js实现四叉树算法
最近在看canvas动画方面教程,里面提到了采用四叉树检测碰撞。之前也看到过四叉树这个名词,但是一直不是很懂。于是就又找了一些四叉树方面的资料看了看,做个笔记,就算日后忘了,也可以回来看看。
QuadTree四叉树顾名思义就是树状的数据结构,其每个节点有四个孩子节点,可将二维平面递归分割子区域。QuadTree常用于空间数据库索引,3D的椎体可见区域裁剪,甚至图片分析处理,我们今天介绍的是QuadTree最常被游戏领域使用到的碰撞检测。采用QuadTree算法将大大减少需要测试碰撞的次数,从而提高游戏刷新性能,
四叉树很简单,就是把一块2d的区域,等分成4份,如下图: 我们把4块区域从右上象限开始编号, 逆时针。
四叉树起始于单节点。对象会被添加到四叉树的单节点上。

当更多的对象被添加到四叉树里时,它们最终会被分为四个子节点。(我是这么理解的:下面的图片不是分为四个区域吗,每个区域就是一个孩子或子节点)然后每个物体根据他在2D空间的位置而被放入这些子节点中的一个里。任何不能正好在一个节点区域内的物体会被放在父节点。(这点我不是很理解,就这幅图来说,那根节点的子节点岂不是有五个节点了。)

如果有更多的对象被添加进来,那么每个子节点要继续划分(成四个节点)。
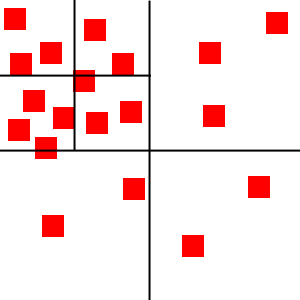
正如你看到的,每个节点仅包括几个物体。这样我们就可以明白前面所说的规则,例如,左上角节点里的物体是不可能和右下角节点里的物体碰撞的。所以我们也就没必要运行消耗很多资源的碰撞检测算法来检验他们之间是否会发生碰撞。
下面我们对四叉树进行实现:
主要代码:(代码是从整个四叉树类里面拷贝出来的,所以带有this,大家不要无视就好,末尾附有完整的代码)
function QuadTree(boundBox, lvl) {
var maxObjects = 10;
this.bounds = boundBox || {
x: 0,
y: 0,
width: 0,
height: 0
};
var objects = [];
this.nodes = [];
var level = lvl || 0;
var maxLevels = 5;
}
maxObjects是每个节点能容纳的最多对象超过 则分割4个节点, 我们并不是事先就分好格子, 而是在插入对象的时候才进行划分。
maxLevels是 四叉树的最大层数 超过 则不再划分 从根节点开始 最多6 层。
level: 当前层数
objects: 当前节点内的待检测的对象。
bounds:当前节点所表示的2d区域的范围
nodes: 4个子节点队列。
四叉树每个节点的面积可以为任意形状。然后,我们会使用五个四叉树里会用到的方法,分别为:clear,split,getIndex,insert和retrieve。
function clear() {
objects = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.nodes.length; i++) {
this.nodes[i].clear();
}
this.nodes = [];
};
Clear函数,是通过循环来清除四叉树所有节点的所有对象。
function split() {
// Bitwise or [html5rocks]
var subWidth = (this.bounds.width / 2) | 0;
var subHeight = (this.bounds.height / 2) | 0;
this.nodes[0] = new QuadTree({
x: this.bounds.x + subWidth,
y: this.bounds.y,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, level+1);
this.nodes[1] = new QuadTree({
x: this.bounds.x,
y: this.bounds.y,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, level+1);
this.nodes[2] = new QuadTree({
x: this.bounds.x,
y: this.bounds.y + subHeight,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, level+1);
this.nodes[3] = new QuadTree({
x: this.bounds.x + subWidth,
y: this.bounds.y + subHeight,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, level+1);
}
Split 方法,就是用来将节点分成相等的四份面积,并用新的边界来初始化四个新的子节点。
function getIndex(obj) {
var index = -1;
var verticalMidpoint = this.bounds.x + this.bounds.width / 2;
var horizontalMidpoint = this.bounds.y + this.bounds.height / 2;
// Object can fit completely within the top quadrant
var topQuadrant = (obj.y < horizontalMidpoint && obj.y + obj.height < horizontalMidpoint);
// Object can fit completely within the bottom quandrant
var bottomQuadrant = (obj.y > horizontalMidpoint);
// Object can fit completely within the left quadrants
if (obj.x < verticalMidpoint &&
obj.x + obj.width < verticalMidpoint) {
if (topQuadrant) {
index = 1;
}
else if (bottomQuadrant) {
index = 2;
}
}
// Object can fix completely within the right quandrants
else if (obj.x > verticalMidpoint) {
if (topQuadrant) {
index = 0;
}
else if (bottomQuadrant) {
index = 3;
}
}
return index;
};
getIndex 方法是个四叉树的辅助方法,在四叉树里,他决定了一个节点的归属,通过检查节点属于哪个象限。(最上面第一幅图不是逆时针在一个面积里划分了四块面积,上面标示了他们的序号,这个方法就是算在一个父节点里他的子节点的序号)
比如当前区域是Rectange(0, 0, 600, 600) 待检测矩形是Rectangel(0, 0, 30, 30) 那么他就在左上象限 index = 1 如果是Rectange(400, 400, 30, 30) 那么他就在右下象限 index = 3
function insert(obj) {
if (typeof obj === "undefined") {
return;
}
if (obj instanceof Array) {
for (var i = 0, len = obj.length; i < len; i++) {
this.insert(obj[i]);
}
return;
}
if (this.nodes.length) {
var index = this.getIndex(obj);
// Only add the object to a subnode if it can fit completely
// within one
if (index != -1) {
this.nodes[index].insert(obj);
return;
}
}
objects.push(obj);
// Prevent infinite splitting
if (objects.length > maxObjects && level < maxLevels) {
if (this.nodes[0] == null) {
this.split();
}
var i = 0;
while (i < objects.length) {
var index = this.getIndex(objects[i]);
if (index != -1) {
this.nodes[index].insert((objects.splice(i,1))[0]);
}
else {
i++;
}
}
}
};
每次插入一个对象 我们都先看看当前节点有没有子节点 如果有 我们就插入子节点。 一直检测到他没有子节点为止 我们就把对象插入到这个节点, 如果这个节点的对象数量 > 10个 并且当前节点的层数 < MAX_LEVELS 我们就把节点继续划分4个子节点。 然后把当前对象循环 删除 并插入子节点。如果对象在中心线上,getIndex会返回-1, 所以这些对象会被插入到父节点上面。
一旦对象添加上后,要看看这个节点会不会分裂,可以通过检查对象被加入节点后有没有超过一个节点最大容纳对象的数量。分裂起源于节点可以插入任何对象,这个对象只要符合子节点都可以被加入。否则就加入到父节点。
function retrieve(returnedObjects, obj) {
if (typeof obj === "undefined") {
console.log("UNDEFINED OBJECT");
return;
}
var index = this.getIndex(obj);
if (index != -1 && this.nodes.length) {
this.nodes[index].findObjects(returnedObjects, obj);
}
for (var i = 0, len = objects.length; i < len; i++) {
returnedObjects.push(objects[i]);
}
return returnedObjects;
};
最后一个四叉树的方法就是 retrieve 方法,他返回了与指定节点可能发生碰撞的所有节点(就是不停寻找与所给节点在同样象限的节点)。这个方法成倍的减少碰撞检测数量。
四叉树的代码就到这里为止了。
完整的代码如下:
完整的代码中retrieve就是findObjects。
/**
* QuadTree object.
*
* The quadrant indexes are numbered as below:
* |
* 1 | 0
* ----+----
* 2 | 3
* |
*/
function QuadTree(boundBox, lvl) {
var maxObjects = 10;
this.bounds = boundBox || {
x: 0,
y: 0,
width: 0,
height: 0
};
var objects = [];
this.nodes = [];
var level = lvl || 0;
var maxLevels = 5; /*
* Clears the quadTree and all nodes of objects
*/
this.clear = function() {
objects = []; for (var i = 0; i < this.nodes.length; i++) {
this.nodes[i].clear();
} this.nodes = [];
}; /*
* Get all objects in the quadTree
*/
this.getAllObjects = function(returnedObjects) {
for (var i = 0; i < this.nodes.length; i++) {
this.nodes[i].getAllObjects(returnedObjects);
} for (var i = 0, len = objects.length; i < len; i++) {
returnedObjects.push(objects[i]);
} return returnedObjects;
}; /*
* Return all objects that the object could collide with
*/
this.findObjects = function(returnedObjects, obj) {
if (typeof obj === "undefined") {
console.log("UNDEFINED OBJECT");
return;
} var index = this.getIndex(obj);
if (index != -1 && this.nodes.length) {
this.nodes[index].findObjects(returnedObjects, obj);
} for (var i = 0, len = objects.length; i < len; i++) {
returnedObjects.push(objects[i]);
} return returnedObjects;
}; /*
* Insert the object into the quadTree. If the tree
* excedes the capacity, it will split and add all
* objects to their corresponding nodes.
*/
this.insert = function(obj) {
if (typeof obj === "undefined") {
return;
} if (obj instanceof Array) {
for (var i = 0, len = obj.length; i < len; i++) {
this.insert(obj[i]);
} return;
} if (this.nodes.length) {
var index = this.getIndex(obj);
// Only add the object to a subnode if it can fit completely
// within one
if (index != -1) {
this.nodes[index].insert(obj); return;
}
} objects.push(obj); // Prevent infinite splitting
if (objects.length > maxObjects && level < maxLevels) {
if (this.nodes[0] == null) {
this.split();
} var i = 0;
while (i < objects.length) { var index = this.getIndex(objects[i]);
if (index != -1) {
this.nodes[index].insert((objects.splice(i,1))[0]);
}
else {
i++;
}
}
}
}; /*
* Determine which node the object belongs to. -1 means
* object cannot completely fit within a node and is part
* of the current node
*/
this.getIndex = function(obj) { var index = -1;
var verticalMidpoint = this.bounds.x + this.bounds.width / 2;
var horizontalMidpoint = this.bounds.y + this.bounds.height / 2; // Object can fit completely within the top quadrant
var topQuadrant = (obj.y < horizontalMidpoint && obj.y + obj.height < horizontalMidpoint);
// Object can fit completely within the bottom quandrant
var bottomQuadrant = (obj.y > horizontalMidpoint); // Object can fit completely within the left quadrants
if (obj.x < verticalMidpoint &&
obj.x + obj.width < verticalMidpoint) {
if (topQuadrant) {
index = 1;
}
else if (bottomQuadrant) {
index = 2;
}
}
// Object can fix completely within the right quandrants
else if (obj.x > verticalMidpoint) {
if (topQuadrant) {
index = 0;
}
else if (bottomQuadrant) {
index = 3;
}
} return index;
}; /*
* Splits the node into 4 subnodes
*/
this.split = function() {
// Bitwise or [html5rocks]
var subWidth = (this.bounds.width / 2) | 0;
var subHeight = (this.bounds.height / 2) | 0; this.nodes[0] = new QuadTree({
x: this.bounds.x + subWidth,
y: this.bounds.y,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, level+1);
this.nodes[1] = new QuadTree({
x: this.bounds.x,
y: this.bounds.y,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, level+1);
this.nodes[2] = new QuadTree({
x: this.bounds.x,
y: this.bounds.y + subHeight,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, level+1);
this.nodes[3] = new QuadTree({
x: this.bounds.x + subWidth,
y: this.bounds.y + subHeight,
width: subWidth,
height: subHeight
}, level+1);
};
}
参考文章:
2、Quick Tip: Use Quadtrees to Detect Likely Collisions in 2D Space
js实现四叉树算法的更多相关文章
- diff.js 列表对比算法 源码分析
diff.js列表对比算法 源码分析 npm上的代码可以查看 (https://www.npmjs.com/package/list-diff2) 源码如下: /** * * @param {Arra ...
- JS实现随机数生成算法示例代码
JS实现随机数生成算法的方法有很多,本文为大家介绍一个比较不错的方法. 1, var MT = []; var index = 0; function initialize_generator(see ...
- JS中常见算法问题
JS中常见算法问题 1. 阐述JS中的变量提升(声明提前) 答:将所有的变量提升当当前作用域的顶部,赋值留在原地.意味着我们可以在某个变量声明前就使用该变量. 虽然JS会进行变量提升,但并不会执行真正 ...
- JS数据结构与算法——栈
JS数据结构与算法--栈 1.栈结构概念 栈(Stack)是一种先进后出(LIFO Last in First out)的线性表,先进栈的将会比后进栈的先出栈. 栈的限制是仅允许在一端进行插入和删除运 ...
- js 实现各种算法 APP
js 实现各种算法 APP 常见算法: 排序,搜索/查找,枚举,遍历,最短路径,二叉树 open source web app desktop app react native app flutter ...
- JS数据结构与算法-概述
JS数据结构与算法概述 数据结构: 计算机存储, 组织数据的方式, 就像锅碗瓢盆 算法: 一系列解决问题的清晰指令, 就像食谱 两者关系: 程序 = 数据结构 + 算法 邂逅数据结构与算法 什么是数据 ...
- js小数点失精算法修正
在用js计算0.07*100时候竟然=7.000000000000001 关于js失精算法你都遇到哪些,让我们一起来细数一下吧 console.log(0.07*100); // 7.00000000 ...
- js 中的算法题,那些经常看到的
js中遇到的算法题不是很多,可以说基本遇不到.但面试的时候,尤其是一些大公司,总是会出这样那样的算法题,考察一个程序员的逻辑思维能力.如下: 1.回文. 回文是指把相同的词汇或句子,在下文中调换位置或 ...
- JS生成GUID算法
//算法1 //Js代码 function uuid() { var s = []; var hexDigits = "0123456789abcdef"; for (var i ...
随机推荐
- UNIGUI集成HTML导航
UNIGUI集成HTML导航 先来一个效果图: ajaxRequest(MainForm.window,'openform',[]); procedure TMainForm.UniFormAjaxE ...
- delphi 窗体自适应屏幕分辨率
delphi 窗体自适应屏幕分辨率 这是个困惑我很长时间的问题,到今天终于得到解决了. 话说Delphi有个很强的窗体设计器,这一点让VC粉丝垂涎三尺而不可得.但是,Delphi里设计的窗体并没有自动 ...
- cxgrid动态多表头
function TForm15.CreateBand(View: TcxGridDBBandedTableView; BandCaption, ParentBandCaption: String) ...
- 利用 LibWebP-NET 解码与编码 WebP 格式图片
此文以后将会在我的新博客更新,有任何疑问可在我的新博文中提出 https://blog.clso.fun/posts/2019-03-02/vb-net-webp.html WebP 格式是谷歌开发并 ...
- wpf Im
- 背水一战 Windows 10 (42) - 控件(导航类): Frame 动画
[源码下载] 背水一战 Windows 10 (42) - 控件(导航类): Frame 动画 作者:webabcd 介绍背水一战 Windows 10 之 控件(导航类) Frame 动画 示例An ...
- 【js】关于正则表达式
正则表达式描述了字符的模式对象 语法: var patt=new RegExp(pattern,modifiers); 或更简单的方法 var patt=/pattern/modifiers; 模式描 ...
- C++调用API获取当前时间
#include <string> #include<iostream> #include<windows.h> #include <sstream> ...
- falcon适配ldap密码同步
问题 小米的openfalcon在使用ldap首次登陆成功后,会在本地创建同名的账号, 这就有个问题当你更新了ldap的密码时,openfalcon是没有同步本地账号密码的功能 二次改造 方便我们de ...
- css3中那些鲜为人知但又很有用的属性
概述 这是我在写移动端页面的时候遇到的,css3中鲜为人知但又很有用的属性,记录下来,供以后开发时参考,相信对其他人也有用. tap-highlight-color 在移动端开发中,我们需要在用户轻按 ...
