苏浪浪 201771010120 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第9周学习总结
实验九异常、断言与日志
实验时间 2018-10-25
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握java异常处理技术;
(2) 了解断言的用法;
(3) 了解日志的用途;
(4) 掌握程序基础调试技巧;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:用命令行与IDE两种环境下编辑调试运行源程序ExceptionDemo1、ExceptionDemo2,结合程序运行结果理解程序,掌握未检查异常和已检查异常的区别。
|
//异常示例1 public class ExceptionDemo1 { public static void main(String args[]) { int a = 0; System.out.println(5 / a); } } |
|
//异常示例2(找不到文件名) import java.io.*; public class ExceptionDemo2 { public static void main(String args[]) { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt");//JVM自动生成异常对象 int b; while((b=fis.read())!=-1) { System.out.print(b); } fis.close(); } } |
更改后的异常1
package aaa;
public class 异常{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 0;
if(a==0)
System.out.println("除数为0");
else
System.out.println(5 / a);
}
}
更改后的异常2
文件名找不到故此出现异常
//异常示例2(找不到文件名)
package aaa;
import java.io.*;
public class b {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException //添加抛出申明
{
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt");//JVM自动生成异常对象
int b;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1)
{
System.out.print(b);
}
fis.close();
}
}
实验2: 导入以下示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 在elipse IDE中编辑、编译、调试运行教材281页7-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
l 掌握Throwable类的堆栈跟踪方法;
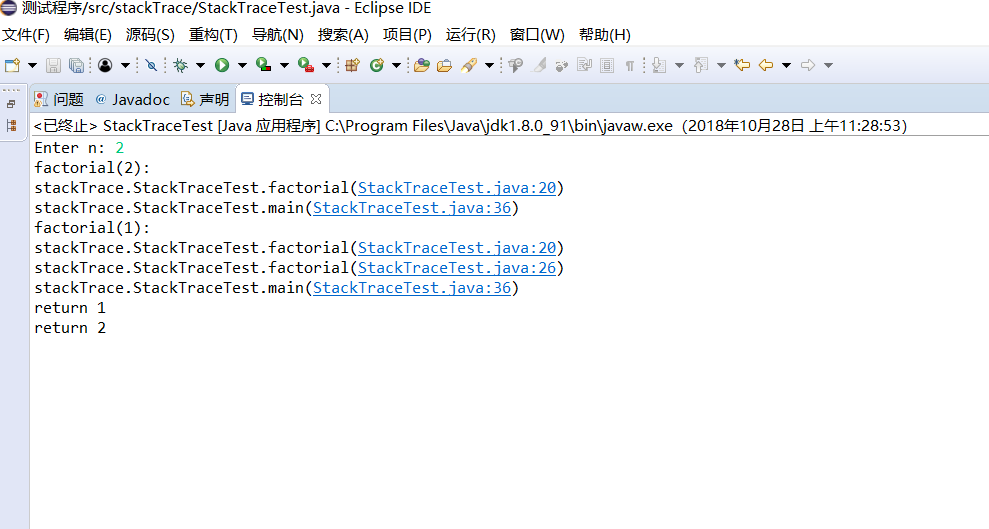
package stackTrace; import java.util.*; /**
* A program that displays a trace feature of a recursive method call.
* @version 1.01 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class StackTraceTest
{
/**
* Computes the factorial of a number
* @param n a non-negative integer
* @return n! = 1 * 2 * . . . * n
*/
public static int factorial(int n)
{
System.out.println("factorial(" + n + "):");
Throwable t = new Throwable();//构造一个Throwable 对象
StackTraceElement[] frames = t.getStackTrace();//获得构造这个对象时调用的对战的跟踪
for (StackTraceElement f : frames)
System.out.println(f);
int r;
if (n <= 1) r = 1;
else r = n * factorial(n - 1);
System.out.println("return " + r);
return r;
} public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter n: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
factorial(n);
}
}
测试程序2:
l Java语言的异常处理有积极处理方法和消极处理两种方式;
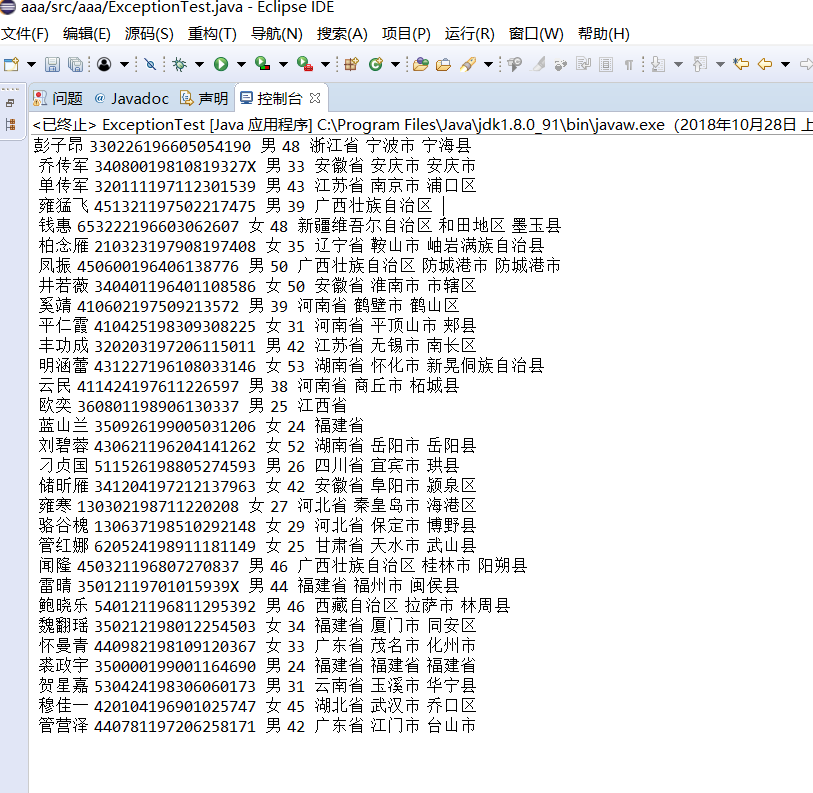
l 下列两个简答程序范例给出了两种异常处理的代码格式。在elipse IDE中编辑、调试运行源程序ExceptionalTest.java,将程序中的text文件更换为身份证号.txt,要求将文件内容读入内容,并在控制台显示;
l 掌握两种异常处理技术的特点。
|
//积极处理方式 import java.io.*; class ExceptionTest { public static void main (string args[]) { try{ FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); } catch(FileNotFoundExcption e) { …… } …… } } |
|
//消极处理方式 import java.io.*; class ExceptionTest { public static void main (string args[]) throws FileNotFoundExcption { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); } } |
异常1
package aaa;
//积极处理方式
import java.io.*;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main (String args[])
{
File fis=new File("身份证号.txt");
try{ FileReader fr = new FileReader(fis);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
try {
String s, s2 = new String();
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
s2 += s + "\n ";
}
br.close(); System.out.println(s2);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} }
}
异常2
package aaa;
//消极处理方式 import java.io.*;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main (String args[]) throws IOException
{
File fis=new File("身份证号.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(fis);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String s, s2 = new String(); while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
s2 += s + "\n ";
}
br.close();
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
实验3: 编程练习
练习1:
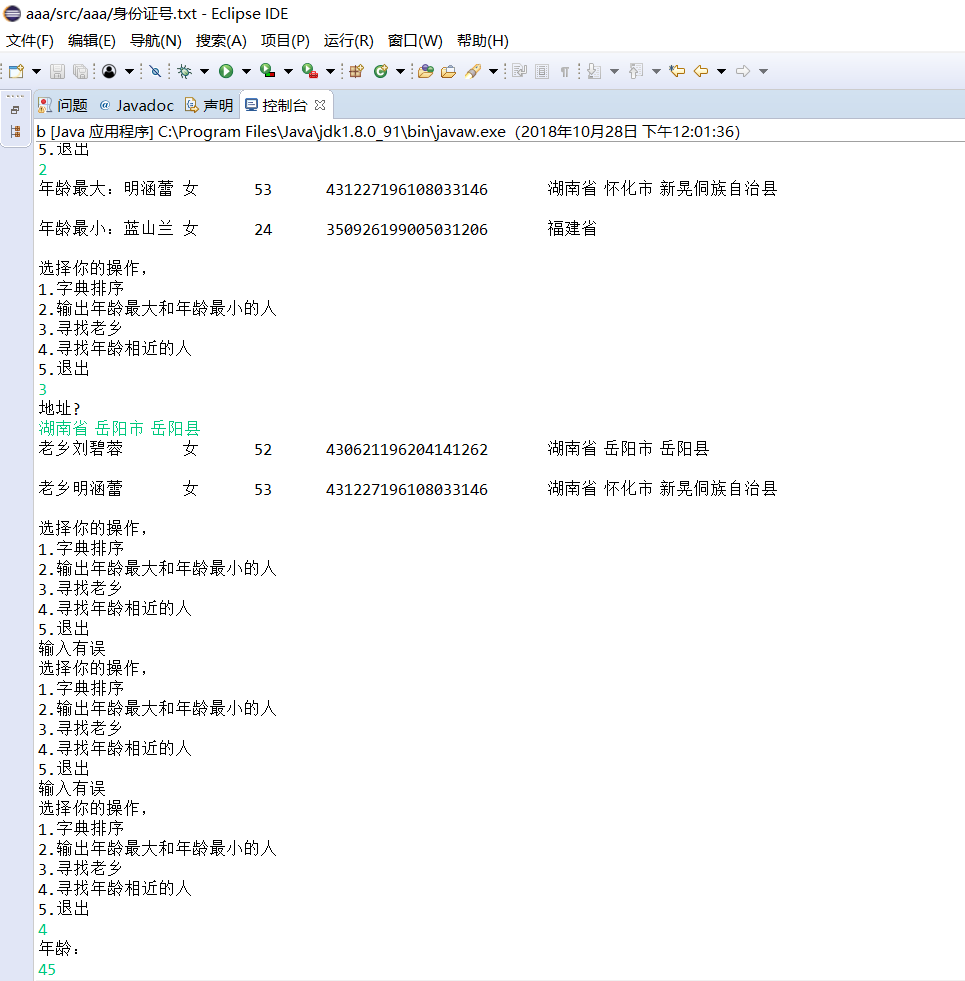
l 编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
l 按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
l 查询最大年龄的人员信息;
l 查询最小年龄人员信息;
l 输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
l 查询人员中是否有你的同乡;
l 在以上程序适当位置加入异常捕获代码。
package aaa; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner; public class b{
private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist;
public static void main(String[] args) {
studentlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("身份证号.txt");
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String number = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String province =linescanner.nextLine();
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(name);
student.setnumber(number);
student.setsex(sex);
int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
student.setage(a);
student.setprovince(province);
studentlist.add(student); }
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean isTrue = true;
while (isTrue) {
System.out.println("选择你的操作, ");
System.out.println("1.字典排序 ");
System.out.println("2.输出年龄最大和年龄最小的人 ");
System.out.println("3.寻找老乡 ");
System.out.println("4.寻找年龄相近的人 ");
System.out.println("5.退出 ");
String m = scanner.next();
switch (m) {
case "1":
Collections.sort(studentlist);
System.out.println(studentlist.toString());
break;
case "2":
int max=0,min=100;
int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++)
{
j=studentlist.get(i).getage();
if(j>max)
{
max=j;
k1=i;
}
if(j<min)
{
min=j;
k2=i;
} }
System.out.println("年龄最大:"+studentlist.get(k1));
System.out.println("年龄最小:"+studentlist.get(k2));
break;
case "3":
System.out.println("地址?");
String find = scanner.next();
String place=find.substring(0,3);
for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++)
{
if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place))
System.out.println("老乡"+studentlist.get(i));
}
break; case "4":
System.out.println("年龄:");
int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
int near=agenear(yourage);
int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage();
System.out.println(""+studentlist.get(near));
break;
case "5 ":
isTrue = false;
System.out.println("退出程序!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误"); }
}
}
public static int agenear(int age) {
int j=0,min=53,value=0,ok=0;
for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++)
{
value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age;
if(value<0) value=-value;
if (value<min)
{
min=value;
ok=i;
}
}
return ok;
}
}
package aaa;
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private String number ;
private String sex ;
private int age;
private String province;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getnumber() {
return number;
}
public void setnumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex ;
}
public void setsex(String sex ) {
this.sex =sex ;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
// int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
this.age= age;
}
public String getprovince() {
return province;
}
public void setprovince(String province) {
this.province=province ;
}
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
}
public String toString() {
return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n";
}
}

注:以下实验课后完成
练习2:
l 编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作;
l 利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
l 将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt;
l 在以上程序适当位置加入异常捕获代码。
package aaa;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner; public class b {
public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Student student=new Student();
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
out = new PrintWriter("text.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {
int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int c= (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3); switch(c)
{
case 0:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"/"+b+"="); while(b==0)
{
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
} int C = in.nextInt();
out.println(a+"/"+b+"="+C);
if (C == student.division(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
} break; case 1:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"*"+b+"=");
int D = in.nextInt();
out.println(a+"*"+b+"="+D);
if (D == student.multiplication(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
}
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"+"+b+"=");
int E = in.nextInt();
out.println(a+"+"+b+"="+E);
if (E == student.add(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
} break ;
case 3:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"-"+b+"=");
int F = in.nextInt();
out.println(a+"-"+b+"="+F);
if (F == student.reduce(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("恭喜答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误");
}
break ;
}
}
System.out.println("成绩"+sum);
out.println("成绩:"+sum);
out.close();
}
}
package aaa;
public class Student {
private int a;
private int b;
public int add(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
public int reduce(int a,int b)
{
return a-b;
}
public int multiplication(int a,int b)
{
return a*b;
}
public int division(int a,int b)
{
if(b!=0)
return a/b;
else return 0;
} }


实验4:断言、日志、程序调试技巧验证实验。
实验程序1:
|
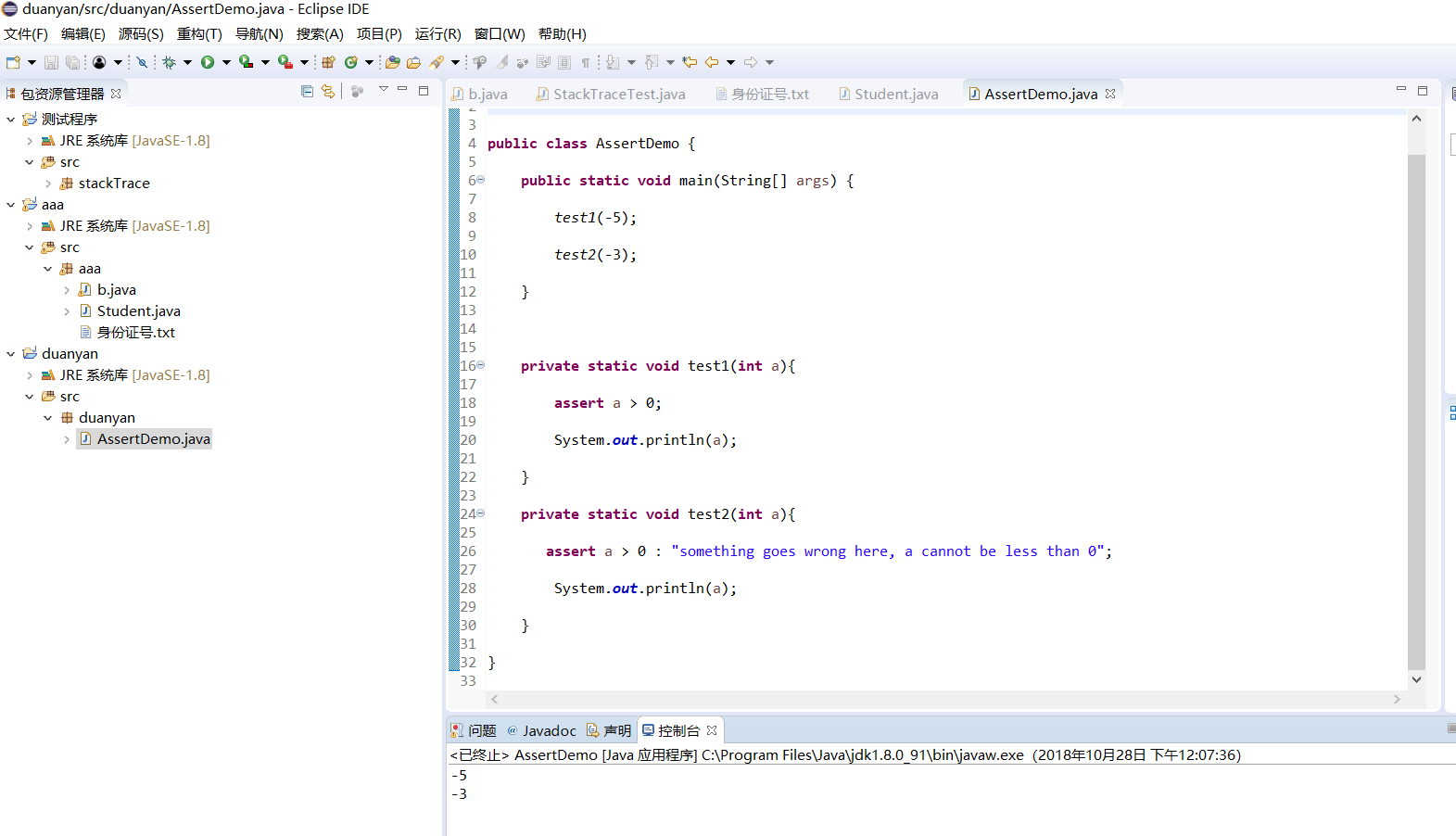
//断言程序示例 public class AssertDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { test1(-5); test2(-3); }
private static void test1(int a){ assert a > 0; System.out.println(a); } private static void test2(int a){ assert a > 0 : "something goes wrong here, a cannot be less than 0"; System.out.println(a); } } |
l 在elipse下调试程序AssertDemo,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 注释语句test1(-5);后重新运行程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握断言的使用特点及用法。
修改后
package duanyan;
public class AssertDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// test1(-5);
test2(-3);
}
private static void test1(int a){
assert a > 0;
System.out.println(a);
}
private static void test2(int a){
assert a > 0 : "something goes wrong here, a cannot be less than 0";
System.out.println(a);
}
}
实验程序2:
l 用JDK命令调试运行教材298页-300页程序7-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 并掌握Java日志系统的用途及用法。
实验程序3:
l 用JDK命令调试运行教材298页-300页程序7-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 按课件66-77内容练习并掌握Elipse的常用调试技术。

实验总结:
在本周的学习中,掌握了java异常处理的一些基础技术;通过调试测试书上的示例程序,以及老师和助教学长的讲解下使我初步的理解了这一章的知识。课后的自主实验在学长帮助的基础上将其做出来,通过这周的学习初步的对于本章知识有了些许的理解。
苏浪浪 201771010120 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第9周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 马凯军201771010116《面向对象与程序设计Java》第九周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 异常.日志.断言和调试 1.异常:在程序的执行过程中所发生的异常事件,它中断指令的正常执行. 2.Java的异常处理机制可以控制程序从错误产生的位置转移到能够进行错误处理的位置. 3 ...
随机推荐
- JAVA企业级应用TOMCAT实战(一)
一. Tomcat简介 Tomcat是Apache软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的Jakarta 项目中的一个核心项目,由Apache.Sun和其他一些公司及个人共 ...
- 移动App性能测评与优化1.4.4 多进程应用
1.4.4 多进程应用 根据上一节中的描述,当一个进程结束后,它所占用的共享库内存将会被其他仍然使用该共享库的进程所分担,共享库消耗的物理内存并不会减少.实际上,对于所有共享使用了这个库的应用,Pss ...
- 《Exchange Server 2010 SP1/SP2管理实践》——第2章 搭建Exchange实验环境2.1 网络环境规划...
本节书摘来自异步社区<Exchange Server 2010 SP1/SP2管理实践>一书中的第2章,第2.1节,作者: 王淑江 更多章节内容可以访问云栖社区"异步社区&quo ...
- 信息竞赛进阶指南--Tire树
// 假设字符串由小写字母构成 int trie[SIZE][26], tot = 1; // Trie的插入 void insert(char* str) { int len = strlen(st ...
- 图论--Floyd总结
Key word: ①最短路 ②传递闭包:大小关系 数值关系 先后关系 联通关系 ③floyd变形 ④实现方式:插点发法 ⑤思想:动态规划 1.最短路: 最短路 ...
- Python爬虫---爬取抖音短视频
目录 前言 抖音爬虫制作 选定网页 分析网页 提取id构造网址 拼接数据包链接 获取视频地址 下载视频 全部代码 实现结果 待解决的问题 前言 最近一直想要写一个抖音爬虫来批量下载抖音的短视频,但是经 ...
- spring boot的核心注解
1.@SpringBootApplication 是SpingBoot的启动类 此注解等同于@Configuration+@EnableAutoConfiguration+@ComponentScan ...
- Linux内核驱动学习(五)KThread学习总结
文章目录 简介 例程 运行结果 参考 简介 使用内核线程需要包含头文件#include <linux/kthread.h>,下面整理了一下常用的api接口,如下表格所示: 函数 功能 st ...
- Linux Charger IC 驱动移植总结
Linux Charger IC 驱动移植总结 文章目录 Linux Charger IC 驱动移植总结 1 设备树的基本知识 设备树的概念 设备树的基本结构 compatible属性 举个栗子 2 ...
- 深入理解CSS定位—浮动模型
前面我们讲到了绝对定位,在这篇文章中,我们将讲到3种定位模型中的浮动模型.主要参考 张鑫旭在慕课网的 深入理解float 那些年我们一起清过的浮动---by 一丝丝凉 精通CSS 注意:第二小节基本参 ...
