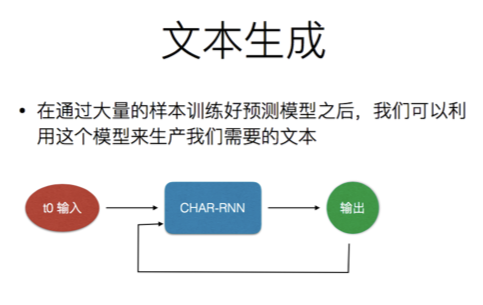
RNN 通过字符语言模型 理解BPTT
链接:https://github.com/karpathy/char-rnn
http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/
https://github.com/Teaonly/beginlearning/tree/master/july

"""
Minimal character-level Vanilla RNN model. Written by Andrej Karpathy (@karpathy)
BSD License
"""
import numpy as np
# data I/O
data = open('input.txt', 'r').read() # should be simple plain text file
chars = list(set(data))
data_size, vocab_size = len(data), len(chars)
print 'data has %d characters, %d unique.' % (data_size, vocab_size)
char_to_ix = { ch:i for i,ch in enumerate(chars) }
ix_to_char = { i:ch for i,ch in enumerate(chars) }
# hyperparameters
hidden_size = 100 # size of hidden layer of neurons
seq_length = 25 # number of steps to unroll the RNN for
learning_rate = 1e-1
# model parameters
Wxh = np.random.randn(hidden_size, vocab_size)*0.01 # input to hidden
Whh = np.random.randn(hidden_size, hidden_size)*0.01 # hidden to hidden
Why = np.random.randn(vocab_size, hidden_size)*0.01 # hidden to output
bh = np.zeros((hidden_size, 1)) # hidden bias
by = np.zeros((vocab_size, 1)) # output bias
def lossFun(inputs, targets, hprev):
"""
inputs,targets are both list of integers.
hprev is Hx1 array of initial hidden state
returns the loss, gradients on model parameters, and last hidden state
"""
xs, hs, ys, ps = {}, {}, {}, {}
hs[-1] = np.copy(hprev)
loss = 0
# forward pass
for t in xrange(len(inputs)):
xs[t] = np.zeros((vocab_size,1)) # encode in 1-of-k representation
xs[t][inputs[t]] = 1
hs[t] = np.tanh(np.dot(Wxh, xs[t]) + np.dot(Whh, hs[t-1]) + bh) # hidden state
ys[t] = np.dot(Why, hs[t]) + by # unnormalized log probabilities for next chars
ps[t] = np.exp(ys[t]) / np.sum(np.exp(ys[t])) # probabilities for next chars
loss += -np.log(ps[t][targets[t],0]) # softmax (cross-entropy loss)
# backward pass: compute gradients going backwards
dWxh, dWhh, dWhy = np.zeros_like(Wxh), np.zeros_like(Whh), np.zeros_like(Why)
dbh, dby = np.zeros_like(bh), np.zeros_like(by)
dhnext = np.zeros_like(hs[0])
for t in reversed(xrange(len(inputs))):
dy = np.copy(ps[t])
dy[targets[t]] -= 1 # backprop into y. see http://cs231n.github.io/neural-networks-case-study/#grad if confused here
dWhy += np.dot(dy, hs[t].T)
dby += dy
dh = np.dot(Why.T, dy) + dhnext # backprop into h
dhraw = (1 - hs[t] * hs[t]) * dh # backprop through tanh nonlinearity
dbh += dhraw
dWxh += np.dot(dhraw, xs[t].T)
dWhh += np.dot(dhraw, hs[t-1].T)
dhnext = np.dot(Whh.T, dhraw)
for dparam in [dWxh, dWhh, dWhy, dbh, dby]:
np.clip(dparam, -5, 5, out=dparam) # clip to mitigate exploding gradients
return loss, dWxh, dWhh, dWhy, dbh, dby, hs[len(inputs)-1]
def sample(h, seed_ix, n):
"""
sample a sequence of integers from the model
h is memory state, seed_ix is seed letter for first time step
"""
x = np.zeros((vocab_size, 1))
x[seed_ix] = 1
ixes = []
for t in xrange(n):
h = np.tanh(np.dot(Wxh, x) + np.dot(Whh, h) + bh)
y = np.dot(Why, h) + by
p = np.exp(y) / np.sum(np.exp(y))
ix = np.random.choice(range(vocab_size), p=p.ravel())
x = np.zeros((vocab_size, 1))
x[ix] = 1
ixes.append(ix)
return ixes
n, p = 0, 0
mWxh, mWhh, mWhy = np.zeros_like(Wxh), np.zeros_like(Whh), np.zeros_like(Why)
mbh, mby = np.zeros_like(bh), np.zeros_like(by) # memory variables for Adagrad
smooth_loss = -np.log(1.0/vocab_size)*seq_length # loss at iteration 0
while True:
# prepare inputs (we're sweeping from left to right in steps seq_length long)
if p+seq_length+1 >= len(data) or n == 0:
hprev = np.zeros((hidden_size,1)) # reset RNN memory
p = 0 # go from start of data
inputs = [char_to_ix[ch] for ch in data[p:p+seq_length]]
targets = [char_to_ix[ch] for ch in data[p+1:p+seq_length+1]]
# sample from the model now and then
if n % 100 == 0:
sample_ix = sample(hprev, inputs[0], 200)
txt = ''.join(ix_to_char[ix] for ix in sample_ix)
print '----\n %s \n----' % (txt, )
# forward seq_length characters through the net and fetch gradient
loss, dWxh, dWhh, dWhy, dbh, dby, hprev = lossFun(inputs, targets, hprev)
smooth_loss = smooth_loss * 0.999 + loss * 0.001
if n % 100 == 0: print 'iter %d, loss: %f' % (n, smooth_loss) # print progress
# perform parameter update with Adagrad
for param, dparam, mem in zip([Wxh, Whh, Why, bh, by],
[dWxh, dWhh, dWhy, dbh, dby],
[mWxh, mWhh, mWhy, mbh, mby]):
mem += dparam * dparam
param += -learning_rate * dparam / np.sqrt(mem + 1e-8) # adagrad update
p += seq_length # move data pointer
n += 1 # iteration counter
RNN 通过字符语言模型 理解BPTT的更多相关文章
- RNN实现字符级语言模型 - 恐龙岛(自己写RNN前向后向版本+keras版本)
问题描述:样本为所有恐龙名字,为了构建字符级语言模型来生成新的名称,你的模型将学习不同的名称模式,并随机生成新的名字. 在这里你将学习到: 如何存储文本数据以便使用rnn进行处理. 如何合成数据,通过 ...
- Python中文字符的理解:str()、repr()、print
Python中文字符的理解:str().repr().print 字数1384 阅读4 评论0 喜欢0 都说Python人不把文字编码这块从头到尾.从古至今全研究通透的话是完全玩不转的.我终于深刻的理 ...
- RNN(1) ------ “理解LSTM”(转载)
原文链接:http://www.jianshu.com/p/9dc9f41f0b29 Recurrent Neural Networks 人类并不是每时每刻都从一片空白的大脑开始他们的思考.在你阅读这 ...
- 用CNTK搞深度学习 (二) 训练基于RNN的自然语言模型 ( language model )
前一篇文章 用 CNTK 搞深度学习 (一) 入门 介绍了用CNTK构建简单前向神经网络的例子.现在假设读者已经懂得了使用CNTK的基本方法.现在我们做一个稍微复杂一点,也是自然语言挖掘中很火 ...
- python基础之Day7part2 史上最清晰字符编码理解
二.字符编码 基础知识: 文本编辑器存取文件原理与py执行原理异同: 存/写:进入文本编辑器 写内容 保存后 内存数据刷到硬盘 取/读:进入文本编辑器 找到内容 从硬盘读到内存 notepad把文件内 ...
- 对GBK的理解(内附全部字符编码列表):扩充的2万汉字低字节的高位不等于1,而且还剩许多编码空间没有利用
各种编码查询表:http://bm.kdd.cc/ 由于GB 2312-80只收录6763个汉字,有不少汉字,如部分在GB 2312-80推出以后才简化的汉字(如“啰”),部分人名用字(如中国前总理朱 ...
- 深入理解Python字符编码--转
http://blog.51cto.com/9478652/2057896 不论你是有着多年经验的 Python 老司机还是刚入门 Python 不久,你一定遇到过UnicodeEncodeError ...
- 深入理解Python字符编码
不论你是有着多年经验的 Python 老司机还是刚入门 Python 不久,你一定遇到过UnicodeEncodeError.UnicodeDecodeError 错误,每当遇到错误我们就拿着 enc ...
- RNN的介绍
一.状态和模型 在CNN网络中的训练样本的数据为IID数据(独立同分布数据),所解决的问题也是分类问题或者回归问题或者是特征表达问题.但更多的数据是不满足IID的,如语言翻译,自动文本生成.它们是一个 ...
随机推荐
- zookeeper 食谱
以示例形式说明 zk 食谱. 假定有 4 个客户端,分别执行 create -s -e /lock/read xx 或 create -s -e /lock/write 获取锁. 一.获取读锁的情况: ...
- 网页定位点击事件js响应函数教程(Chrome)
一.背景说明 在前端页面调试或者渗透测试(尤其是XSS)时,我们经常想定位js函数位置:比如点击了某个位置弹出了一个对话框,这是哪个文件的哪个js函数在响应. 本文以Chrome浏览器定位点击事件响应 ...
- [转]一次CMS GC问题排查过程(理解原理+读懂GC日志)
这个是之前处理过的一个线上问题,处理过程断断续续,经历了两周多的时间,中间各种尝试,总结如下.这篇文章分三部分: 1.问题的场景和处理过程:2.GC的一些理论东西:3.看懂GC的日志 先说一下问题吧 ...
- 转:Java工程师成神之路~(2018修订版)
转: http://www.hollischuang.com/archives/489 阿里大牛珍藏架构资料,点击链接免费获取 针对本文,博主最近在写<成神之路系列文章> ,分章分节介绍所 ...
- C/C++ 运算符优先级(转载)
最讨厌这个了.在这里记录下. 优先级 操作符 描述 例子 结合性 1 ()[]->.::++-- 调节优先级的括号操作符数组下标访问操作符通过指向对象的指针访问成员的操作符通过对象本身访问成员的 ...
- sql2008r2安装失败的解决办法
setup fails with: '.', hexadecimal value 0x00, is an invalid character.SQL 2012 Setup issues - hexad ...
- Java反射《二》获取构造器
package com.study.reflect; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Invocation ...
- [BZOJ1588]营业额统计
Problem 每次给你一个数,找出前面的数与这个数的差的绝对值的最小值 Solution Splay Notice 找不到前驱和后继时,会出错. Code #include<cmath> ...
- jquery 操作table样式拖动参考
参考: http://blog.csdn.net/kdiller/article/details/6059727 http://www.jb51.net/article/59795.htm
- 【阿圆实验】Grafana HA高可用方案
一.实现Grafana高可用 1.Grafana实现高可用性有两步: >>使用共享数据库存储仪表板,用户和其他持久数据>>决定如何存储会话数据. 2.Grafana高可用部署图 ...
