Servlet中的装饰者模式
装饰者模式
Decorator模式或者Wrapper模式允许修饰或者封装(在字面意义中,即修改行为)一个对象,即使你没有该对象的源代码或者该对象标识为final。
Decorator模式适用于无法继承该类(例如,对象的实现类使用final标识)或者无法创建该类的实例,但可以从另外的系统中可以取得该类的实现时。例如,Servlet容器方法。只有一种方法可以修改ServletRequest或者ServletResponse行为,即在另外的对象中封装该实例。唯一的限制是,修饰对象必须继承一个接口,然后实现接口以封装这些方法。
UML类图
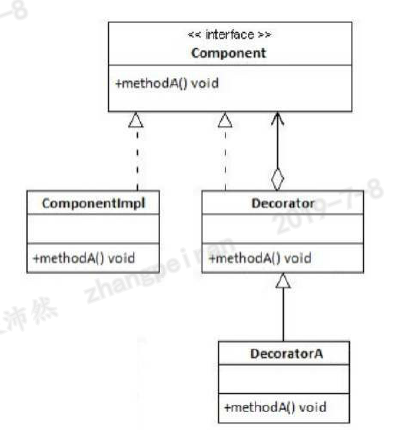
上面类图说明了一个Component接口以及它的实现类ComponentImpl。Component接口定义了A的方法。为了修饰ComponentImpl的实例,需要创建一个Decorator类,并实现Component的接口,然后在子类中扩展Decorator的新行为。在类图中DecoratorA就是Decorator的一个子类。每个Decorator实例需要包含Component的一个实例。Decorator类代码如下(注意在构建函数中获取了Component的实例,这意味着创建Decorator对象只能传入Component的实例)
在Decorator类中,有修饰的方法就是可能在子类中需要修改行为的方法,在子类中不需要修饰的方法可以不需要实现。所有的方法,无论是否需要修饰,都叫作Component中的配对方法。Decorator是一个非常简单的类,便于提供每个方法的默认实现。修改行为在它的子类中。需要牢记一点,Decorator类及被修饰对象的类需要实现相同的接口。为了实现Decorator,可以在Decorator中封装修饰对象,并把Decorator作为Component的一个实现。任何Component的实现都可以在Decorator中注入。事实上,你可以把一个修饰的对象传入另一个修饰的对象,以实现双重的修饰。
Servlet API中的装饰者模式应用
Servlet API源自于4个实现类,它很少被使用,但是十分强大:ServletRequestWrapper、ServletResponseWrapper以及HttpServletRequestWrapper、HttpServletResponseWrapper。ServletRequestWrapper(或者其他3个Wrapper类)非常便于使用,因为它提供了每个方法的默认实现:即ServletRequest封闭的配置方法。通过继承ServletRequestWrapper,只需要实现你需要变更的方法就可以了。如果不用ServletRequestWrapper,则需要继承ServletRequest并实现ServletRequest中所有的方法。
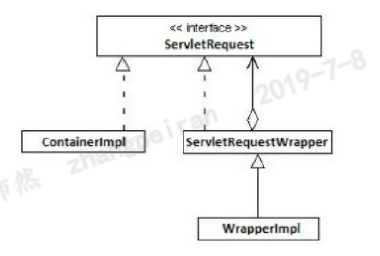
下图所示为Decorator模式中ServletRequestWrapper的类图。Servlet容器在每次Servlet服务调用时创建ServletRequest、ContainerImpl。直接扩展ServletRequestWrapper就可以修饰ServletRequest了。
ServletRequestWrapper源码
public class ServletRequestWrapper implements ServletRequest {
private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.LocalStrings";
private static final ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.LocalStrings");
private ServletRequest request;
public ServletRequestWrapper(ServletRequest request) {
if (request == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(lStrings.getString("wrapper.nullRequest"));
} else {
this.request = request;
}
}
public ServletRequest getRequest() {
return this.request;
}
public void setRequest(ServletRequest request) {
if (request == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(lStrings.getString("wrapper.nullRequest"));
} else {
this.request = request;
}
}
public Object getAttribute(String name) {
return this.request.getAttribute(name);
}
public Enumeration<String> getAttributeNames() {
return this.request.getAttributeNames();
}
public String getCharacterEncoding() {
return this.request.getCharacterEncoding();
}
public void setCharacterEncoding(String enc) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
this.request.setCharacterEncoding(enc);
}
public int getContentLength() {
return this.request.getContentLength();
}
public long getContentLengthLong() {
return this.request.getContentLengthLong();
}
public String getContentType() {
return this.request.getContentType();
}
public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return this.request.getInputStream();
}
public String getParameter(String name) {
return this.request.getParameter(name);
}
public Map<String, String[]> getParameterMap() {
return this.request.getParameterMap();
}
public Enumeration<String> getParameterNames() {
return this.request.getParameterNames();
}
public String[] getParameterValues(String name) {
return this.request.getParameterValues(name);
}
public String getProtocol() {
return this.request.getProtocol();
}
public String getScheme() {
return this.request.getScheme();
}
public String getServerName() {
return this.request.getServerName();
}
public int getServerPort() {
return this.request.getServerPort();
}
public BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException {
return this.request.getReader();
}
public String getRemoteAddr() {
return this.request.getRemoteAddr();
}
public String getRemoteHost() {
return this.request.getRemoteHost();
}
public void setAttribute(String name, Object o) {
this.request.setAttribute(name, o);
}
public void removeAttribute(String name) {
this.request.removeAttribute(name);
}
public Locale getLocale() {
return this.request.getLocale();
}
public Enumeration<Locale> getLocales() {
return this.request.getLocales();
}
public boolean isSecure() {
return this.request.isSecure();
}
public RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path) {
return this.request.getRequestDispatcher(path);
}
/** @deprecated */
@Deprecated
public String getRealPath(String path) {
return this.request.getRealPath(path);
}
public int getRemotePort() {
return this.request.getRemotePort();
}
public String getLocalName() {
return this.request.getLocalName();
}
public String getLocalAddr() {
return this.request.getLocalAddr();
}
public int getLocalPort() {
return this.request.getLocalPort();
}
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return this.request.getServletContext();
}
public AsyncContext startAsync() throws IllegalStateException {
return this.request.startAsync();
}
public AsyncContext startAsync(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws IllegalStateException {
return this.request.startAsync(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
public boolean isAsyncStarted() {
return this.request.isAsyncStarted();
}
public boolean isAsyncSupported() {
return this.request.isAsyncSupported();
}
public AsyncContext getAsyncContext() {
return this.request.getAsyncContext();
}
public boolean isWrapperFor(ServletRequest wrapped) {
if (this.request == wrapped) {
return true;
} else {
return this.request instanceof ServletRequestWrapper ? ((ServletRequestWrapper)this.request).isWrapperFor(wrapped) : false;
}
}
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> wrappedType) {
if (wrappedType.isAssignableFrom(this.request.getClass())) {
return true;
} else {
return this.request instanceof ServletRequestWrapper ? ((ServletRequestWrapper)this.request).isWrapperFor(wrappedType) : false;
}
}
public DispatcherType getDispatcherType() {
return this.request.getDispatcherType();
}
}
只需继承ServletRequestWrapper类,覆盖需要修改的方法,即可自定实现类。
内容源自《Servlet、JSP和Srping MVC学习指南》
Servlet中的装饰者模式的更多相关文章
- Netty中的装饰者模式
装饰者的应用 所谓装饰者,说白了,目的就是对现有的对象进行增强,装饰者设计模式最大的优点就是,它在扩展类原有功能的基础上还避免的类爆炸的情况 Netty中的装饰者模式的应用 ByteBuf是netty ...
- 设计模式(三):“花瓶+鲜花”中的装饰者模式(Decorator Pattern)
在前两篇博客中详细的介绍了"策略模式"和“观察者模式”,今天我们就通过花瓶与鲜花的例子来类比一下“装饰模式”(Decorator Pattern).在“装饰模式”中很好的提现了开放 ...
- Java中InputStream装饰器模式的大家族
本文写在po主初学JAVA时,在学习inputStream摸不着头脑,受Java IO-InputStream家族 -装饰者模式一文启发,所以在理清思路时写下本文.因为初学,如有错误,望指正. 因为和 ...
- RecyclerView中装饰者模式应用
近段时间一直在加班,在赶一个项目,现在项目接近尾声,那么需要对过去一段时间工作内容进行复盘,总结下比较好的解决方案,积累一些经验,我认为的学习方式,是「理论-实践-总结-分享」,这一种很好的沉淀方式. ...
- .NET/ASP.NETMVC 深入剖析 Model元数据、HtmlHelper、自定义模板、模板的装饰者模式(三)
阅读目录: 7.HtmlHelper.HtmlHelper<T>中的ViewModel的类型推断 8.控制ViewModel中的某个属性的呈现(使用PartialView部分视图细粒度控制 ...
- javascript设计模式学习之十五——装饰者模式
一.装饰者模式定义 装饰者模式可以动态地给某个对象添加一些额外的职责,而不会影响从这个类中派生的其他对象.这种为对象动态添加职责的方式就称为装饰者模式.装饰者对象和它所装饰的对象拥有一致的接口,对于用 ...
- 【设计模式 - 9】之装饰者模式(Decorator)
1 模式简介 装饰者模式允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构. 装饰者模式的思路是用"调料"对象将原始对象进行层层包裹,同时其属性.动作层层传递,达到最终 ...
- java I/O之装饰者模式
装饰者: Decorator模式(别名Wrapper):动态将职责附加到对象上,若要扩展功能,装饰者提供了比继承更具弹性的代替方案. 装饰者模式意图: 动态的给一个对象添加额外的职责.Decorato ...
- Java设计模式之装饰者模式
要实现装饰者模式,注意一下几点内容: 1.装饰者类要实现真实类同样的接口 2.装饰者类内有一个真实对象的引用(可以通过装饰者类的构造器传入) 3.装饰类对象在主类中接受请求,将请求发送给真实的对象(相 ...
随机推荐
- Linux学习 - 02 使用 - Centos8 - 『更换rpm/epel包源为国内源』
1. Centos8 - 『更换rpm/epel包源为国内源』 centos 8 默认是会读取centos.org的mirrorlist的,所以一般来说是不需要配置镜像的. 如果你的网络访问mirro ...
- MathType总结编辑括号的类型(下)
在数学中,所涉及到的公式总是会有各种各样的情况,对于括号这些都是最常见的了.在最开始的四则基本运算中我们学会了使用括号,而随着学习的不断深入,所涉及到的符号与公式都越来越多,对于括号的类型也是使用得非 ...
- 关于Folx一些使用方面的问题详细解答
Folx作为一款的专业的Mac系统文件下载工具,相信大家或多或少都对它的主打功能,如智能限速.制定计划任务.直链文件下载等功能有所了解,但是对于它的一些相对少见.冷门的功能,却不太熟悉. 下面小编将通 ...
- 对于order by子句
order by子句指定排序顺序 select username from user order by username; 依据username的字母顺序对于查找出来的username进行排序,默认是 ...
- leetcode 1046
class Solution { public int lastStoneWeight(int[] stones) { MaxHeap s=new MaxHeap(stone ...
- api-hook,更轻量的接口测试工具
前言 在网站的开发过程中,接口联调和测试是至关重要的一环,其直接影响产品的核心价值,而目前也有许多技术方案和工具加持,让我们的开发测试工作更加便捷.接口作为数据传输的重要载体,数据格式和内容具有多样性 ...
- mfc 双缓存
CRect rect; //获取显示区域大小(该值为据对坐标,使用时需转换) GetWindowRect(rect); rect.SetRect(0, 0, rect.Width(), rect.He ...
- How tomcat works(深入剖析tomcat)servlet容器
How tomcat works (5)servlet容器阅读笔记 第四章阅读了tomcat默认连接器的实现,当时connector中的使用的容器是自定义的容器,也是非常之简单奥,一个人就干完了所有的 ...
- 冲刺随笔——Day_Six
这个作业属于哪个课程 软件工程 (福州大学至诚学院 - 计算机工程系) 这个作业要求在哪里 团队作业第五次--Alpha冲刺 这个作业的目标 团队进行Alpha冲刺 作业正文 正文 其他参考文献 无 ...
- springboot补充
springboot中的日志: 在默认的spring-boot-starter中,会引入spring-boot-starter-logging, 而springboot-starte-longing中 ...
