CompletableFuture笔记
CompletableFuture是java8引入的一个很实用的特性,可以视为Future的升级版本,以下几个示例可以说明其主要用法(注:示例来自《java8实战》一书第11章)
一、引子:化同步为异步
为了方便描述,假设"查询电商报价"的场景:有一个商家Shop类,对外提供价格查询的服务getPrice
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.Future; public class Shop { public String name; private Random random = new Random(); public Shop(String name) {
this.name = name;
} /**
* 计算价格
*
* @param product
* @return
*/
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
return random.nextDouble() * product.charAt(0) + product.charAt(1);
} /**
* 模拟计算价格的耗时
*/
private static void delay() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} /**
* 对外提供的报价服务方法
*
* @param product
* @return
*/
public double getPrice(String product) {
return calculatePrice(product);
} }
平台可以调用getPrice方法获取某个商家的报价:
public static void main(String[] args) {
testSyncGetPrice();
}
private static void doSomethingElse() {
System.out.println("do something else");
}
public static void testSyncGetPrice() {
Shop shop = new Shop("BestShop");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("Price is %.2f\n", shop.getPrice("my favorite product"));
doSomethingElse();
System.out.println("(SyncGetPrice) Invocation returned after : " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + " ms\n");
}
显然,这是1个同步调用,在shop.getPrice()方法执行完前,后面的doSomethingElse()只能等着,输出结果如下:
Price is 222.01
do something else
(SyncGetPrice) Invocation returned after : 1015 ms
为了消除同步阻塞,可以借用Future将同步的getPrice方法调用,转换成异步。
public Future<Double> getPriceAsync(String product) {
Future<Double> submit = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1).submit(() -> calculatePrice(product));
return submit;
}
上面的submit方法,最终调用的是java.util.concurrent.AbstractExecutorService#submit(java.util.concurrent.Callable<T>)
/**
* @throws RejectedExecutionException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
}
如果继续追下去的话,execute方法,又是调用的java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor#execute方法,创建一个线程来异步执行。将同步转换成异步后,doSomethingElse方法,在getPriceAsync执行期间,就能并发执行了。
public static void doSomethingElse() {
System.out.println("do something else");
}
public static void testAsyncGetPrice() {
Shop shop = new Shop("BestShop");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Future<Double> futurePrice = shop.getPriceAsync("my favorite product");
doSomethingElse();
try {
Double price = futurePrice.get();
System.out.printf("Price is %.2f\n", price);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("(AsyncGetPrice) Invocation returned after : " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + " ms\n");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testAsyncGetPrice();
}
输出结果:
do something else
Price is 201.69
(AsyncGetPrice) Invocation returned after : 1111 ms
二、同步转换成异步的其它方式
CompletableFuture出现后,"同步调用"转换成"异步调用"的方式,有了新的选择:
public Future<Double> getPriceAsync1(String product) {
CompletableFuture<Double> futurePrice = new CompletableFuture<Double>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
futurePrice.complete(price);
} catch (Exception e) {
futurePrice.completeExceptionally(e);
}
}).start();
return futurePrice;
}
public Future<Double> getPriceAsync2(String product) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> calculatePrice(product));
}
上面这2种方法效果等价,显然第2种supplyAsync的写法更简洁。需要说明的是:CompletableFuture内部其实也是使用线程池来处理的,只不过这个线程池的类型默认是ForkJoinPool,这一点可以从java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture#asyncPool源码看出来:
/**
* Default executor -- ForkJoinPool.commonPool() unless it cannot
* support parallelism.
*/
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
三、CompletableFuture中使用自定义线程池
如果需要查询报价的商家有很多,比如:6个,逐一同步调用getPrice方法,时长大约就是6个商家的总时长累加
static List<Shop> shops = Arrays.asList(
new Shop("1-shop"),
new Shop("2-shop"),
new Shop("3-shop"),
new Shop("4-shop"),
new Shop("5-shop"),
new Shop("6-shop")
); public static void main(String[] args) {
testFindPrices();
} public static List<String> findPrices(String product) {
return shops.stream()
.map(shop -> String.format("%s price is %.2f", shop.name, shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
输出:
[1-shop price is 180.36, 2-shop price is 206.13, 3-shop price is 205.49, 4-shop price is 184.62, 5-shop price is 222.73, 6-shop price is 143.19]
do something else
(findPrices-Stream) Invocation returned after : 6102 ms
这显然太慢了,要知道现代计算机都是多核cpu体系,很容易想到把stream换成parallelStream,可以充分发挥多核优势:
public static List<String> findPricesParallel(String product) {
return shops.parallelStream()
.map(shop -> String.format("%s price is %.2f", shop.name, shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
还是刚才的测试场景,这时输出结果类似下面这样:(注:测试机器为mac 4核笔记本)
[1-shop price is 137.42, 2-shop price is 168.93, 3-shop price is 182.89, 4-shop price is 154.60, 5-shop price is 192.70, 6-shop price is 179.06]
do something else
(findPrices-parallelStream) Invocation returned after : 2102 ms
比刚才好多了,耗时从6s缩短到2s,但仔细想一想:6个商家的getPrice处理,分摊到4个核上,还是有2个核会出现阻塞(即:平均1个核并行处理1个task,6-4=2,仍然有2个task要排队)。
如果换成用CompletableFuture默认的ForkJoinPool呢,性能会不会好一些?
public static List<String> findPricesFuture() {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> priceFutures = shops.parallelStream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
String.format("%s price is %.2f", shop.name, shop.getPrice("myPhone27"))))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return priceFutures.parallelStream().map(CompletableFuture::join).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static void testFindPricesCompletableFuture() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf(findPricesFuture().toString() + "\n");
doSomethingElse();
System.out.println("(findPrices-CompletableFuture) Invocation returned after : " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + " ms\n");
}
输出结果(注:上面代码中的parallelStream换成stream,下面的输出结果也差不多)
[1-shop price is 168.57, 2-shop price is 159.43, 3-shop price is 200.08, 4-shop price is 165.64, 5-shop price is 195.11, 6-shop price is 206.83]
do something else
(findPrices-CompletableFuture) Invocation returned after : 2092 ms
从结果上看,使用CompletableFuture与使用仅使用parallelStream的耗时差不多,并没有性能上的提升。原因在于默认的ForkJoinPool,其默认线程数也是跟CPU核数相关的。在这个场景中,我们至少要6个线程(即:shops.size()),才能让6个商家的getPrice并发处理。按这个思路,我们可以自定义一个线程池,然后传入supplyAsync方法中:
private static final Executor executor =
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Math.min(shops.size(), 100),
new ThreadFactory() {
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.setDaemon(true);
return t;
}
}); public static List<String> findPricesFutureWithExecutor() {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> priceFutures = shops.stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
String.format("%s price is %.2f", shop.name, shop.getPrice("myPhone27")), executor))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return priceFutures.stream().map(CompletableFuture::join).collect(Collectors.toList());
} public static void testFindPricesExecutor() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf(findPricesFutureWithExecutor().toString() + "\n");
doSomethingElse();
System.out.println("(findPrices-FutureWithExecutor) Invocation returned after : " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + " ms\n");
} public static void main(String[] args) {
testFindPricesExecutor();
}
输出结果如下:
[1-shop price is 177.26, 2-shop price is 227.09, 3-shop price is 179.98, 4-shop price is 127.19, 5-shop price is 208.93, 6-shop price is 229.91]
do something else
(findPrices-FutureWithExecutor) Invocation returned after : 1121 ms
从耗时上看,仅相当于单个商家getPrice的耗时,已经达到最佳效果。
四、多个异步操作组合
前面提到的商家报价场景,我们再加点料,引入“打折”功能。先把shop调整下:
package future; import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.Future; public class Shop { public String name; private static Random random = new Random(); public Shop(String name) {
this.name = name;
} private double calculatePrice(String product) {
randomDelay();
return random.nextDouble() * product.charAt(0) + product.charAt(1);
} public static void randomDelay() {
int delay = 500 + random.nextInt(2000);
try {
Thread.sleep(delay);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} /**
* 查询“(原始)价格”及"对应的折扣"
*
* @param product
* @return
*/
public String getPriceWithDiscount(String product) {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
Discount.Code code = Discount.Code.values()[random.nextInt(Discount.Code.values().length)];
String result = String.format("%s:%.2f:%s", name, price, code);
System.out.println(result);
return result;
} }
主要有2处改动:
1 是delay方法引入了随机数,模拟不同商家查询价格时,有着不同的处理时间,显得更真实。
2 是getPriceWithDiscount方法,返回的价格不再是1个double,而是类似下面这样的字符串
1-shop:212.78:NONE
2-shop:182.22:DIAMOND
3-shop:148.91:PLATINUM
4-shop:203.78:SILVER
5-shop:152.75:DIAMOND
6-shop:212.43:NONE
同时包括了原始的价格,以及打折等级(无折扣、白银等级、钻石等级...之类),这里有一个Discount类,代码如下:
package future;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Discount {
/**
* 打折类型
*/
public enum Code {
NONE(0), SILVER(5), GOLD(10), PLATINUM(15), DIAMOND(20);
/**
* 折扣百分比
*/
private final int percentage;
Code(int percentage) {
this.percentage = percentage;
}
}
/**
* 计算折扣后的价格
* @param price
* @param code
* @return
*/
private static double apply(double price, Code code) {
Shop.randomDelay();
return format(price * (100 - code.percentage) / 100);
}
private static double format(double d) {
BigDecimal decimal = new BigDecimal(d);
return decimal.setScale(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_DOWN).doubleValue();
}
/**
* 应用折扣,输出最后的处理结果
*
* @param quote
* @return
*/
public static String applyDiscount(Quote quote) {
return quote.shopName + " price is " + apply(quote.price, quote.discountCode);
}
}
apply模拟了计算折扣价时,需要一定的耗时randomDelay(),而getPriceWithDiscount返回的字符串,还需要有1个Quota类专门解析其中的原始价格以及折扣等级
/**
* 带折扣的报价
*/
public class Quote { public final String shopName;
public final double price;
public final Discount.Code discountCode; public Quote(String shopName, double price, Discount.Code code) {
this.shopName = shopName;
this.price = price;
this.discountCode = code;
} /**
* 解析价格结果
*
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static Quote parse(String s) {
String[] split = s.split(":");
String shopName = split[0];
double price = Double.parseDouble(split[1]);
Discount.Code discountCode = Discount.Code.valueOf(split[2]);
return new Quote(shopName, price, discountCode);
}
}
引入折扣功能后,原来的“查询商家价格”,可分解成3个步骤:
1. 先调用shop.getPriceWithDiscount 返回“原始价格及折扣等级”字符串
2. 解析1中返回的字符串,将price与discount信息提取出来,并最终封装成Quota对象
3. 调用Discount的applyDiscount,返回最终打折后的价格信息
而且,上面的步骤,3依赖2的完成,2依赖1的完成,用标准写出来的话,大致是下面这个样子:
public static List<String> findDiscountPrices() {
return shops.stream()
.map(shop -> shop.getPriceWithDiscount("myPhone27"))
.map(Quote::parse)
.map(Discount::applyDiscount)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static void testFindDiscountPrices() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf(findDiscountPrices().toString() + "\n");
doSomethingElse();
System.out.println("(findDiscountPrices-stream) Invocation returned after : " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + " ms\n");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testFindDiscountPrices();
}
这是同步的调用方式,可想而知,最终耗时会很大:
1-shop:157.77:DIAMOND
2-shop:138.03:DIAMOND
3-shop:204.60:DIAMOND
4-shop:202.52:NONE
5-shop:155.14:GOLD
6-shop:224.15:SILVER
[1-shop price is 126.22, 2-shop price is 110.42, 3-shop price is 163.68, 4-shop price is 202.52, 5-shop price is 139.63, 6-shop price is 212.94]
do something else
(findDiscountPrices-stream) Invocation returned after : 16449 ms
使用CompletableFuture,可以把1-2-3 这3个步骤都转换成异步,且保证相互之间的依赖关系,代码如下:
public static List<String> findDiscountPricesFuture() {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> list = shops.stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPriceWithDiscount("myPhone27"), executor))
.map(f -> f.thenApply(Quote::parse))
.map(f -> f.thenCompose(quote -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> Discount.applyDiscount(quote), executor)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return list.stream().map(CompletableFuture::join).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
输出结果如下:
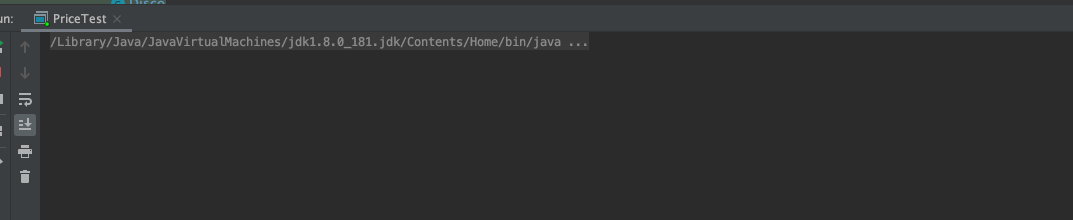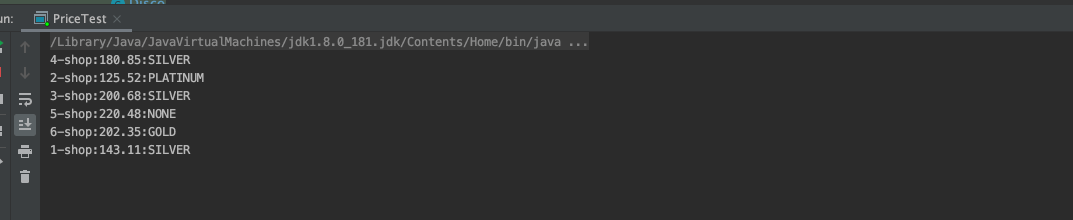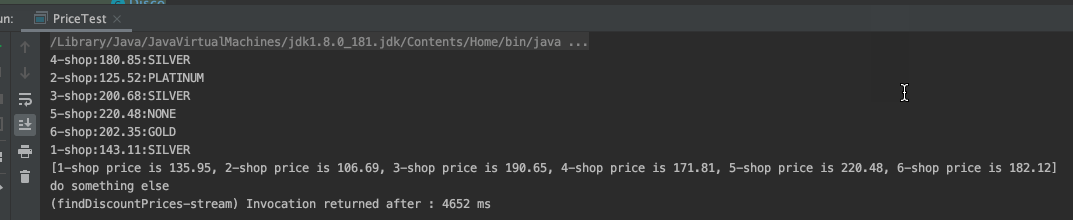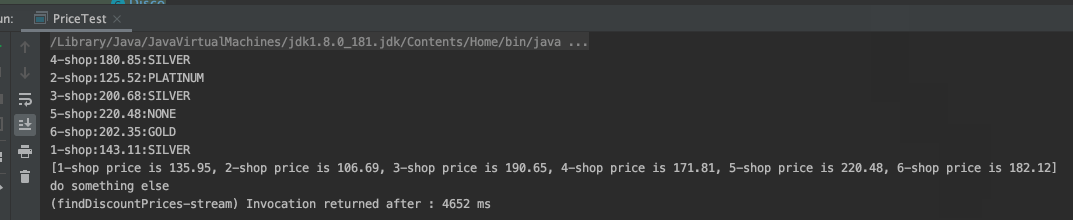
从结果上看,确实已经是异步了(1个线程处理1个商家的getPrice及Discount计算),整体耗时也大幅下降。但是有一个细节问题,6个商家的最终结果(即:最后的[...]列表输出),是等所有异步操作都执行完,1次性输出的,这在实际应用中,意味着,最终买家能多快看到价格输出,取决于最慢的那个商家,这是不能接受的,理想情况下,应该是哪个商家的服务快,能先计算出结果 ,就应该第1时间展示这家店的价格。
修正后的代码如下:
public static void findDiscountPricesFuture() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture[] futureArray = shops.stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPriceWithDiscount("myPhone27"), executor))
.map(f -> f.thenApply(Quote::parse))
.map(f -> f.thenCompose(quote -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> Discount.applyDiscount(quote), executor)))
.map(f -> f.thenAccept(s -> System.out.println(s + " (done in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + " ms)")))
.toArray(size -> new CompletableFuture[size]);
CompletableFuture.allOf(futureArray).join();
}
解释:主要是利用了CompletableFuture.allOf()方法,该方法会把数组结果,按完成时间快慢,快的先返回。

从运行效果上看,最终的报价输出,不再是等6个商家全计算好才返回。
CompletableFuture笔记的更多相关文章
- Java8 增强的Future:CompletableFuture(笔记)
CompletableFuture是Java8新增的一个超大型工具类,为什么说她大呢?因为一方面它实现了Future接口,更重要的是,它实现了CompletionStage接口.这个接口也是Java8 ...
- Java8 CompletableFuture组合式的编程(笔记)
* 实现异步API public double getPrice(String product) { return calculatePrice(product); } /** * 同步计算商品价格的 ...
- 《Java学习笔记(第8版)》学习指导
<Java学习笔记(第8版)>学习指导 目录 图书简况 学习指导 第一章 Java平台概论 第二章 从JDK到IDE 第三章 基础语法 第四章 认识对象 第五章 对象封装 第六章 继承与多 ...
- 响应式编程笔记三:一个简单的HTTP服务器
# 响应式编程笔记三:一个简单的HTTP服务器 本文我们将继续前面的学习,但将更多的注意力放在用例和编写实际能用的代码上面,而非基本的APIs学习. 我们会看到Reactive是一个有用的抽象 - 对 ...
- 20145230《java学习笔记》第七周学习总结
20145230 <Java程序设计>第7周学习总结 教材学习内容 Lambda语法概览 我们在许多地方都会有按字符串长度排序的需求,如果在同一个方法内,我们可以使用一个byName局部变 ...
- Java开发笔记(一百一十三)HttpClient实现下载与上传
前面介绍了通过HttpClient实现HTTP接口的GET方式调用和POST方式调用,那么文件下载与文件上传又该如何操作呢?其实在HttpClient看来,文件下载属于特殊的GET调用,只不过应答报文 ...
- JUC并发编程学习笔记
JUC并发编程学习笔记 狂神JUC并发编程 总的来说还可以,学到一些新知识,但很多是学过的了,深入的部分不多. 线程与进程 进程:一个程序,程序的集合,比如一个音乐播发器,QQ程序等.一个进程往往包含 ...
- JUC源码学习笔记5——1.5w字和你一起刨析线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码,全网最细doge
源码基于JDK8 文章1.5w字,非常硬核 系列文章目录和关于我 一丶从多鱼外卖开始 话说,王多鱼给好友胖子钱让其投资,希望亏得血本无归.胖子开了一个外卖店卖国宴,主打高端,外卖小哥都是自己雇佣,并且 ...
- git-简单流程(学习笔记)
这是阅读廖雪峰的官方网站的笔记,用于自己以后回看 1.进入项目文件夹 初始化一个Git仓库,使用git init命令. 添加文件到Git仓库,分两步: 第一步,使用命令git add <file ...
- js学习笔记:webpack基础入门(一)
之前听说过webpack,今天想正式的接触一下,先跟着webpack的官方用户指南走: 在这里有: 如何安装webpack 如何使用webpack 如何使用loader 如何使用webpack的开发者 ...
随机推荐
- 第三章 Spring Boot 整合 Kafka消息队列 消息者
前言 Kafka 是一个消息队列产品,基于Topic partitions的设计,能达到非常高的消息发送处理性能.本文主是基于Spirng Boot封装了Apache 的Kafka-client, ...
- rust引入含有openssl相关包报错(openssl未找到和编译运行报错等相关问题)解决方案
1. 问题描述 某天在我的rust程序里引入了actix-proxy = "0.2"这个包,我的程序编译通不过了,rust-analyser也罢工了,错误也提示不出来了,查看错误提 ...
- B1092 最好吃的月饼
描述 月饼是久负盛名的中国传统糕点之一,自唐朝以来,已经发展出几百品种. 若想评比出一种"最好吃"的月饼,那势必在吃货界引发一场腥风血雨-- 在这里我们用数字说话,给出全国各地各种 ...
- codeup之统计同成绩学生人数
Description 读入N名学生的成绩,将获得某一给定分数的学生人数输出. Input 测试输入包含若干测试用例,每个测试用例的格式为 第1行:N 第2行:N名学生的成绩,相邻两数字用一个空格间隔 ...
- Third Maximum Number——LeetCode⑬
//原题链接https://leetcode.com/problems/third-maximum-number/ 题目描述 Given a non-empty array of integers, ...
- 互联网的前世今生:Web 1.0、2.0、3.0
101链视界:区块链.隐私计算与金融科技领域的专业知识分享者. ▲ 点击上方第二个"101链视界"关注公众号 2021年,元宇宙成为一个爆火的概念,而Web 3.0也悄悄在海外科技 ...
- 在Avalonia中使用相对单位
Avalonia目前不具备相对单位功能,要使用相对单位需要安装RelativeControl.Avalonia包 RelativeControl.Avalonia 开始使用 添加NuGet包: dot ...
- 一看就懂!任务提交的资源判断在Taier中的实践
Taier 介绍 Taier 是袋鼠云开源项目之一,是一个分布式可视化的DAG任务调度系统. 旨在降低ETL开发成本.提高大数据平台稳定性,大数据开发人员可以在 Taier 直接进行业务逻辑的开发,而 ...
- 东方财富服务端开发暑期实习面试,已拿offer!!
这是一位球友投稿的东方财富服务端开发暑期实习面经,问的内容还是比较多的,难度也相对比较大.下面是正文. 最近参与了东方财富服务端开发暑期实习的招聘,并最终收获了 Offer.整个过程持续了大约一周,从 ...
- FastAPI中的敏感数据如何在不泄露的情况下翩翩起舞?
扫描二维码 关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长 发现1000+提升效率与开发的AI工具和实用程序:https://tools.cmdragon.cn/ 以下是关于FastAPI框架中敏 ...
