Spring Boot高频面试题:Spring Boot执行原理
之前一篇文章Spring Boot快速入门文章中,我们已经体会到Spring Boot的神器,不再像之前Spring那样需要繁琐的XML,甚至几秒钟就能搭建出Spring的项目骨架。接下来我们简单分析Spring Boot的基本原理,让我们揭开它神秘的面纱吧。
1 @SpringBootApplication
首先,我从引导类开始
/**
* Spring Boot引导类
* 一点教程网 - www.yiidian.com
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyBootApplication.class,args);
}
}
引导类代码很简单,但可以看出最关键的是@SpringBootApplication注解以及在main方法中运行的SpringAppliation.run()了,我们进去@SpringBootApplication的源码:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
......
}
我们看到@SpringBootApplication其实是一个复合的注解,它就是由@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration以及@ComponentScan 三个注解组成,所以如果我们把SpringBoot启动类改写成如下方式,整个SpringBoot应用依然可以与之前的启动类功能一样:
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public class SpringbootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
因为我们每次新建项目时都要写上三个注解来完成配置,这显然太繁琐了,SpringBoot就为我们提供了@SpringBootApplication这样注解来简化我们的操作。接着,我们重点分析这三个注解的作用。
2 @SpringBootConfiguration
我们来看@SpringBootConfiguration注解的源码:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
}
我们可以看到,SpringBoot为了区别@Configuration而新提供的专属于SpringBoot的注解,功能其实和@Configuration一模一样。而这里的@Configuration注解对于我们来说并不陌生,它就是是个IoC容器的配置类。看到这里,我们其实可以把SpringBoot的启动类这样来看就清楚了:
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan
public class SpringbootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
启动类SpringbootDemoApplication其实就是一个标准的Spring纯注解下的启动类,也并没有什么特殊。
3 @EnableAutoConfiguration
看到这个注解,我们不禁联想出Spring 中很多以“@Enable”开头的注解,比如:@EnableScheduling、@EnableCaching以及@EnableMBeanExport等,@EnableAutoConfiguration注解的理念和工作原理和它们其实一脉相承。简单的来说,就是该注解借助@Import注解的支持,Spring的IoC容器收集和注册特定场景相关的Bean定义:
@EnableScheduling是通过@Import将Spring调度框架相关的bean都加载到IoC容器。
@EnableMBeanExport是通过@Import将JMX相关的bean定义加载到IoC容器。
而@EnableAutoConfiguration注解也是借助@Import将所有复合配置条件的bean定义加载到IoC容器,仅此而已!@EnableAutoConfiguration注解的源码如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
...
}
这其中最关键的就是@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)了,它借助EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class可以帮助SpringBoot应用将所有符合条件的@Configuration配置类都加载到当前SpringBoot创建并使用的IoC容器,就像下图一样。
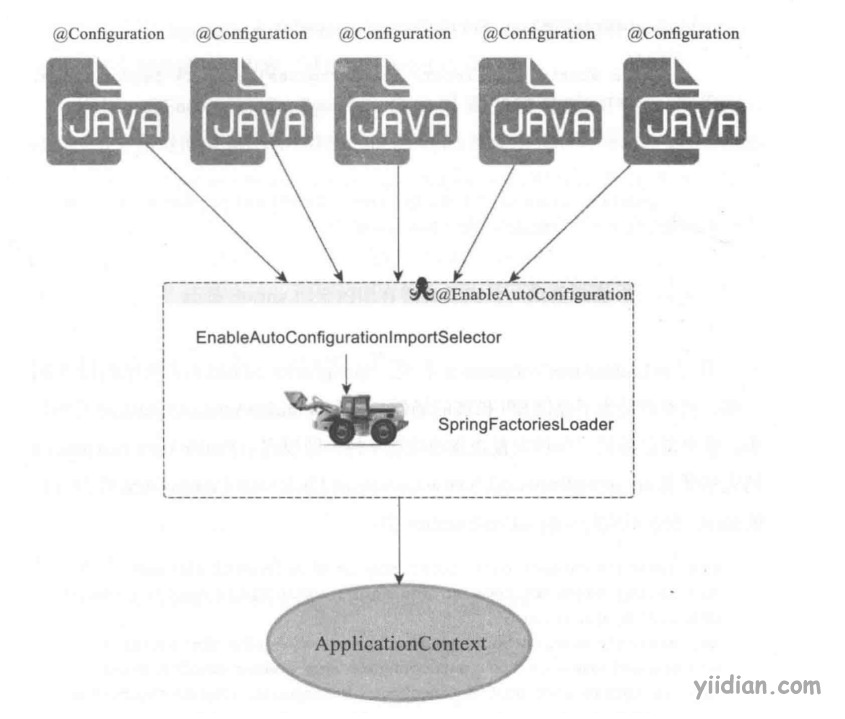
下面我们给出EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.java的父类AutoConfigurationImportSelector.java的部分源码,来解释和验证上图:
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector
implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, ResourceLoaderAware,
BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered {
protected List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> getAutoConfigurationImportFilters() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportFilter.class,
this.beanClassLoader);
}
protected List<AutoConfigurationImportListener> getAutoConfigurationImportListeners() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportListener.class,
this.beanClassLoader);
}
}
以上源码可以看出,@EnableAutoConfiguration正是借助SpringFactoriesLoader的支持,才能完成所有配置类的加载!
4 SpringFactoriesLoader
SpringFactoriesLoader属于Spring框架专属的一种扩展方案(其功能和使用方式类似于Java的SPI方案:java.util.ServiceLoader),它的主要功能就是从指定的配置文件META-INF/spring.factories中加载配置,spring.factories是一个非常经典的java properties文件,内容格式是Key=Value形式,只不过这Key以及Value都非常特殊,为Java类的完整类名(Fully Qualified Name),比如:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
然后Spring框架就可以根据某个类型作为Key来查找对应的类型名称列表了,SpringFactories源码如下:
public abstract class SpringFactoriesLoader {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(SpringFactoriesLoader.class);
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader){
...
}
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
...
}
// ...
}
对于@EnableAutoConfiguraion来说,SpringFactoriesLoader的用途和其本意稍微不同,它本意是为了提供SPI扩展,而在@EnableAutoConfiguration这个场景下,它更多的是提供了一种配置查找的功能的支持,也就是根据@EnableAutoConfiguration的完整类名org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration作为Key来获取一组对应的@Configuration类:
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudServiceConnectorsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.rest.RestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.core.ReactorCoreAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
在SpringBoot的autoconfigure依赖包中的META-INF文件下的spring.factories文件中,我们可以找到以上内容。
总结来说,@EnableAutoConfiguration能实现自动配置的原理就是:SpringFactoriesLoader从classpath中搜寻所有META-INF/spring.fatories文件,并将其中Key[org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration]对应的Value配置项通过反射的方式实例化为对应的标注了@Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IoC容器配置类,然后汇总到当前使用的IoC容器中。
5 @ComponentScan
@ComponentScan注解在Spring Boot启动的时候其实不是必需的!因为我们知道作为Spring框架里的老成员,@ComponentScan的功能就是自动扫描并加载复合条件的组件或Bean定义,最终将这些Bean定义加载到当前使用的容器中。这个过程,我们可以手工单个进行注册,不是一定要通过这个注解批量扫描和注册,所以说@ComponentScan是非必需的。
所以,如果我们当前应用没有任何Bean定义需要通过@ComponentScan加载到当前SpringBoot应用对应的IoC容器,那么,去掉@ComponentScan注解,当前的SpringBoot应用依旧可以完美运行!

欢迎关注我的公众号::一点教程。获得独家整理的学习资源和日常干货推送。
如果您对我的系列教程感兴趣,也可以关注我的网站:yiidian.com
Spring Boot高频面试题:Spring Boot执行原理的更多相关文章
- Spring经典高频面试题,原来是长这个样子
Spring经典高频面试题,原来是长这个样子 2019年08月23日 15:01:32 博文视点 阅读数 719 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文 ...
- 松哥整理了 15 道 Spring Boot 高频面试题,看完当面霸
什么是面霸?就是在面试中,神挡杀神佛挡杀佛,见招拆招,面到面试官自惭形秽自叹不如!松哥希望本文能成为你面霸路上的垫脚石! 做 Java 开发,没有人敢小觑 Spring Boot 的重要性,现在出去面 ...
- 15 道 Spring Boot 高频面试题,看完直接当面霸【入门实用】
前言 本文转自松哥(网名:江南一点雨)的一篇实用入门文章,写的挺好的,希望对各位有所帮助. 什么是面霸?就是在面试中,神挡杀神佛挡杀佛,见招拆招,面到面试官自惭形秽自叹不如!松哥希望本文能成为你面霸路 ...
- 整理了 15 道 Spring Boot 高频面试题,看完当面霸!
转载:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/fj-DeDfGcIAs8jQbs6bbPA 什么是面霸?就是在面试中,神挡杀神佛挡杀佛,见招拆招,面到面试官自惭形秽自叹不如!松哥希望本文 ...
- 大厂高频面试题Spring Bean生命周期最详解
Spring作为当前Java最流行.最强大的轻量级框架.Spring Bean的生命周期也是面试高频题,了解Spring Bean周期也能更好地帮助我们解决日常开发中的问题.程序员应该都知道Sprin ...
- 面试题Spring Boot
Spring Boot 是微服务中最好的 Java 框架. 我们建议你能够成为一名 Spring Boot 的专家. 问题一 Spring Boot.Spring MVC 和 Spring 有什么区别 ...
- 互联网大厂Java面试题集—Spring boot常见面试题(二)
Spring Boot的核心功能与使用优点? 核心功能: 1)Spring Boot项目为独立运行的spring项目,java -jar xx.jar即可运行. 2)内嵌servlet容器(可以选择内 ...
- spring cloud教程之使用spring boot创建一个应用
<7天学会spring cloud>第一天,熟悉spring boot,并使用spring boot创建一个应用. Spring Boot是Spring团队推出的新框架,它所使用的核心技术 ...
- 【Spring】关于Boot应用中集成Spring Security你必须了解的那些事
Spring Security Spring Security是Spring社区的一个顶级项目,也是Spring Boot官方推荐使用的Security框架.除了常规的Authentication和A ...
随机推荐
- 页面内容不满屏幕高度时,footer底部显示
底部高度固定的情况下 <style> body,html{ height: 100%; margin: 0; } .content{ min-height: 100%; padding-b ...
- 松软科技课堂:jQuery 事件函数
jQuery 事件函数 jQuery 事件处理方法是 jQuery 中的核心函数. 事件处理程序指的是当 HTML 中发生某些事件时所调用的方法.术语由事件“触发”(或“激发”)经常会被使用. 通常会 ...
- 在cc.EventListener.TOUCH_ONE_BY_ONE事件中判断拖动物离哪边近飞向那边
需将拖动物坐标和要飞向物坐标转化为整个layer的坐标,因为人们判断远近是根据整个layer来看的.
- jdk8-》reduce操作
什么是reduce操作 聚合操作,中⽂意思是 “减少” 根据⼀定的规则将Stream中的元素进⾏计算后返回⼀个唯⼀的值 常⽤⽅法⼀: Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOp ...
- AcWing 1013. 机器分配
//分组背包 for物品 for体积 for 决策 #include <iostream> using namespace std; ; int n, m; int w[N][N]; in ...
- loadrunner11破解失败,已解决“ license security violation.Operation is not allowed ”问题
参考链接https://blog.csdn.net/yongrong/article/details/7891738,亲测可以解决问题 在64位win7系统中安装LR11时,采用普通的方法无法授权.最 ...
- 自己动手系列----使用数组实现一个简单的Map
数组对于每一门编程语言来说都是重要的数据结构之一,当然不同语言对数组的实现及处理也不尽相同.Java 语言中提供的数组是用来存储固定大小的同类型元素. 这里提一下,数组的优缺点: 优点: 1. 使用索 ...
- c#中的yield词法
yield关键字的作用是将当前集合中的元素立即返回,实例: 通过断点可以看到,控制台每显示一个集合中的元素,都会到query方法中去取集合元素. 其实yield return是“语法糖”,其本质是生成 ...
- 银行贷款利率低到“令人发指”,很多人还坚持借高利贷,why?
编辑 | 于斌 出品 | 于见(mpyujian) 网络上,每隔一段时间,就会出现因为借了高利贷,家破人亡的新闻. 这种现象,层出不求,但其实,我们每次看了这些新闻,只是为其感到惋惜,并没有进一步去发 ...
- 「题解」「CF1103B」Game with modulo
简易中文题目 猜一个数字 \(a\),而你可以向机器提问一对 \((x,y)\) ,如果 \(x\bmod a\ge y \bmod a\) 机器返回字符串 x,反之返回字符串 y . 询问不能超过 ...
