Python的平凡之路(11)

#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
#创建连接
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
'localhost'))
#创建隧道
channel = connection.channel()
#声明queue
channel.queue_declare(queue='duilie')
#Send RabbitMQ a message can never be sent directly to the queue,it always needs to go throngh an exchange
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='duilie',
body='Hello,World!')
print("[x] Sent 'Hello World!'")
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
#创建连接
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters('localhost'))
#创建隧道
channel = connection.channel()
#声明queue
channel.queue_declare(queue='duilie')
def callback(ch,method,properties,body):
print("[x] Received %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='duilie',
no_ack=True)
print('[x] Waiting for messages. To exit press CRTL+C')
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
import time
#n RabbitMQ a message can never be sent directly to the queue,it always
#needs to go through an exchange.
for i in range(100):
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key = 'task_queue',
body = 'Hello world! %s' %i,
properties = pika.BasicProperties(
delivery_mode=2, # make message persistent,把消息持久化
))
time.sleep(0.8)
print("[x] Sent 'Hello World! The %s")
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
print("[x] Received %r" % body)
time.sleep(body.count(b'.'))
print(" [x] Done")
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='task_queue',
)
print('[x] Waiting for messages. To exit press CRTL+C')
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
channel.queue_declare(queue='task_queue_other',durable=True) #加上durable=True,队列持久化
#n RabbitMQ a message can never be sent directly to the queue,it always
#needs to go through an exchange.
for i in range(100):
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key = 'task_queue_other',
body = 'Hello world! %s' %i,
properties = pika.BasicProperties(
delivery_mode=2, # make message persistent,把消息持久化
))
time.sleep(0.8)
print("[x] Sent 'Hello World! The %s")
connection.close()
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
channel.queue_declare(queue='task_queue_other',durable=True)#队列持久化
def callback(ch,method,properties,body):
print("[x] Received %r" % body)
time.sleep(body.count(b'.'))
print(" [x] Done")
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='task_queue_other',
)
print('[x] Waiting for messages. To exit press CRTL+C')
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
channel.queue_declare(queue='task_queue_other',durable=True) #加上durable=True,队列持久化
#n RabbitMQ a message can never be sent directly to the queue,it always
#needs to go through an exchange.
for i in range(100):
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key = 'task_queue_other',
body = 'Hello world! %s' %i,
properties = pika.BasicProperties(
delivery_mode=2, # make message persistent,把消息持久化
))
time.sleep(0.8)
print("[x] Sent 'Hello World! The %s")
connection.close()
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
print("[x] Received %r" % body)
time.sleep(body.count(b'.'))
print(" [x] Done")
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)#平均分发queue='task_queue_other',
)
print('[x] Waiting for messages. To exit press CRTL+C')
direct: 通过routingKey和exchange决定的那个唯一的queue可以接收消息
topic:所有符合routingKey(此时可以是一个表达式)的routingKey所bind的queue可以接收消息
表达式符号说明:#代表一个或多个字符,*代表任何字符
例:#.a会匹配a.a,aa.a,aaa.a等
*.a会匹配a.a,b.a,c.a等
注:使用RoutingKey为#,Exchange Type为topic的时候相当于使用fanout
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
import sys
type='fanout') #fanout类型-所有bind到此exchange的queue都可以接收消息
#message = ' '.join(sys.argv[1:]) or "info: Hello World!"
message = "info: Hello World!"
body='message %s' %i) #通过一个循环查看效果
time.sleep(1)
print(" [x] Sent %r" % message)
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
#创建连接
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
#创建隧道
channel = connection.channel()
#声明exchange和类型
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs',
type='fanout')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True) # 不指定queue名字,rabbit会随机分配一个名字,exclusive=True会在使用此queue的消费者断开后,自动将queue删除
queue_name = result.method.queue
print(queue_name)
channel.queue_bind(exchange='logs',#fanout类型-所有bind到此exchange的queue都可以接收消息
queue=queue_name)
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
print(" [x] %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
import sys
#创建连接
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
#创建隧道
channel = connection.channel()
#声明exchange和类型
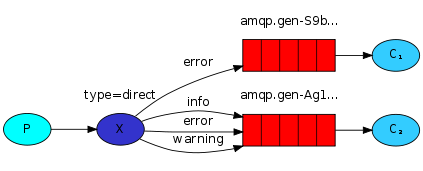
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',type='direct')
severity = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 'info'
message = ''.join(sys.argv[2:]) or 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='direct_logs',
routing_key=severity,
body = message)
print("[X] Sent %r:%r" % (severity,message))
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',
type='direct')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s [info] [warning] [error]\n" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
for severity in severities:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='direct_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=severity) #routing_key就是队列绑定的一些关键字
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r:%r" % (method.routing_key, body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)

rpc-client.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
import uuid class FibonacciRpcClient(object):
def __init__(self):
self.connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
self.channel = self.connection.channel()
result = self.channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
self.callback_queue = result.method.queue
self.channel.basic_consume(self.on_response,no_ack=True,
queue=self.callback_queue)
def on_response(self,ch,method,props,body):
if self.corr_id == props.correlation_id:
self.response = body def call(self,n):
self.response = None
self.corr_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
self.channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='rpc_queue',
properties=pika.BasicProperties(
reply_to = self.callback_queue,
correlation_id= self.corr_id,
),
body=str(n))
while self.response is None:
self.connection.process_data_events()
return int(self.response) fibonacci_rpc = FibonacciRpcClient()
print("[X] Requesting fib(30)")
response = fibonacci_rpc.call(30)
print("[.] Got %r" % response)
#!/usr/bin/env python
#Author is wspikh
# -*- coding: encoding -*-
import pika
import time
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host = 'localhost')) channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='rpc_queue')
def fib(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
else:
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2) def on_request(ch,method,props,body):
n = int(body)
print("[.] fib(%s)" % n)
response = fib(n) ch.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key=props.reply_to,
properties=pika.BasicProperties(correlation_id= \
props.correlation_id),
body = str(response))
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag= method.delivery_tag) channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1) #配置perfetch=1,意思就是告诉RabbitMQ在我这个消费者当前消息还没处理完的时候就不要再给我发新消息了。
channel.basic_consume(on_request, queue='rpc_queue')
print("[X] Awaiting RPC requests")
channel.start_consuming()
1、操作模式
redis-py提供两个类Redis和StrictRedis用于实现Redis的命令,StrictRedis用于实现大部分官方的命令,并使用官方的语法和命令,Redis是StrictRedis的子类,用于向后兼容旧版本的redis-py。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import redisr = redis.Redis(host='10.211.55.4', port=6379)r.set('foo', 'Bar')print r.get('foo') |
2、连接池
redis-py使用connection pool来管理对一个redis server的所有连接,避免每次建立、释放连接的开销。默认,每个Redis实例都会维护一个自己的连接池。可以直接建立一个连接池,然后作为参数Redis,这样就可以实现多个Redis实例共享一个连接池。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import redispool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='10.211.55.4', port=6379)r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)r.set('foo', 'Bar')print r.get('foo') |
(一)、key pattern 查询相应的key
(1)redis允许模糊查询key 有3个通配符 *、?、[]
(2)randomkey:返回随机key
(3)type key:返回key存储的类型
(4)exists key:判断某个key是否存在
(5)del key:删除key
(6)rename key newkey:改名
(7)renamenx key newkey:如果newkey不存在则修改成功
(8)move key 1:将key移动到1数据库
(9)ttl key:查询key的生命周期(秒)
(10)expire key 整数值:设置key的生命周期以秒为单位
(11)pexpire key 整数值:设置key的生命周期以毫秒为单位
(12)pttl key:查询key 的生命周期(毫秒)
(13)perisist key:把指定key设置为永久有效
(二)、字符串类型的操作
(1)set key value [ex 秒数] [px 毫秒数] [nx/xx]
如果ex和px同时写,则以后面的有效期为准
nx:如果key不存在则建立
xx:如果key存在则修改其值
(2)get key:取值
(3)mset key1 value1 key2 value2 一次设置多个值
(4)mget key1 key2 :一次获取多个值
(5)setrange key offset value:把字符串的offset偏移字节改成value
如果偏移量 > 字符串长度,该字符自动补0x00
(6)append key value :把value追加到key 的原值上
(7)getrange key start stop:获取字符串中[start, stop]范围的值
注意:当start>length,则返回空字符串
当stop>=length,则截取至字符串尾
如果start所处位置在stop右边,则返回空字符串
(8)getset key nrevalue:获取并返回旧值,在设置新值
(9)incr key:自增,返回新值,如果incr一个不是int的value则返回错误,incr一个不存在的key,则设置key为1
(10)incrby key 2:跳2自增
(11)incrbyfloat by 0.7: 自增浮点数
(12)setbit key offset value:设置offset对应二进制上的值,返回该位上的旧值
注意:如果offset过大,则会在中间填充0
offset最大到多少
2^32-1,即可推出最大的字符串为512M
(14)strlen key:取指定key的value值的长度
(15)setex key time value:设置key对应的值value,并设置有效期为time秒
(三)、链表操作
Redis的list类型其实就是一个每个子元素都是string类型的双向链表,链表的最大长度是2^32。list既可以用做栈,也可以用做队列。
list的pop操作还有阻塞版本,主要是为了避免轮询
(1)lpush key value:把值插入到链表头部
(2)rpush key value:把值插入到链表尾部
(3)lpop key :返回并删除链表头部元素
(4)rpop key: 返回并删除链表尾部元素
(5)lrange key start stop:返回链表中[start, stop]中的元素
(7)ltrim key start stop:剪切key对应的链接,切[start, stop]一段并把改制重新赋给key
(8)lindex key index:返回index索引上的值
(9)llen key:计算链表的元素个数
(10)linsert key after|before search value:在key 链表中寻找search,并在search值之前|之后插入value
(11)rpoplpush source dest:把source 的末尾拿出,放到dest头部,并返回单元值
应用场景: task + bak 双链表完成安全队列

业务逻辑: rpoplpush task bak
(四)、hashes类型及操作
Redis hash 是一个string类型的field和value的映射表,它的添加、删除操作都是O(1)(平均)。hash特别适用于存储对象,将一个对象存储在hash类型中会占用更少的内存,并且可以方便的存取整个对象。
配置: hash_max_zipmap_entries 64 #配置字段最多64个
hash_max_zipmap_value 512 #配置value最大为512字节
(1)hset myhash field value:设置myhash的field为value
(2)hsetnx myhash field value:不存在的情况下设置myhash的field为value
(3)hmset myhash field1 value1 field2 value2:同时设置多个field
(4)hget myhash field:获取指定的hash field
(5)hmget myhash field1 field2:一次获取多个field
(6)hincrby myhash field 5:指定的hash field加上给定的值
(7)hexists myhash field:测试指定的field是否存在
(8)hlen myhash:返回hash的field数量
(9)hdel myhash field:删除指定的field
(10)hkeys myhash:返回hash所有的field
(11)hvals myhash:返回hash所有的value
(12)hgetall myhash:获取某个hash中全部的field及value
特点:无序性、确定性、唯一性
(1)sadd key value1 value2:往集合里面添加元素
(2)smembers key:获取集合所有的元素
(3)srem key value:删除集合某个元素
(4)spop key:返回并删除集合中1个随机元素(可以坐抽奖,不会重复抽到某人)
(5)srandmember key:随机取一个元素
(6)sismember key value:判断集合是否有某个值
(7)scard key:返回集合元素的个数
(8)smove source dest value:把source的value移动到dest集合中
(9)sinter key1 key2 key3:求key1 key2 key3的交集
(10)sunion key1 key2:求key1 key2 的并集
(11)sdiff key1 key2:求key1 key2的差集
(12)sinterstore res key1 key2:求key1 key2的交集并存在res里
(六)、有序集合
概念:它是在set的基础上增加了一个顺序属性,这一属性在添加修改元素的时候可以指定,每次指定后,zset会自动按新的值调整顺序。可以理解为有两列的mysql表,一列存储value,一列存储顺序,操作中key理解为zset的名字。
和set一样sorted,sets也是string类型元素的集合,不同的是每个元素都会关联一个double型的score。sorted set的实现是skip list和hash table的混合体。
当元素被添加到集合中时,一个元素到score的映射被添加到hash table中,所以给定一个元素获取score的开销是O(1)。另一个score到元素的映射被添加的skip list,并按照score排序,所以就可以有序地获取集合中的元素。添加、删除操作开销都是O(logN)和skip list的开销一致,redis的skip list 实现是双向链表,这样就可以逆序从尾部去元素。sorted set最经常使用方式应该就是作为索引来使用,我们可以把要排序的字段作为score存储,对象的ID当元素存储。
(1)zadd key score1 value1:添加元素
(2)zrange key start stop [withscore]:把集合排序后,返回名次[start,stop]的元素 默认是升续排列 withscores 是把score也打印出来
(3)zrank key member:查询member的排名(升序0名开始)
(4)zrangebyscore key min max [withscores] limit offset N:集合(升序)排序后取score在[min, max]内的元素,并跳过offset个,取出N个
(5)zrevrank key member:查询member排名(降序 0名开始)
(6)zremrangebyscore key min max:按照score来删除元素,删除score在[min, max]之间
(7)zrem key value1 value2:删除集合中的元素
(8)zremrangebyrank key start end:按排名删除元素,删除名次在[start, end]之间的
(9)zcard key:返回集合元素的个数
(10)zcount key min max:返回[min, max]区间内元素数量
(11)zinterstore dest numkeys key1[key2..] [WEIGHTS weight1 [weight2...]] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]
求key1,key2的交集,key1,key2的权值分别是weight1,weight2
聚合方法用 sum|min|max
聚合结果 保存子dest集合内
注意:weights,aggregate如何理解?
答:如果有交集,交集元素又有score,score怎么处理?aggregate num->score相加,min最小score,max最大score,另外可以通过weights设置不同的key的权重,交集时 score*weight
(七)、服务器相关命令
(1)ping:测定连接是否存活
(2)echo:在命令行打印一些内容
(3)select:选择数据库
(4)quit:退出连接
(5)dbsize:返回当前数据库中key的数目
(6)info:获取服务器的信息和统计
(7)monitor:实时转储收到的请求
(8)config get 配置项:获取服务器配置的信息
config set 配置项 值:设置配置项信息
(9)flushdb:删除当前选择数据库中所有的key
(10)flushall:删除所有数据库中的所有的key
(11)time:显示服务器时间,时间戳(秒),微秒数
(12)bgrewriteaof:后台保存rdb快照
(13)bgsave:后台保存rdb快照
(14)save:保存rdb快照
(15)lastsave:上次保存时间
(16)shutdown [save/nosave]
注意:如果不小心运行了flushall,立即shutdown nosave,关闭服务器,然后手工编辑aof文件,去掉文件中的flushall相关行,然后开启服务器,就可以倒回原来是数据。如果flushall之后,系统恰好bgwriteaof了,那么aof就清空了,数据丢失。
(17)showlog:显示慢查询
问:多慢才叫慢?
答:由slowlog-log-slower-than 10000,来指定(单位为微秒)
问:服务器存储多少条慢查询记录
redis-py默认在执行每次请求都会创建(连接池申请连接)和断开(归还连接池)一次连接操作,如果想要在一次请求中指定多个命令,则可以使用pipline实现一次请求指定多个命令,并且默认情况下一次pipline 是原子性操作。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import redispool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='10.211.55.4', port=6379)r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)# pipe = r.pipeline(transaction=False)pipe = r.pipeline(transaction=True)r.set('name', 'alex')r.set('role', 'sb')pipe.execute() |
Python的平凡之路(11)的更多相关文章
- Python的平凡之路(8)
(本文是对平凡之路(7)的补充等) 一.动态导入模块 import importlib __import__('import_lib.metaclass') #这是解释器自己内部用的 #importl ...
- Python的平凡之路(19)
一.Django请求生命周期 对于所有的web框架来说本质就是一个socket服务端,浏览器是socket客户端 ...
- Python的平凡之路(16)
一.HTML+CSS补充 0.常用页面布局 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"><head> <meta ch ...
- Python的平凡之路(13)
一.Python的paramiko模块介绍 Python 的paramiko模块,该模块和SSH用于连接远程服务器并执行相关操作 SSH client 用于连接远程服务器并执行基本命令 基于用户名和密 ...
- Python的平凡之路(12)
一.数据库介绍 数据库(Database)是按照数据结构来组织.存储和管理数据的仓库,每个数据库都有一个或多个不同的API用于创建,访问,管理,搜索和复制所保存的数据.我们也可以将数据存储在文件中,但 ...
- Python的平凡之路(9)
一.Paramiko模块练习 1. Paramiko模块介绍 Paramiko是用python语言写的一个模块,遵循SSH2协议,支持以加密和认证的方式,进行远程服务器的连接 2 .SSHclie ...
- Python的平凡之路(5)
一.模块介绍 定义: 模块--用来从逻辑上组织python代码(变量,函数,类,逻辑:实现一个功能),本质就是.py结尾的python文件(文件名test.py,模块名test) 包—用来从逻辑上组织 ...
- Python的平凡之路(3)
一.函数基本语法及特性 面向对象:(华山派)—类 —class 面向过程:(少林派)—过程 —df 函数式编程:逍遥派 —函数— df 一般的,在一个变化过程中,如果有两个变量x和y,并且对于 ...
- Python的平凡之路(20)
(提问复习为主) 一.Django请求的生命周期 武彦涛: 路由系统 -> 视图函数(获取模板+数据=>渲染) -> 字符串返回给用户 二.路由 ...
随机推荐
- servlet定义
. 运行在服务器上的java类
- POJ 1852 Ants
题目的意思是说一个长度为m的杆,上面有n个蚂蚁,告诉每个蚂蚁的初始位置,每个蚂蚁速度都是一样的,问所有的蚂蚁离开杆的最短和最长时间是多少. 模拟题,所有的蚂蚁看成一样的,可以这样理解,即使相撞按反方向 ...
- C++头文件的组织
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/archive/2012/04/17/2454568.html C++编译模式通常,在一个C++程序中,只包含两类文件——.cpp文件 ...
- [问题2015S04] 复旦高等代数 II(14级)每周一题(第五教学周)
[问题2015S04] 设 \(A\) 为 \(n\) 阶方阵, \(C\) 为 \(k\times n\) 矩阵, 且对任意的 \(\lambda\in\mathbb{C}\), \(\begin{ ...
- 第九天 内容提供者 ContentResolver
重点:理解ContentProvider 的作用和创建流程 1. 内容提供者,提供 其他数据库的访问. 特点 - 描述 : 它是android 四大组件之一,需要androidManife ...
- GZFramwork数据库层《前言》Demo简介
本系列旨在熟悉GZFramwork数据库层操作,对数据库表进行增删改查,单据编号生成等: 详细见图: 普通单表操作: 数据库建模: 创建表脚本: from sys.sysreferences r jo ...
- C#中的多线程 - 基础知识
原文:http://www.albahari.com/threading/ 文章来源:http://blog.gkarch.com/threading/part1.html 1简介及概念 C# 支持通 ...
- 值得学习的C语言开源项目
值得学习的C语言开源项目 - 1. Webbench Webbench是一个在linux下使用的非常简单的网站压测工具.它使用fork()模拟多个客户端同时访问我们设定的URL,测试网站在压力下工 ...
- Linux_命令_积累
1.ps 查看进程状态 ZC: "ps -a" 和 "ps a" 有区别... (具体查看 "man ps") 1.1.ps aux 1.2 ...
- SQL基础--完整性约束
完整性约束是保证用户所做的修改不会破坏数据的一致性,是保护数据正确性和相容性的一种手段. 常见的5种约束: NOT NULL 非空约束C 指定的列不允许为空值 UNIQUE ...
