codeforces 854 problem E
Ilya is sitting in a waiting area of Metropolis airport and is bored of looking at time table that shows again and again that his plane is delayed. So he took out a sheet of paper and decided to solve some problems.
First Ilya has drawn a grid of size n × n and marked n squares on it, such that no two marked squares share the same row or the same column. He calls a rectangle on a grid with sides parallel to grid sides beautiful if exactly two of its corner squares are marked. There are exactly n·(n - 1) / 2 beautiful rectangles.
Ilya has chosen q query rectangles on a grid with sides parallel to grid sides (not necessarily beautiful ones), and for each of those rectangles he wants to find its beauty degree. Beauty degree of a rectangle is the number of beautiful rectangles that share at least one square with the given one.
Now Ilya thinks that he might not have enough time to solve the problem till the departure of his flight. You are given the description of marked cells and the query rectangles, help Ilya find the beauty degree of each of the query rectangles.
The first line of input contains two integers n and q (2 ≤ n ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ q ≤ 200 000) — the size of the grid and the number of query rectangles.
The second line contains n integers p1, p2, ..., pn, separated by spaces (1 ≤ pi ≤ n, all pi are different), they specify grid squares marked by Ilya: in column i he has marked a square at row pi, rows are numbered from 1 to n, bottom to top, columns are numbered from 1 to n, left to right.
The following q lines describe query rectangles. Each rectangle is described by four integers: l, d, r, u (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n, 1 ≤ d ≤ u ≤ n), here land r are the leftmost and the rightmost columns of the rectangle, d and u the bottommost and the topmost rows of the rectangle.
For each query rectangle output its beauty degree on a separate line.
2 3
1 2
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 2
1 1 2 2
1
1
1
4 2
1 3 2 4
4 1 4 4
1 1 2 3
3
5
The first sample test has one beautiful rectangle that occupies the whole grid, therefore the answer to any query is 1.
In the second sample test the first query rectangle intersects 3 beautiful rectangles, as shown on the picture below:
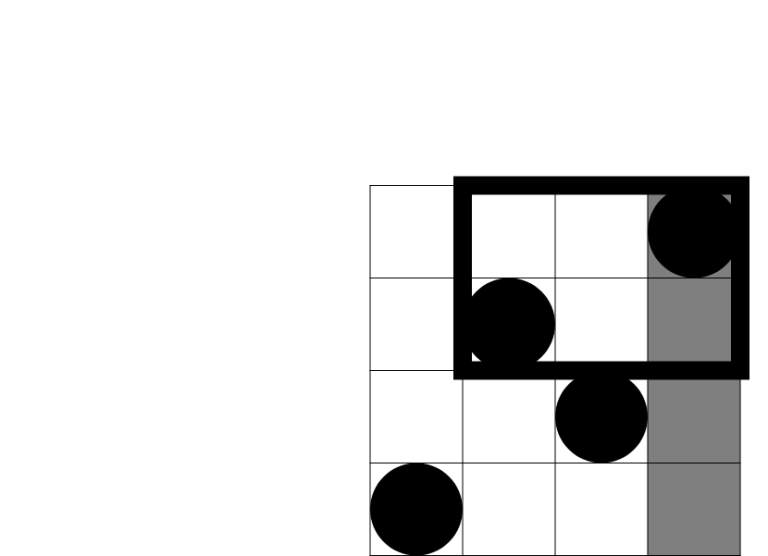
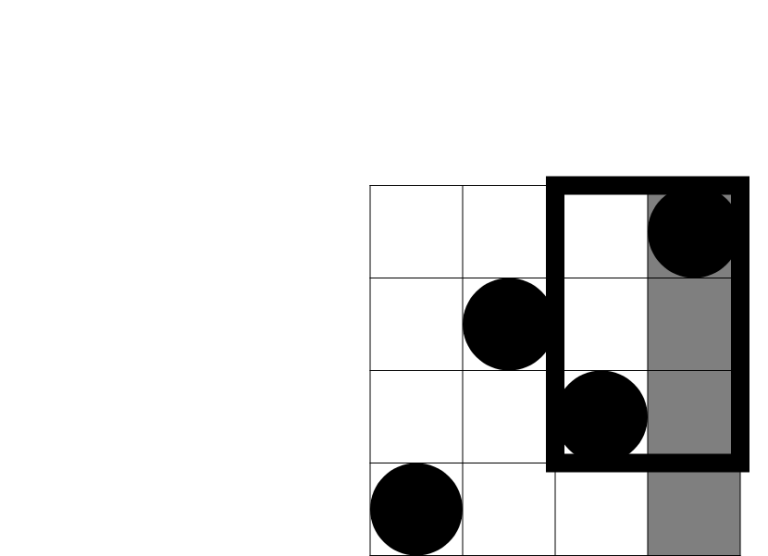
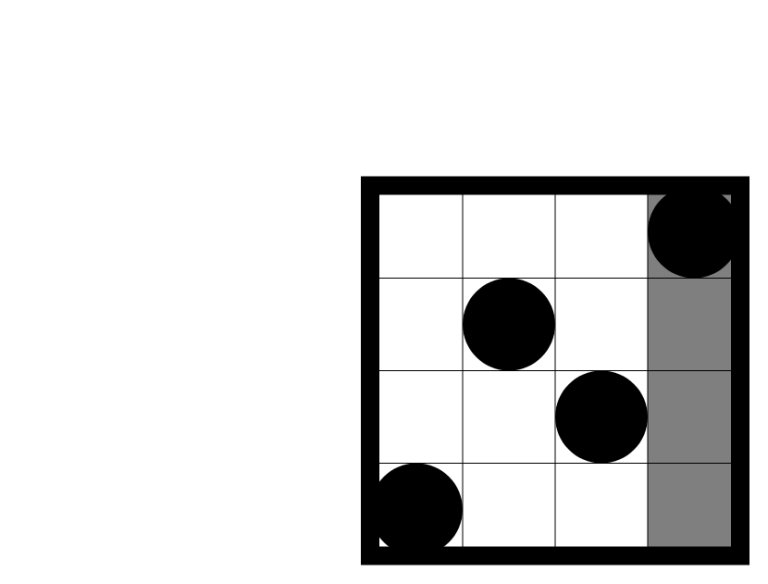
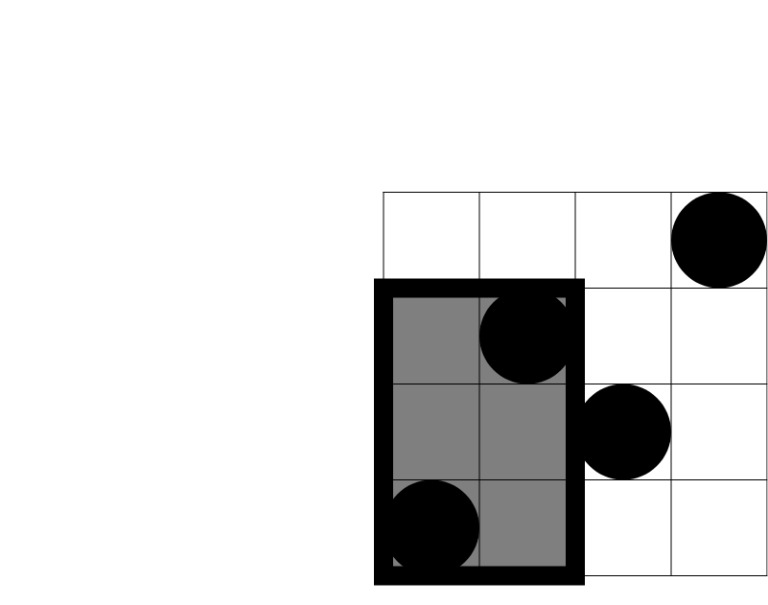
There are 5 beautiful rectangles that intersect the second query rectangle, as shown on the following picture:
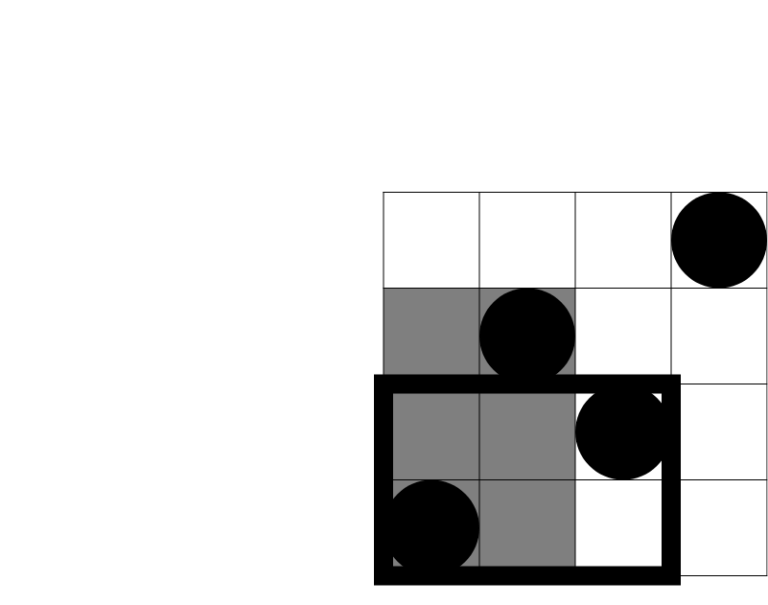
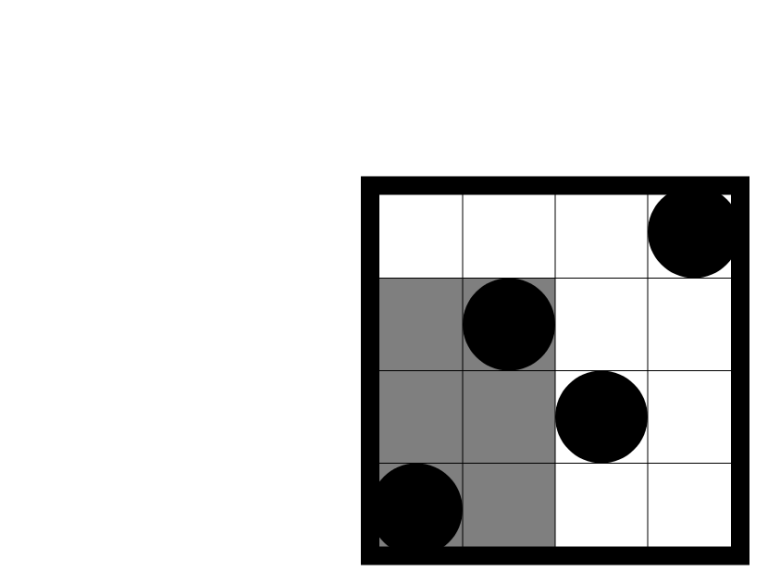
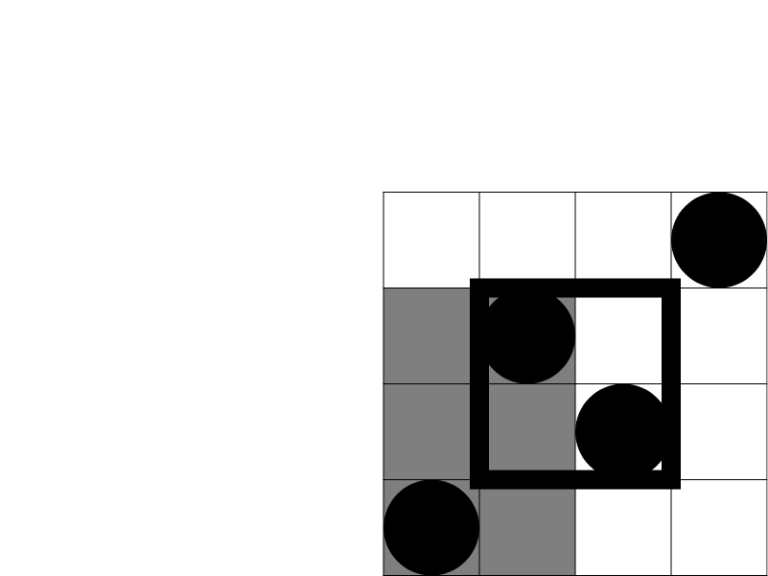
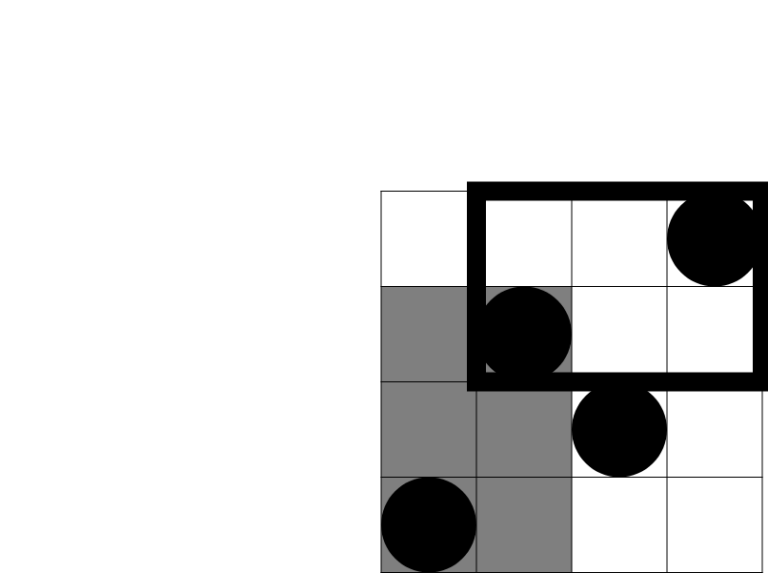
这道题 题意就是给你n个点 这n个点 两两可以组成一个矩阵(作为两个角的位置)
然后给你q个询问 询问给你一个矩阵的左上角和右上角 求 n个点两两配对组成的矩阵有多少个和他有交
这道题我的写法可能有点暴力
就是把一个矩阵的四条边延长 延长之后呢 就变成了九个矩阵
这样就变成了这九个矩阵之间两两配对之后是否和矩阵有交
这个画一下图应该就可以了 至于求每个矩阵中有多少个点
就可以利用扫描线来实现 一个询问拆成9个 容斥一下就可以得到全部答案了
复杂度主要是排序的nlogn 当然因为拆询问的缘故 n要乘9
代码略丑QAQ
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
const int M=2e6+;
int read(){
int ans=,f=,c=getchar();
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-') f=-; c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+(c-''); c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
LL tot;
int s[*M];
LL ans[M][];
int n,m,xp,qp,ep;
int lowbit(int x){return x&-x;}
void add(int x,LL v){
while(x<=n){
s[x]+=v;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int query(int x){
LL ans=;
while(x){
ans+=s[x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
struct Q{
int r,h,id,pos;
bool operator <(const Q& x)const{return h<x.h;}
void calc(){ans[id][pos]=query(r);}
}q[*M];
struct pos{
int x,y,w;
bool operator <(const pos& h)const{return y<h.y;}
void calc(){add(x,w);}
}e[M];
int main()
{
int x1,y1,x2,y2;
n=read(); m=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
y1=read();
e[ep++]=(pos){i,y1,};
}
for(int i=;i<=m;i++){
x1=read(); y1=read(); x2=read(); y2=read();
q[qp++]=(Q){x1-,y1-,i,};
q[qp++]=(Q){x1-,y2,i,};
q[qp++]=(Q){x1-,n,i,};
q[qp++]=(Q){x2,y1-,i,};
q[qp++]=(Q){x2,y2,i,};
q[qp++]=(Q){x2,n,i,};
q[qp++]=(Q){n,y1-,i,};
q[qp++]=(Q){n,y2,i,};
q[qp++]=(Q){n,n,i,};
}
sort(e,e+ep); sort(q,q+qp);
for(int i=,j=;i<qp;i++){
while(j<ep&&e[j].y<=q[i].h) e[j++].calc();
q[i].calc();
}
for(int i=;i<=m;i++){
tot=;
LL h[];
h[]=ans[i][];
h[]=ans[i][]-ans[i][];
h[]=ans[i][]-ans[i][];
h[]=ans[i][]-ans[i][];
h[]=ans[i][]-ans[i][]-ans[i][]+ans[i][];
h[]=ans[i][]-ans[i][]-ans[i][]+ans[i][];
h[]=ans[i][]-ans[i][];
h[]=ans[i][]-ans[i][]-ans[i][]+ans[i][];
h[]=ans[i][]-ans[i][]-ans[i][]+ans[i][];
tot=tot+h[]*(h[]+h[]+h[]+h[]+h[]+h[]+h[]+h[]);
tot=tot+h[]*(h[]-)/;
tot=tot+h[]*(h[]+h[]+h[]);
tot=tot+h[]*(h[]+h[]);
tot=tot+h[]*(h[]+h[]+h[]);
tot=tot+h[]*(h[]+h[]+h[]);
tot=tot+h[]*(h[]+h[]+h[]+h[]+h[]);
printf("%I64d\n",tot);
}
return ;
}
codeforces 854 problem E的更多相关文章
- CodeForces 1151C Problem for Nazar
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1151/C 题目大意: 有一个只存奇数的集合A = {1, 3, 5……2*n - 1,……},和只存偶数 ...
- codeforces gym100801 Problem G. Graph
传送门:https://codeforces.com/gym/100801 题意: 给你一个DAG图,你最多可以进行k次操作,每次操作可以连一条有向边,问你经过连边操作后最小拓扑序的最大值是多少 题解 ...
- codeforces gym100801 Problem J. Journey to the “The World’s Start”
传送门:https://codeforces.com/gym/100801 题意: 小明坐地铁,现在有n-1种类型的地铁卡卖,现在小明需要买一种地铁票,使得他可以在t的时间内到达终点站,地铁票的属性为 ...
- Codeforces 1188E - Problem from Red Panda(找性质+组合数学)
Codeforces 题面传送门 & 洛谷题面传送门 咦,题解搬运人竟是我? 一道很毒的计数题. 先转化下题意,每一次操作我们可以视作选择一种颜色并将其出现次数 \(+k\),之后将所有颜色的 ...
- CodeForces 688C-NP-Hard Problem
题意: 给你一个无向图,判断是否能够构成一个二分图,如果能的话,输出二分图左边的集合和右边的集合 分析: 先给每一个顶点的color初始化-1,表示没有被染色,用vector数组v[a],表示元素a所 ...
- codeforces #583 problem D(搜索好题)
题目大意:在一个已经有障碍的地图上,设置尽可能少的障碍使得(1,1)无法到达(n,m),行进路线位向下或向右. 数据范围:n*m<=1e6 解题思路:答案一定是小于等于2的,因为可以直接阻碍(1 ...
- Codeforces Round #433 (Div. 2, based on Olympiad of Metropolises)
A. Fraction 题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/854/problem/A 题目意思:给出一个数n,求两个数a+b=n,且a/b不可约分,如果存在多组满足 ...
- Codeforces 854B Maxim Buys an Apartment:贪心
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/854/problem/B 题意: 有n栋房子从1到n排成一排,有k栋房子已经被售出. 现在你要买一栋“好房子”. 一栋房子是“好 ...
- #433 Div2 Problem C Planning (贪心 && 优先队列)
链接 : http://codeforces.com/contest/854/problem/C 题意 : 有 n 架飞机需要分别在 1~n 秒后起飞,允许起飞的时间是从 k 秒后开始,给出每一架飞机 ...
随机推荐
- ora-12154 TNS:"无法处理服务名"的一个解决方法
http://www.cnblogs.com/xh3/archive/2007/04/21/722217.html 很怪异的一个问题,在网络环境下配置客户端,竟然怎么也连不上主机了,看了不少帖子,大多 ...
- Linux 下 PHP 扩展Soap 编译安装
1.进入 PHP 的软件包 pdo 扩展目录中(注:不是 PHP 安装目录) [root@tester /]# /home/tdweb/php-5.4.34/ext/soap 执行 phpize 命令 ...
- OBS源码编译开发
本文来自网易云社区 作者:梁敏 OBS简介 OBS(Open Broadcaster Software)是免费开源的视频录制和直播软件,支持运行在windows,Mac和linux平台.官方链接 ht ...
- BZOJ1222[HNOI 2001]产品加工
题面描述 某加工厂有A.B两台机器,来加工的产品可以由其中任何一台机器完成,或者两台机器共同完成.由于受到机器性能和产品特性的限制,不同的机器加工同一产品所需的时间会不同,若同时由两台机器共同进行加工 ...
- Mac下安装pear库+phpDocumentor
1. 首先安装pear: curl -o go-pear.php https://pear.php.net/go-pear.phar 看见这个就安装OK: % Total % Received % X ...
- [转]Hibernate入门:批量插入数据
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/xiazdong/article/details/7709068 一般如果要插入100万条数据,则会写如下代码: package org.xiazdon ...
- 简单的java采集程序二
继[简单的java采集程序],这里将完成对整个网站的号码段的采集任务. [使用预编译+批处理采集网页内容至数据库表中] 在之前我们用statement类来创建sql语句的执行对象,以 ...
- mysql初识(5)
将mysql数据库内的表导出为execel格式文件: 方法1:mysql命令:select * into outfile '/tmp/test.xls' from table_name;(需要注意的是 ...
- java面向对象课程设计-数学表达式计算器
项目简介 设计一个计算器,其能够: 1)由用户输入一个简单的四则运算表达式,求出其计算结果后显示. 2)特殊数学函数,如:绝对值.取整.三角函数.倒数.平方根.平方.立方等. 3)对一定范围内的数字将 ...
- lintcode-94-二叉树中的最大路径和
94-二叉树中的最大路径和 给出一棵二叉树,寻找一条路径使其路径和最大,路径可以在任一节点中开始和结束(路径和为两个节点之间所在路径上的节点权值之和) 样例 给出一棵二叉树: 返回 6 标签 动态规划 ...
