Secure Spring REST API using Basic Authentication
What is Basic Authentication?
Traditional authentication approaches like login pages or session identification are good for web based clients involving human interaction but does not really fit well when communicating with [REST] clients which may not even be a web application. Think of an API over a server which tries to communicate with another API on a totally different server, without any human intervention.
Basic Authentication provides a solution for this problem, although not very secure. With Basic Authentication, clients send it’s Base64 encoded credentials with each request, using HTTP [Authorization] header . That means each request is independent of other request and server may/does not maintain any state information for the client, which is good for scalability point of view.
Shown below is the sample code for preparing the header.
String plainClientCredentials="myusername:mypassword";
String base64ClientCredentials = new String(Base64.encodeBase64(plainClientCredentials.getBytes())); HttpHeaders headers = getHeaders();
headers.add("Authorization", "Basic " + base64ClientCredentials);
which may in turn produce something like:Authorization : Basic bXktdHJ1c3RlZC1jbGllbnQ6c2VjcmV0...
This header will be sent with ech request. Since Credentials [Base 64 encoded, not even encrypted] are sent with each request, they can be compromised. One way to prevent this is using HTTPS in conjunction with Basic Authentication.
Basic Authentication & Spring Security
With two steps, you can enable the Basic Authentication in Spring Security Configuration.
1. Configure httpBasic : Configures HTTP Basic authentication. [http-basic in XML]
2. Configure authentication entry point with BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint : In case the Authentication fails [invalid/missing credentials], this entry point will get triggered. It is very important, because we don’t want [Spring Security default behavior] of redirecting to a login page on authentication failure [ We don't have a login page].
Shown below is the complete Spring Security configuration with httpBasic and entry point setup.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy; @Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { private static String REALM="MY_TEST_REALM"; @Autowired
public void configureGlobalSecurity(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("bill").password("abc123").roles("ADMIN");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("tom").password("abc123").roles("USER");
} @Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.and().httpBasic().realmName(REALM).authenticationEntryPoint(getBasicAuthEntryPoint())
.and().sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);//We don't need sessions to be created.
} @Bean
public CustomBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint getBasicAuthEntryPoint(){
return new CustomBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint();
} /* To allow Pre-flight [OPTIONS] request from browser */
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring().antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**");
}
}
And the actual Entry point, which will get triggerd if authentication failed. You can customize it to send custom content in response.
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint; public class CustomBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint extends BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint { @Override
public void commence(final HttpServletRequest request,
final HttpServletResponse response,
final AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
//Authentication failed, send error response.
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
response.addHeader("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=" + getRealmName() + ""); PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("HTTP Status 401 : " + authException.getMessage());
} @Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
setRealmName("MY_TEST_REALM");
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
That’s all you need to configure basic security. Now let’s see everything in action, with our good old REST API
REST API
Simple Spring REST API, which serves user(s). A client can perform CRUD operations using Standard HTML verbs, compliant with REST style.
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.User;
import com.websystique.springmvc.service.UserService; @RestController
public class HelloWorldRestController { @Autowired
UserService userService; //Service which will do all data retrieval/manipulation work //-------------------Retrieve All Users-------------------------------------------------------- @RequestMapping(value = "/user/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<List<User>> listAllUsers() {
List<User> users = userService.findAllUsers();
if(users.isEmpty()){
return new ResponseEntity<List<User>>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);//You many decide to return HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND
}
return new ResponseEntity<List<User>>(users, HttpStatus.OK);
} //-------------------Retrieve Single User-------------------------------------------------------- @RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET,
produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE,MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE})
public ResponseEntity<User> getUser(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
System.out.println("Fetching User with id " + id);
User user = userService.findById(id);
if (user == null) {
System.out.println("User with id " + id + " not found");
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
return new ResponseEntity<User>(user, HttpStatus.OK);
} //-------------------Create a User-------------------------------------------------------- @RequestMapping(value = "/user/", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<Void> createUser(@RequestBody User user, UriComponentsBuilder ucBuilder) {
System.out.println("Creating User " + user.getName()); if (userService.isUserExist(user)) {
System.out.println("A User with name " + user.getName() + " already exist");
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(HttpStatus.CONFLICT);
} userService.saveUser(user); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setLocation(ucBuilder.path("/user/{id}").buildAndExpand(user.getId()).toUri());
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(headers, HttpStatus.CREATED);
} //------------------- Update a User -------------------------------------------------------- @RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public ResponseEntity<User> updateUser(@PathVariable("id") long id, @RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("Updating User " + id); User currentUser = userService.findById(id); if (currentUser==null) {
System.out.println("User with id " + id + " not found");
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
} currentUser.setName(user.getName());
currentUser.setAge(user.getAge());
currentUser.setSalary(user.getSalary()); userService.updateUser(currentUser);
return new ResponseEntity<User>(currentUser, HttpStatus.OK);
} //------------------- Delete a User -------------------------------------------------------- @RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public ResponseEntity<User> deleteUser(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
System.out.println("Fetching & Deleting User with id " + id); User user = userService.findById(id);
if (user == null) {
System.out.println("Unable to delete. User with id " + id + " not found");
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
} userService.deleteUserById(id);
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);
} //------------------- Delete All Users -------------------------------------------------------- @RequestMapping(value = "/user/", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public ResponseEntity<User> deleteAllUsers() {
System.out.println("Deleting All Users"); userService.deleteAllUsers();
return new ResponseEntity<User>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);
} }
Running the application
Build and deploy the application [on tomcat e.g]. Run it and test it using two different clients.
Using Client 1: Postman
Send a request to get the list of users. You would get a 401 instead.
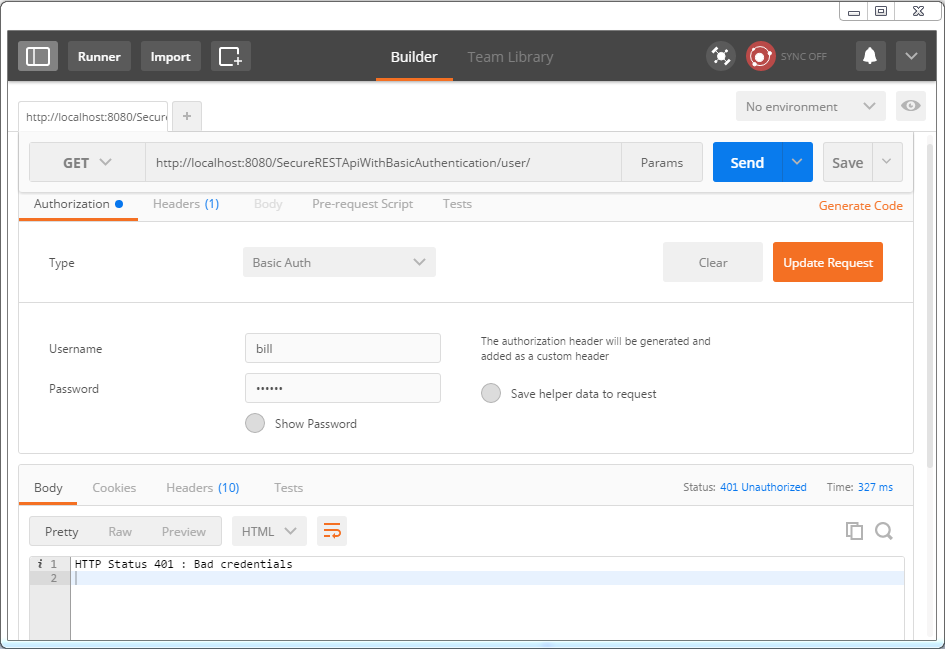
Now select type as ‘Basic Auth’ from dropdown, fill in username/password [bill/abc123], click on ‘update request’.
Click on Headers tab. You should see the new header. Let’s add ‘accept’ header as well to enforce json response.
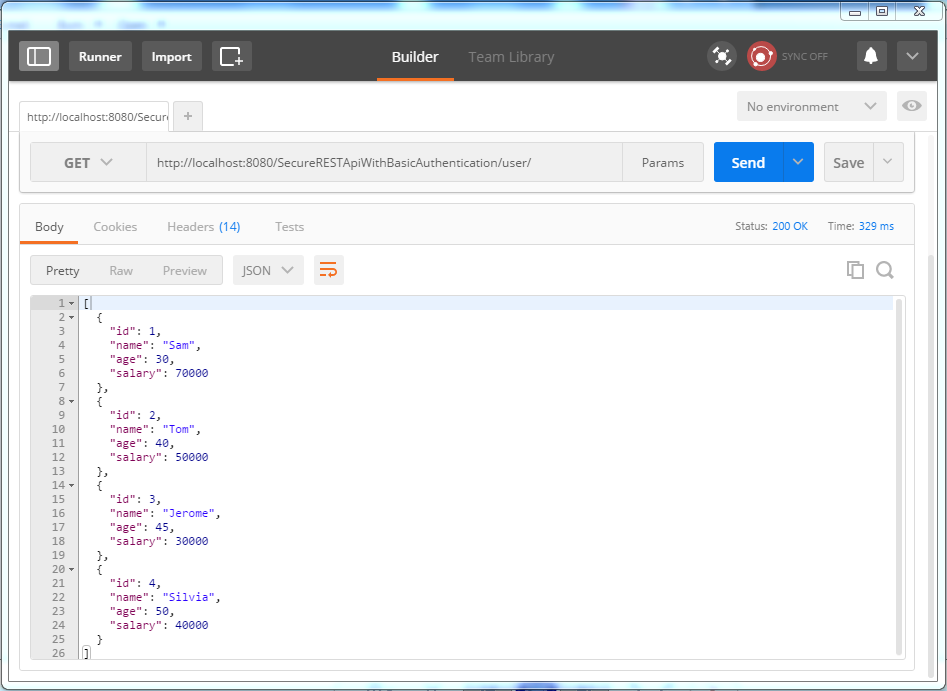
Now send the request. You should see the list of users in response this time.
Using Client 2: RestTemplate based Java Application
Let’s use a full fledged Java client to access our REST API. We will be sending request using Spring RestTemplate. Take special note about how we are setting up the headers for each request, before sending the request.
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List; import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; import com.websystique.springmvc.model.User; public class SpringRestClient { public static final String REST_SERVICE_URI = "http://localhost:8080/SecureRESTApiWithBasicAuthentication"; /*
* Add HTTP Authorization header, using Basic-Authentication to send user-credentials.
*/
private static HttpHeaders getHeaders(){
String plainCredentials="bill:abc123";
String base64Credentials = new String(Base64.encodeBase64(plainCredentials.getBytes())); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Authorization", "Basic " + base64Credentials);
headers.setAccept(Arrays.asList(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON));
return headers;
} /*
* Send a GET request to get list of all users.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static void listAllUsers(){
System.out.println("\nTesting listAllUsers API-----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>(getHeaders());
ResponseEntity<List> response = restTemplate.exchange(REST_SERVICE_URI+"/user/", HttpMethod.GET, request, List.class);
List<LinkedHashMap<String, Object>> usersMap = (List<LinkedHashMap<String, Object>>)response.getBody(); if(usersMap!=null){
for(LinkedHashMap<String, Object> map : usersMap){
System.out.println("User : id="+map.get("id")+", Name="+map.get("name")+", Age="+map.get("age")+", Salary="+map.get("salary"));;
}
}else{
System.out.println("No user exist----------");
}
} /*
* Send a GET request to get a specific user.
*/
private static void getUser(){
System.out.println("\nTesting getUser API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>(getHeaders());
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.exchange(REST_SERVICE_URI+"/user/1", HttpMethod.GET, request, User.class);
User user = response.getBody();
System.out.println(user);
} /*
* Send a POST request to create a new user.
*/
private static void createUser() {
System.out.println("\nTesting create User API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
User user = new User(,"Sarah",,);
HttpEntity<Object> request = new HttpEntity<Object>(user, getHeaders());
URI uri = restTemplate.postForLocation(REST_SERVICE_URI+"/user/", request, User.class);
System.out.println("Location : "+uri.toASCIIString());
} /*
* Send a PUT request to update an existing user.
*/
private static void updateUser() {
System.out.println("\nTesting update User API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
User user = new User(,"Tomy",, );
HttpEntity<Object> request = new HttpEntity<Object>(user, getHeaders());
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate.exchange(REST_SERVICE_URI+"/user/1", HttpMethod.PUT, request, User.class);
System.out.println(response.getBody());
} /*
* Send a DELETE request to delete a specific user.
*/
private static void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("\nTesting delete User API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>(getHeaders());
restTemplate.exchange(REST_SERVICE_URI+"/user/3", HttpMethod.DELETE, request, User.class);
} /*
* Send a DELETE request to delete all users.
*/
private static void deleteAllUsers() {
System.out.println("\nTesting all delete Users API----------");
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>(getHeaders());
restTemplate.exchange(REST_SERVICE_URI+"/user/", HttpMethod.DELETE, request, User.class);
} public static void main(String args[]){ listAllUsers(); getUser(); createUser();
listAllUsers(); updateUser();
listAllUsers(); deleteUser();
listAllUsers(); deleteAllUsers();
listAllUsers();
}
}
And the output is :
Testing listAllUsers API-----------
User : id=, Name=Sam, Age=, Salary=70000.0
User : id=, Name=Tom, Age=, Salary=50000.0
User : id=, Name=Jerome, Age=, Salary=30000.0
User : id=, Name=Silvia, Age=, Salary=40000.0 Testing getUser API----------
User [id=, name=Sam, age=, salary=70000.0] Testing create User API----------
Location : http://localhost:8080/SecureRESTApiWithBasicAuthentication/user/5 Testing listAllUsers API-----------
User : id=, Name=Sam, Age=, Salary=70000.0
User : id=, Name=Tom, Age=, Salary=50000.0
User : id=, Name=Jerome, Age=, Salary=30000.0
User : id=, Name=Silvia, Age=, Salary=40000.0
User : id=, Name=Sarah, Age=, Salary=134.0 Testing update User API----------
User [id=, name=Tomy, age=, salary=70000.0] Testing listAllUsers API-----------
User : id=, Name=Tomy, Age=, Salary=70000.0
User : id=, Name=Tom, Age=, Salary=50000.0
User : id=, Name=Jerome, Age=, Salary=30000.0
User : id=, Name=Silvia, Age=, Salary=40000.0
User : id=, Name=Sarah, Age=, Salary=134.0 Testing delete User API---------- Testing listAllUsers API-----------
User : id=, Name=Tomy, Age=, Salary=70000.0
User : id=, Name=Tom, Age=, Salary=50000.0
User : id=, Name=Silvia, Age=, Salary=40000.0
User : id=, Name=Sarah, Age=, Salary=134.0 Testing all delete Users API---------- Testing listAllUsers API-----------
No user exist----------
Secure Spring REST API using Basic Authentication的更多相关文章
- Web API: Security: Basic Authentication
原文地址: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/dn201748.aspx Custom HttpModule code: using System; u ...
- 一个HTTP Basic Authentication引发的异常
这几天在做一个功能,其实很简单.就是调用几个外部的API,返回数据后进行组装然后成为新的接口.其中一个API是一个很奇葩的API,虽然是基于HTTP的,但既没有基于SOAP规范,也不是Restful风 ...
- Web API 基于ASP.NET Identity的Basic Authentication
今天给大家分享在Web API下,如何利用ASP.NET Identity实现基本认证(Basic Authentication),在博客园子搜索了一圈Web API的基本认证,基本都是做的Forms ...
- HTTP Basic Authentication认证(Web API)
当下最流行的Web Api 接口认证方式 HTTP Basic Authentication: http://smalltalllong.iteye.com/blog/912046 什么是HTTP B ...
- Basic Authentication in ASP.NET Web API
Basic authentication is defined in RFC 2617, HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentica ...
- HTTP Basic Authentication
Client端发送请求, 要在发送请求的时候添加HTTP Basic Authentication认证信息到请求中,有两种方法:1. 在请求头中添加Authorization: Authoriz ...
- HTTP Basic Authentication认证的各种语言 后台用的
访问需要HTTP Basic Authentication认证的资源的各种语言的实现 无聊想调用下嘀咕的api的时候,发现需要HTTP Basic Authentication,就看了下. 什么是HT ...
- Setting Up Swagger 2 with a Spring REST API
Last modified: August 30, 2016 REST, SPRING by baeldung If you're new here, join the next webinar: & ...
- HTTP Basic Authentication认证
http://smalltalllong.iteye.com/blog/912046 ******************************************** 什么是HTTP Basi ...
随机推荐
- android 检查能否上网
文章一: 首先在,AndroidManifest.xml 中增加访问权限: <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCE ...
- Android内存优化13 内存泄漏常见情况4 资源泄漏
资源未关闭或释放导致内存泄露 在使用IO.File流或者Sqlite.Cursor等资源时要及时关闭.这些资源在进行读写操作时通常都使用了缓冲,如果及时不关闭,这些缓冲对象就会一直被占用而得不到释放, ...
- 游戏用户接口设计的一些小原则(摘自 game coding complete)
1.没有坏之前不要修理 2.简单的操作却有非常复杂的结果时,要小心设计. 3.记得给玩家反馈. 4.玩家不知道该功能,可能就根本不会用这个功能. 5.观察并持续改进.(给不熟悉该设计的人玩,站在他们后 ...
- 用WM_COPYDATA消息来实现两个进程之间传递数据
文着重讲述了如果用WM_COPYDATA消息来实现两个进程之间传递数据. 进程之间通讯的几种方法:在Windows程序中,各个进程之间常常需要交换数据,进行数据通讯.常用的方法有 1.使用内存映射 ...
- string c++ 转义序列
std::string shaderVS = "\struct PSInput \{ \float4 position : SV_POSITION;\float4 color : COLOR ...
- 新闻焦点切换flash应用
pixviewer.zip <!-- pixviewer.swf使用--> <script language="javascript" type="te ...
- 切换样式.toggleClass()
切换样式.toggleClass() 在做某些效果的时候,可能会针对同一节点的某一个样式不断的切换,也就是addClass与removeClass的互斥切换,比如隔行换色效果 jQuery提供一个to ...
- activemq5.14.5单节点安装Demo
什么情况下使用ActiveMQ? 1 多个项目之间集成 (1) 跨平台 (2) 多语言 (3) 多项目 2 降低系统间模块的耦合度,解耦 软件扩展性 3 系统前后端隔离 前后端 ...
- 基于paramiko进行远程执行Linux命令
直接贴一段代码import paramiko class remote_start(object): def __init__(self,host,username,pwd): self.ssh = ...
- Unity3D实现3D立体游戏原理及过程,需偏振眼镜3D显
http://tieba.baidu.com/p/3038509618?fr=ala0&pstaala=3
