SciTech-Mathematics-Probability+Statistics-{Problem,Study,Experiment,Conclusion}-Variables: Confounding/Controlled/{Antecedent,Manipulated,Moderating,Intervening,Response}/Extraneous
Problem>Study>Experiment>Conclusion
Study:
- Communication and Networking: Beliefs, Interests, Requirements.
- Organization: Individuals with common goals.
- Strategy: based on certainty, reduce uncertainty also risk.
- Plan: Management
Experiment :
An experiment is a controlled scientific study.{Conditions,Processes,Outcomes}
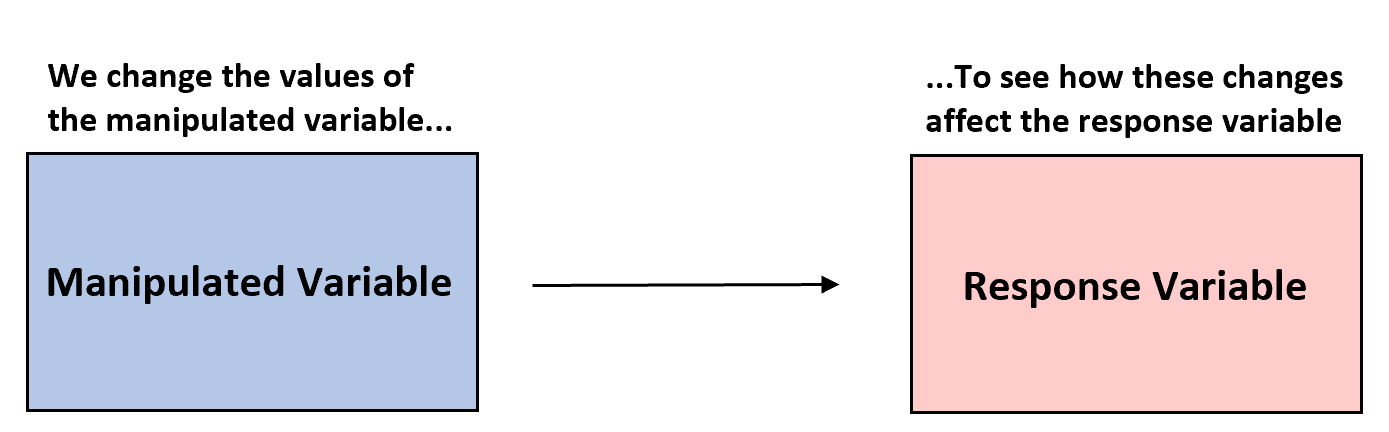
- In statistics, we often conduct experiments to understand how changing one variable affects another variable.
- Goal: The goal of an experiment is to "keep" all variables "constant except for" the manipulated variable so that we can attribute any change in the response variable to the changes made in the manipulated variable.
controlled variable : a variable that are intentionally kept constant.
manipulated variable
a variable that we "change or manipulate" to see how that change "affects" some other variable.
it is also sometimes called an independent variable.
response variable
The variable that changes as a result of the manipulated variable being changed.
It is sometimes called a dependent variable because its value often depends on the value of the "manipulated variable".
Variables: Qualitative or Quantitative.
- Qualitative variables are variables that take on names or labels.
Examples include:Gender(Male or Female), Education Level(Bachelor's Degree, Master's Degree, Doctor's Degree, etc.), Marital Status(Single, Married, Divorced) - Quantitative variables are variables that take on numerical values.
Examples include: Age, Height, Square Footage, Population Size
SciTech-Mathematics-Probability+Statistics
Confounding
Confounding variable: A variable that is not included in an experiment,
yet affects the relationship between the two variables(dependent and independent) in an experiment.
This type of variable can confound the results of an experiment and lead to unreliable findings.
it can confound the results of a study and make it appear that there exists "some type of cause-and-effect" relationship between two variables that doesn't actually exist.
In order for a variable to be a confounding variable, it must meet the following requirements:- It must be correlated with the independent variable.
- It must have a causal relationship with the dependent variable.
Moderating Variable
moderating variable is a type of variable that affects the relationship between a dependent variable and an independent variable.- Moderating variables can be qualitative or quantitative.
- Moderating variables can affect the relationship between an independent and dependent variable in a variety of ways.
Moderating variables can have the following effects: Strengthen/Weaken/Negate the relationship between two variables.
Depending on the situation, a moderating variable can moderate the relationship between two variables in many different ways.
Antecedent
A variable that occurs before the independent and dependent variables under study and can help explain the relationship between the two.
You can remember this definition by remembering that the word "antecedent" literally means "previous or preexisting".Intervening
Intervening variables pop up in many different research situations.
Variables that come between independent and dependent variables and have a direct effect on the relationship between the two.
Often this type of variable can appear when researchers are studying the relationship between two variables and don't realize that another variable is actually intervening in the relationship.Extraneous
Variables that are not of interest in a study, but can affect both the independent and dependent variables.
Manipulated variable
Often in experiments there are also controlled variables, which are variables that are intentionally kept constant.
The goal of an experiment is to keep all variables constant except for the manipulated variable so that we can attribute any change in the response variable to the changes made in the manipulated variable.
Let's check out a couple examples of different experiments to gain a better understanding of manipulated variables.
| Figure0 | Example 1 | Example 2 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
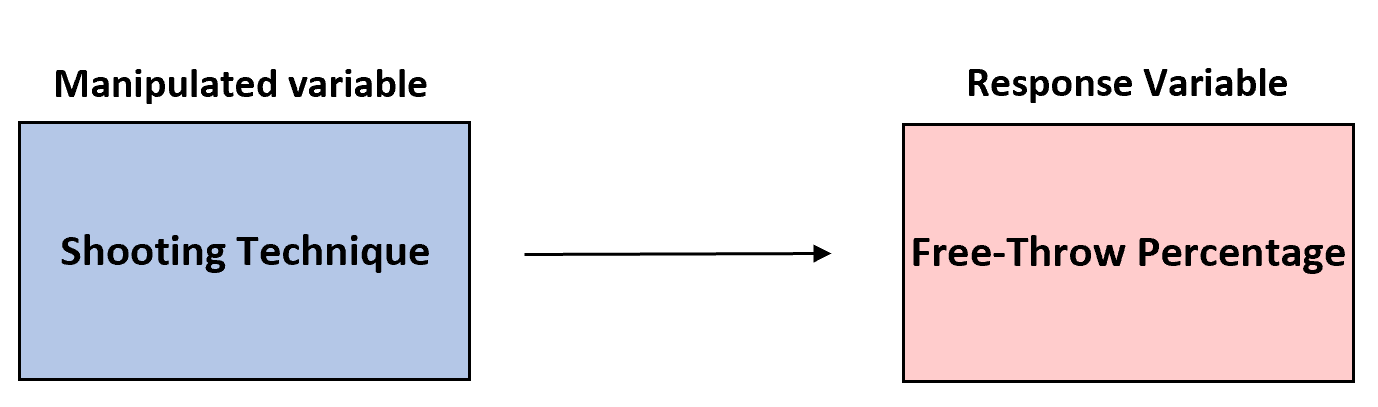
Example 1: Free-Throw Shooting
- Suppose a basketball coach wants to conduct an experiment, to determine if three different shooting techniques affect the free-throw percentage of his players.
- He divides his team into three groups and has each group use a different technique to shoot 100 free-throws.
- He then records the average free-throw percentage for each group.
In this experiment, we would have the following variables:
- Manipulated variable: The shooting technique.
This is the variable that we manipulate to see how it affects free-throw percentage. - Response variable: The free-throw percentage.
This is the variable that changes as a result of the manipulated variable being changed. - Controlled variables:
We would want to make sure that each of the three groups shoot free-throws under the same conditions.
So, variables that we might control include (1) gym lighting, (2) time of day, and (3) gym temperature.
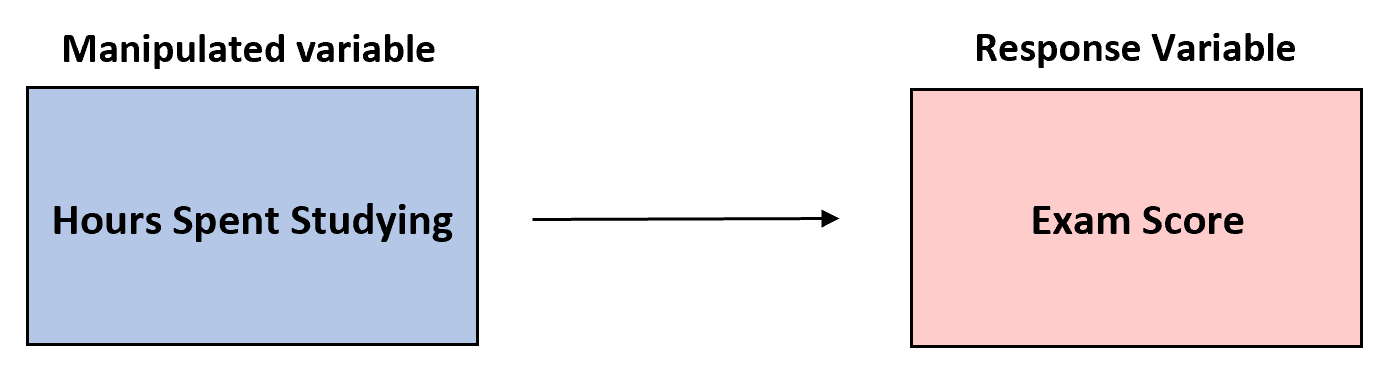
Example 2: Exam Scores
- Suppose a teacher wants to understand how the number of hours spent studying affects exam scores.
- She intentionally has groups of students study for 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 hours prior to an exam.
She then has each group take the same exam and records the average scores for each group.
In this experiment, we would have the following variables:
- Manipulated variable: The number of hours spent studying.
This is the variable that the teacher manipulates to see how it affects exam scores. - Response variable: The exam scores.
This is the variable that changes as a result of the manipulated variable being changed. - Controlled variables:
We would want to make sure that each of the groups of students take the exam under the same conditions.
So, variables that we might control include (1) time available to complete exam, (2) number of breaks given during exam, and (3) time of day when exam is administered.
SciTech-Mathematics-Probability+Statistics-{Problem,Study,Experiment,Conclusion}-Variables: Confounding/Controlled/{Antecedent,Manipulated,Moderating,Intervening,Response}/Extraneous的更多相关文章
- Probability&Statistics 概率论与数理统计(1)
基本概念 样本空间: 随机试验E的所有可能结果组成的集合, 为E的样本空间, 记为S 随机事件: E的样本空间S的子集为E的随机事件, 简称事件, 由一个样本点组成的单点集, 称为基本事件 对立事件/ ...
- How do I learn mathematics for machine learning?
https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-learn-mathematics-for-machine-learning How do I learn mathematics f ...
- 实验9:Problem G: 克隆人来了!
想要输出""的话: cout<<"A person whose name is \""<<name<<" ...
- 概率论 --- Uva 11181 Probability|Given
Uva 11181 Probability|Given Problem's Link: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/problem/viewProblem.acti ...
- 实验12:Problem I: 成绩排序
Home Web Board ProblemSet Standing Status Statistics Problem I: 成绩排序 Problem I: 成绩排序 Time Limit: 1 ...
- 实验12:Problem H: 整型数组运算符重载
Home Web Board ProblemSet Standing Status Statistics Problem H: 整型数组运算符重载 Problem H: 整型数组运算符重载 Tim ...
- 实验12:Problem F: 求平均年龄
Home Web Board ProblemSet Standing Status Statistics Problem F: 求平均年龄 Problem F: 求平均年龄 Time Limit: ...
- 实验12:Problem C: 重载字符的加减法
Home Web Board ProblemSet Standing Status Statistics Problem C: 重载字符的加减法 Problem C: 重载字符的加减法 Time ...
- 实验12:Problem J: 动物爱好者
#define null ""是用来将字符串清空的 #define none -1是用来当不存在这种动物时,返回-1. 其实这种做法有点多余,不过好理解一些. Home Web B ...
- 实验12:Problem G: 强悍的矩阵运算来了
这个题目主要是乘法运算符的重载,卡了我好久,矩阵的乘法用3个嵌套的for循环进行,要分清楚矩阵的乘法结果是第一个矩阵的行,第二个矩阵的列所组成的矩阵. 重载+,*运算符时,可以在参数列表中传两个矩阵引 ...
随机推荐
- Python3正则表达式(一)
Python3正则表达式 正则表达式是一个特殊的字符序列,它能帮助你方便的检查一个字符串是否与某种模式匹配. Python 自1.5版本起增加了re 模块,它提供 Perl 风格的正则表达式模式. r ...
- Burp插件Fiora联动nuclei(windows)
大佬写的插件出来好久了 今天朋友问我Fiora联动nuclei,我突然忘了咋配的的了.. 记录一下 一.下载nuclei https://github.com/projectdiscovery/nuc ...
- Oracle 使用UTL_HTTP发送http请求--转载
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/tmaczt/article/details/82665885 GET方式 CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION FN_HTTP_GE ...
- Java Objects.equals(a,b)的说明
一:值是null的情况: a.equals(b), a 是null, 抛出NullPointException异常. a.equals(b), a不是null, b是null, 返回false Obj ...
- 操作系统综合题之“采用二级页表的分页存储管理方式,计算页目录号的位数 和 页大小,给定页目录项大小计算页目录表大小,给定逻辑地址计算页内偏移量和物理地址[0x00200643]”
一.问题:某计算机系统的主存按字节编址,逻辑地址和物理地址都是32位,其内存管理采用两级页表的分页存储管理方式.逻辑地址中页号位10位,页内偏移地址为10位.该计算机系统的两级页表结构如下图所示,图中 ...
- 奶奶都能看懂的 CSS 选择器基础语法&常用属性&优先级
标题都是奶奶都能看懂了,那么我们肯定从最基础的开始讲.之所以这么自信是因为能踩的坑全帮你们踩过了-- 开始之前,先来首诗感受一下,具体啥意思你看完本文就懂了. 点类井号逗为或,类多号单连为且. id ...
- Django实例(3)-用户连数据库登入系统
App01--->urls.py from django.contrib import adminfrom django.conf.urls import urlfrom app01 impor ...
- 编译原理:剖析python编译阶段
Python编译器 GDB跟踪python编译器的执行过程,在tokenizer.c的tok_get()函数中打一个断点,通过GDB查看python的运行,使用bt命令打印输出,结果如下图所示 整理后 ...
- python 读写、创建文件
python中对文件.文件夹(文件操作函数)的操作设计到os模块以及shutil模块 os模块提供了对目录或者文件的新建/删除/查看文件属性,还提供了对文件以及目录的路径操作,比如:绝对路径,父路径等 ...
- Numpy 的广播机制
广播机制在numpy中居于非常重要的位置,也是numpy高效计算的秘密武器,有必要进行深入彻底的理解,简而言之,它的规则如下: 规则1:如果两个数组在维度上不一样,那么维度低的数组用1(1个或者多个) ...
