Hibernate 单项多对1
自己理解:
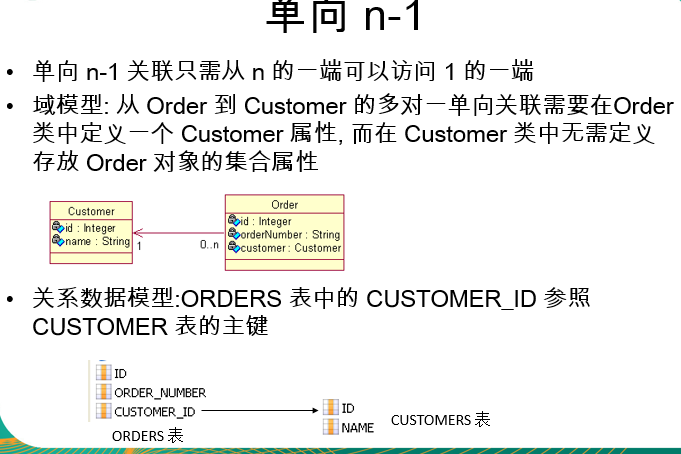
单向1对多。
一个客户可以发出多个订单。但是一个订单只属于一个客户。
写对象的时候。在多的那个类对象把1的作为自己的一个属性。
写配置文件
<many-to-one name=1的属性名。class=1的类名。column=1的主键名>
多的1方的Java类。 把1的作为一个属性放到多的里面。
package com.hibernate.n21;
public class Order {
private Integer orderId;
private String orderName;
private Customer customer;
private Integer getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public void setOrderId(Integer orderId) {
this.orderId = orderId;
}
public String getOrderName() {
return orderName;
}
public void setOrderName(String orderName) {
this.orderName = orderName;
}
public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public void setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
public Order(String orderName, Customer customer) {
super();
this.orderName = orderName;
this.customer = customer;
}
}
映射文件:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="com.hibernate.n21"> <class name="Order" table="orders" > <id name="orderId" type="java.lang.Integer">
<column name="order_Id" />
<!-- 指定主键的生成方式, native: 使用数据库本地方式 -->
<generator class="native" />
</id> <property name="orderName"
type="java.lang.String" column="order_Name" >
</property> <!-- 映射n-1的关联关系
name:1的属性名。把1当成多的一个属性。
class 1的类名。
column 1的主键名。
-->
<many-to-one name="customer" class="Customer" column="customer_Id"></many-to-one>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
1的类名:
package com.hibernate.n21;
public class Customer {
private Integer customerId;
private String customerName;
public Integer getCustomerId() {
return customerId;
}
public void setCustomerId(Integer customerId) {
this.customerId = customerId;
}
public String getCustomerName() {
return customerName;
}
public void setCustomerName(String customerName) {
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public Customer() {
super();
}
public Customer(String customerName) {
super();
this.customerName = customerName;
}
}
映射文件:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="com.hibernate.n21"> <class name="Customer" table="customer" > <id name="customerId" type="java.lang.Integer">
<column name="customer_Id" />
<!-- 指定主键的生成方式, native: 使用数据库本地方式 -->
<generator class="native" />
</id> <property name="customerName"
type="java.lang.String" column="customer_Name" >
</property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
然后在主的映射文件hibernate.cfg.xml文件中加上映射
<mapping resource="com/hibernate/n21/Customer.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="com/hibernate/n21/Order.hbm.xml"/>
SAVE():
先保存1的一端 只是三条insert语句。
@org.junit.Test
public void testN21Save(){
Customer customer=new Customer();
customer.setCustomerName("C1");
Order order1 =new Order();
order1.setOrderName("O1");
Order order2 =new Order();
order2.setOrderName("O2"); //设置关联关系。就是给多的一方设置外键
order1.setCustomer(customer);
order2.setCustomer(customer);
session.save(customer);
session.save(order1);
session.save(order2); }
先保存多的一端。3条insert语句。2条update语句
因为在插入多的一端时,无法确定1的一端的外键值。所以只能先为null。等1的一端插入后。再进行修改。
@org.junit.Test
public void testN21Save(){
Customer customer=new Customer();
customer.setCustomerName("C1");
Order order1 =new Order();
order1.setOrderName("O1");
Order order2 =new Order();
order2.setOrderName("O2"); //设置关联关系。就是给多的一方设置外键
order1.setCustomer(customer);
order2.setCustomer(customer); session.save(order1);
session.save(order2);
session.save(customer);
}
select()方法:
如果在第5行关闭session。就会出现懒加载异常。因为System.out.println(order.getCustomer().getClass()); class com.hibernate.n21.Customer_$$_javassist_0
得到的是一个customer代理对象。
1 @org.junit.Test
public void testN21Select(){
Order order=(Order) session.get(Order.class, 5);
System.out.println(order.getOrderName());
session.close();
Customer customer = order.getCustomer();
System.out.println(customer.getCustomerName());
}
对于懒加载异常。我们可以在hibernate.cfg.xml中设置立即加载。
<class name="Customer" table="customer" lazy="false"> 我们设置懒加载为否。就是立即加载
Update():
@org.junit.Test
public void testN21Update(){
Order order=(Order) session.get(Order.class, 5);
Customer customer=order.getCustomer();
customer.setCustomerName("N21Update");
}
Delete:
//删除多的,直接删除
@org.junit.Test
public void testN21Delete(){
Order order=(Order) session.get(Order.class, 5);
session.delete(order);
}
//不设置级联删除的话。删除1的一方。会出现异常。因为1的一方。对应好几个
//但是1的一方没有被引用的话。是可以删除的 1 @org.junit.Test
public void testN21Delete(){
Customer customer=(Customer) session.get(Customer.class, 3);
session.delete(customer);
}
org.hibernate.exception.ConstraintViolationException: could not execute statement
at org.hibernate.exception.internal.SQLExceptionTypeDelegate.convert(SQLExceptionTypeDelegate.java:74)
at org.hibernate.exception.internal.StandardSQLExceptionConverter.convert(StandardSQLExceptionConverter.java:49)
at org.hibernate.engine.jdbc.spi.SqlExceptionHelper.convert(SqlExceptionHelper.java:125)
at org.hibernate.engine.jdbc.spi.SqlExceptionHelper.convert(SqlExceptionHelper.java:110)
at org.hibernate.engine.jdbc.internal.ResultSetReturnImpl.executeUpdate(ResultSetReturnImpl.java:136)
at org.hibernate.engine.jdbc.batch.internal.NonBatchingBatch.addToBatch(NonBatchingBatch.java:58)
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.delete(AbstractEntityPersister.java:3343)
at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.delete(AbstractEntityPersister.java:3546)
at org.hibernate.action.internal.EntityDeleteAction.execute(EntityDeleteAction.java:100)
at org.hibernate.engine.spi.ActionQueue.execute(ActionQueue.java:377)
at org.hibernate.engine.spi.ActionQueue.executeActions(ActionQueue.java:369)
at org.hibernate.engine.spi.ActionQueue.executeActions(ActionQueue.java:293)
at org.hibernate.event.internal.AbstractFlushingEventListener.performExecutions(AbstractFlushingEventListener.java:339)
at org.hibernate.event.internal.DefaultFlushEventListener.onFlush(DefaultFlushEventListener.java:52)
at org.hibernate.internal.SessionImpl.flush(SessionImpl.java:1234)
at org.hibernate.internal.SessionImpl.managedFlush(SessionImpl.java:404)
at org.hibernate.engine.transaction.internal.jdbc.JdbcTransaction.beforeTransactionCommit(JdbcTransaction.java:101)
at org.hibernate.engine.transaction.spi.AbstractTransactionImpl.commit(AbstractTransactionImpl.java:175)
at com.hibernate.n21.Test.destroy(Test.java:39)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:44)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:15)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:41)
at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.RunAfters.evaluate(RunAfters.java:37)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runNotIgnored(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:79)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:71)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:49)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:193)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:52)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:191)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:42)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:184)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:236)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit4.runner.JUnit4TestReference.run(JUnit4TestReference.java:50)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.TestExecution.run(TestExecution.java:38)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:467)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:683)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.run(RemoteTestRunner.java:390)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.main(RemoteTestRunner.java:197)
Caused by: com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.jdbc4.MySQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException: Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails (`luwei`.`orders`, CONSTRAINT `FK_qaw4j85b8ppgne3sg6f218msv` FOREIGN KEY (`customer_Id`) REFERENCES `customer` (`customer_Id`))
at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.java:27)
at java.lang.reflect.Constructor.newInstance(Constructor.java:513)
at com.mysql.jdbc.Util.handleNewInstance(Util.java:406)
at com.mysql.jdbc.Util.getInstance(Util.java:381)
at com.mysql.jdbc.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:1015)
at com.mysql.jdbc.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:956)
at com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlIO.checkErrorPacket(MysqlIO.java:3515)
at com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlIO.checkErrorPacket(MysqlIO.java:3447)
at com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlIO.sendCommand(MysqlIO.java:1951)
at com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlIO.sqlQueryDirect(MysqlIO.java:2101)
at com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl.execSQL(ConnectionImpl.java:2554)
at com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement.executeInternal(PreparedStatement.java:1761)
at com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement.executeUpdate(PreparedStatement.java:2046)
at com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement.executeUpdate(PreparedStatement.java:1964)
at com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement.executeUpdate(PreparedStatement.java:1949)
at com.mchange.v2.c3p0.impl.NewProxyPreparedStatement.executeUpdate(NewProxyPreparedStatement.java:147)
at org.hibernate.engine.jdbc.internal.ResultSetReturnImpl.executeUpdate(ResultSetReturnImpl.java:133)
... 37 more
Hibernate 单项多对1的更多相关文章
- Hibernate 单项多对一的关联映射
在日常开发中会出现很对多对一的情况,本文介绍hibernate中多对一的关联映射. 1.设计表结构 2.创建student对象 3.创建Grade对象 4.写hbm.xml文件 5.生成数据库表 生成 ...
- hibernate中多对多关联
hibernate中多对多关联 “计应134(实验班) 凌豪” 在关系数据库中有一种常见的关系即多对多关系,例如课程和学生的关系,一个学生可以选择多门课程,同时一门课程也可以被多个学生选择, 因此课程 ...
- 【SSH系列】Hibernate映射 -- 多对多关联映射
映射原理 在数据库学习阶段,我们知道,如果实体和实体之间的关系是多对多,那么我们就抽出来第三张表,第一张表和第二张表的主键作为第三表的联合主键,结合我们的hibernate,多对多关联,无论 ...
- Hibernate的多对多实例
在完成了一对多的实例的基础上,继续做多对多实例.例子是老师和学生,一个老师教多个学生,一个学生也有多个老师. 文档结构如图:
- Hibernate的多对多映射关系
example: 老师(teacher)和学生(Student)就是一个多对多的关系吧?老师可以有多个学生,学生也可以由多个老师,那在Hibernate中多对多是怎样实现的呢?? 在Hibernate ...
- Hibernate中多对多的annotation的写法(中间表可以有多个字段)
2011-07-04 6:52 一般情况下,多对多的关联关系是需要中间表的: 情况一:如果中间表仅仅是做关联用的,它里面仅有2个外键做联合主键,则使用ManyToMany(不用写中间表的Model,只 ...
- hibernate关联关系 (多对多)
hibernate的多对多 hibernate可以直接映射多对多关联关系(看作两个一对多 多对多关系注意事项 一定要定义一个主控方 多对多删除 主控方直接删除 被控方先通过主控方解除多对多关系,再删 ...
- hibernate之多对多关系
hibernate的多对多hibernate可以直接映射多对多关联关系(看作两个一对多) 下面我们拿三张表来做实例 t_book_hb t_book_category_hb(桥接表) t_catego ...
- Hibernate关联映射(单项多对一和一对多、双向一对多)
最近总是接触着新的知识点来扩展自己的知识面:不停的让自己在原地接触天空的感觉真的很美好!!!革命没有成功,程序员的我们怎么能不努力呢...... 一.用员工和部门来剖析关联映射的原理. 1)从这张截图 ...
随机推荐
- Android SDK的下载与安装*(PC版)
Android SDK的下载与安装 一.Android SDK简介下载地址:https://www.androiddevtools.cn/ 将下载后的安装包解压到相应的目录下,如下图: 三.安装A ...
- LDD快速参考
第二章 快速参考 本节中出现的条目会以它们在文中出现的顺序列出: insmod modprobe rmmod 用来装载模块到正运行的内核和移除模块的用户空间工具: #include <linux ...
- bugku | sql注入2
http://123.206.87.240:8007/web2/ 全都tm过滤了绝望吗? 提示 !,!=,=,+,-,^,% uname=admin&passwd=1' and '1 : 一个 ...
- tomcat启动前端项目
前后端分离项目,前端使用vue,部署启动前端项目可以使用NodeJS,Nginx,Tomcat. *)使用Tomcat部署启动: 1.把vue项目build生成的dist包,放到Tomcat的weba ...
- Android入门:广播发送者与广播接收者
参考: Android入门:广播发送者与广播接收者 - xiazdong - CSDN博客http://blog.csdn.net/xiazdong/article/details/7768807 一 ...
- Menu [D3D9 Source]
源代码下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/wd844125365_/8008779
- git 裸库
初始化一个空的裸仓库 $ cd /home/repo $ mkdir tproject.git $ cd tproject.git $ git init - -bare 注:这是在服务器上运 ...
- [360前端星计划]BlackJack(21点)(纯JS,附总部学习笔记)
[360前端星计划]总部学习笔记(6/6) [360前端星计划]详情跳转 游戏界面预览 目录 一.游戏介绍 1.起源 2.规则 3.技巧 二.游戏设计 1.整体UI构思 2.素材采集 3.游戏总规划 ...
- Spring 官方文档笔记---Bean
In Spring, the objects that form the backbone of your application and that are managed by the Spring ...
- Appium移动端自动化:Appium-Desktp的使用以及定位元素方式总结
一.appium-desktop功能介绍 1.打开appium-desktop,点击start session 2.打开后,点击屏幕右上角的搜索按钮 3.然后会打开配置页面,在本地服务配置信息同上面写 ...
