Weekly Contest 131
1021. Remove Outermost Parentheses
A valid parentheses string is either empty
(""),"(" + A + ")", orA + B, whereAandBare valid parentheses strings, and+represents string concatenation. For example,"","()","(())()", and"(()(()))"are all valid parentheses strings.A valid parentheses string
Sis primitive if it is nonempty, and there does not exist a way to split it intoS = A+B, withAandBnonempty valid parentheses strings.Given a valid parentheses string
S, consider its primitive decomposition:S = P_1 + P_2 + ... + P_k, whereP_iare primitive valid parentheses strings.Return
Safter removing the outermost parentheses of every primitive string in the primitive decomposition ofS.
Example 1:
Input: "(()())(())"
Output: "()()()"
Explanation:
The input string is "(()())(())", with primitive decomposition "(()())" + "(())".
After removing outer parentheses of each part, this is "()()" + "()" = "()()()".Example 2:
Input: "(()())(())(()(()))"
Output: "()()()()(())"
Explanation:
The input string is "(()())(())(()(()))", with primitive decomposition "(()())" + "(())" + "(()(()))".
After removing outer parentheses of each part, this is "()()" + "()" + "()(())" = "()()()()(())".Example 3:
Input: "()()"
Output: ""
Explanation:
The input string is "()()", with primitive decomposition "()" + "()".
After removing outer parentheses of each part, this is "" + "" = "".
Note:
S.length <= 10000S[i]is"("or")"Sis a valid parentheses string
Approach #1: Stack. [C++]
class Solution {
public:
string removeOuterParentheses(string S) {
stack<char> sta;
int left = 0, right = 0;
string ans = "";
for (int i = 0; i < S.length(); ++i) {
if (sta.empty()) {
right = i - 1;
if (right - left - 1 >= 2) {
string s = S.substr(left+1, right-left-1);
ans += s;
}
left = i;
sta.push(S[i]);
} else {
if (sta.top() == '(' && S[i] == ')') {
sta.pop();
} else {
sta.push(S[i]);
}
}
}
string s = S.substr(left+1, S.length()-left-2);
ans += s;
return ans;
}
};
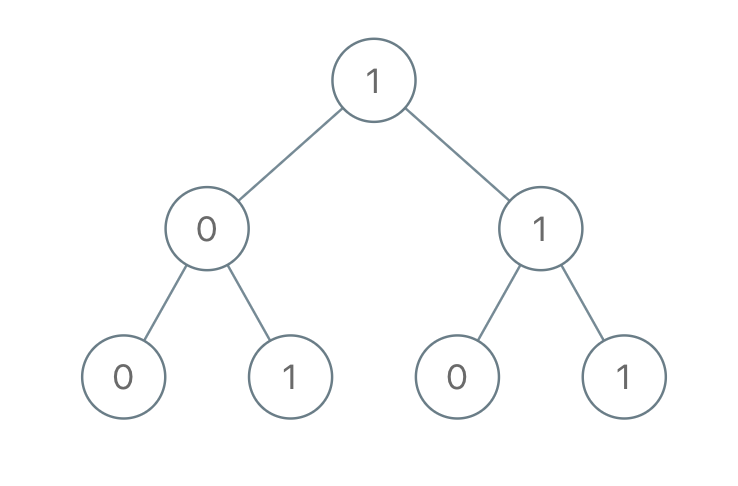
1022. Sum of Root To Leaf Binary Numbers
Given a binary tree, each node has value
0or1. Each root-to-leaf path represents a binary number starting with the most significant bit. For example, if the path is0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1, then this could represent01101in binary, which is13.For all leaves in the tree, consider the numbers represented by the path from the root to that leaf.
Return the sum of these numbers.
Example 1:
Input: [1,0,1,0,1,0,1]
Output: 22
Explanation: (100) + (101) + (110) + (111) = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 22
Note:
- The number of nodes in the tree is between
1and1000.- node.val is
0or1.- The answer will not exceed
2^31 - 1.
Approach #1: [C++]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumRootToLeaf(TreeNode* root, int val = 0) {
const static int mod = 1000000007;
if (!root) return 0;
val = val * 2 + root->val;
return (root->left == root->right ? val : sumRootToLeaf(root->left, val) + sumRootToLeaf(root->right, val)) % mod;
}
};
1023. Camelcase Matching
A query word matches a given
patternif we can insert lowercase letters to the pattern word so that it equals thequery. (We may insert each character at any position, and may insert 0 characters.)Given a list of
queries, and apattern, return ananswerlist of booleans, whereanswer[i]is true if and only ifqueries[i]matches thepattern.
Example 1:
Input: queries = ["FooBar","FooBarTest","FootBall","FrameBuffer","ForceFeedBack"], pattern = "FB"
Output: [true,false,true,true,false]
Explanation:
"FooBar" can be generated like this "F" + "oo" + "B" + "ar".
"FootBall" can be generated like this "F" + "oot" + "B" + "all".
"FrameBuffer" can be generated like this "F" + "rame" + "B" + "uffer".Example 2:
Input: queries = ["FooBar","FooBarTest","FootBall","FrameBuffer","ForceFeedBack"], pattern = "FoBa"
Output: [true,false,true,false,false]
Explanation:
"FooBar" can be generated like this "Fo" + "o" + "Ba" + "r".
"FootBall" can be generated like this "Fo" + "ot" + "Ba" + "ll".Example 3:
Input: queries = ["FooBar","FooBarTest","FootBall","FrameBuffer","ForceFeedBack"], pattern = "FoBaT"
Output: [false,true,false,false,false]
Explanation:
"FooBarTest" can be generated like this "Fo" + "o" + "Ba" + "r" + "T" + "est".
Note:
1 <= queries.length <= 1001 <= queries[i].length <= 1001 <= pattern.length <= 100- All strings consists only of lower and upper case English letters.
Approach #1: [C++]
class Solution {
public:
vector<bool> camelMatch(vector<string>& queries, string pattern) {
vector<bool> res;
for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i) {
res.push_back(judge(queries[i], pattern));
}
return res;
}
private:
bool judge(string str, string pattern) {
int pnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); ++i) {
if (str[i] == pattern[pnt]) pnt++;
else if (islower(str[i])) continue;
else return false;
}
return pnt == pattern.length();
}
};
1024. Video Stitching
You are given a series of video clips from a sporting event that lasted
Tseconds. These video clips can be overlapping with each other and have varied lengths.Each video clip
clips[i]is an interval: it starts at timeclips[i][0]and ends at timeclips[i][1]. We can cut these clips into segments freely: for example, a clip[0, 7]can be cut into segments[0, 1] + [1, 3] + [3, 7].Return the minimum number of clips needed so that we can cut the clips into segments that cover the entire sporting event (
[0, T]). If the task is impossible, return-1.
Example 1:
Input: clips = [[0,2],[4,6],[8,10],[1,9],[1,5],[5,9]], T = 10
Output: 3
Explanation:
We take the clips [0,2], [8,10], [1,9]; a total of 3 clips.
Then, we can reconstruct the sporting event as follows:
We cut [1,9] into segments [1,2] + [2,8] + [8,9].
Now we have segments [0,2] + [2,8] + [8,10] which cover the sporting event [0, 10].Example 2:
Input: clips = [[0,1],[1,2]], T = 5
Output: -1
Explanation:
We can't cover [0,5] with only [0,1] and [0,2].Example 3:
Input: clips = [[0,1],[6,8],[0,2],[5,6],[0,4],[0,3],[6,7],[1,3],[4,7],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6],[3,4],[4,5],[5,7],[6,9]], T = 9
Output: 3
Explanation:
We can take clips [0,4], [4,7], and [6,9].Example 4:
Input: clips = [[0,4],[2,8]], T = 5
Output: 2
Explanation:
Notice you can have extra video after the event ends.
Note:
1 <= clips.length <= 1000 <= clips[i][0], clips[i][1] <= 1000 <= T <= 100
Approach #1: [C++]
class Solution {
public:
int videoStitching(vector<vector<int>>& clips, int T) {
int n = clips.size();
sort(clips.begin(), clips.end(), [](vector<int>& u, vector<int>& v) {
return u[1] < v[1];
});
vector<int> dp(n+1, 0);
int ret = INF;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
dp[i] = (clips[i][0] == 0) ? 1 : INF;
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if (clips[j][1] >= clips[i][0]) {
dp[i] = min(dp[j] + 1, dp[i]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (clips[i][1] >= T)
ret = min(dp[i], ret);
}
return (ret == INF) ? -1 : ret;
}
private:
const int INF = 1 << 30;
};
Weekly Contest 131的更多相关文章
- LeetCode Weekly Contest 8
LeetCode Weekly Contest 8 415. Add Strings User Accepted: 765 User Tried: 822 Total Accepted: 789 To ...
- Leetcode Weekly Contest 86
Weekly Contest 86 A:840. 矩阵中的幻方 3 x 3 的幻方是一个填充有从 1 到 9 的不同数字的 3 x 3 矩阵,其中每行,每列以及两条对角线上的各数之和都相等. 给定一个 ...
- leetcode weekly contest 43
leetcode weekly contest 43 leetcode649. Dota2 Senate leetcode649.Dota2 Senate 思路: 模拟规则round by round ...
- LeetCode Weekly Contest 23
LeetCode Weekly Contest 23 1. Reverse String II Given a string and an integer k, you need to reverse ...
- LeetCode之Weekly Contest 91
第一题:柠檬水找零 问题: 在柠檬水摊上,每一杯柠檬水的售价为 5 美元. 顾客排队购买你的产品,(按账单 bills 支付的顺序)一次购买一杯. 每位顾客只买一杯柠檬水,然后向你付 5 美元.10 ...
- LeetCode Weekly Contest
链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/leetcode-weekly-contest-33/ A.Longest Harmonious Subsequence 思路:hash ...
- LeetCode Weekly Contest 47
闲着无聊参加了这个比赛,我刚加入战场的时候时间已经过了三分多钟,这个时候已经有20多个大佬做出了4分题,我一脸懵逼地打开第一道题 665. Non-decreasing Array My Submis ...
- 75th LeetCode Weekly Contest Champagne Tower
We stack glasses in a pyramid, where the first row has 1 glass, the second row has 2 glasses, and so ...
- LeetCode之Weekly Contest 102
第一题:905. 按奇偶校验排序数组 问题: 给定一个非负整数数组 A,返回一个由 A 的所有偶数元素组成的数组,后面跟 A 的所有奇数元素. 你可以返回满足此条件的任何数组作为答案. 示例: 输入: ...
随机推荐
- JTemplate学习(二)
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DT ...
- Nginx 分析access日志文件
Nginx Access Log日志统计分析常用命令 IP相关统计 统计IP访问量 awk '{print $1}' access.log | sort -n | uniq | wc -l 查看某一时 ...
- pip安装python模块方法
网上搜索了很多,主流的配置方法分为两种: 摘自 1.http://www.jb51.net/article/83617.htm 安装pip的包并确定pip安装时的镜像源地址,国内常用的地址有: htt ...
- Spring官方文档翻译(1~6章)
Spring官方文档翻译(1~6章) 转载至 http://blog.csdn.net/tangtong1/article/details/51326887 Spring官方文档.参考中文文档 一.S ...
- Netty 系列(三)Netty 入门
Netty 系列(三)Netty 入门 Netty 是一个提供异步事件驱动的网络应用框架,用以快速开发高性能.高可靠性的网络服务器和客户端程序.更多请参考:Netty Github 和 Netty中文 ...
- jquery报.live() is not a function的解决方法
jquery报.live() is not a function的解决方法: jquery中的live()方法在jquery1.9及以上的版本中已被废弃了,如果使用,会抛出TypeError: $(. ...
- 2018.09.26洛谷P3957 跳房子(二分+单调队列优化dp)
传送门 表示去年考普及组的时候失了智,现在看来并不是很难啊. 直接二分答案然后单调队列优化dp检验就行了. 注意入队和出队的条件. 代码: #include<bits/stdc++.h> ...
- Yii框架请求
$request = Yii::$app->request; $get = $request->get(); // 等价于: $get = $_GET; $id = $request-&g ...
- flask_数据库
我们将使用 Flask-SQLAlchemy扩展来管理我们应用程序的数据.这个扩展封装了SQLAlchemy 项目,这是一个 对象关系映射器 或者 ORM.ORMs 允许数据库应用程序与对象一起工作, ...
- Unable to load tag handler class "com.showId.Id.ShowId" for tag "ShowId:ShowId"] with root cause错误的解决方案
严重: Servlet.service() for servlet [jsp] in context with path [/Biaoqian] threw exception [/1.jsp (l ...