Mahout 系列之----共轭梯度
无预处理共轭梯度
要求解线性方程组 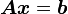 ,稳定双共轭梯度法从初始解
,稳定双共轭梯度法从初始解
 开始按以下步骤迭代:
开始按以下步骤迭代:

- 任意选择向量
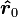 使得
使得
 ,例如,
,例如,

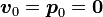
- 对
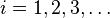



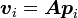





- 若
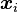 足够精确则退出
足够精确则退出 
预处理共轭梯度
预处理通常被用来加速迭代方法的收敛。要使用预处理子  来求解线性方程组
来求解线性方程组
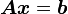 ,预处理稳定双共轭梯度法从初始解
,预处理稳定双共轭梯度法从初始解
 开始按以下步骤迭代:
开始按以下步骤迭代:

- 任意选择向量
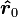 使得
使得
 ,例如,
,例如,

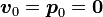
- 对
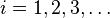



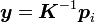
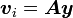



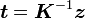

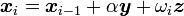
- 若
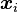 足够精确则退出
足够精确则退出 
这个形式等价于将无预处理的稳定双共轭梯度法应用于显式预处理后的方程组
 ,
,
其中 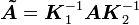 ,
,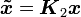 ,
,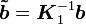 。换句话说,左预处理和右预处理都可以通过这个形式实施。
。换句话说,左预处理和右预处理都可以通过这个形式实施。
Mahout 分布式共轭梯度实现:
package org.apache.mahout.math.solver;
import org.apache.mahout.math.CardinalityException;
import org.apache.mahout.math.DenseVector;
import org.apache.mahout.math.Vector;
import org.apache.mahout.math.VectorIterable;
import org.apache.mahout.math.function.Functions;
import org.apache.mahout.math.function.PlusMult;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* <p>Implementation of a conjugate gradient iterative solver for linear systems. Implements both
* standard conjugate gradient and pre-conditioned conjugate gradient.
*
* <p>Conjugate gradient requires the matrix A in the linear system Ax = b to be symmetric and positive
* definite. For convenience, this implementation allows the input matrix to be be non-symmetric, in
* which case the system A'Ax = b is solved. Because this requires only one pass through the matrix A, it
* is faster than explictly computing A'A, then passing the results to the solver.
*
* <p>For inputs that may be ill conditioned (often the case for highly sparse input), this solver
* also accepts a parameter, lambda, which adds a scaled identity to the matrix A, solving the system
* (A + lambda*I)x = b. This obviously changes the solution, but it will guarantee solvability. The
* ridge regression approach to linear regression is a common use of this feature.
*
* <p>If only an approximate solution is required, the maximum number of iterations or the error threshold
* may be specified to end the algorithm early at the expense of accuracy. When the matrix A is ill conditioned,
* it may sometimes be necessary to increase the maximum number of iterations above the default of A.numCols()
* due to numerical issues.
*
* <p>By default the solver will run a.numCols() iterations or until the residual falls below 1E-9.
*
* <p>For more information on the conjugate gradient algorithm, see Golub & van Loan, "Matrix Computations",
* sections 10.2 and 10.3 or the <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conjugate_gradient">conjugate gradient
* wikipedia article</a>.
*/
public class ConjugateGradientSolver {
public static final double DEFAULT_MAX_ERROR = 1.0e-9;
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ConjugateGradientSolver.class);
private static final PlusMult PLUS_MULT = new PlusMult(1.0);
private int iterations;
private double residualNormSquared;
public ConjugateGradientSolver() {
this.iterations = 0;
this.residualNormSquared = Double.NaN;
}
/**
* Solves the system Ax = b with default termination criteria. A must be symmetric, square, and positive definite.
* Only the squareness of a is checked, since testing for symmetry and positive definiteness are too expensive. If
* an invalid matrix is specified, then the algorithm may not yield a valid result.
*
* @param a The linear operator A.
* @param b The vector b.
* @return The result x of solving the system.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if a is not square or if the size of b is not equal to the number of columns of a.
*
*/
public Vector solve(VectorIterable a, Vector b) {
return solve(a, b, null, b.size(), DEFAULT_MAX_ERROR);
}
/**
* Solves the system Ax = b with default termination criteria using the specified preconditioner. A must be
* symmetric, square, and positive definite. Only the squareness of a is checked, since testing for symmetry
* and positive definiteness are too expensive. If an invalid matrix is specified, then the algorithm may not
* yield a valid result.
*
* @param a The linear operator A.
* @param b The vector b.
* @param precond A preconditioner to use on A during the solution process.
* @return The result x of solving the system.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if a is not square or if the size of b is not equal to the number of columns of a.
*
*/
public Vector solve(VectorIterable a, Vector b, Preconditioner precond) {
return solve(a, b, precond, b.size(), DEFAULT_MAX_ERROR);
}
/**
* Solves the system Ax = b, where A is a linear operator and b is a vector. Uses the specified preconditioner
* to improve numeric stability and possibly speed convergence. This version of solve() allows control over the
* termination and iteration parameters.
*
* @param a The matrix A.
* @param b The vector b.
* @param preconditioner The preconditioner to apply.
* @param maxIterations The maximum number of iterations to run.
* @param maxError The maximum amount of residual error to tolerate. The algorithm will run until the residual falls
* below this value or until maxIterations are completed.
* @return The result x of solving the system.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the matrix is not square, if the size of b is not equal to the number of
* columns of A, if maxError is less than zero, or if maxIterations is not positive.
*/
// 共轭梯度实现的主题部分。很明显该方法是既可以用预处理的方式,也可以不用预处理的方式。Mahout中提供了单机模式的雅克比预处理,但是没有提供分布式处理的雅克比预处理,这个需要自己写。很简单,只要将对角线元素去倒数,组成一个对角阵即可。
public Vector solve(VectorIterable a,
Vector b,
Preconditioner preconditioner,
int maxIterations,
double maxError) {
if (a.numRows() != a.numCols()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Matrix must be square, symmetric and positive definite.");
}
if (a.numCols() != b.size()) {
throw new CardinalityException(a.numCols(), b.size());
}
if (maxIterations <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Max iterations must be positive.");
}
if (maxError < 0.0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Max error must be non-negative.");
}
Vector x = new DenseVector(b.size());
iterations = 0;
Vector residual = b.minus(a.times(x));
residualNormSquared = residual.dot(residual);
log.info("Conjugate gradient initial residual norm = {}", Math.sqrt(residualNormSquared));
double previousConditionedNormSqr = 0.0;
Vector updateDirection = null;
while (Math.sqrt(residualNormSquared) > maxError && iterations < maxIterations) {
Vector conditionedResidual;
double conditionedNormSqr;
if (preconditioner == null) {
conditionedResidual = residual;
conditionedNormSqr = residualNormSquared;
} else {
conditionedResidual = preconditioner.precondition(residual);
conditionedNormSqr = residual.dot(conditionedResidual);
}
++iterations;
if (iterations == 1) {
updateDirection = new DenseVector(conditionedResidual);
} else {
double beta = conditionedNormSqr / previousConditionedNormSqr;
// updateDirection = residual + beta * updateDirection
updateDirection.assign(Functions.MULT, beta);
updateDirection.assign(conditionedResidual, Functions.PLUS);
}
Vector aTimesUpdate = a.times(updateDirection);
double alpha = conditionedNormSqr / updateDirection.dot(aTimesUpdate);
// x = x + alpha * updateDirection
PLUS_MULT.setMultiplicator(alpha);
x.assign(updateDirection, PLUS_MULT);
// residual = residual - alpha * A * updateDirection
PLUS_MULT.setMultiplicator(-alpha);
residual.assign(aTimesUpdate, PLUS_MULT);
previousConditionedNormSqr = conditionedNormSqr;
residualNormSquared = residual.dot(residual);
log.info("Conjugate gradient iteration {} residual norm = {}", iterations, Math.sqrt(residualNormSquared));
}
return x;
}
/**
* Returns the number of iterations run once the solver is complete.
*
* @return The number of iterations run.
*/
public int getIterations() {
return iterations;
}
/**
* Returns the norm of the residual at the completion of the solver. Usually this should be close to zero except in
* the case of a non positive definite matrix A, which results in an unsolvable system, or for ill conditioned A, in
* which case more iterations than the default may be needed.
*
* @return The norm of the residual in the solution.
*/
public double getResidualNorm() {
return Math.sqrt(residualNormSquared);
}
}
DistributedConjugateGradientSolver 是上CG的扩展,DCG和CG的区别在于,DCG矩阵和向量相乘时需要MR实现矩阵相乘。
Mahout 系列之----共轭梯度的更多相关文章
- Mahout系列之----共轭梯度预处理
对于大型矩阵,预处理是很重要的.常用的预处理方法有: (1) 雅克比预处理 (2)块状雅克比预处理 (3)半LU 分解 (4)超松弛法
- 共轭梯度算法求最小值-scipy
# coding=utf-8 #共轭梯度算法求最小值 import numpy as np from scipy import optimize def f(x, *args): u, v = x a ...
- 机器学习: 共轭梯度算法(PCG)
今天介绍数值计算和优化方法中非常有效的一种数值解法,共轭梯度法.我们知道,在解大型线性方程组的时候,很少会有一步到位的精确解析解,一般都需要通过迭代来进行逼近,而 PCG 就是这样一种迭代逼近算法. ...
- Mahout系列之----kmeans 聚类
Kmeans是最经典的聚类算法之一,它的优美简单.快速高效被广泛使用. Kmeans算法描述 输入:簇的数目k:包含n个对象的数据集D. 输出:k个簇的集合. 方法: 从D中任意选择k个对象作为初始簇 ...
- Mahout 系列之--canopy 算法
Canopy 算法,流程简单,容易实现,一下是算法 (1)设样本集合为S,确定两个阈值t1和t2,且t1>t2. (2)任取一个样本点p属于S,作为一个Canopy,记为C,从S中移除p. (3 ...
- Mahout系列之-----相似度
Mahout推荐系统中有许多相似度实现,这些组件实现了计算不能User之间或Item之间的相似度.对于数据量以及数据类型不同的数据源,需要不同的相似度计算方法来提高推荐性能,在mahout提供了大量用 ...
- Mahout系列之----距离度量
x = (x1,...,xn) 和y = (y1,...,yn) 之间的距离为 (1)欧氏距离 EuclideanDistanceMeasure (2)曼哈顿距离 ManhattanDis ...
- mahout系列----Dirichlet 分布
Dirichlet分布可以看做是分布之上的分布.如何理解这句话,我们可以先举个例子:假设我们有一个骰子,其有六面,分别为{1,2,3,4,5,6}.现在我们做了10000次投掷的实验,得到的实验结果是 ...
- mahout系列之---谱聚类
1.构造亲和矩阵W 2.构造度矩阵D 3.拉普拉斯矩阵L 4.计算L矩阵的第二小特征值(谱)对应的特征向量Fiedler 向量 5.以Fiedler向量作为kmean聚类的初始中心,用kmeans聚类 ...
随机推荐
- ROS新功能包PlotJuggler绘图
http://www.ros.org/news/2017/01/new-package-plotjuggler.html PlotJuggler,一个基于Qt的应用程序,允许用户加载,搜索和绘图数据. ...
- 20160219.CCPP体系详解(0029天)
程序片段(01):ReplaceAll.c 内容概要:ReplaceAll #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #incl ...
- [OpenCV] GpuMat and Mat, compare cvtColor perforemence
Introduction I am going to measure the performence of my two GT650M and compare GPU with CPU version ...
- 剑指Offer——好未来视频面知识点储备+面后总结
剑指Offer--好未来视频面知识点储备+面后总结 情景介绍 时间:2016.10.12 13:00- 地点:宿舍 事件:好未来视频面 知识点储备 数据结构 单链表反转 public class Li ...
- 【Netty源码学习】BootStrap
BootStrap是客户端的启动类,其主要功能就是设置必要的参数然后启动客户端. 实现如下: Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.group(group) .channe ...
- 【问题汇总】ScrollView嵌套ListView的问题
因产品的需求,需要在ScrollView中嵌套ListView来达到效果.众所周知,ScrollVIew和ListView都是可滑动的容器,嵌套使用一定会出现一些问题. [html] view pla ...
- 详解EBS接口开发之采购申请导入
更多内容可以参考我的博客 详解EBS接口开发之采购订单导入 http://blog.csdn.net/cai_xingyun/article/details/17114697 /*+++++++ ...
- UITableView如何撤销移动操作
大熊猫猪·侯佩原创或翻译作品.欢迎转载,转载请注明出处. 如果觉得写的不好请多提意见,如果觉得不错请多多支持点赞.谢谢! hopy ;) 我们知道使用UITableView的委托方法canMoveRo ...
- Java之恋
初次见面那是一个河北的夏天风随沙散落天涯蝴蝶依旧恋着花回首走过的日子手指和键盘之间的梦想之光已恍如昨日 那年我还是一个刚踏进这个曾经只在地理课本上狂念南稻北麦,南油北花的土地那年你只是我必须要学的编程 ...
- UNIX/LINUX程序设计教程(1)-- 获取系统信息
1.主机标识 每一台机器都有一个主机名,主机名由系统管理员指定,在网络中主机名可能是一个网络域名. 函数 gethostname() 和 sethostname() 可以用来获取和设置主机 ...
