Dubbo消费方服务调用过程源码分析
参考:
dubbo消费方服务调用过程源码分析
dubbo基于spring的构建分析
Dubbo概述--调用过程
dubbo 请求调用过程分析
dubbo集群容错机制代码分析1
dubbo集群容错策略的代码分析2
dubbo spi机制源码学习
Dubbo-服务调用过程
一、通过分析一个典型rpc方法调用的调用栈来说明调用过程。
1.定义一个接口
public interface DemoService {
/**
* class_name: sayHello
* param: [param]
* describe: say hello
* creat_user: CoderZZ
* creat_date: 2018-10-11
* creat_time: 23:06
**/
String sayHello(String param);
/**
* class_name: sayGoodbye
* param: [param]
* describe: TODO
* creat_user: CoderZZ
* creat_date: 2018-10-12
* creat_time: 0:27
**/
String sayGoodbye(String param);
Person getPerson(String name);
}
2.实现该接口
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService{
public String sayHello(String param) {
// 本端是否为提供端,这里会返回true
boolean isProviderSide = RpcContext.getContext().isProviderSide();
System.out.println("isProviderSide:"+isProviderSide);
// 获取调用方IP地址
String clientIP = RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost();
System.out.println("clientIP:"+clientIP);
// 获取当前服务配置信息,所有配置信息都将转换为URL的参数
String application = RpcContext.getContext().getUrl().getParameter("application");
System.out.println("application:"+application);
String address = RpcContext.getContext().getUrl().getAddress();
System.out.println("address:"+address);
String index = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachment("index");
System.out.println("getAttachment index:"+index);
return "Hello "+param;
}
//以下省略
...............
}
3.服务端通过注册中心发布服务,默认是dubbo协议发布(dubbo-provider.xml)
<dubbo:registry id="workpalceRegistry" address="zookeeper://192.168.33.117:2181" default="true"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" dispatcher="all" threadpool="fixed" threads="100" accepts="10" status="test"/>
<dubbo:service interface="com.zxd.dubbo.learning.api.DemoService" ref="demoServiceImpl" protocol="dubbo" registry="workpalceRegistry" executes="10" timeout="60000"/>
<bean id="demoServiceImpl" class="com.zxd.dubbo.learning.provider.DemoServiceImpl"/>
4.客户端通过注册中心引用这个服务,注册中心用zookeepr协议实现(dubbo-consumer2.xml)
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://192.168.33.117:2181"/>
<!--客户端连接控制-->
<!--connections="10"-->
<!--限制客户端服务使用连接不能超过 10 个-->
<dubbo:reference interface="com.zxd.dubbo.learning.api.DemoService" id="demoService" retries="2" loadbalance="random" actives="10" connections="10"/>
<!--如果是线上需求需要点对点,可在 <dubbo:reference> 中配置 url 指向提供者,将绕过注册中心,多个地址用分号隔开-->
<!--<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="com.zxd.dubbo.learning.api.DemoService" url="dubbo://localhost:20880"/>-->
5.启动服务端,客户端调用Dubbo服务
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:dubbo-consumer2.xml");
// classPathXmlApplicationContext.start();
System.out.println("Consumer started!");
DemoService demoService = classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("demoService",DemoService.class);
//隐式参数
//注意:path, group, version, dubbo, token, timeout 几个 key 是保留字段,请使用其它值
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment("index","1");
String rt = demoService.sayHello("world");
System.out.println(rt);
}
6.执行main方法获得以下输出
log4j:WARN No appenders could be found for logger (org.springframework.core.env.StandardEnvironment).
log4j:WARN Please initialize the log4j system properly.
log4j:WARN See http://logging.apache.org/log4j/1.2/faq.html#noconfig for more info.
Consumer started!
SLF4J: Failed to load class "org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder".
SLF4J: Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#StaticLoggerBinder for further details.
Hello world Process finished with exit code 0
二、断点跟踪(dubbo默认底层的传输框架是netty)
看下 com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty.NettyClient 类 doOpen 方法
/***
* 打开到远端服务机器的连接
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
NettyHelper.setNettyLoggerFactory();
bootstrap = new ClientBootstrap(channelFactory);
// config
// @see org.jboss.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannelConfig
bootstrap.setOption("keepAlive", true);
bootstrap.setOption("tcpNoDelay", true);
bootstrap.setOption("connectTimeoutMillis", getConnectTimeout());
final NettyHandler nettyHandler = new NettyHandler(getUrl(), this);
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
@Override
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() {
NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyClient.this);
ChannelPipeline pipeline = Channels.pipeline();
//设置消息流的处理handler,发出去的消息先经过handler再经过encoder,
//这里断点可以设置在nettyHandler类里。
pipeline.addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("handler", nettyHandler);
return pipeline;
}
});
}
NettyHandler 类继承了netty的 SimpleChannelHandler 类,并实现了 writeRequested 方法:
@Override
public void writeRequested(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
super.writeRequested(ctx, e);//此处打断点
NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.getChannel(), url, handler);
try {
handler.sent(channel, e.getMessage());
} finally {
NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ctx.getChannel());
}
}
NettyHandler类的继承关系图: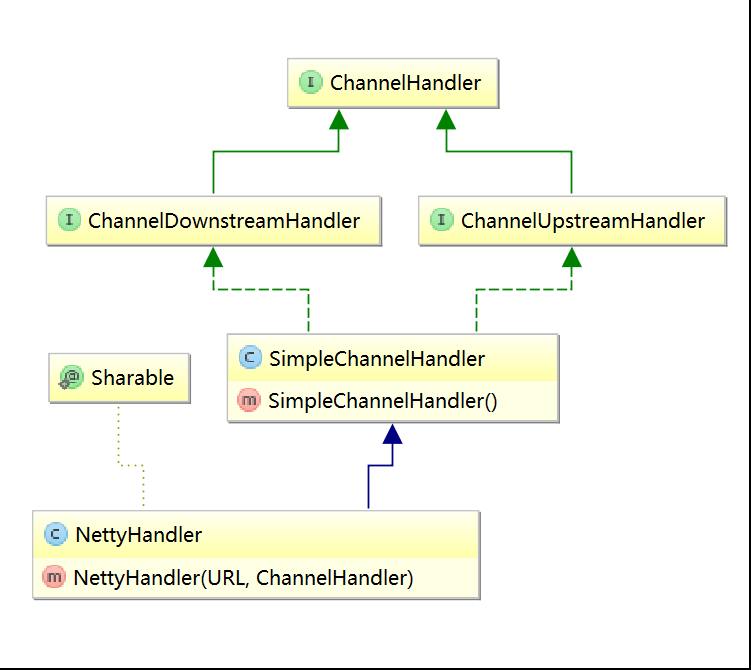
在 super.writeRequested(ctx, e); 处打断点,然后运行main方法,在程序断点处得到以下线程堆栈信息:
"main@1" prio=5 tid=0x1 nid=NA runnable
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty.NettyHandler.writeRequested(NettyHandler.java:98)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.SimpleChannelHandler.handleDownstream(SimpleChannelHandler.java:266)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline.sendDownstream(DefaultChannelPipeline.java:591)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline.sendDownstream(DefaultChannelPipeline.java:582)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.Channels.write(Channels.java:611)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.Channels.write(Channels.java:578)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.AbstractChannel.write(AbstractChannel.java:251)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty.NettyChannel.send(NettyChannel.java:100)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.AbstractClient.send(AbstractClient.java:265)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.AbstractPeer.send(AbstractPeer.java:53)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.exchange.support.header.HeaderExchangeChannel.request(HeaderExchangeChannel.java:116)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.exchange.support.header.HeaderExchangeClient.request(HeaderExchangeClient.java:90)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboInvoker.doInvoke(DubboInvoker.java:95)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.AbstractInvoker.invoke(AbstractInvoker.java:155)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.listener.ListenerInvokerWrapper.invoke(ListenerInvokerWrapper.java:77)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor.support.MonitorFilter.invoke(MonitorFilter.java:75)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper$1.invoke(ProtocolFilterWrapper.java:72)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.filter.FutureFilter.invoke(FutureFilter.java:54)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper$1.invoke(ProtocolFilterWrapper.java:72)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.filter.ActiveLimitFilter.invoke(ActiveLimitFilter.java:70)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper$1.invoke(ProtocolFilterWrapper.java:72)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.filter.ConsumerContextFilter.invoke(ConsumerContextFilter.java:49)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper$1.invoke(ProtocolFilterWrapper.java:72)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.InvokerWrapper.invoke(InvokerWrapper.java:56)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke(FailoverClusterInvoker.java:78)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke(AbstractClusterInvoker.java:244)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.wrapper.MockClusterInvoker.invoke(MockClusterInvoker.java:75)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke(InvokerInvocationHandler.java:52)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0.sayHello(proxy0.java:-1)
at com.zxd.dubbo.learning.consumer.Consumer2.main(Consumer2.java:37)
从下向上看,可以看到客户端方法调用经过的类和方法。
第二行栈信息:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0.sayHello(proxy0.java:-1)
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0 类是一个代理类,代理了所有RPC服务接口的方法调用。
这个类实例什么时候创建,类代码是什么样的?参见博文dubbo基于spring的构建分析。
大体过程为:
//Dubbo xml scheme解析处理类
public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static {
Version.checkDuplicate(DubboNamespaceHandler.class);
} @Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false));//处理<dubbo:reference>标签
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new AnnotationBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
以下为 ReferenceBean 的类继承关系图: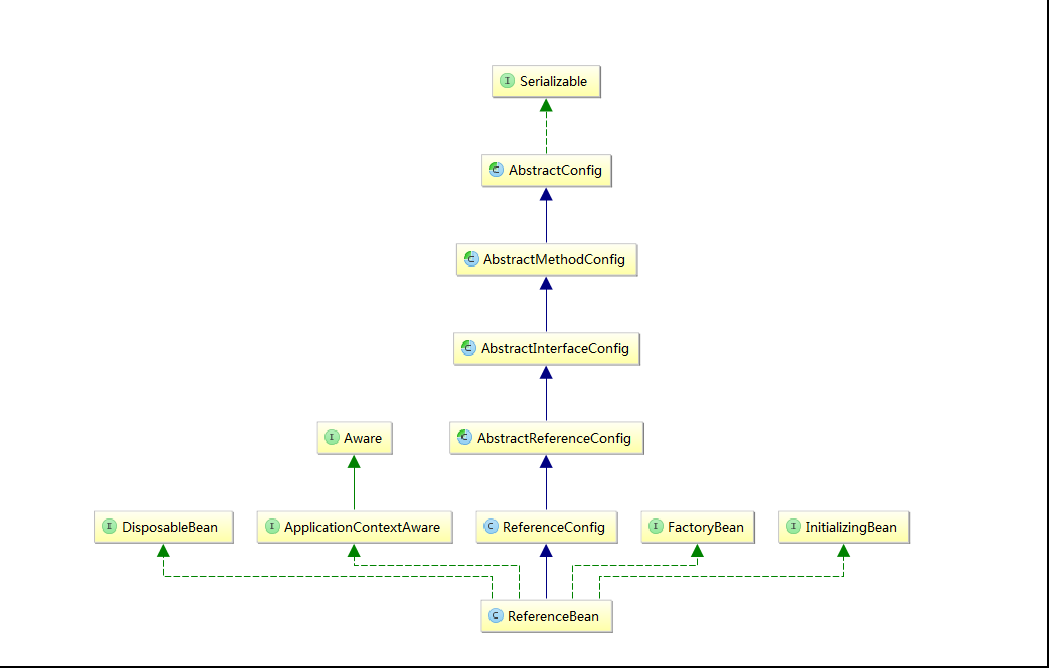
代理的创建是由 ReferenceBean 类里的 getObject() 方法里触发:
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return get();
}
get() 方法在 ReferenceConfig 类中:
public synchronized T get() {
if (destroyed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already destroyed!");
}
if (ref == null) {
init();
}
return ref;
}
private void init() {
.............
ref = createProxy(map);
.............
}
/***
* 创建客户端rpc调用代理
* @param map
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes", "deprecation"})
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
//....用于生成invoker的逻辑
//创建服务代理
// create service proxy
return (T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
}
proxyFactory 的声明为:
private static final ProxyFactory proxyFactory = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ProxyFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
由博文dubbo spi机制源码学习可以得到 ProxyFactory 接口的 Adaptive 类的 getProxy 方法源码如下:
public class ProxyFactory$Adpative implements com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory {
public java.lang.Object getProxy(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker arg0) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName = url.getParameter("proxy", "javassist");
if (extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([proxy])");
//这里默认用了ProxyFactory javassist扩展的getProxy方法创建代理
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.getProxy(arg0);
}
}
ProxyFactory 为接口类,实现类有抽象类 AbstractProxyFactory 和类 StubProxyFactoryWrapper 。 AbstractProxyFactory 包含抽象方法 public abstract <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] types); ,该抽象方法实现类有 JavassistProxyFactory 和 JdkProxyFactory ,如下: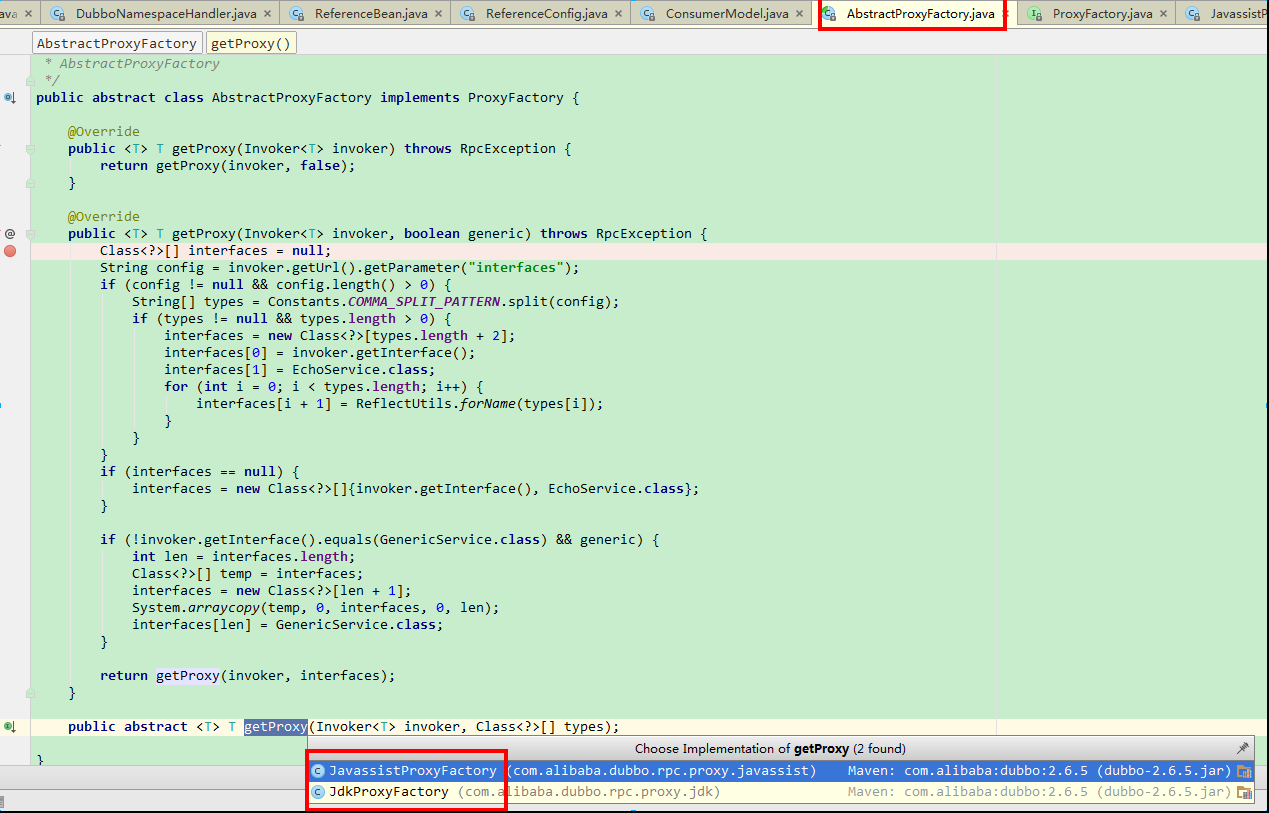
ProxyFactory 接口的javassist扩展类 JavassistProxyFactory 的 getProxy 方法实现如下:
/**
* JavaassistRpcProxyFactory
*/
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory { @Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
//代理类实现化以new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker)为参数
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
}
生成动态代理的 Proxy 类
/**
* Get proxy.
*
* @param ics interface class array.
* @return Proxy instance.
*/
public static Proxy getProxy(Class<?>... ics) {
return getProxy(ClassHelper.getClassLoader(Proxy.class), ics);
}
/**
* Get proxy.
*
* @param cl class loader.
* @param ics interface class array.可以实现多个接口
* @return Proxy instance.
*/
public static Proxy getProxy(ClassLoader cl, Class<?>... ics) {
if (ics.length > 65535)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded"); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < ics.length; i++) {
String itf = ics[i].getName();
if (!ics[i].isInterface())
throw new RuntimeException(itf + " is not a interface."); Class<?> tmp = null;
try {
tmp = Class.forName(itf, false, cl);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
} if (tmp != ics[i])
throw new IllegalArgumentException(ics[i] + " is not visible from class loader"); sb.append(itf).append(';');
} // use interface class name list as key.
// 用接口类名做key,多个接口以";"分开。
String key = sb.toString(); // get cache by class loader.
// 缓存
Map<String, Object> cache;
synchronized (ProxyCacheMap) {
cache = ProxyCacheMap.get(cl);
if (cache == null) {
cache = new HashMap<String, Object>();
ProxyCacheMap.put(cl, cache);
}
} Proxy proxy = null;
synchronized (cache) {
do {
Object value = cache.get(key);
if (value instanceof Reference<?>) {
//如果有存在引用对象,返回缓存对象。
proxy = (Proxy) ((Reference<?>) value).get();
if (proxy != null)
return proxy;
}
//对象正在生成,线程挂起,等待
if (value == PendingGenerationMarker) {
try {
cache.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
} else {
//放入正在生成标识
cache.put(key, PendingGenerationMarker);
break;
}
}
while (true);
}
//类名称后自动加序列号 0,1,2,3...
long id = PROXY_CLASS_COUNTER.getAndIncrement();
String pkg = null;
//ClassGenerator dubbo用javassist实现的工具类
ClassGenerator ccp = null, ccm = null;
try {
ccp = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl); Set<String> worked = new HashSet<String>();
List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<Method>(); for (int i = 0; i < ics.length; i++) {
//检查包名称及不同包的修饰符
if (!Modifier.isPublic(ics[i].getModifiers())) {
String npkg = ics[i].getPackage().getName();
if (pkg == null) {
pkg = npkg;
} else {
if (!pkg.equals(npkg))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("non-public interfaces from different packages");
}
}
//代理类添加要实现的接口Class对象
ccp.addInterface(ics[i]); for (Method method : ics[i].getMethods()) {
//获取方法描述符,不同接口,同样的方法,只能被实现一次。
String desc = ReflectUtils.getDesc(method);
if (worked.contains(desc))
continue;
worked.add(desc); int ix = methods.size();
//方法返回类型
Class<?> rt = method.getReturnType();
//方法参数类型列表
Class<?>[] pts = method.getParameterTypes();
//生成接口的实现代码,每个方法都一样
StringBuilder code = new StringBuilder("Object[] args = new Object[").append(pts.length).append("];");
for (int j = 0; j < pts.length; j++)
code.append(" args[").append(j).append("] = ($w)$").append(j + 1).append(";");
code.append(" Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[" + ix + "], args);");
if (!Void.TYPE.equals(rt))
code.append(" return ").append(asArgument(rt, "ret")).append(";"); methods.add(method);
ccp.addMethod(method.getName(), method.getModifiers(), rt, pts, method.getExceptionTypes(), code.toString());
}
} if (pkg == null)
pkg = PACKAGE_NAME; // create ProxyInstance class.
// 具体代理类名称,这里是类全名
String pcn = pkg + ".proxy" + id;
ccp.setClassName(pcn);
ccp.addField("public static java.lang.reflect.Method[] methods;");
ccp.addField("private " + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " handler;");
//创建构造函数
ccp.addConstructor(Modifier.PUBLIC, new Class<?>[]{InvocationHandler.class}, new Class<?>[0], "handler=$1;");
ccp.addDefaultConstructor();
Class<?> clazz = ccp.toClass();
//通过反射,把method数组放入,静态变量methods中,
clazz.getField("methods").set(null, methods.toArray(new Method[0])); // create Proxy class.
String fcn = Proxy.class.getName() + id;
ccm = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl);
ccm.setClassName(fcn);
ccm.addDefaultConstructor();
//设置父类为Proxy类
ccm.setSuperClass(Proxy.class);
//生成实现它的抽象方法newInstance代码,new 的实例对象,是上面生成的代理类 pcn
ccm.addMethod("public Object newInstance(" + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " h){ return new " + pcn + "($1); }");
Class<?> pc = ccm.toClass();
proxy = (Proxy) pc.newInstance();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
// release ClassGenerator
if (ccp != null)
ccp.release();
if (ccm != null)
ccm.release();
synchronized (cache) {
if (proxy == null)
cache.remove(key);
else
//放入缓存,key:实现的接口名,value 代理对象,这个用弱引用,
//当jvm gc时,会打断对实例对象的引用,对象接下来就等待被回收。
cache.put(key, new WeakReference<Proxy>(proxy));
cache.notifyAll();
}
}
return proxy;
}
通过 javaagent 可以导出动态代理class文件源码,以下为生成的代理类源码,动态生成了两个类:
package com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; public class Proxy0 extends Proxy
implements ClassGenerator.DC
{
public Object newInstance(InvocationHandler paramInvocationHandler)
{
return new proxy0(paramInvocationHandler);
}
}
这个类继承了抽象类 Proxy ,实现了它的抽象方法 newInstance ,接口 ClassGenerator.DC 是dubbo内部作为动态类标识的接口。
还有一个类 proxy0 ,就是在开始方法栈里看到的代理类,源码如下:
package com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode; import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.service.EchoService;
import com.zxd.dubbo.learning.api.DemoService;
import com.zxd.dubbo.learning.api.Person;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class proxy0
implements ClassGenerator.DC, EchoService, DemoService
{
public static Method[] methods;
private InvocationHandler handler;
//实现了接口方法
public String sayHello(String paramString)
{
Object[] arrayOfObject = new Object[1];
arrayOfObject[0] = paramString;
Object localObject = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[0], arrayOfObject);//实际调用逻辑
return (String)localObject;
}
//实现了接口方法
public String sayGoodbye(String paramString)
{
Object[] arrayOfObject = new Object[1];
arrayOfObject[0] = paramString;
Object localObject = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[1], arrayOfObject);
return (String)localObject;
}
//实现了接口方法
public Person getPerson(String paramString)
{
Object[] arrayOfObject = new Object[1];
arrayOfObject[0] = paramString;
Object localObject = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[2], arrayOfObject);
return (Person)localObject;
}
//回显测试接口
public Object $echo(Object paramObject)
{
Object[] arrayOfObject = new Object[1];
arrayOfObject[0] = paramObject;
Object localObject = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[3], arrayOfObject);
return (Object)localObject;
} public proxy0()
{
} public proxy0(InvocationHandler paramInvocationHandler)
{
//public构造函数,这里handler是
//由Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker))语句传入的InvokerInvocationHandler对象
this.handler = paramInvocationHandler;
}
}
可以看到代理类实现了3个接口。
ClassGeneratr.DC 是dubbo动态类标识接口;
DemoService 是实际业务接口。这样代理就可以调用服务方法了;
EchoService 是回显测试接口,它能为所有dubbo rpc服务加上的一个回显测试方法,只有一个方法:
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.service; /**
* Echo service.
* @export
*/
public interface EchoService { /**
* echo test.
*
* @param message message.
* @return message.
*/
Object $echo(Object message); }
EchoService echoService = (EchoService) demoService; // 通过强制转型为EchoService,可以测试。
通过查看 proxy0.class 的 sayHello 方法,其实际调用的是O bject localObject = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[0], arrayOfObject);
与上述堆栈信息第三行一致:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke(InvokerInvocationHandler.java:52)
InvokerInvocationHandler 如下:
public class InvokerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Invoker<?> invoker;
//通过构造函数传入invoker
public InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker<?> handler) {
this.invoker = handler;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
//如果是Object类方法
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
//反射调用
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
//对3个特殊方法的调用,做了处理
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
//其他业务方法通过invoker.invoke方法调用
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}
}
这里的 invoker 对象,通过 InvokerInvocationHandler 构造方法传入,而 InvokerInvocationHandler 对象是由 JavassistProxyFactory 类 getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) 方法创建。
回到调用 proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker); 方法的地方,即 ReferenceConfig 类的 createProxy(Map<String, String> map) 方法:
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes", "deprecation"})
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
URL tmpUrl = new URL("temp", "localhost", 0, map);
final boolean isJvmRefer;
if (isInjvm() == null) {
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { // if a url is specified, don't do local reference
isJvmRefer = false;
} else if (InjvmProtocol.getInjvmProtocol().isInjvmRefer(tmpUrl)) {
// by default, reference local service if there is
isJvmRefer = true;
} else {
isJvmRefer = false;
}
} else {
isJvmRefer = isInjvm().booleanValue();
}
if (isJvmRefer) {
URL url = new URL(Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.LOCALHOST, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map);
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Using injvm service " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
} else {
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { // user specified URL, could be peer-to-peer address, or register center's address.
String[] us = Constants.SEMICOLON_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url);
if (us != null && us.length > 0) {
for (String u : us) {
URL url = URL.valueOf(u);
if (url.getPath() == null || url.getPath().length() == 0) {
url = url.setPath(interfaceName);
}
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
urls.add(url.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
} else {
urls.add(ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(url, map));
}
}
}
} else { // assemble URL from register center's configuration
List<URL> us = loadRegistries(false);
if (us != null && !us.isEmpty()) {
for (URL u : us) {
URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(u);
if (monitorUrl != null) {
map.put(Constants.MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString()));
}
urls.add(u.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
}
}
if (urls.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such any registry to reference " + interfaceName + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please config <dubbo:registry address=\"...\" /> to your spring config.");
}
}
//只有一个直连地址或一个注册中心配置地址
if (urls.size() == 1) {
//这里的urls.get(0)协议,可能是直连地址(默认dubbo协议),也可能是regiter注册地址(zookeeper协议)
//本例通过配置一个注册中心的形式
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
} else {
//多个直连地址或者多个注册中心地址,甚至是两者的组合。
List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>();
URL registryURL = null;
for (URL url : urls) {
//创建invoker放入invokers
invokers.add(refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url));
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
// 多个注册中心,用最后一个registry url
registryURL = url; // use last registry url
}
}
//有注册中心协议的URL,
//对多个url,其中存在有注册中心的,写死用AvailableCluster集群策略
//这其中包括直连和注册中心混合或者都是注册中心两种情况
if (registryURL != null) { // registry url is available
// use AvailableCluster only when register's cluster is available
URL u = registryURL.addParameter(Constants.CLUSTER_KEY, AvailableCluster.NAME);
invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers));
} else { // not a registry url (多个直连的url)
invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers));
}
}
}
Boolean c = check;
if (c == null && consumer != null) {
c = consumer.isCheck();
}
if (c == null) {
c = true; // default true
}
if (c && !invoker.isAvailable()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to check the status of the service " + interfaceName + ". No provider available for the service " + (group == null ? "" : group + "/") + interfaceName + (version == null ? "" : ":" + version) + " from the url " + invoker.getUrl() + " to the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion());
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refer dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " from url " + invoker.getUrl());
}
// create service proxy
return (T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
}
可以看到 invoker 是通过 refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0)); 或者 cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers)); 、 cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers)); 三种构建语句依照条件选一种调用生成。
这里分析第一种生成 invokder 的情况,根据spi机制这里 refprotocol 对象是 Protocol$Adpative 实例,具体refer实现是:
public com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker refer(java.lang.Class arg0, com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL arg1) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg1 == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg1;
String extName = (url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol());
if (extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.refer(arg0, arg1);
}
通过代码可以得知,Protocol具体实现要根据url的Protocol值再通过spi得到.如果是直连地址,这里就是dubbo协议,最后走 DubboProtocol 类的refer方法.
具体实现是:
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
optimizeSerialization(url);
// create rpc invoker.
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
如果是注册中心,这里protocol是 register ,会走 RegistryProtocol 类的 refer 方法:
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
//通过register 可以获取具体注册中心协议,这里是zookeeper,并设置为url的协议值。
url = url.setProtocol(url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REGISTRY)).removeParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY);
//获取zookeeper Registry 实现,即ZookeeperRegistryFactory ,并调用getRegistry方法实现
//获取zookeeper类型的registry对象
Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(url);
if (RegistryService.class.equals(type)) {
return proxyFactory.getInvoker((T) registry, type, url);
} // group="a,b" or group="*"
Map<String, String> qs = StringUtils.parseQueryString(url.getParameterAndDecoded(Constants.REFER_KEY));
String group = qs.get(Constants.GROUP_KEY);
if (group != null && group.length() > 0) {
if ((Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(group)).length > 1
|| "*".equals(group)) {
return doRefer(getMergeableCluster(), registry, type, url);
}
}
//这里cluster是Cluster$Adpative类对象
return doRefer(cluster, registry, type, url);
} private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) {
//这里的RegistryDirectory和StaticDirectory向对应的,前者是动态从注册中心获取url目录对象,后者是静态指定url目录。
RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url);
directory.setRegistry(registry);
directory.setProtocol(protocol);
// all attributes of REFER_KEY
Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>(directory.getUrl().getParameters());
URL subscribeUrl = new URL(Constants.CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, parameters.remove(Constants.REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, type.getName(), parameters);
if (!Constants.ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())
&& url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTER_KEY, true)) {
registry.register(subscribeUrl.addParameters(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.CONSUMERS_CATEGORY,
Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)));
}
//订阅注册中心,可以获取服务提供方地址等信息
directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY,
Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY));
//通过调用Cluster$Adpative类的join方法返回Invoker对象(***看这里***)
Invoker invoker = cluster.join(directory);
ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerConsumer(invoker, url, subscribeUrl, directory);
return invoker;
}
这里看下 Cluster$Adpative 类 join 方法实现:
public com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker join(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory arg0) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory argument getUrl() == null");
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
//通过cluster获取集群策略,默认是failover
//本例是使用failover机制
String extName = url.getParameter("cluster", "failover");
if(extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([cluster])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster.class).getExtension(extName);
//通过spi这里得到FailoverCluster对象
return extension.join(arg0);
}
再看下 FailoverCluster 的 join 方法:
public class FailoverCluster implements Cluster {
public final static String NAME = "failover";
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
//返回FailoverClusterInvoker对象
return new FailoverClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
}
由于Cluster spi实现中有个 MockClusterWrapper 是包装类,这里牵涉到是dubbo的aop机制,这里先调用它的join方法:
public class MockClusterWrapper implements Cluster {
private Cluster cluster;
public MockClusterWrapper(Cluster cluster) {
this.cluster = cluster;
}
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new MockClusterInvoker<T>(directory,
this.cluster.join(directory));
}
}
又由于 FailoverClusterInvoker 是 AbstractClusterInvoker 的子类,它的 invoke 方法实现在其父类中的,所以如下方法栈信息:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke(FailoverClusterInvoker.java:78)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke(AbstractClusterInvoker.java:244)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.wrapper.MockClusterInvoker.invoke(MockClusterInvoker.java:75)
这些类都是dubbo的集群容错.博文dubbo集群容错机制代码分析是关于集群容错的介绍.
再往下看 AbstractClusterInvoker 的 invoke 方法实现:
@Override
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
LoadBalance loadbalance = null; // binding attachments into invocation.
Map<String, String> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).addAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
//会调用directory的list方法 返回要调用invokers集合。
//其实是AbstractDirectory的list方法,这个方法里就是利用路由规则(如果有),从所有
//提供者中,选出符合规则的提供者
//接下里才是,集群容错和负载均衡。
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
if (invokers != null && !invokers.isEmpty()) {
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(invokers.get(0).getUrl()
.getMethodParameter(RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation), Constants.LOADBALANCE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE));
}
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
} protected void checkWhetherDestroyed() { if (destroyed.get()) {
throw new RpcException("Rpc cluster invoker for " + getInterface() + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion()
+ " is now destroyed! Can not invoke any more.");
}
}
list方法:
protected List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = directory.list(invocation);
return invokers;
}
跟到 RegistryDirectory 类的 list 方法,实现在其父类 AbstractDirectory 中:
@Override
public List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (destroyed) {
throw new RpcException("Directory already destroyed .url: " + getUrl());
}
//获取所有的提供者
//这里doList是个抽象方法,由RegistryDirectory实现具体:
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = doList(invocation);
List<Router> localRouters = this.routers; // local reference
if (localRouters != null && !localRouters.isEmpty()) {
for (Router router : localRouters) {
try {
if (router.getUrl() == null || router.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.RUNTIME_KEY, false)) {
//Router接口,实现类的rout的方法。路由获取服务提供者
invokers = router.route(invokers, getConsumerUrl(), invocation);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Failed to execute router: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
}
return invokers;
}
RegistryDirectory 实现具体的 doList 方法:
@Override
public List<Invoker<T>> doList(Invocation invocation) {
if (forbidden) {
// 1. 没有服务提供者 2. 服务提供者被禁用
// 1. No service provider 2. Service providers are disabled
throw new RpcException(RpcException.FORBIDDEN_EXCEPTION,
"No provider available from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " for service " + getConsumerUrl().getServiceKey() + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please check status of providers(disabled, not registered or in blacklist).");
}
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = null;
//methodInvokerMap在refreshInvoker方法里赋值
Map<String, List<Invoker<T>>> localMethodInvokerMap = this.methodInvokerMap; // local reference
if (localMethodInvokerMap != null && localMethodInvokerMap.size() > 0) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
Object[] args = RpcUtils.getArguments(invocation);
if (args != null && args.length > 0 && args[0] != null
&& (args[0] instanceof String || args[0].getClass().isEnum())) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName + "." + args[0]); // The routing can be enumerated according to the first parameter(可根据第一个参数枚举路由)
}
if (invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName);
}
if (invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(Constants.ANY_VALUE);
}
if (invokers == null) {
Iterator<List<Invoker<T>>> iterator = localMethodInvokerMap.values().iterator();
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
invokers = iterator.next();
}
}
}
return invokers == null ? new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(0) : invokers;
}
下面是 refreshInvoker(List<URL> invokerUrls) 方法:
private void refreshInvoker(List<URL> invokerUrls) {
if (invokerUrls != null && invokerUrls.size() == 1 && invokerUrls.get(0) != null
&& Constants.EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(invokerUrls.get(0).getProtocol())) {
this.forbidden = true; // Forbid to access
this.methodInvokerMap = null; // Set the method invoker map to null
destroyAllInvokers(); // Close all invokers
} else {
this.forbidden = false; // Allow to access
Map<String, Invoker<T>> oldUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
if (invokerUrls.isEmpty() && this.cachedInvokerUrls != null) {
invokerUrls.addAll(this.cachedInvokerUrls);
} else {
this.cachedInvokerUrls = new HashSet<URL>();
this.cachedInvokerUrls.addAll(invokerUrls);//Cached invoker urls, convenient for comparison
}
if (invokerUrls.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//生成Invoker方法 toInvokers
Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = toInvokers(invokerUrls);// Translate url list to Invoker map
Map<String, List<Invoker<T>>> newMethodInvokerMap = toMethodInvokers(newUrlInvokerMap); // Change method name to map Invoker Map
// state change
// If the calculation is wrong, it is not processed.
//如果计算错误,则不进行处理
if (newUrlInvokerMap == null || newUrlInvokerMap.size() == 0) {
logger.error(new IllegalStateException("urls to invokers error .invokerUrls.size :" + invokerUrls.size() + ", invoker.size :0. urls :" + invokerUrls.toString()));
return;
}
this.methodInvokerMap = multiGroup ? toMergeMethodInvokerMap(newMethodInvokerMap) : newMethodInvokerMap;
this.urlInvokerMap = newUrlInvokerMap;
try {
destroyUnusedInvokers(oldUrlInvokerMap, newUrlInvokerMap); // Close the unused Invoker(关闭未使用的Invoker)
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("destroyUnusedInvokers error. ", e);
}
}
}
refreshInvoker() 方法会在 RegistryDirectory 类的 notify(List<URL> urls) 方法里调用,这个方法也是订阅注册中心回调方法.
以下是 toInvokers 方法:
/**
* Turn urls into invokers, and if url has been refer, will not re-reference.
* 将urls转成invokers,如果url已经被refer过,不再重新引用。
* @param urls
* @return invokers
*/
private Map<String, Invoker<T>> toInvokers(List<URL> urls) {
Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = new HashMap<String, Invoker<T>>();
if (urls == null || urls.isEmpty()) {
return newUrlInvokerMap;
}
Set<String> keys = new HashSet<String>();
String queryProtocols = this.queryMap.get(Constants.PROTOCOL_KEY);
for (URL providerUrl : urls) {
// If protocol is configured at the reference side, only the matching protocol is selected
//如果reference端配置了protocol,则只选择匹配的protocol
if (queryProtocols != null && queryProtocols.length() > 0) {
boolean accept = false;
String[] acceptProtocols = queryProtocols.split(",");
for (String acceptProtocol : acceptProtocols) {
if (providerUrl.getProtocol().equals(acceptProtocol)) {
accept = true;
break;
}
}
if (!accept) {
continue;
}
}
if (Constants.EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(providerUrl.getProtocol())) {
continue;
}
if (!ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).hasExtension(providerUrl.getProtocol())) {
logger.error(new IllegalStateException("Unsupported protocol " + providerUrl.getProtocol() + " in notified url: " + providerUrl + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " to consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ ", supported protocol: " + ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getSupportedExtensions()));
continue;
}
URL url = mergeUrl(providerUrl); String key = url.toFullString(); // The parameter urls are sorted(URL参数是排序的)
if (keys.contains(key)) { // Repeated url(重复URL)
continue;
}
keys.add(key);
// Cache key is url that does not merge with consumer side parameters, regardless of how the consumer combines parameters, if the server url changes, then refer again
//缓存key为没有合并消费端参数的URL,不管消费端如何合并参数,如果服务端URL发生变化,则重新refer
Map<String, Invoker<T>> localUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
Invoker<T> invoker = localUrlInvokerMap == null ? null : localUrlInvokerMap.get(key);
if (invoker == null) { // Not in the cache, refer again( 缓存中没有,重新refer)
try {
boolean enabled = true;
if (url.hasParameter(Constants.DISABLED_KEY)) {
enabled = !url.getParameter(Constants.DISABLED_KEY, false);
} else {
enabled = url.getParameter(Constants.ENABLED_KEY, true);
}
if (enabled) {
//这里是invoker的创建的地方
invoker = new InvokerDelegate<T>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Failed to refer invoker for interface:" + serviceType + ",url:(" + url + ")" + t.getMessage(), t);
}
if (invoker != null) { // Put new invoker in cache(将新的引用放入缓存)
newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker);
}
} else {
newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker);
}
}
keys.clear();
return newUrlInvokerMap;
}
invoker = new InvokerDelegate<T>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl) 是 invoker 的创建语句。
InvokerDelegate 是 RegistryDirectory 的内部类:
/**
* The delegate class, which is mainly used to store the URL address sent by the registry,and can be reassembled on the basis of providerURL queryMap overrideMap for re-refer.
* 代理类,主要用于存储注册中心下发的url地址, 用于重新refer时能够根据providerURL queryMap overrideMap重新组装
* @param <T>
*/
private static class InvokerDelegate<T> extends InvokerWrapper<T> {
private URL providerUrl; public InvokerDelegate(Invoker<T> invoker, URL url, URL providerUrl) {
//调用父类构造方法
super(invoker, url);
this.providerUrl = providerUrl;
} public URL getProviderUrl() {
return providerUrl;
}
}
invoke 方法在其父类 InvokerWrapper 里实现:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
//这里的invoker是从它的构造方法里传入的
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
所以方法栈里可以看到下面一行栈信息:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.InvokerWrapper.invoke(InvokerWrapper.java:56)
InvokerDelegete 构造方法调用的父类 InvokerWrapper 的构造方法并传入 invoker ,回头看 new InvokerDelegete<T>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl); 这句。可知上面的 invoker 是由 protocol.refer(serviceType, url) 创建的。
通过debug,可知这里的 protocol 是 Protocol$Adpative 类型,这里的url的Protocol是dubbo,通过spi可以得到这里最后走 DubboProtocol 类refer方法但是由于 Protocal 接口实现中,有两个包装类:
filter=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper
listener=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolListenerWrapper
所以这里先执行 ProtocolFilterWrapper 的 refer 方法,再执行 ProtocolListenerWrapper 的 refer 方法,最后才执行 DubboProtocol 类 refer 方法。
ProtocolFilterWrapper 的 refer 方法如下:
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
return protocol.refer(type, url);
}
return buildInvokerChain(protocol.refer(type, url), Constants.REFERENCE_FILTER_KEY, Constants.CONSUMER);
} private static <T> Invoker<T> buildInvokerChain(final Invoker<T> invoker, String key, String group) {
Invoker<T> last = invoker;
//先获取激活的过滤器,我们这里手动配置了monitor MonitorFilter过滤器,
// 另外两个自动激活的过滤器是FutureFilter,ConsumerContextFilter
//这里需要看spi机制的getActivateExtension方法相关代码
List<Filter> filters = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Filter.class).getActivateExtension(invoker.getUrl(), key, group);
if (!filters.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = filters.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final Filter filter = filters.get(i);
final Invoker<T> next = last;
last = new Invoker<T>() { @Override
public Class<T> getInterface() {
return invoker.getInterface();
} @Override
public URL getUrl() {
return invoker.getUrl();
} @Override
public boolean isAvailable() {
return invoker.isAvailable();
} //实现invoker的 invoke方法
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
//嵌套进过滤器链
return filter.invoke(next, invocation);
} @Override
public void destroy() {
invoker.destroy();
} @Override
public String toString() {
return invoker.toString();
}
};
}
}
return last;
}
所以有以下调用栈信息:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor.support.MonitorFilter.invoke(MonitorFilter.java:75)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper$1.invoke(ProtocolFilterWrapper.java:72)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.filter.FutureFilter.invoke(FutureFilter.java:54)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper$1.invoke(ProtocolFilterWrapper.java:72)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.filter.ActiveLimitFilter.invoke(ActiveLimitFilter.java:70)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper$1.invoke(ProtocolFilterWrapper.java:72)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.filter.ConsumerContextFilter.invoke(ConsumerContextFilter.java:49)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper$1.invoke(ProtocolFilterWrapper.java:72)
接着 ProtocolListenerWrapper 的 refer 方法:
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
return protocol.refer(type, url);
}
return new ListenerInvokerWrapper<T>(protocol.refer(type, url),
//获取激活的监听器,目前dubbo没有提供合适的监听器,只有一个DeprecatedInvokerListener实现类,还是个Deprecated的
//所以这里为空
Collections.unmodifiableList( ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(InvokerListener.class).getActivateExtension(url, Constants.INVOKER_LISTENER_KEY)));
}
这个可以解释下面这句堆栈信息:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.listener.ListenerInvokerWrapper.invoke(ListenerInvokerWrapper.java:77)
最后看下 DubboProtocol 类 refer 方法,这里创建了 DubboInvoker 对象:
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
optimizeSerialization(url);
// create rpc invoker.
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
DubboInvoker 的父类 AbstractInvoker 实现了 invoke 方法:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
// if invoker is destroyed due to address refresh from registry, let's allow the current invoke to proceed
if (destroyed.get()) {
logger.warn("Invoker for service " + this + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " is destroyed, "
+ ", dubbo version is " + Version.getVersion() + ", this invoker should not be used any longer");
} RpcInvocation invocation = (RpcInvocation) inv;
invocation.setInvoker(this);
if (attachment != null && attachment.size() > 0) {
invocation.addAttachmentsIfAbsent(attachment);
}
Map<String, String> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
/**
* invocation.addAttachmentsIfAbsent(context){@link RpcInvocation#addAttachmentsIfAbsent(Map)}should not be used here,
* because the {@link RpcContext#setAttachment(String, String)} is passed in the Filter when the call is triggered
* by the built-in retry mechanism of the Dubbo. The attachment to update RpcContext will no longer work, which is
* a mistake in most cases (for example, through Filter to RpcContext output traceId and spanId and other information).
*/
invocation.addAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
if (getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.ASYNC_KEY, false)) {
invocation.setAttachment(Constants.ASYNC_KEY, Boolean.TRUE.toString());
}
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation); try {
//doInvoke 具体实现在子类中
return doInvoke(invocation);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) { // biz exception
Throwable te = e.getTargetException();
if (te == null) {
return new RpcResult(e);
} else {
if (te instanceof RpcException) {
((RpcException) te).setCode(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION);
}
return new RpcResult(te);
}
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
return new RpcResult(e);
} else {
throw e;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
return new RpcResult(e);
}
}
DubboInvoker 实现的 doInvoke 方法:
@Override
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
inv.setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, version); ExchangeClient currentClient;
if (clients.length == 1) {
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];
}
try {
boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
int timeout = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
if (isOneway) {
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return new RpcResult();
} else if (isAsync) {
ResponseFuture future = currentClient.request(inv, timeout);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(new FutureAdapter<Object>(future));
return new RpcResult();
} else {
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
//实际的请求语句 ,这里的currentClient是自身对象属性clients[0]值
return (Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get();
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
所以有以下两句调用栈输出信息:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboInvoker.doInvoke(DubboInvoker.java:95)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.AbstractInvoker.invoke(AbstractInvoker.java:155)
接下来看用于发起请求的 currentClient 对象的的实现,它的实现可追踪到 DubboProtocol 类 refer 方法里:
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
optimizeSerialization(url);
// create rpc invoker.
//getClients(url) 创建 DubboInvoker 属性clients对象,
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
} private ExchangeClient[] getClients(URL url) {
// whether to share connection
//是否共享连接
boolean service_share_connect = false;
int connections = url.getParameter(Constants.CONNECTIONS_KEY, 0);
// if not configured, connection is shared, otherwise, one connection for one service
//如果connections不配置,则共享连接,否则一个连接一个服务
if (connections == 0) {
service_share_connect = true;
connections = 1;
} ExchangeClient[] clients = new ExchangeClient[connections];
for (int i = 0; i < clients.length; i++) {
if (service_share_connect) {
//获取共享连接
clients[i] = getSharedClient(url);
} else {
//初始化client,本例子不是共享连接,走这个逻辑
clients[i] = initClient(url);
}
}
return clients;
} /**
* Create new connection
*/
private ExchangeClient initClient(URL url) { // client type setting.
String str = url.getParameter(Constants.CLIENT_KEY, url.getParameter(Constants.SERVER_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REMOTING_CLIENT)); url = url.addParameter(Constants.CODEC_KEY, DubboCodec.NAME);
// enable heartbeat by default
//默认开启heartbeat
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.HEARTBEAT_KEY, String.valueOf(Constants.DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT)); // BIO is not allowed since it has severe performance issue.
// BIO存在严重性能问题,暂时不允许使用
if (str != null && str.length() > 0 && !ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).hasExtension(str)) {
throw new RpcException("Unsupported client type: " + str + "," +
" supported client type is " + StringUtils.join(ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getSupportedExtensions(), " "));
} ExchangeClient client;
try {
// connection should be lazy
//设置连接应该是lazy的
if (url.getParameter(Constants.LAZY_CONNECT_KEY, false)) {
client = new LazyConnectExchangeClient(url, requestHandler);
} else {
//通过 Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler); 构建client ,接下来跟踪Exchangers.connect方法
//这里会传入一个requestHandler,这个是客户端接收服务端方法返回回调的
client = Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler);
}
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException("Fail to create remoting client for service(" + url + "): " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
return client;
}
这里用到了 facade 设计模式, Exchangers 是个门面类,封装了具体查找合适的 Exchanger 实现,并调用 connect 方法返回 ExchangeClient 的过程,相关方法代码如下:
public static ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
}
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null");
}
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.CODEC_KEY, "exchange");
//把codec key 设置为exchange
return getExchanger(url).connect(url, handler);
}
public static Exchanger getExchanger(URL url) {
String type = url.getParameter(Constants.EXCHANGER_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_EXCHANGER);
//通过exchanger key 获取 Exchanger的spi实现,默认是header,这里是HeaderExchanger类
return getExchanger(type);
}
public static Exchanger getExchanger(String type) {
//这里返回Exchanger接口的header扩展类HeaderExchanger
return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Exchanger.class).getExtension(type);
}
HeaderExchanger 类 connect 方法如下:
public class HeaderExchanger implements Exchanger {
public static final String NAME = "header";
//客户端的连接操作
@Override
public ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
//返回HeaderExchangeClient对象
return new HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))), true);
}
@Override
public ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
return new HeaderExchangeServer(Transporters.bind(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))));
}
}
所以有栈信息:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.exchange.support.header.HeaderExchangeClient.request(HeaderExchangeClient.java:90)
再看 HeaderExchangeClient 的 request 方法:
@Override
public ResponseFuture request(Object request) throws RemotingException {
//这里channel对象是从类构造函数中赋值,this.channel = new HeaderExchangeChannel(client);如下
return channel.request(request);
} public HeaderExchangeClient(Client client, boolean needHeartbeat) {
if (client == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("client == null");
}
this.client = client;
this.channel = new HeaderExchangeChannel(client);//channel赋值
String dubbo = client.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY);
this.heartbeat = client.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.HEARTBEAT_KEY, dubbo != null && dubbo.startsWith("1.0.") ? Constants.DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT : 0);
this.heartbeatTimeout = client.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT_KEY, heartbeat * 3);
if (heartbeatTimeout < heartbeat * 2) {
throw new IllegalStateException("heartbeatTimeout < heartbeatInterval * 2");
}
if (needHeartbeat) {
startHeartbeatTimer();
}
}
所以有栈信息:
atcom.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.exchange.support.header.HeaderExchangeChannel.request(HeaderExchangeChannel.java:116)
继续查看 HeaderExchangeChannel 类 request 方法:
@Override
public ResponseFuture request(Object request) throws RemotingException {
return request(request, channel.getUrl().getPositiveParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT));
} @Override
public ResponseFuture request(Object request, int timeout) throws RemotingException {
if (closed) {
throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send request " + request + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!");
}
// create request.
Request req = new Request();
req.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion());
req.setTwoWay(true);
req.setData(request);
DefaultFuture future = new DefaultFuture(channel, req, timeout);
try {
//通过具体channel 发送请求
channel.send(req);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
future.cancel();
throw e;
}
return future;
}
这里有 channel 对象,这里的 channel 对象也是通过 HeaderExchangeChannel 类的构造函数,从上层方法传进来的,而 HeaderExchangeChannel 是由 HeaderExchangeClient 构造的, HeaderExchangeClient 对象是由 HeaderExchanger 的 connect 方法里创建的。这里回到 HeaderExchanger 的 connect 方法:
/**
* DefaultMessenger
*
*
*/
public class HeaderExchanger implements Exchanger { public static final String NAME = "header"; @Override
public ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
return new HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))), true);
} @Override
public ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
return new HeaderExchangeServer(Transporters.bind(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))));
} }
可以看到上文中 HeaderExchangeChannel 类中发送消息的 channel 对象是 Transporters.connect(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))) 这句创建的。这里的 Transporters 也是个门面类,是 facade 设计模式的实现, Transporters 具体 connect 方法实现如下:
public static Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler... handlers) throws RemotingException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
}
ChannelHandler handler;
if (handlers == null || handlers.length == 0) {
handler = new ChannelHandlerAdapter();
} else if (handlers.length == 1) {
handler = handlers[0];
} else {
handler = new ChannelHandlerDispatcher(handlers);
}
//这里具体走 NettyTransporter.connect
// public Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler listener) throws RemotingException {
// return new NettyClient(url, listener);
// }
/所以这里默认返回的NettyClient
return getTransporter().connect(url, handler);
}
//这个方法根据spi返回NettyTransporter扩展类
public static Transporter getTransporter() {
//这里通过生成的Transporter$Adaptive 的实现如下:
return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
}
所以最后是通过 NettyClient 类实例的 send 方法发送的具体请求, NettyClient 类 send 方法实现在其祖先类 AbstractPeer 中:
@Override
public void send(Object message) throws RemotingException {
send(message, url.getParameter(Constants.SENT_KEY, false));
}
这个实现又调用 NettyClient 父类 AbstractClient 的 send 方法实现:
@Override
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException {
if (send_reconnect && !isConnected()) {
connect();
}
//获取具体channel实例
Channel channel = getChannel();
//TODO Can the value returned by getChannel() be null? need improvement.
//TODO getChannel返回的状态是否包含null需要改进
if (channel == null || !channel.isConnected()) {
throw new RemotingException(this, "message can not send, because channel is closed . url:" + getUrl());
}
channel.send(message, sent);
}
这里的 getChannel() 方法由NettyClient自身实现,如下:
@Override
protected com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Channel getChannel() {
Channel c = channel;
if (c == null || !c.isConnected())
return null;
return NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(c, getUrl(), this);
} //再到NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel方法
static NettyChannel getOrAddChannel(org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel ch, URL url, ChannelHandler handler) {
if (ch == null) {
return null;
}
//返回NettyChannel类
NettyChannel ret = channelMap.get(ch);
if (ret == null) {
NettyChannel nc = new NettyChannel(ch, url, handler);
if (ch.isConnected()) {
ret = channelMap.putIfAbsent(ch, nc);
}
if (ret == null) {
ret = nc;
}
}
return ret;
}
所以有以下栈信息:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty.NettyChannel.send(NettyChannel.java:100)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.AbstractClient.send(AbstractClient.java:265)
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.AbstractPeer.send(AbstractPeer.java:53)
后面就是jboss内部的调用和消息转换:
at org.jboss.netty.channel.SimpleChannelHandler.handleDownstream(SimpleChannelHandler.java:266)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline.sendDownstream(DefaultChannelPipeline.java:591)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline.sendDownstream(DefaultChannelPipeline.java:582)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.Channels.write(Channels.java:611)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.Channels.write(Channels.java:578)
at org.jboss.netty.channel.AbstractChannel.write(AbstractChannel.java:251)
最后就走到开始打断点的 NettyHandler 类 writeRequested 方法:
at com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty.NettyHandler.writeRequested(NettyHandler.java:98)
Dubbo消费方服务调用过程源码分析的更多相关文章
- Dubbo服务调用过程源码解析④
目录 0.服务的调用 1.发送请求 2.请求编码 3.请求的解码 4.调用具体服务 5.返回调用结果 6.接收调用结果 Dubbo SPI源码解析① Dubbo服务暴露源码解析② Dubbo服务引用源 ...
- SpringCloud(4)---Ribbon服务调用,源码分析
SpringCloud(4)---Ribbon 本篇模拟订单服务调用商品服务,同时商品服务采用集群部署. 注册中心服务端口号7001,订单服务端口号9001,商品集群端口号:8001.8002.800 ...
- (转)Dubbo服务暴露过程源码分析
参考
- SDP服务搜索流程源码分析
BREDR的设备 在进行配对完成之后,进行;连接之前都要进行服务的搜索,服务搜索走的流程是SDP,这篇文章就分析一下,bluedroid中SDP的代码流程,我们从配对完成的回调函数开始分析: /*** ...
- 【图解源码】Zookeeper3.7源码分析,包含服务启动流程源码、网络通信源码、RequestProcessor处理请求源码
Zookeeper3.7源码剖析 能力目标 能基于Maven导入最新版Zookeeper源码 能说出Zookeeper单机启动流程 理解Zookeeper默认通信中4个线程的作用 掌握Zookeepe ...
- Android应用程序绑定服务(bindService)的过程源码分析
Android应用程序组件Service与Activity一样,既能够在新的进程中启动,也能够在应用程序进程内部启动:前面我们已经分析了在新的进程中启动Service的过程,本文将要介绍在应用程序内部 ...
- Netty入门一:服务端应用搭建 & 启动过程源码分析
最近周末也没啥事就学学Netty,同时打算写一些博客记录一下(写的过程理解更加深刻了) 本文主要从三个方法来呈现:Netty核心组件简介.Netty服务端创建.Netty启动过程源码分析 如果你对Ne ...
- [Android]Android系统启动流程源码分析
以下内容为原创,欢迎转载,转载请注明 来自天天博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/tiantianbyconan/p/5013863.html Android系统启动流程源码分析 首先 ...
- Spring加载流程源码分析03【refresh】
前面两篇文章分析了super(this)和setConfigLocations(configLocations)的源代码,本文来分析下refresh的源码, Spring加载流程源码分析01[su ...
随机推荐
- python3笔记二十一:时间操作datetime和calendar
一:学习内容 datetime calendar 二:datetime 1.模块说明:可以理解为datetime基于time进行了封装,提供了各种使用的函数,datetime模块的接口更直接,更容易调 ...
- 【黑马JavaSE】1_1_9_流程控制:顺序结构、判断结构、选择结构、循环结构
文章目录 1_1_9_01_ 流程控制概述 1_1_9_01_ 顺序结构 1_1_9_ 判断结构 1_1_9_02_ 判断语句1--if 1_1_9_03_ 判断语句2--if...else 1_1_ ...
- airflow当触发具有多层subDAG的任务的时候,出现[Duplicate entry ‘xxxx’ for key dag_id]的错误的问题处理
当触发一个具有多层subDAG的任务时,会发现执行触发的task任务运行失败,但是需要触发的目标DAG已经在运行了,dag log 错误内容: [2019-11-21 17:47:56,825] {b ...
- 重入锁 ReentrantLock (转)(学习记录)
重入锁(ReentrantLock)是一种递归无阻塞的同步机制.以前一直认为它是synchronized的简单替代,而且实现机制也不相差太远.不过最近实践过程中发现它们之间还是有着天壤之别. 以下是官 ...
- LC 856. Score of Parentheses
Given a balanced parentheses string S, compute the score of the string based on the following rule: ...
- GNU项目
目标在于建立一个完全相容于UNIX的自由软件环境.发展GNU系统的计划,最早由理查德•斯托曼在1983 年启动,它是自由软件基金会最早致力的目标.最近一个GNU系统版本,是于2011年4月1日释出的G ...
- javascript控制流程语句
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- flutter json转字符串 字符串转json
一段json字符串 var jsonStr = '{\"errorCode\": \"0\", \"message\": \"成功 ...
- layui相关总结
表格操作实例1: https://sun_zoro.gitee.io/layuitableplug/testTableCheckboxDisabled?v0.1.9
- 远程发送文件失败(scp)
出现这种情况的原因是之前保存过192.168.210.134的密钥. 碰到这种情况进行如下操作: ①查看隐藏文件 [root@localhost ~]# ls -a .ssh ②切换到 .ssh ...
