果你知道它的工作原理,那么在学习JSP开发中的某些知识就可以易如反掌了. 一,HTTP协议详解之URL篇 http(超文本传输协议)是一个基于请求 ...
