Python_4day
函数
- 函数可以用来定义可重复代码,组织和简化
- 一般来说一个函数在实际开发中为一个小功能
- 一个类为一个大功能
- 同样函数的长度不要超过一屏
Python中的所有函数实际上都是有返回值(return None),
如果你没有设置return,那么Python将不显示None.
如果你设置return,那么将返回出return这个值.
def HJN():
print('Hello')
return 1000
b=HJN()
print(b)
Hello
1000
HJN
<function __main__.HJN()>
def panduan(number):
if number % 2 == 0:
print('O')
else:
print('J')
panduan(number=1)
J
panduan(2)
O
定义一个函数
def function_name(list of parameters):
do something


- 以前使用的random 或者range 或者print.. 其实都是函数或者类
函数的参数如果有默认值的情况,当你调用该函数的时候: 可以不给予参数值,那么就会走该参数的默认值 否则的话,就走你给予的参数值.
import random
def hahah():
n = random.randint(0,5)
while 1:
N = eval(input('>>'))
if n == N:
print('smart')
break
elif n < N:
print('太小了')
elif n > N:
print('太大了')
调用一个函数
- functionName()
- "()" 就代表调用
def H():
print('hahaha')
def B():
H()
B()
hahaha
def A(f):
f()
A(B)
hahaha


带返回值和不带返回值的函数
- return 返回的内容
- return 返回多个值
- 一般情况下,在多个函数协同完成一个功能的时候,那么将会有返回值


- 当然也可以自定义返回None
EP:


def main():
print(min(min(5,6),(51,6)))
def min(n1,n2):
a = n1
if n2 < a:
a = n2
main()
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-9-263240bbee7e> in <module>
----> 1 main() <ipython-input-8-a7c84f32bfda> in main()
1 def main():
----> 2 print(min(min(5,6),(51,6)))
3 def min(n1,n2):
4 a = n1
5 if n2 < a: <ipython-input-8-a7c84f32bfda> in min(n1, n2)
3 def min(n1,n2):
4 a = n1
----> 5 if n2 < a:
6 a = n2 TypeError: '<' not supported between instances of 'tuple' and 'NoneType'
类型和关键字参数
- 普通参数
- 多个参数
- 默认值参数
- 不定长参数
普通参数
多个参数
默认值参数
强制命名
def U(str_):
xiaoxie = 0
for i in str_:
ASCII = ord(i)
if 97<=ASCII<=122:
xiaoxie +=1
elif xxxx:
daxie += 1
elif xxxx:
shuzi += 1
return xiaoxie,daxie,shuzi
U('HJi12')
H
J
i
1
2
不定长参数
- *args
- 不定长,来多少装多少,不装也是可以的
- 返回的数据类型是元组
- args 名字是可以修改的,只是我们约定俗成的是args
- **kwargs
- 返回的字典
- 输入的一定要是表达式(键值对)
- name,*args,name2,**kwargs 使用参数名
def TT(a,b)
def TT(*args,**kwargs):
print(kwargs)
print(args)
TT(1,2,3,4,6,a=100,b=1000)
{'a': 100, 'b': 1000}
(1, 2, 3, 4, 6)
{'key':'value'}
()
TT(1,2,4,5,7,8,9,)
(1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9)
def B(name1,nam3):
pass
B(name1=100,2)
File "<ipython-input-39-bd6a38e58465>", line 1
B(name1=100,2)
^
SyntaxError: positional argument follows keyword argument
def sum_(*args,A='sum'):
res = 0
count = 0
for i in args:
res +=i
count += 1
if A == "sum":
return res
elif A == "mean":
mean = res / count
return res,mean
else:
print(A,'还未开放')
sum_(-1,0,1,4,A='var')
var 还未开放
'aHbK134'.__iter__
b = 'asdkjfh'
for i in b :
print(i)
a
s
d
k
j
f
h
2,5
2 + 22 + 222 + 2222 + 22222
变量的作用域
- 局部变量 local
- 全局变量 global
- globals 函数返回一个全局变量的字典,包括所有导入的变量
- locals() 函数会以字典类型返回当前位置的全部局部变量。
a = 1000
b = 10
def Y():
global a,b
a += 100
print(a)
Y()
1100
def YY(a1):
a1 += 100
print(a1)
YY(a)
print(a)
1200
1100
注意:
- global :在进行赋值操作的时候需要声明
- 官方解释:This is because when you make an assignment to a variable in a scope, that variable becomes local to that scope and shadows any similarly named variable in the outer scope.


Homework
- 1


import math
def getPentagonalNumber():
count = 0
for i in range(1, 101):
a = i * ( 3*i - 1) / 2
print(int(a),end = ' ')
count += 1
if count % 10 == 0:
print('\n')
getPentagonalNumber()
- 2


def sumDigits(n):
a = n % 10
b = n // 100
c = (n // 10) - ((n // 100)*10)
d = a + b + c
print(d)
sumDigits(234)
9
- 3


def displaySortedNumbers(num1,num2,num3):
if num1 > num2 > num3:
print(num1,num2,num3)
elif num1 > num3 > num2:
print(num1,num3,num2)
elif num2 > num1 > num3:
print(num2,num1,num3)
elif num2 > num3 > num1:
print(num2,num3,num1)
elif num3 > num1 > num2:
print(num3,num1,num2)
elif num3 > num2 > num1:
print(num3,num2,num1)
displaySortedNumbers(3,8,1)
8 3 1
- 4


def futureInvestmentValue(principal,rate,years):
for i in range(years):
principal = principal * (1+rate)
print("{}年内总额{}: ".format(i+1,principal))
principal = eval(input("输入存款金额: "))
rate = eval(input("输入利率: "))
years = eval(input("输入年份:" ))
futureInvestmentValue(principal,rate,years)
输入存款金额: 10000
输入利率: 0.003
输入年份:10
1年内总额10029.999999999998:
2年内总额10060.089999999997:
3年内总额10090.270269999995:
4年内总额10120.541080809995:
5年内总额10150.902704052423:
6年内总额10181.35541216458:
7年内总额10211.899478401072:
8年内总额10242.535176836274:
9年内总额10273.262782366783:
10年内总额10304.082570713881:
- 5


li = [chr(i) for i in range(ord("A"),ord("Z")+1)]
count=0
for i in li:
print(i,end=' ')
count += 1
if(count%10==0):
print(end='\n')
A B C D E F G H I J
K L M N O P Q R S T
U V W X Y Z
- 6


import math
def numberOfDaysInAYear():
for i in range(2010,2021):
if i % 4 == 0 and i % 100 != 0 or i % 400 == 0:
print(i,'是366天')
else:
print(i,'是365天')
numberOfDaysInAYear()
2010 是365天
2011 是365天
2012 是366天
2013 是365天
2014 是365天
2015 是365天
2016 是366天
2017 是365天
2018 是365天
2019 是365天
2020 是366天
- 7


import numpy as np
import math
def xsj(x1,y1,x2,y2):
p1=np.array([x1,y1])
p2=np.array([x2,y2])
p3=p2-p1
p4=math.hypot(p3[0],p3[1])
print(p4)
x1,y1,x2,y2=map(int,input().split(','))
xsj(x1,y1,x2,y2)
1,2,3,4
2.8284271247461903
- 8


def a():
for i in range(2, 32):
p = (2 ** i) - 1
print(i,p)
a()
- 9



import time
localtime = time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time()))
print("本地时间为 :", localtime)
本地时间为 : Sun Aug 4 19:00:10 2019
- 10

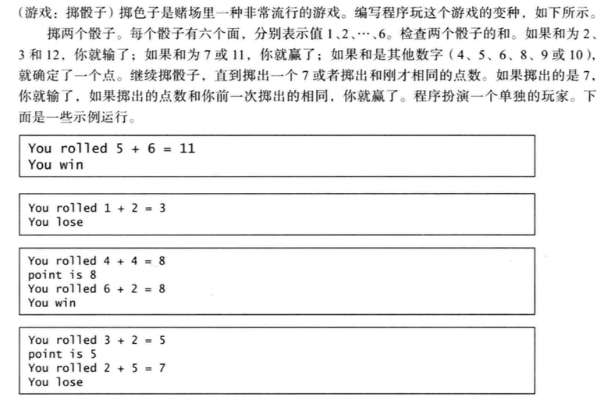
import random
random1 = random.randint(1,7)
random2 = random.randint(1,7)
random3 = random.randint(1,7)
total = random1 + random2
print('第一次摇到:{}'.format(random1))
print('第二次摇到:{}'.format(random2))
if total ==7 or total==11:
print('{}+{}={} you win!'.format(random1,random2,total))
elif total ==2 or total==3 or total ==12:
print('{}+{}={} you lose!'.format(random1,random2,total))
elif total==4 or total ==5 or total==6 or total==8 or total==9 or total==10:
total=total+random3
print('第三次摇到:{}'.format(random3))
print('diercihe{}'.format(total))
第一次摇到:2
第二次摇到:1
2+1=3 you lose!
- 11
去网上寻找如何用Python代码发送邮件
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
def send_mail(username, passwd, recv, title, content, mail_host='smtp.163.com', port=25):
'''
发送邮件函数,默认使用163smtp
:param username: 邮箱账号 xx@163.com
:param passwd: 邮箱密码
:param recv: 邮箱接收人地址,多个账号以逗号隔开
:param title: 邮件标题
:param content: 邮件内容
:param mail_host: 邮箱服务器
:param port: 端口号
:return:
'''
msg = MIMEText(content) # 邮件内容
msg['Subject'] = title # 邮件主题
msg['From'] = username # 发送者账号
msg['To'] = recv # 接收者账号列表
smtp = smtplib.SMTP(mail_host, port=port) # 连接邮箱,传入邮箱地址,和端口号,smtp的端口号是25
smtp.login(username, passwd) # 发送者的邮箱账号,密码
smtp.sendmail(username, recv, msg.as_string())
# 参数分别是发送者,接收者,第三个是把上面的发送邮件的内容变成字符串
smtp.quit() # 发送完毕后退出smtp
print('email send success.')
email_user = 'xxxx@163.com' # 发送者账号
email_pwd = 'xxxxx' # 发送者密码
maillist = 'XXX@XXX.com'
title = '测试邮件标题'
content = '这里是邮件内容'
send_mail(email_user, email_pwd, maillist, title, content)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
SMTPAuthenticationError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-4-240ad3b9e6b5> in <module>
32 title = '测试邮件标题'
33 content = '这里是邮件内容'
---> 34 send_mail(email_user, email_pwd, maillist, title, content) <ipython-input-4-240ad3b9e6b5> in send_mail(username, passwd, recv, title, content, mail_host, port)
20 msg['To'] = recv # 接收者账号列表
21 smtp = smtplib.SMTP(mail_host, port=port) # 连接邮箱,传入邮箱地址,和端口号,smtp的端口号是25
---> 22 smtp.login(username, passwd) # 发送者的邮箱账号,密码
23 smtp.sendmail(username, recv, msg.as_string())
24 # 参数分别是发送者,接收者,第三个是把上面的发送邮件的内容变成字符串 D:\anacoda\lib\smtplib.py in login(self, user, password, initial_response_ok)
728
729 # We could not login successfully. Return result of last attempt.
--> 730 raise last_exception
731
732 def starttls(self, keyfile=None, certfile=None, context=None): D:\anacoda\lib\smtplib.py in login(self, user, password, initial_response_ok)
719 (code, resp) = self.auth(
720 authmethod, getattr(self, method_name),
--> 721 initial_response_ok=initial_response_ok)
722 # 235 == 'Authentication successful'
723 # 503 == 'Error: already authenticated' D:\anacoda\lib\smtplib.py in auth(self, mechanism, authobject, initial_response_ok)
640 if code in (235, 503):
641 return (code, resp)
--> 642 raise SMTPAuthenticationError(code, resp)
643
644 def auth_cram_md5(self, challenge=None): SMTPAuthenticationError: (535, b'Error: authentication failed')
Python_4day的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- Tishreen-CPC 2018 G. Colors Overflow(分块)
Problem G. Colors Overflow Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Balloon Color: Da ...
- JavaWeb-SpringBoot(抖音)_一、抖音项目制作
JavaWeb-SpringBoot(抖音)_一.抖音项目制作 传送门 JavaWeb-SpringBoot(抖音)_二.服务器间通讯 传送门 JavaWeb-SpringBoot(抖音)_三.抖音项 ...
- PHP-配置MySQL
安装mysql 修改PHP配置文件 修改php安装路径下 php.ini extension=php_mysqli.dll 在代码路径下添加php文件,在里面编辑 <?php phpinfo() ...
- gcd表(欧几里得定理)
题目:http://acm.nyist.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problem.php?pid=797 gcd表 时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:3 ...
- vscode 插件推荐 - 献给所有前端工程师(2018.4.29更新)
大家好,我是Moer.VScode现在已经越来越完善.性能远超Atom和webstorm,你有什么理由不用它?在这里,我会给你们推荐很多实用的插件,让你对 vscode 有更深刻的体会,渐渐地你就会知 ...
- Fragment全解析系列
(一):那些年踩过的坑 开始之前 最新版知乎,单Activity多Fragment的架构,响应可以说非常“丝滑”,非要说缺点的话,就是没有转场动画,并且转场会有类似闪屏现象.我猜测可能和Fragmen ...
- IDEA 常用插件及快捷键总结
现在开发中和日常自己开发都统一换成了 IDEA 进行开发了.现在针对自己常用到的插件和快捷键进行总结记录下. 插件 Alibaba Java Coding Guidelines:阿里巴巴编码规约 Gr ...
- python在shell中环境变量使用
1.用Python Shell设置或获取环境变量的方法: 设置系统环境变量 os.environ['环境变量名称']='环境变量值' #其中key和value均为string类型 os.putenv( ...
- Python操作SQLite
1. 导入sqlite3数据库模块,从python2.5以后,sqlite3成为内置模块,不需要额外安装,只需要导入即可. import sqlite3 2.创建/打开数据库 使用connect方法打 ...
- spring-boot集成2:集成lombok
Why lombok? lombok可以帮我们从实体类的getter.setter.constructor和toString等样板代码中解脱出来,使用lombok可以开发出更优雅的代码 1.maven ...
