CF-503div2-A/B/C
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are looking at the floor plan of the Summer Informatics School's new building. You were tasked with SIS logistics, so you really care about travel time between different locations: it is important to know how long it would take to get from the lecture room to the canteen, or from the gym to the server room.
The building consists of n towers, h floors each, where the towers are labeled from 1 to n, the floors are labeled from 1 to h. There is a passage between any two adjacent towers (two towers i and i + 1 for all i: 1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) on every floor x, where a ≤ x ≤ b. It takes exactly one minute to walk between any two adjacent floors of a tower, as well as between any two adjacent towers, provided that there is a passage on that floor. It is not permitted to leave the building.
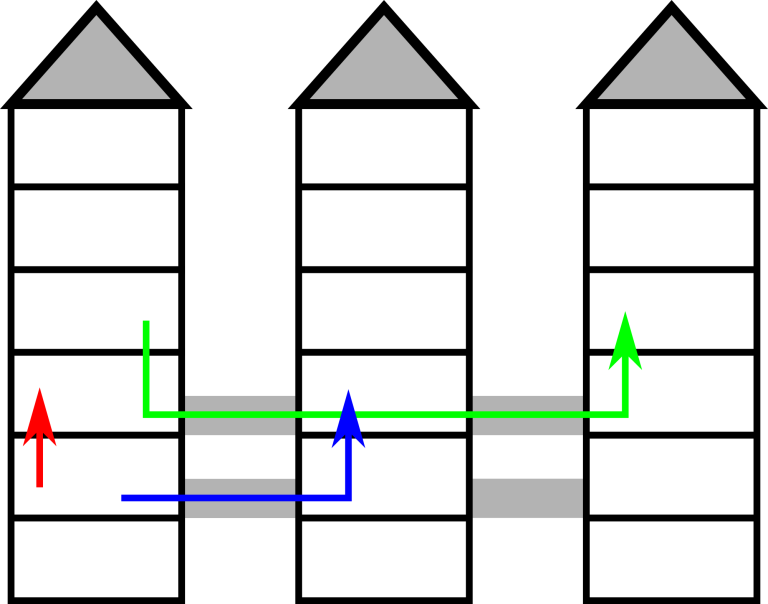
The picture illustrates the first example.
You have given k pairs of locations (ta, fa), (tb, fb): floor fa of tower ta and floor fb of tower tb. For each pair you need to determine the minimum walking time between these locations.
The first line of the input contains following integers:
- n: the number of towers in the building (1 ≤ n ≤ 108),
- h: the number of floors in each tower (1 ≤ h ≤ 108),
- a and b: the lowest and highest floor where it's possible to move between adjacent towers (1 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ h),
- k: total number of queries (1 ≤ k ≤ 104).
Next k lines contain description of the queries. Each description consists of four integers ta, fa, tb, fb (1 ≤ ta, tb ≤ n, 1 ≤ fa, fb ≤ h). This corresponds to a query to find the minimum travel time between fa-th floor of the ta-th tower and fb-th floor of the tb-th tower.
For each query print a single integer: the minimum walking time between the locations in minutes.
3 6 2 3 3
1 2 1 3
1 4 3 4
1 2 2 3
1
4
2
询问从t1的f1层到t2的f2层的最短时间,注意特判下在同一座塔的情况。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<deque>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
int main()
{
int n,h,a,b,k,i,j;
int t1,f1,t2,f2;
while(scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&n,&h,&a,&b,&k)!=EOF){
while(k--){
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&t1,&f1,&t2,&f2);
if(t1>t2){
swap(t1,t2),swap(f1,f2);
}
if(t1==t2){
cout<<abs(f1-f2)<<endl;
}
else{
if(f1>=a&&f1<=b){
cout<<t2-t1+abs(f1-f2)<<endl;
}
else{
cout<<min(abs(a-f1)+t2-t1+abs(a-f2),
abs(b-f1)+t2-t1+abs(b-f2))<<endl;
}
}
}
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
In Summer Informatics School, if a student doesn't behave well, teachers make a hole in his badge. And today one of the teachers caught a group of nn students doing yet another trick.
Let's assume that all these students are numbered from 11 to nn. The teacher came to student aa and put a hole in his badge. The student, however, claimed that the main culprit is some other student papa.
After that, the teacher came to student papa and made a hole in his badge as well. The student in reply said that the main culprit was student ppappa.
This process went on for a while, but, since the number of students was finite, eventually the teacher came to the student, who already had a hole in his badge.
After that, the teacher put a second hole in the student's badge and decided that he is done with this process, and went to the sauna.
You don't know the first student who was caught by the teacher. However, you know all the numbers pipi. Your task is to find out for every student aa, who would be the student with two holes in the badge if the first caught student was aa.
The first line of the input contains the only integer nn (1≤n≤10001≤n≤1000) — the number of the naughty students.
The second line contains nn integers p1p1, ..., pnpn (1≤pi≤n1≤pi≤n), where pipi indicates the student who was reported to the teacher by student ii.
For every student aa from 11 to nn print which student would receive two holes in the badge, if aa was the first student caught by the teacher.
3
2 3 2
2 2 3
3
1 2 3
1 2 3
The picture corresponds to the first example test case.
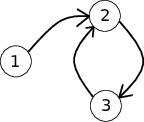
When a=1a=1, the teacher comes to students 11, 22, 33, 22, in this order, and the student 22 is the one who receives a second hole in his badge.
When a=2a=2, the teacher comes to students 22, 33, 22, and the student 22 gets a second hole in his badge. When a=3a=3, the teacher will visit students 33, 22, 33 with student 33 getting a second hole in his badge.
For the second example test case it's clear that no matter with whom the teacher starts, that student would be the one who gets the second hole in his badge.
直接模拟,找第一个被访问两次的点就好了。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<deque>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
bool vis[];
int main()
{
int n,m,i,j,k,p[];
while(scanf("%d",&n)==){
for(i=;i<=n;++i)scanf("%d",p+i);
for(i=;i<=n;++i){
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
j=i;
while(!vis[j]){
vis[j]=;
j=p[j];
}
printf("%d%c",j,i==n?'\n':' ');
}
}
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
As you know, majority of students and teachers of Summer Informatics School live in Berland for the most part of the year. Since corruption there is quite widespread, the following story is not uncommon.
Elections are coming. You know the number of voters and the number of parties — nn and mm respectively. For each voter you know the party he is going to vote for. However, he can easily change his vote given a certain amount of money. In particular, if you give ii-th voter cicibytecoins you can ask him to vote for any other party you choose.
The United Party of Berland has decided to perform a statistical study — you need to calculate the minimum number of bytecoins the Party needs to spend to ensure its victory. In order for a party to win the elections, it needs to receive strictly more votes than any other party.
The first line of input contains two integers nn and mm (1≤n,m≤30001≤n,m≤3000) — the number of voters and the number of parties respectively.
Each of the following nn lines contains two integers pipi and cici (1≤pi≤m1≤pi≤m, 1≤ci≤1091≤ci≤109) — the index of this voter's preferred party and the number of bytecoins needed for him to reconsider his decision.
The United Party of Berland has the index 11.
Print a single number — the minimum number of bytecoins needed for The United Party of Berland to win the elections.
1 2
1 100
0
5 5
2 100
3 200
4 300
5 400
5 900
500
5 5
2 100
3 200
4 300
5 800
5 900
600
In the first sample, The United Party wins the elections even without buying extra votes.
In the second sample, The United Party can buy the votes of the first and the fourth voter. This way The Party gets two votes, while parties 33, 44 and 55 get one vote and party number 22 gets no votes.
In the third sample, The United Party can buy the votes of the first three voters and win, getting three votes against two votes of the fifth party.
考虑枚举1的最终得票数,然后计算是否能当选以及最小的费用,选取一个最小的作为答案。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<deque>
#include<list>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
int p[],c[],tot[],n,m;
LL ans;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q[];
vector<LL> v[]; int main()
{
int i,j;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=;i<=n;++i)scanf("%d%d",p+i,c+i),tot[p[i]]++,q[p[i]].push(c[i]);
for(i=;i<=m;++i){
v[i].push_back();
while(!q[i].empty()){
v[i].push_back(*(v[i].end()-)+q[i].top());
q[i].pop();
}
}
LL ans=1LL*;
for(i=tot[];i<=n;++i){
LL res=,buy=;
for(j=;j<=m;++j){
if(tot[j]>=i){
buy+=tot[j]-i+;
res+=v[j][tot[j]-i+];
}
}
if(buy>i-tot[]) continue;
//q[0].clear();
while(!q[].empty())q[].pop();
//cout<<"i="<<i<<' '<<res<<' '<<buy<<endl;
for(int ii=;ii<=m;++ii){
j=;
if(tot[ii]>=i) j=tot[ii]-i++;
for(;j<v[ii].size();++j){
q[].push(v[ii][j]-v[ii][j-]);
}
}
while(!q[].empty()&&buy<i-tot[]){
//cout<<"JI"<<q[0].top()<<endl;
res+=q[].top();
q[].pop();
buy++;
}
if(tot[]+buy<i)continue;
//cout<<i<<' '<<res<<endl;
if(res<ans)ans=res;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
CF-503div2-A/B/C的更多相关文章
- ORA-00494: enqueue [CF] held for too long (more than 900 seconds) by 'inst 1, osid 5166'
凌晨收到同事电话,反馈应用程序访问Oracle数据库时报错,当时现场现象确认: 1. 应用程序访问不了数据库,使用SQL Developer测试发现访问不了数据库.报ORA-12570 TNS:pac ...
- cf之路,1,Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 2)
cf之路,1,Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 2) ps:昨天第一次参加cf比赛,比赛之前为了熟悉下cf比赛题目的难度.所以做了round#345连试试水的深浅..... ...
- cf Round 613
A.Peter and Snow Blower(计算几何) 给定一个点和一个多边形,求出这个多边形绕这个点旋转一圈后形成的面积.保证这个点不在多边形内. 画个图能明白 这个图形是一个圆环,那么就是这个 ...
- ARC下OC对象和CF对象之间的桥接(bridge)
在开发iOS应用程序时我们有时会用到Core Foundation对象简称CF,例如Core Graphics.Core Text,并且我们可能需要将CF对象和OC对象进行互相转化,我们知道,ARC环 ...
- [Recommendation System] 推荐系统之协同过滤(CF)算法详解和实现
1 集体智慧和协同过滤 1.1 什么是集体智慧(社会计算)? 集体智慧 (Collective Intelligence) 并不是 Web2.0 时代特有的,只是在 Web2.0 时代,大家在 Web ...
- CF memsql Start[c]UP 2.0 A
CF memsql Start[c]UP 2.0 A A. Golden System time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 m ...
- CF memsql Start[c]UP 2.0 B
CF memsql Start[c]UP 2.0 B B. Distributed Join time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 25 ...
- CF #376 (Div. 2) C. dfs
1.CF #376 (Div. 2) C. Socks dfs 2.题意:给袜子上色,使n天左右脚袜子都同样颜色. 3.总结:一开始用链表存图,一直TLE test 6 (1)如果需 ...
- CF #375 (Div. 2) D. bfs
1.CF #375 (Div. 2) D. Lakes in Berland 2.总结:麻烦的bfs,但其实很水.. 3.题意:n*m的陆地与水泽,水泽在边界表示连通海洋.最后要剩k个湖,总要填掉多 ...
- CF #374 (Div. 2) D. 贪心,优先队列或set
1.CF #374 (Div. 2) D. Maxim and Array 2.总结:按绝对值最小贪心下去即可 3.题意:对n个数进行+x或-x的k次操作,要使操作之后的n个数乘积最小. (1)优 ...
随机推荐
- CSU 2005 Nearest Maintenance Point(最短路+bitset)
https://vjudge.net/problem/CSU-2005 题意:给出带权值的图,图上有一些特殊点,现在给出q个询问,对于每个询问,输出离该点最近的特殊点,如果有多个,则按升序输出. 思路 ...
- Java基础 --Unix与Mac系统 文件路径分隔符(一)
斜杠‘/’与反斜杠‘\’在不同系统的使用 1)Window平台使用反斜杠'\'作为文件层级分隔符:Windows使用反斜杠作为DOS命令提示符的参数标志,随着发展DOS命令符逐渐被淘汰,大部分情况下斜 ...
- bzoj 2243: [SDOI2011]染色 线段树区间合并+树链剖分
2243: [SDOI2011]染色 Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MBSubmit: 7925 Solved: 2975[Submit][Status ...
- 浅谈 equals 和 == 的区别
在初学Java时,可能会经常碰到下面的代码: 1 String str1 = new String("hello"); 2 String str2 = new String(&qu ...
- 一: vue的基本使用
一: vue的下载 vue.js是目前前端web开发最流行的工具库之一,由尤雨溪在2014年2月发布的. 另外几个常见的工具库:react.js /angular.js 官方网站: 中文:http ...
- JDBC的通用查询的方法
PreparedStatement 1.Why 1):使用Statement需要进行拼写SQL语句,很辛苦,而且容易出错. 2):使用Statement可以发生SQL注入. SQl注入: SQL注入是 ...
- PHP中json数组与对象的问题
在PHP后端,对于数组和对象的区分不是很大,主要用到的数组居多,而PHP提供接口时响应的一般是json数据(为什么使用json呢,总体来说就是体积小速度快).但是前端对数组对象很'敏感',所以对PHP ...
- 2d游戏和 3d游戏的区别
2D游戏和3D游戏的主要区别 一.总结 一句话总结:2D中的单位就是贴图,3D中的单位还有高 1. 3D 和 2D 游戏的区别主要体现在呈现画面和文件体积上: 2. 借助 3D 引擎可以提升 2D 游 ...
- CRC分段校验
crc16 modbus分段校验码: const uint8_t ModbusCRCHighTab[] = { 0x00, 0xC1, 0x81, 0x40, 0x01, 0xC0, 0x80, 0x ...
- HTML第七章总结
Getting started with CSS 前言 CSS 的 rule 作者做了一个非常形象的比喻,将 CSS 必做 renovate the house,在这里,CSS 包括了三个部分: Se ...
