PocketSphinx语音识别和turtlebot的语音控制--18
摘要: 原创博客:转载请表明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/zxouxuewei/
1.首先安装 PocketSphinx 语音识别:
$ sudo apt-get install gstreamer0.-pocketsphinx
$ sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-pocketsphinx
$ sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-audio-common
$ sudo apt-get install libasound2
$ sudo apt-get install gstreamer0.-gconf(有些书本没有说要安装,但经过在indigo版本测试,必须安装)
2.测试PocketSphinx 语音识别,首先在系统设置里sound中input设置内置语音音量,不要太大。安装完成后我们就可以运行测试了。
首先,插入你的麦克风设备,然后在系统设置里测试麦克风是否有语音输入。
然后,运行包中的测试程序:
然后启动launch文件:
$ roslaunch pocketsphinx robocup.launch
此时,在终端中会看到一大段的信息。尝试说一些简单的语句,当然,必须是英语,例如:bring me the glass,come with me,看看能不能识别出来。
我们也可以直接看ROS最后发布的结果消息:
$ rostopic echo /recognizer/output

3.这个语音识别时一种离线识别的方法,将一些常用的词汇放到一个文件中,作为识别的文本库,然后分段识别语音信号,最后在库中搜索对应的文本信息。如果想看语音识别库中有哪些文本信息,可以通过下面的指令进行查询:
$ roscd pocketsphinx/demo
$ more robocup.corpus
4.添加语音库。 我们可以自己向语音库中添加其他的文本识别信息《ros by example》自带的例程中是带有语音识别的例程的,而且有添加语音库的例子。 首先看看例子中要添加的文本息:
$ roscd rbx1_speech/config
$ more nav_commands.txt
以下是需要添加的文本,我们也可以修改其中的某些文本,改成自己需要的。然后我们要把这个文件在线生成语音信息和库文件,这一步需要登陆网站http://www.speech.cs.cmu.edu/tools/lmtool-new.html,根据网站的提示上传文件,然后在线编译生成库文件。

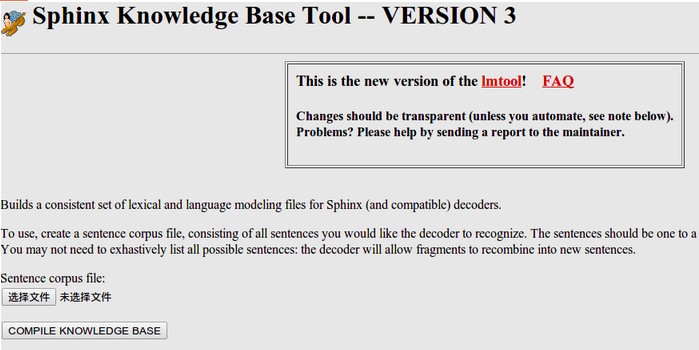
把下载的文件都解压放在rbx1_speech包的config文件夹下。我们可以给这些文件改个名字:
$ roscd rbx1_speech/config
$ rename -f 's/3026/nav_commands/'
5.在rbx1_speech/launch文件夹下看看voice_nav_commands.launch这个文件:
<launch>
<node name="recognizer" pkg="pocketsphinx" type="recognizer.py"
output="screen">
<param name="lm" value="$(find rbx1_speech)/config/nav_commands.lm"/>
<param name="dict" value="$(find rbx1_speech)/config/nav_commands.dic"/>
</node>
</launch>
可以看到,这个launch文件在运行recognizer.py节点的时候使用了我们生成的语音识别库和文件参数,这样就可以实用我们自己的语音库来进行语音识别了。
通过之前的命令来测试一下效果如何吧:
$ roslaunch rbx1_speech voice_nav_commands.launch
$ rostopic echo /recognizer/output
6.语音控制turtlrbot机器人移动:recognizer.py会将最后识别的文本信息通过消息发布,那么我们来编写一个机器人控制节点接收这个消息,进行相应的控制即可。在pocketsphinx包中本身有一个语音控制发布Twist消息的例程voice_cmd_vel.py,rbx1_speech包对其进行了一些简化修改,在nodes文件夹里可以查看voice_nav.py文件:
#!/usr/bin/env python """
voice_nav.py - Version 1.1 -- Allows controlling a mobile base using simple speech commands. Based on the voice_cmd_vel.py script by Michael Ferguson in
the pocketsphinx ROS package. See http://www.ros.org/wiki/pocketsphinx
""" import rospy
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
from std_msgs.msg import String
from math import copysign class VoiceNav:
def __init__(self):
rospy.init_node('voice_nav') rospy.on_shutdown(self.cleanup) # Set a number of parameters affecting the robot's speed
self.max_speed = rospy.get_param("~max_speed", 0.4)
self.max_angular_speed = rospy.get_param("~max_angular_speed", 1.5)
self.speed = rospy.get_param("~start_speed", 0.1)
self.angular_speed = rospy.get_param("~start_angular_speed", 0.5)
self.linear_increment = rospy.get_param("~linear_increment", 0.05)
self.angular_increment = rospy.get_param("~angular_increment", 0.4) # We don't have to run the script very fast
self.rate = rospy.get_param("~rate", )
r = rospy.Rate(self.rate) # A flag to determine whether or not voice control is paused
self.paused = False # Initialize the Twist message we will publish.
self.cmd_vel = Twist() # Publish the Twist message to the cmd_vel topic
self.cmd_vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=) # Subscribe to the /recognizer/output topic to receive voice commands.
rospy.Subscriber('/recognizer/output', String, self.speech_callback) # A mapping from keywords or phrases to commands
self.keywords_to_command = {'stop': ['stop', 'halt', 'abort', 'kill', 'panic', 'off', 'freeze', 'shut down', 'turn off', 'help', 'help me'],
'slower': ['slow down', 'slower'],
'faster': ['speed up', 'faster'],
'forward': ['forward', 'ahead', 'straight'],
'backward': ['back', 'backward', 'back up'],
'rotate left': ['rotate left'],
'rotate right': ['rotate right'],
'turn left': ['turn left'],
'turn right': ['turn right'],
'quarter': ['quarter speed'],
'half': ['half speed'],
'full': ['full speed'],
'pause': ['pause speech'],
'continue': ['continue speech']} rospy.loginfo("Ready to receive voice commands") # We have to keep publishing the cmd_vel message if we want the robot to keep moving.
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
self.cmd_vel_pub.publish(self.cmd_vel)
r.sleep() def get_command(self, data):
# Attempt to match the recognized word or phrase to the
# keywords_to_command dictionary and return the appropriate
# command
for (command, keywords) in self.keywords_to_command.iteritems():
for word in keywords:
if data.find(word) > -:
return command def speech_callback(self, msg):
# Get the motion command from the recognized phrase
command = self.get_command(msg.data) # Log the command to the screen
rospy.loginfo("Command: " + str(command)) # If the user has asked to pause/continue voice control,
# set the flag accordingly
if command == 'pause':
self.paused = True
elif command == 'continue':
self.paused = False # If voice control is paused, simply return without
# performing any action
if self.paused:
return # The list of if-then statements should be fairly
# self-explanatory
if command == 'forward':
self.cmd_vel.linear.x = self.speed
self.cmd_vel.angular.z = elif command == 'rotate left':
self.cmd_vel.linear.x =
self.cmd_vel.angular.z = self.angular_speed elif command == 'rotate right':
self.cmd_vel.linear.x =
self.cmd_vel.angular.z = -self.angular_speed elif command == 'turn left':
if self.cmd_vel.linear.x != :
self.cmd_vel.angular.z += self.angular_increment
else:
self.cmd_vel.angular.z = self.angular_speed elif command == 'turn right':
if self.cmd_vel.linear.x != :
self.cmd_vel.angular.z -= self.angular_increment
else:
self.cmd_vel.angular.z = -self.angular_speed elif command == 'backward':
self.cmd_vel.linear.x = -self.speed
self.cmd_vel.angular.z = elif command == 'stop':
# Stop the robot! Publish a Twist message consisting of all zeros.
self.cmd_vel = Twist() elif command == 'faster':
self.speed += self.linear_increment
self.angular_speed += self.angular_increment
if self.cmd_vel.linear.x != :
self.cmd_vel.linear.x += copysign(self.linear_increment, self.cmd_vel.linear.x)
if self.cmd_vel.angular.z != :
self.cmd_vel.angular.z += copysign(self.angular_increment, self.cmd_vel.angular.z) elif command == 'slower':
self.speed -= self.linear_increment
self.angular_speed -= self.angular_increment
if self.cmd_vel.linear.x != :
self.cmd_vel.linear.x -= copysign(self.linear_increment, self.cmd_vel.linear.x)
if self.cmd_vel.angular.z != :
self.cmd_vel.angular.z -= copysign(self.angular_increment, self.cmd_vel.angular.z) elif command in ['quarter', 'half', 'full']:
if command == 'quarter':
self.speed = copysign(self.max_speed / , self.speed) elif command == 'half':
self.speed = copysign(self.max_speed / , self.speed) elif command == 'full':
self.speed = copysign(self.max_speed, self.speed) if self.cmd_vel.linear.x != :
self.cmd_vel.linear.x = copysign(self.speed, self.cmd_vel.linear.x) if self.cmd_vel.angular.z != :
self.cmd_vel.angular.z = copysign(self.angular_speed, self.cmd_vel.angular.z) else:
return self.cmd_vel.linear.x = min(self.max_speed, max(-self.max_speed, self.cmd_vel.linear.x))
self.cmd_vel.angular.z = min(self.max_angular_speed, max(-self.max_angular_speed, self.cmd_vel.angular.z)) def cleanup(self):
# When shutting down be sure to stop the robot!
twist = Twist()
self.cmd_vel_pub.publish(twist)
rospy.sleep() if __name__=="__main__":
try:
VoiceNav()
rospy.spin()
except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
rospy.loginfo("Voice navigation terminated.")
7.仿真测试
$ roslaunch rbx1_bringup fake_turtlebot.launch 首先是运行一个机器人模型:
$ rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find rbx1_nav`/sim.rviz 然后打开rviz:
$ roslaunch rbx1_speech voice_nav_commands.launch 再打开语音识别的节点:
$ roslaunch rbx1_speech turtlebot_voice_nav.launch 最后就是机器人的控制节点了:
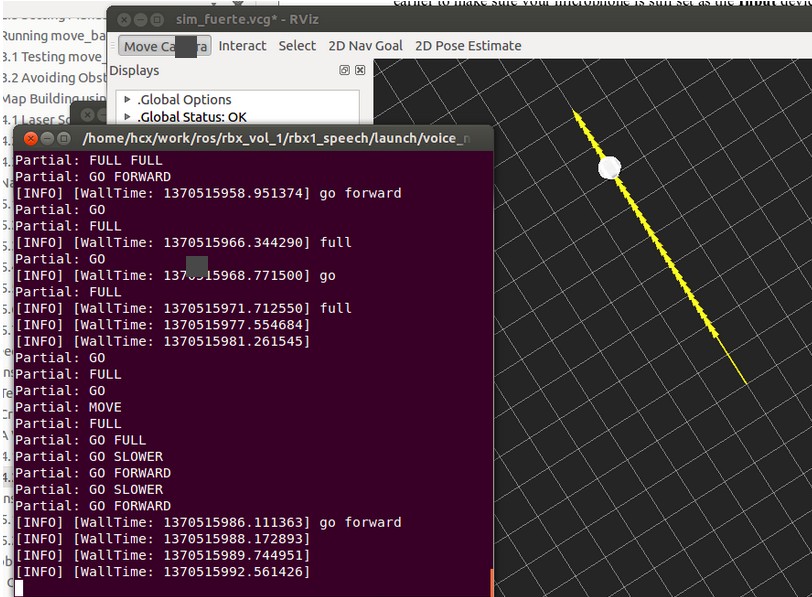
下图是我的测试结果,不过感觉准确度还是欠佳:
8.播放语音
现在机器人已经可以按照我们说的话行动了,要是机器人可以和我们对话就更好了。ROS中已经集成了这样的包,下面就来尝试一下。
运行下面的命令:
$ rosrun sound_play soundplay_node.py
$ rosrun sound_play say.py "Greetings Humans. Take me to your leader."
有没有听见声音!ROS通过识别我们输入的文本,让机器人读了出来。发出这个声音的人叫做kal_diphone,如果不喜欢,我们也可以换一个人来读:
$ sudo apt-get install festvox-don
$ rosrun sound_play say.py "Welcome to the future" voice_don_diphone
在rbx1_speech/nodes文件夹中有一个让机器人说话的节点talkback.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""
talkback.py - Version 0.1 --
Use the sound_play client to say back what is heard by the pocketsphinx recognizer.
Created for the Pi Robot Project: http://www.pirobot.org
Copyright (c) Patrick Goebel. All rights reserved.
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation; either version of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details at:
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.htmlPoint
"""
import roslib; roslib.load_manifest('rbx1_speech')
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import String
from sound_play.libsoundplay import SoundClient
import sys
class TalkBack:
def __init__(self, script_path):
rospy.init_node('talkback')
rospy.on_shutdown(self.cleanup)
# Set the default TTS voice to use
self.voice = rospy.get_param("~voice", "voice_don_diphone")
# Set the wave file path if used
self.wavepath = rospy.get_param("~wavepath", script_path + "/../sounds")
# Create the sound client object
self.soundhandle = SoundClient()
# Wait a moment to let the client connect to the
# sound_play server
rospy.sleep()
# Make sure any lingering sound_play processes are stopped.
self.soundhandle.stopAll()
# Announce that we are ready for input
self.soundhandle.playWave(self.wavepath + "/R2D2a.wav")
rospy.sleep()
self.soundhandle.say("Ready", self.voice)
rospy.loginfo("Say one of the navigation commands...")
# Subscribe to the recognizer output and set the callback function
rospy.Subscriber('/recognizer/output', String, self.talkback)
def talkback(self, msg):
# Print the recognized words on the screen
rospy.loginfo(msg.data)
# Speak the recognized words in the selected voice
self.soundhandle.say(msg.data, self.voice)
# Uncomment to play one of the built-in sounds
#rospy.sleep()
#self.soundhandle.play()
# Uncomment to play a wave file
#rospy.sleep()
#self.soundhandle.playWave(self.wavepath + "/R2D2a.wav")
def cleanup(self):
self.soundhandle.stopAll()
rospy.loginfo("Shutting down talkback node...")
if __name__=="__main__":
try:
TalkBack(sys.path[])
rospy.spin()
except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
rospy.loginfo("Talkback node terminated.")
我们来运行看一下效果:
$ roslaunch rbx1_speech talkback.launch
PocketSphinx语音识别和turtlebot的语音控制--18的更多相关文章
- PocketSphinx语音识别系统语言模型的训练和声学模型的改进
PocketSphinx语音识别系统语言模型的训练和声学模型的改进 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 关于语音识别的基础知识和sphinx的知识, ...
- android智能家居在线语音控制
对于android 智能家居项目,如果能实现语音控制,无疑会丰富项目功能,改善用户体验,android语音识别的方法有三种:一是使用intent调用语音识别程序,二 是应用程序自己调用语音识别库,三是 ...
- 语音控制的tab选项卡
前端开发whqet,csdn,王海庆,whqet,前端开发专家 ladies and 乡亲们,程序猿同志们,周末仍然坚守工作岗位,或者学习不辍的童鞋们,福音来了. 语音识别高不高端.难不难? 今天给大 ...
- 使用Olami SDK 语音控制一个支持HomeKit的智能家居的iOS程序
前言 HomeKit是苹果发布的智能家居平台.通过HomeKit组件,用户可以通过iphone.iPad和ipod Touch来控制智能灯泡,风扇.空调等支持HomeKit的智能家居,尤其是可以通过S ...
- 在unity3d游戏中添加中文语音控制
最近打算尝试一下OLAMI在游戏中应用的可能性,这里做一下记录. unity官方教程中的几个项目很精简,但看起来很不错,里面有全套的资源.最后我选择了tanks-tutorial来做这个实验. 下载和 ...
- arduino 语音音箱 :语音控制、MP3播放、报时、回复温湿度情况
arduino 语音音箱 :语音控制.MP3播放.报时.回复温湿度情况 效果图 线路图 包装后的效果 功能 需要材料 arduino板 MP3播放模块及喇叭 时钟模块 温湿度模块 语音识别模块 面包板 ...
- 在iPhone上同时关闭语音控制和siri的方法
分享 步骤及要点:1.在设置里打开siri.语音控制就自动关闭了.2.在siri里的"仅语言拨号"语言项里选择"土耳其文"或者"阿拉伯文". ...
- Chrome下的语音控制框架MyVoix.js使用篇(四)
在上一篇博文中,我为大家介绍了myvoix.js中的smart learning模块,以及何如使用该功能.(myvoix.js的源码地址会在每一篇文章末尾放出) 文本将拓展 Chrome下的语音控制框 ...
- blinker语音控制Arduino/esp8266开关灯-滑动条使用-文本框交互
总链接: https://www.arduino.cn/thread-78393-1-1.html 语音控制:https://doc.blinker.app/?file=005-App%E4%BD% ...
随机推荐
- sqlite3 SQL常用语句
1. select SELECT LastName,FirstName FROM Persons; SELECT * FROM Persons; 2. where SELECT * FROM Pers ...
- beanUtil
mvc中,页面传值进来,struts2框架是用modeldriven spingmvc是model 不用框架的话,要手动一个一个的设置,然后在用dao方法与数据库联系 servlet框架有BeanUt ...
- 【python】dict。字典
特点:以空间换取时间,使用HASH算法通过key算出了value的内存地址,建立索引,拿到key后查找速度快,但内存浪费多 因为是用key值算的内存地址,所以key为不可变变量 (set,和dict类 ...
- exec方法
如果 exec 方法没有找到匹配,将返回 null.如果找到匹配项,则 exec 方法返回一个数组,并将更新全局 RegExp 对象的属性以反映匹配结果.数组元素 0 包含了完整的匹配项,而元素 1 ...
- Javascript ----字符串(String)中的方法
涉及字符串时,常用到的几个方法... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- 一个简单的Dump转文本工具—Dump2Text
每次电脑重装都得烦心,要把庞大的IDE重新配置一次,正准备安装Visual Stdio 2010,上网找镜像的时候发现,Visual Stdio 2013推出了Community版,不仅没有lite掉 ...
- Android中Preference的使用以及监听事件分析
在Android系统源码中,绝大多数应用程序的UI布局采用了Preference的布局结构,而不是我们平时在模拟器中构建应用程序时使用的View布局结构,例如,Setting模块中布局.当然,凡事都有 ...
- C++面向对象编程解决三阶矩阵相加减
/*此处用面向对象编程*/ #include<iostream> #include<string.h> using namespace std; class Matrices ...
- 修改主机名Ubuntu
主机名存放在/etc/hostname 修改保存即可
- Eclipse的maven构建一个web项目,以构建SpringMVC项目为例
http://www.cnblogs.com/javaTest/archive/2012/04/28/2589574.html springmvc demo实例教程源代码下载:http://zuida ...
